Abstract: 2072
J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 2072-2078
Absorption, Tissue Distribution, and Excretion of Tritium-Labeled
Ivermectin in Cattle, Sheep, and Rat
Shuet-Hing Lee Chiu,' Marilyn L. Green, Francis P. Baylis, Diana Eline, Avery Rosegay,
Henry Meriwether, a n d Theodore A. Jacob
Department of Animal and Exploratory Drug Metabolism, Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories,
P.O. Box 2000, Rahway, New Jersey 07065
Tritium-labeled ivermectin was studied in cattle, sheep, and rat for absorption, tissue residue distribution,
and excretion at doses of 0.3 mg/ kg of body weight. The drug was absorbed by various dosing routes.
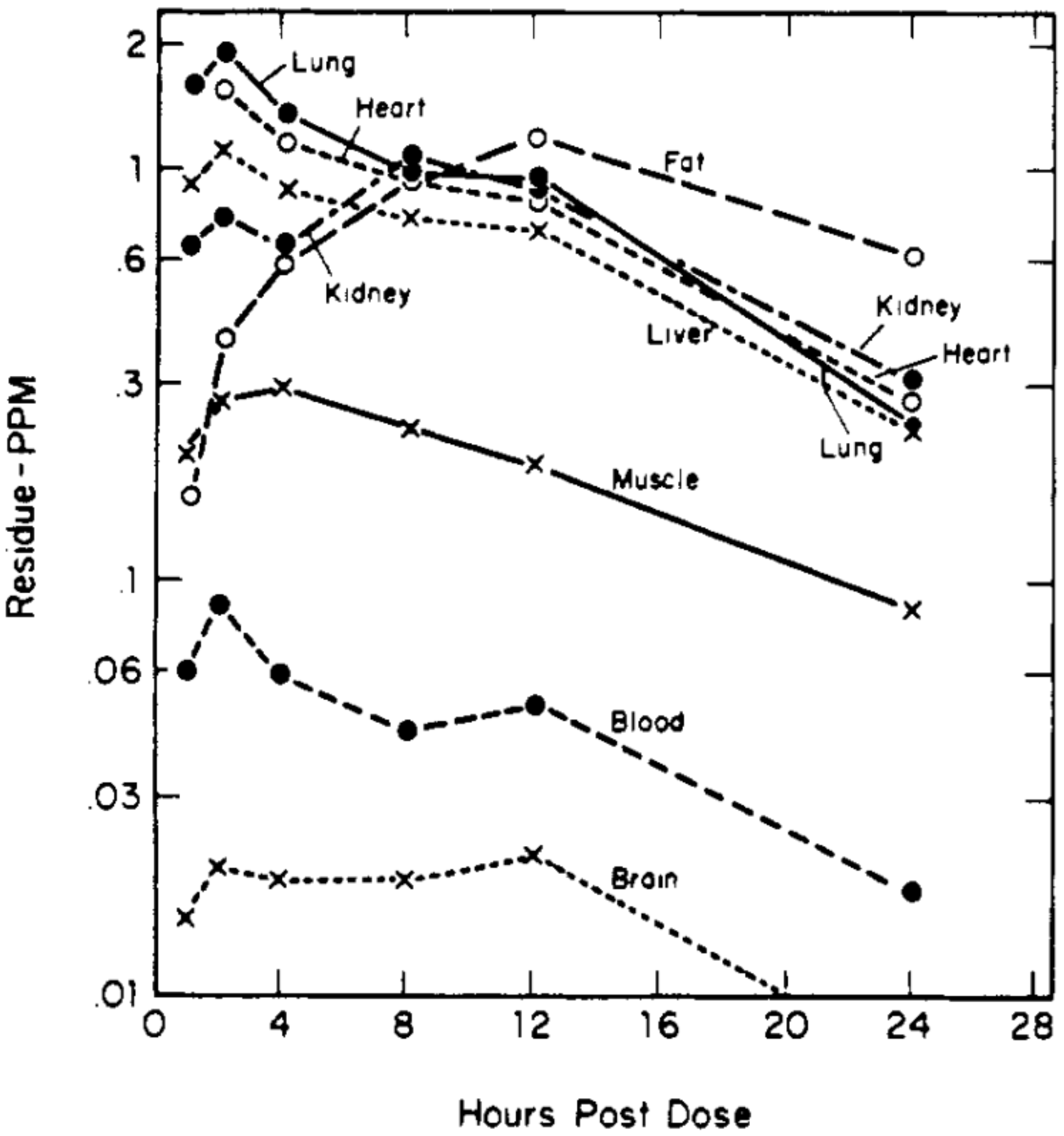
By intraruminal and subcutaneous dosing routes, highest tissue residues were present in fat and liver
of cattle, with half-lives of 6-8 and 4-5 days, respectively. Shorter half-lives (1-2 days) were observed
in sheep and rat. The tissue residue distribution pattern was essentially the same for all species studied
and similar in male and female rats. With doses of tritium-labeled avermectin B1, ranging from 0.06
to 7.5 mg/kg of body weight, plasma and tissue residue concentrations increased proportionally with
the dose. When ivermectin was administered by various routes (ip, sc, iv, oral, and intraruminal), blood
residue levels converged to 20-50 ppb 4 h after dosing and then depleted a t a similar rate regardless
of the dosing route. Ivermectin was excreted primarily in the feces, with only less than 25;) of the doses
being eliminated in the urine in all three species studied.
