Enhanced In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Ivermectin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus via Improved Intracellular Delivery
Xiaolin Xu, Shasha Gao, Qindan Zuo, Jiahao Gong, Xinhao Song, Yongshi Liu, Jing Xiao, Xiaofeng Zhai, Haifeng Sun, Mingzhi Zhang, Xiuge Gao, Dawei Guo
Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16050601
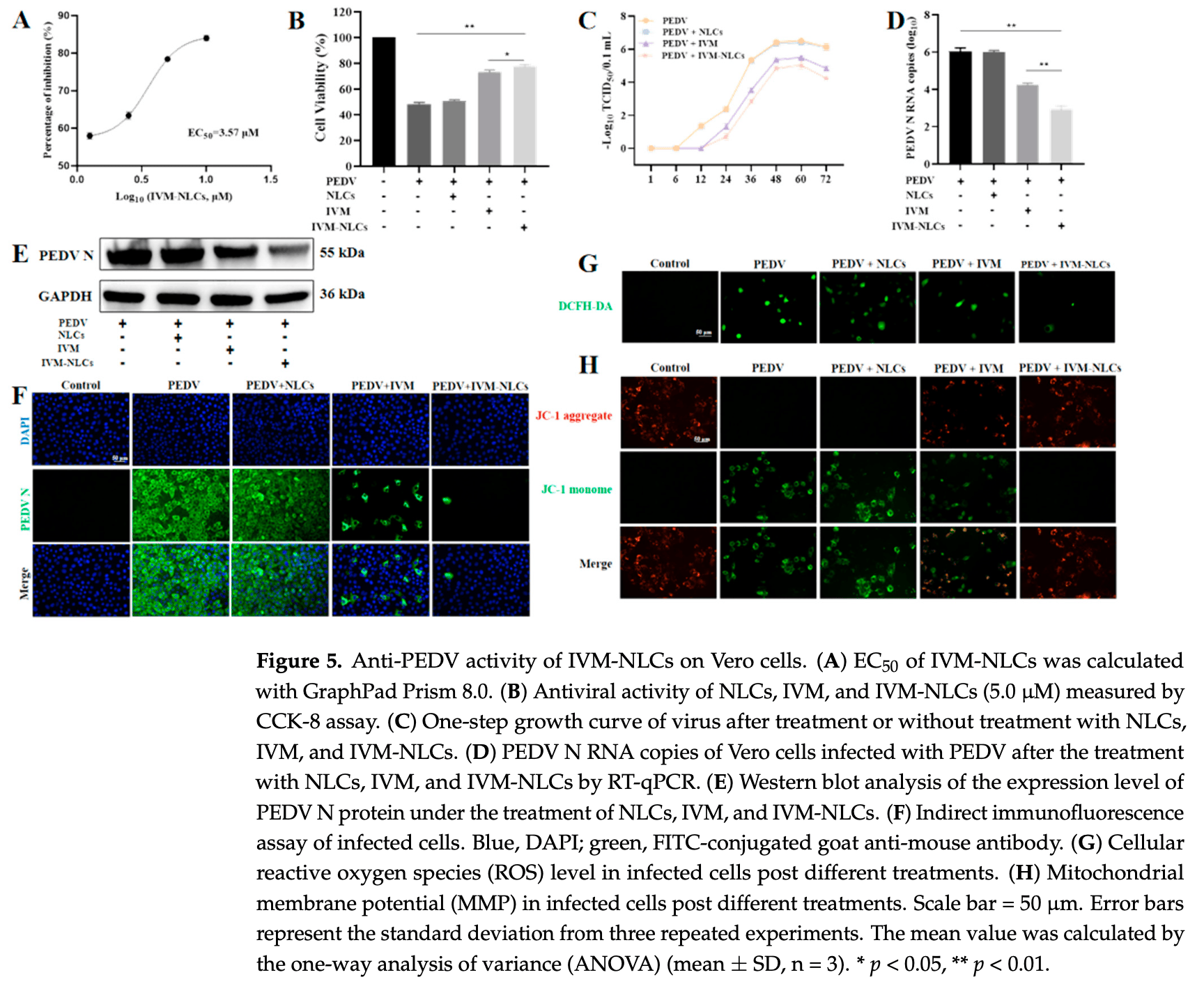
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) is an acute enteric coronavirus, inducing watery diarrhea and high mortality in piglets, leading to huge economic losses in global pig industry. Ivermectin (IVM), an FDA-approved antiparasitic agent, is characterized by high efficacy and wide applicability. However, the poor bioavailability limits its application. Since the virus is parasitized inside the host cells, increasing the intracellular drug uptake can improve antiviral efficacy. Hence, we aimed to develop nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) to enhance the antiviral efficacy of IVM. The findings first revealed the capacity of IVM to inhibit the infectivity of PEDV by reducing viral replication with a certain direct inactivation effect. The as-prepared IVM-NLCs possessed hydrodynamic diameter of 153.5 nm with a zeta potential of -31.5 mV and high encapsulation efficiency (95.72%) and drug loading (11.17%). IVM interacted with lipids and was enveloped in lipid carriers with an amorphous state. Furthermore, its encapsulation in NLCs could enhance drug internalization. Meanwhile, IVM-NLCs inhibited PEDV proliferation by up to three orders of magnitude in terms of viral RNA copies, impeding the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and mitigating the mitochondrial dysfunction caused by PEDV infection. Moreover, IVM-NLCs markedly decreased the apoptosis rate of PEDV-induced Vero cells. Hence, IVM-NLCs showed superior inhibitory effect against PEDV compared to free IVM. Together, these results implied that NLCs is an efficient delivery system for IVM to improve its antiviral efficacy against PEDV via enhanced intracellular uptake.
