Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against Sars-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation
Emmanuel Chuks Oranu, Esther Oluchukwu Eze, Adanna Ijeawele, Chisom George Obidimma, Belinda Chinecherem Umeh, Perpetua Chinonyelum Ejezie, Ic Uzochukwu
GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030
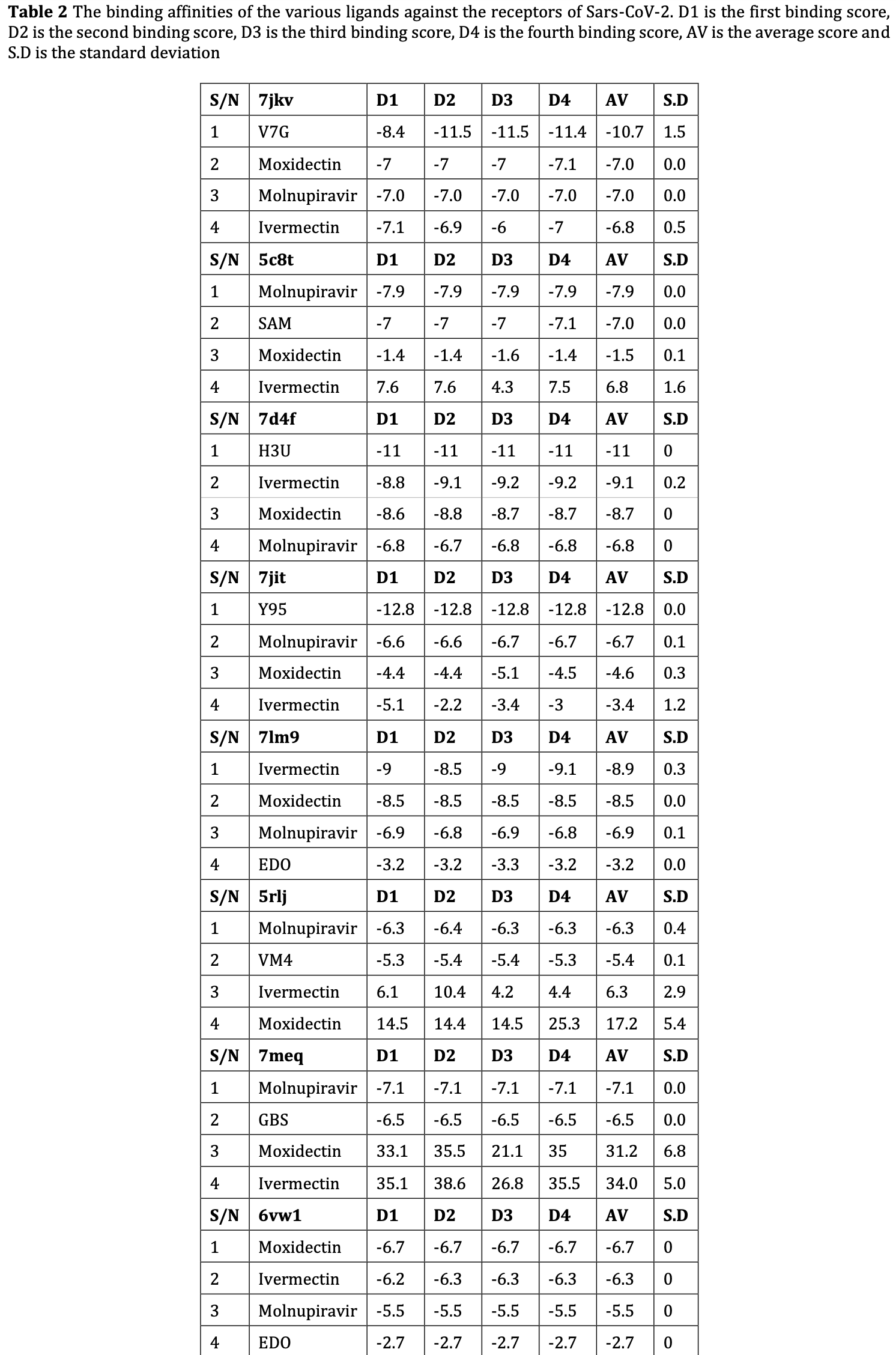
Corona-viruses (CoVs), a large family of single-stranded RNA viruses, can infect animals and also humans, causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, hepatic, and neurologic disease. As the largest known RNA viruses, they are further divided into four genera: alpha-coronavirus, beta-corona-virus, gamma-corona virus and delta-coronavirus. SARS-CoV-2 belong to genus betacoronavirus. The viral genome of SARS-CoV-2 codes 4 major structural proteins: the nucleocapsid (N) protein, the transmembrane (M) protein, the envelope (E) protein, and the spike (S) protein. It also encodes 16 nonstructural proteins (NSPs) and 9 accessory proteins required for replication and pathogenesis. The Molecular docking simulations was used to determine the binding affinities of Ivermectin, Moxidectin and Molnupiravir against NSP13 receptor of SARS-CoV-2. The experimental crystal structures of the receptor was obtained from the protein data bank (PDB). The receptor was prepared using Chimera-1.10.1 and AutoDock tools-1.5.6. The 3D structure of the selected approved drugs and the reference ligand was obtained from PDB and Drugbank and prepared using AutoDock tools-1.5.6. Validation of docking protocol was done by reproducing the PDB crystal structures insilico. Molecular docking