Ivermectin is the 22,23-dihydro derivative of avermectin B1, a macrocyclic lactone produced by a n actinomycetes, Streptomyces avermitilis (Chabala et al., 1980;
Burg et al., 1979; Miller e t al., 1979; Egerton et al., 1979).
It is active a t extremely low dosage against a wide variety
of nematode and arthropod parasites. I t is widely used
for the treatment and control of parasites in cattle, horses,
sheep, swine, and dogs (Campbell et al., 1983). Ivermectin consists of two closely related homologues containing
no less than 80!( 22,23-dihydroavermectin B1, (H2Bla)and
no more than 20 22,23-dihydroavermectin Blb ( H & , )
as shown in Figure 1. In vivo metabolism and in vitro
metabolism of ivermectin have been studied previously in
cattle, sheep and rat (Chiu et al., 1986, 1988) and by hepatic microsomes from cattle and rat (Miwa et al., 1982).
A similar in vitro study was also carried out with swine
hepatic microsomes (Chiu et al., 1984, 1987). Pharmacokinetics of ivermectin using various formulations have
also been reported in various species, e.g., swine, dog, sheep,
and cattle (Lo et al., 1985; Wilkinson et al., 1985; Prichard et al., 1985; Fink and Porras, 1989). The biological
half-lives (t1p) of the drug increase among these species
in the same order, ranging from 0.5 day (swine) to 1.8 (dog),
2.7 (sheep), and 2.8 days (cattle). T h e studies herein
described were carried out with the radiolabeled drug in
target animals of drug use (cattle, sheep) as well as the
laboratory animal (rat) mainly for tissue residue levels,
distribution, a n d excretion of t h e radioactive dose.
Absorption of the radioactive dose was also studied for
comparison with tissue residue levels.
'(
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Radiolabeled Chemicals. [22,23-3H]Ivermectinconsisting
of [22,23-3H]H2B1,and [22,23-3H]H2Blb(4:l) was prepared by
reduction of avermectins B1, and Blb separately with tritium in
the presence of Wilkinson's catalyst [PhaPJsRhCl (Chabala et
al.,..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jf00101a015",
"ISSN": [
"0021-8561",
"1520-5118"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf00101a015",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1021/jf00101a015"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiu",
"given": "Shuet Hing Lee",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "Marilyn L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baylis",
"given": "Francis P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eline",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosegay",
"given": "Avery",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meriwether",
"given": "Henry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "Theodore A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry",
"container-title-short": "J. Agric. Food Chem.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2005,
3,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2005-03-18T08:01:38Z",
"timestamp": 1111132898000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-06T14:21:15Z",
"timestamp": 1680790875000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-10T02:15:08Z",
"timestamp": 1712715308192
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 90,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
1990,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
1990,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/jf00101a015",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "316",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2072-2078",
"prefix": "10.1021",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
1990,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2002,
5,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
1990,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Chemical Society (ACS)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf00101a015"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Absorption, tissue distribution, and excretion of tritium-labeled ivermectin in cattle, sheep, and rat",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "38"
}