to biological tests, IVM-NLCs exhibited stronger antiviral activity against PEDV than free IVM and reduced PEDV-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, which prevented ROS generation and improved viability of infected Vero cell. Moreover, IVM-NLCs also reduced PEDV-induced cell apoptosis rate. In view of the in vitro results, it would be necessary to carry out in vivo tests as soon as possible, to explore its potential in the clinical treatment of PEDV. Consequently, IVM-NLCs were demonstrated to be a potential drug against PEDV, which might provide a basis for the development of novel drugs to antagonize PEDV.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www. mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050601/s1, Figure S1 : Cytotoxicity of Vero cells treated with different concentration of IVM at the appointed time via CCK-8 assay; Figure S2 : Antiviral activity of IVM-NLCs was measured by CCK-8 assay; Table S1 Characterization of as-prepared IVM-NLCs. Author Contributions: Conceptualization, D.G. and X.X.; methodology, X.X., S.G., Q.Z., J.G. and X.S.; formal analysis, X.X., S.G., Q.Z., J.G., X.S., Y.L., J.X., M.Z. and X.G.; investigation, X.X., S.G., Q.Z. and D.G.; resources, Y.L., J.X. and M.Z.; data curation, X.Z. and H.S.; writing-original draft preparation, X.X., S.G., Q.Z., X.S. and J.X.; writing-review and editing, D.G., J.G., Y.L., H.S., X.Z., M.Z. and X.G.; supervision, D.G., X.G., X.Z. and H.S,; project administration,..
References
Aref, Bazeed, Hassan, Hassan, Rashad et al., Biochemical and Molecular Evaluations of Ivermectin Mucoadhesive Nanosuspension Nasal Spray in Reducing Upper Respiratory Symptoms of Mild COVID-19, IJN,
doi:10.2147/IJN.S313093Baram-Pinto, Shukla, Gedanken, Sarid, Inhibition of HSV-1 Attachment, Entry, and Cell-to-Cell Spread by Functionalized Multivalent Gold Nanoparticles, Small,
doi:10.1002/smll.200902384Bugnicourt, Peers, Dalverny, Ladavière, Tunable morphology of lipid/chitosan particle assemblies, J. Colloid. Interface Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.098Das, Lee, Chia, Chow, Macbeath et al., Development of microemulsion based topical ivermectin formulations: Pre-formulation and formulation studies, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces,
doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110823Date, Nimbalkar, Kamat, Mittal, Mahato et al., Lipid-polymer hybrid nanocarriers for delivering cancer therapeutics, J. Control. Release,
doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.016Guo, Dou, Li, Zhang, Bhutto et al., Ivermection-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Preparation, characterisation, stability and transdermal behaviour, Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol,
doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1307207Götz, Magar, Dornfeld, Giese, Pohlmann et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci. Rep,
doi:10.1038/srep23138Hamanaka, Chandel, Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate biological outcomes, Trends Biochem. Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2010.04.002Hou, Ke, Kim, Yoo, Su et al., Engineering a Live Attenuated Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Vaccine Candidate via Inactivation of the Viral 2 ′ -O.-Methyltransferase and the Endocytosis Signal of the Spike Protein, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00406-19Jaru-Ampornpan, Jengarn, Wanitchang, Jongkaewwattana, Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus 3C-Like Protease-Mediated Nucleocapsid Processing: Possible Link to Viral Cell Culture Adaptability, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.01660-16Liu, Liu, Jiang, Yang, Huang et al., Surface-Displayed Porcine IFN-λ3 in Lactobacillus plantarum Inhibits Porcine Enteric Coronavirus Infection of Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol,
doi:10.4014/jmb.1909.09041Lv, Liu, Wang, Dang, Qiu et al., Ivermectin inhibits DNA polymerase UL42 of pseudorabies virus entrance into the nucleus and proliferation of the virus in vitro and vivo, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.09.010Mastrangelo, Pezzullo, De Burghgraeve, Kaptein, Pastorino et al., Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: New prospects for an old drug, J. Antimicrob. Chemother,
doi:10.1093/jac/dks147Pina, Pinto, Sousa, Craig, Zhao, Generation of hydrate forms of paroxetine HCl from the amorphous state: An evaluation of thermodynamic and experimental predictive approaches, Int. J. Pharm,
doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.12.033Pushpakom, Iorio, Eyers, Escott, Hopper et al., Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov,
doi:10.1038/nrd.2018.168Rehman, Tong, Jafari, Assadpour, Shehzad et al., Carotenoid-loaded nanocarriers: A comprehensive review, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.cis.2019.102048Schorey, Cheng, Singh, Smith, Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in host-pathogen interactions, EMBO Rep,
doi:10.15252/embr.201439363Sun, Chen, Ming, Bo, Shin et al., Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection Induces Caspase-8-Mediated G3BP1 Cleavage and Subverts Stress Granules To Promote Viral Replication, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.02344-20Tay, Fraser, Chan, Moreland, Rathore et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002Thomas, Lundberg, Pinkham, Shechter, Debono et al., Identification of novel antivirals inhibiting recognition of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus capsid protein by the Importin α/β1 heterodimer through high-throughput screening, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.01.007Ud-Din, Roujeinikova, Cloning, purification, crystallization and X-ray crystallographic analysis of the periplasmic sensing domain of Pseudomonas fluorescens chemotactic transducer of amino acids type A (CtaA), BST,