simulations were performed using AutoDockVina-4.2.6 on the Linux operating system (ubuntu) 20.04. Then the docking results were analysed and visualized using Pymol-2.3.0. Molecular dynamics of the frontrunners with the reference ligand and protein was done in 10000 ps. Moxidectin, molnupiravir and Ivermectin showed high binding affinities to the receptors. Moxidectin and Ivermectin showed stability after molecular dynamics simulation to further validate the claim. These drugs are predicted as possible antivirals in the treatment of Covid-19.
Flexibility Profile analysis Figure 6 RMSF Plot of the molecular dynamics simulation of the drug target and ligands Root Mean Square Fluctuation is a measure of the displacement of a particular atom or group of atoms, relative to the reference structure, averaged over the number of atoms. It is used for the analysis of time-dependent motions of the structures [14] . From the results in 7JIT, In the RMS fluctuation plot, the system was reasonably stable between 1500 atoms and 2000 atoms which indicates that above 2000 atoms, some amino acid residues caused fluctuation within the system with the least fluctuations between 800 atoms and 1800 atoms From the results in 7JKV,from point 1 atom to 2700 atoms the system was more stable than from point 2800 atoms to 3100 atoms. It can also be seen that Moxidectin exhibited better stability than Ivermectin. From the results in 5rlj,in the graph above, it can be deduced that there were a lot of fluctuations which might be due to the presence of amino acid residues in the system. However, there was still stability at points 3600 pico seconds to 4600 pico seconds.