doi:10.5582/bst.2016.01059Ungaro, Yzet, Bossuyt, Baert, Vanasek et al., Deep Remission at 1 Year Prevents Progression of Early Crohn's Disease, Gastroenterology,
doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.039Valencia-Lazcano, Hassan, Pourmadadi, Shamsabadipour, Behzadmehr et al., 5-Fluorouracil nano-delivery systems as a cutting-edge for cancer therapy, Eur. J. Med. Chem,
doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114995Wang, Kong, Jiao, Dong, Sun et al., EGR1 Suppresses Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Regulating IRAV to Degrade Viral Nucleocapsid Protein, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00645-21Wilson, Prud'homme, Nanoparticle size distribution quantification from transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of ruthenium tetroxide stained polymeric nanoparticles, J. Colloid. Interface Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.081Wu, Wu, Zhang, Yuan, Lu et al., Colloid properties of hydrophobic modified alginate: Surface tension, ζ-potential, viscosity and emulsification, Carbohydr. Polym,
doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.052Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760Ye, Shao, Li, Guo, Zuo et al., Antiviral Activity of Graphene Oxide: How Sharp Edged Structure and Charge Matter, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,
doi:10.1021/acsami.5b06876Zhai, Wang, Jiao, Zhang, Li et al., Melatonin and other indoles show antiviral activities against swine coronaviruses in vitro at pharmacological concentrations, J. Pineal Res,
doi:10.1111/jpi.12754Zhang, Chen, Li, Wen, Song et al., Construction of ivermectin producer by domain swaps of avermectin polyketide synthase in Streptomyces avermitilis, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol,
doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0361-2Zhang, Yang, Sahito, Li, Peng et al., Nanostructured lipid carriers with exceptional gastrointestinal stability and inhibition of P-gp efflux for improved oral delivery of tilmicosin, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces,
doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110649DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics16050601",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4923"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050601",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) is an acute enteric coronavirus, inducing watery diarrhea and high mortality in piglets, leading to huge economic losses in global pig industry. Ivermectin (IVM), an FDA-approved antiparasitic agent, is characterized by high efficacy and wide applicability. However, the poor bioavailability limits its application. Since the virus is parasitized inside the host cells, increasing the intracellular drug uptake can improve antiviral efficacy. Hence, we aimed to develop nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) to enhance the antiviral efficacy of IVM. The findings first revealed the capacity of IVM to inhibit the infectivity of PEDV by reducing viral replication with a certain direct inactivation effect. The as-prepared IVM-NLCs possessed hydrodynamic diameter of 153.5 nm with a zeta potential of −31.5 mV and high encapsulation efficiency (95.72%) and drug loading (11.17%). IVM interacted with lipids and was enveloped in lipid carriers with an amorphous state. Furthermore, its encapsulation in NLCs could enhance drug internalization. Meanwhile, IVM-NLCs inhibited PEDV proliferation by up to three orders of magnitude in terms of viral RNA copies, impeding the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and mitigating the mitochondrial dysfunction caused by PEDV infection. Moreover, IVM-NLCs markedly decreased the apoptosis rate of PEDV-induced Vero cells. Hence, IVM-NLCs showed superior inhibitory effect against PEDV compared to free IVM. Together, these results implied that NLCs is an efficient delivery system for IVM to improve its antiviral efficacy against PEDV via enhanced intracellular uptake.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"pharmaceutics16050601"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Xiaolin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Shasha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Zuo",
"given": "Qindan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Gong",
"given": "Jiahao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Xinhao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yongshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Xiao",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
},
{
"name": "Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhai",
"given": "Xiaofeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Haifeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8439-8989",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Pesticide Science, College of Sciences, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Mingzhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Xiuge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Engineering Center of Innovative Veterinary Drugs, Center for Veterinary Drug Research and Evaluation, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 1 Weigang, Nanjing 210095, China"
}
],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Dawei",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"container-title-short": "Pharmaceutics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-02T07:57:56Z",
"timestamp": 1714636676000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-02T08:27:48Z",
"timestamp": 1714638468000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"KYCXJC2023005",
"KYCYXT2022010"
],
"name": "Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities"
},
{
"name": "Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-03T00:35:16Z",