Compliance with ethical standards
Disclosure of conflict of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
References
Aier, Structural insights into conformational stability of both wild-type and mutant EZH2 receptor, Sci. Rep,
doi:10.1038/srep34984Alok, Ramakant, Ivermectin : Potential Role as Repurposed Drug for COVID-19
Awad, Hassan, Dweek, Aboelata, Rawas-Qalaji et al., Repurposing Potential of the Antiparasitic Agent Ivermectin for the Treatment and/or Prophylaxis of COVID-19, Pharmaceuticals, MDPI
Beckstein, Position restraints MD, ADK Tutorial
Chuks Oranu, Ijeawele, Egbuna, Ifejirika Ezeonyi, Chukwubuikem et al., Previous and potential mutations of Sars-cov-2 receptors and their interaction with known inhibitors, GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences
Eweas, Alhossary, Abdel-Moneim, Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs AgainstSARS-CoV-2, Front. Microbiol
Ferreira, Rn Dos Santos, Oliva, Andricopulo, Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies, Molecules
Gierer, Bertram, Kaup, Wrensch, Heurich et al., The spike protein of the emerging betacoronavirus EMC uses a novel coronavirus receptor for entry, can be activated by TMPRSS2, and is targeted by neutralizing antibodies, JVirol
Hofmann, Pyrc, Hoek, Van Der, Geier et al., Human coronavirus NL63 employs the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor,
doi:10.1073/pnas.0409465102Hwa, Chaudhary, Mishra, (n.D, A Review on Molecular Docking : Novel Tool for Drug Discovery Related papers A Review on Molecular Docking : Novel Tool for Drug Discovery
López-Vallejo, Caulfield, Martínez-Mayorga, Giulianotti, Houghten et al., Integrating virtual screening and combinatorial chemistry for accelerated drug discovery, Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen
Marak, (n.D, Step toward repurposing drug discovery for COVID-19 therapeutics through in silico approach,
doi:10.1002/ddr.21757Roy, Narayan Das, Kar, understanding the basics of QSAR for application in Pharmaceutical sciences and risk assessment, Computational chemistry chapter,
doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801505-6.00005-3Tuckerman, Martyna, Understanding Modern Molecular Dynamics : Techniques and Applications
Yoshimoto, The Proteins of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus -2 ( SARS CoV -2 or n -COV19 ), the Cause of COVID -19, The Protein Journal,
doi:10.1007/s10930-020-09901-4DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030",
"ISSN": [
"2581-3250"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Corona-viruses (CoVs), a large family of single-stranded RNA viruses, can infect animals and also humans, causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, hepatic, and neurologic disease. As the largest known RNA viruses, they are further divided into four genera: alpha-coronavirus, beta- corona- virus, gamma-corona virus and delta-coronavirus. SARS-CoV-2 belong to genus betacoronavirus. The viral genome of SARS-CoV-2 codes 4 major structural proteins: the nucleocapsid (N) protein, the transmembrane (M) protein, the envelope (E) protein, and the spike (S) protein. It also encodes 16 nonstructural proteins (NSPs) and 9 accessory proteins required for replication and pathogenesis. The Molecular docking simulations was used to determine the binding affinities of Ivermectin, Moxidectin and Molnupiravir against NSP13 receptor of SARS-CoV-2. The experimental crystal structures of the receptor was obtained from the protein data bank (PDB). The receptor was prepared using Chimera-1.10.1 and AutoDock tools-1.5.6. The 3D structure of the selected approved drugs and the reference ligand was obtained from PDB and Drugbank and prepared using AutoDock tools-1.5.6. Validation of docking protocol was done by reproducing the PDB crystal structures insilico. Molecular docking simulations were performed using AutoDockVina-4.2.6 on the Linux operating system (ubuntu) 20.04. Then the docking results were analysed and visualized using Pymol-2.3.0. Molecular dynamics of the frontrunners with the reference ligand and protein was done in 10000 ps. Moxidectin, molnupiravir and Ivermectin showed high binding affinities to the receptors. Moxidectin and Ivermectin showed stability after molecular dynamics simulation to further validate the claim. These drugs are predicted as possible antivirals in the treatment of Covid-19.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emmanuel Chuks Oranu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esther Oluchukwu Eze",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adanna Ijeawele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chisom George Obidimma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belinda Chinecherem Umeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perpetua Chinonyelum Ejezie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "IC Uzochukwu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences",
"container-title-short": "GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.gsconlinepress.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-29T15:32:57Z",
"timestamp": 1706542377000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-29T15:32:58Z",
"timestamp": 1706542378000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-30T00:22:49Z",
"timestamp": 1706574169178
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://gsconlinepress.com/journals/gscbps/content/validation-binding-affinities-and-stabilities-ivermectin-and-moxidectin-against-sars-cov-2",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "12033",
"original-title": [],
"page": "303-314",
"prefix": "10.30574",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "GSC Online Press",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://gsconlinepress.com/journals/gscbps/content/validation-binding-affinities-and-stabilities-ivermectin-and-moxidectin-against-sars-cov-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against Sars-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.ourcrossmarkpolicy",
"volume": "26"
}