"timestamp": 1714696516369
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714348800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/16/5/601/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "601",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9",
"article-title": "Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02344-20",
"article-title": "Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection Induces Caspase-8-Mediated G3BP1 Cleavage and Subverts Stress Granules To Promote Viral Replication",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02344-20",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198045",
"article-title": "Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV)_An update on etiology, transmission, pathogenesis, and prevention and control",
"author": "Jung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198045",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32588-3",
"article-title": "In situ structure and dynamics of an alphacoronavirus spike protein by cryo-ET and cryo-EM",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4877",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00406-19",
"article-title": "Engineering a Live Attenuated Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Vaccine Candidate via Inactivation of the Viral 2′-O.-Methyltransferase and the Endocytosis Signal of the Spike Protein",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00406-19",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12754",
"article-title": "Melatonin and other indoles show antiviral activities against swine coronaviruses in vitro at pharmacological concentrations",
"author": "Zhai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e12754",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00645-21",
"article-title": "EGR1 Suppresses Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Regulating IRAV to Degrade Viral Nucleocapsid Protein",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00645-21",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2021.01.003",
"article-title": "Drug Repurposing for Rare Diseases",
"author": "Roessler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107930",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing for COVID-19: Approaches, challenges and promising candidates",
"author": "Ng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107930",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.039",
"article-title": "Deep Remission at 1 Year Prevents Progression of Early Crohn’s Disease",
"author": "Ungaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd.2018.168",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations",
"author": "Pushpakom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S313093",
"article-title": "Clinical, Biochemical and Molecular Evaluations of Ivermectin Mucoadhesive Nanosuspension Nasal Spray in Reducing Upper Respiratory Symptoms of Mild COVID-19",
"author": "Aref",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4063",
"journal-title": "IJN",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00253-006-0361-2",
"article-title": "Construction of ivermectin producer by domain swaps of avermectin polyketide synthase in Streptomyces avermitilis",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "986",
"journal-title": "Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2016.1231494",
"article-title": "Ivermectin induces PAK1-mediated cytostatic autophagy in breast cancer",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2498",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2020.10.005",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: An Anthelmintic, an Insecticide, and Much More",
"author": "Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.09.010",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits DNA polymerase UL42 of pseudorabies virus entrance into the nucleus and proliferation of the virus in vitro and vivo",
"author": "Lv",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002",
"article-title": "Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1–4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "301",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dks147",
"article-title": "Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: New prospects for an old drug",
"author": "Mastrangelo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1884",
"journal-title": "J. Antimicrob. Chemother.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep23138",
"article-title": "Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import",
"author": "Magar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23138",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.01.007",
"article-title": "Identification of novel antivirals inhibiting recognition of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus capsid protein by the Importin α/β1 heterodimer through high-throughput screening",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"article-title": "The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104760",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110823",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Das, S., Lee, S.H., Chia, V.D., Chow, P.S., Macbeath, C., Liu, Y., and Shlieout, G. (2020). Development of microemulsion based topical ivermectin formulations: Pre-formulation and formulation studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 189."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.04.013",
"article-title": "Prediction of positive food effect: Bioavailability enhancement of BCS class II drugs",
"author": "Raman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "506",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.12.030",
"article-title": "New surface-modified lipid nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for salmon calcitonin",
"author": "Garciafuentes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "122",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "296",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114995",
"article-title": "5-Fluorouracil nano-delivery systems as a cutting-edge for cancer therapy",
"author": "Hassan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114995",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "246",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cis.2019.102048",
"article-title": "Carotenoid-loaded nanocarriers: A comprehensive review",
"author": "Rehman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102048",
"journal-title": "Adv. Colloid Interface Sci.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.016",
"article-title": "Lipid-polymer hybrid nanocarriers for delivering cancer therapeutics",
"author": "Date",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "60",
"journal-title": "J. Control. Release",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "271",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110649",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Zhang, Q., Yang, H., Sahito, B., Li, X., Peng, L., Gao, X., Ji, H., Wang, L., Jiang, S., and Guo, D. (2020). Nanostructured lipid carriers with exceptional gastrointestinal stability and inhibition of P-gp efflux for improved oral delivery of tilmicosin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 187."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21691401.2017.1307207",
"article-title": "Ivermection-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Preparation, characterisation, stability and transdermal behaviour",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/smll.200902384",
"article-title": "Inhibition of HSV-1 Attachment, Entry, and Cell-to-Cell Spread by Functionalized Multivalent Gold Nanoparticles",
"author": "Shukla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1044",
"journal-title": "Small",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsami.5b06876",
"article-title": "Antiviral Activity of Graphene Oxide: How Sharp Edged Structure and Charge Matter",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21571",
"journal-title": "ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4014/jmb.1909.09041",
"article-title": "Surface-Displayed Porcine IFN-λ3 in Lactobacillus plantarum Inhibits Porcine Enteric Coronavirus Infection of Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2023.2181615",
"article-title": "N protein of PEDV plays chess game with host proteins by selective autophagy",
"author": "Zhai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2338",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01660-16",
"article-title": "Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus 3C-Like Protease-Mediated Nucleocapsid Processing: Possible Link to Viral Cell Culture Adaptability",
"author": "Jengarn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01660-16",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.052",
"article-title": "Colloid properties of hydrophobic modified alginate: Surface tension, ζ-potential, viscosity and emulsification",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "Carbohydr. Polym.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.081",
"article-title": "Nanoparticle size distribution quantification from transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of ruthenium tetroxide stained polymeric nanoparticles",
"author": "Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "208",
"journal-title": "J. Colloid. Interface Sci.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.098",
"article-title": "Tunable morphology of lipid/chitosan particle assemblies",
"author": "Bugnicourt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105",
"journal-title": "J. Colloid. Interface Sci.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "534",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.12.033",
"article-title": "Generation of hydrate forms of paroxetine HCl from the amorphous state: An evaluation of thermodynamic and experimental predictive approaches",
"author": "Pina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "481",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5582/bst.2016.01059",
"article-title": "Cloning, purification, crystallization and X-ray crystallographic analysis of the periplasmic sensing domain of Pseudomonas fluorescens chemotactic transducer of amino acids type A (CtaA)",
"author": "Roujeinikova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "BST",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.201439363",
"article-title": "Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in host–pathogen interactions",
"author": "Schorey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drup.2021.100762",
"article-title": "Targeted nanomedicine modalities for prostate cancer treatment",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100762",
"journal-title": "Drug Resist. Updates",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tibs.2010.04.002",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate biological outcomes",
"author": "Hamanaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Trends Biochem. Sci.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00026.2013",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and ROS-Induced ROS Release",
"author": "Zorov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "909",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/16/5/601"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Enhanced In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Ivermectin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus via Improved Intracellular Delivery",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}