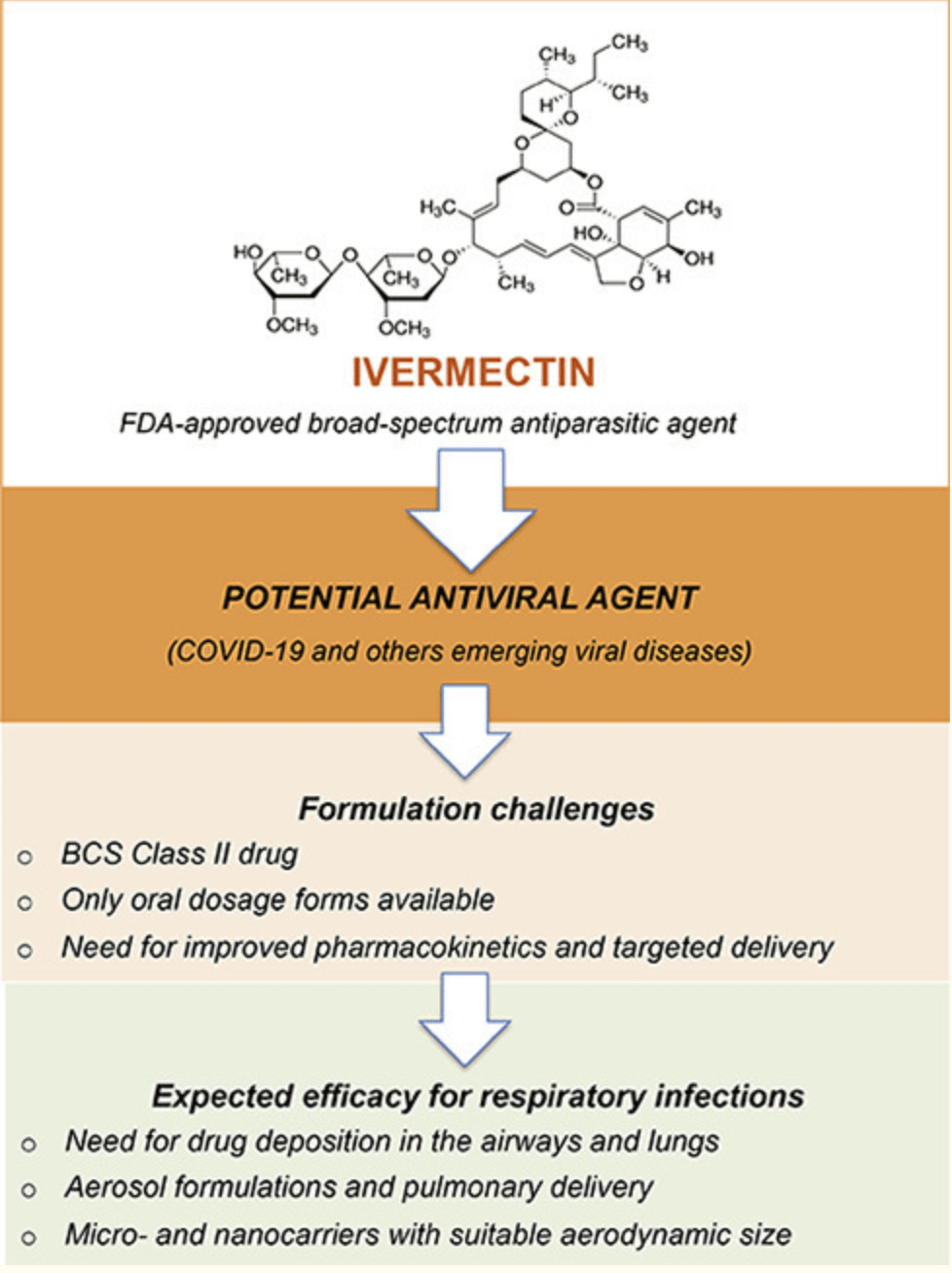
Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19
Fabio Rocha Formiga, Roger Leblanc, Juliana De Souza Rebouças, Leonardo Paiva Farias, Ronaldo Nascimento De Oliveira, Lindomar Pena
Journal of Controlled Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors deny the existence of any conflicts of interest.
References
Ali, Afzal, Verma, Bhattacharya, Ahmad et al., Therapeutic efficacy of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles encapsulated ivermectin (nano-ivermectin) against brugian filariasis in experimental rodent model, Parasitol. Res,
doi:10.1007/s00436-013-3696-5Ali, Afzal, Verma, Misra-Bhattacharya, Ahmad et al., Improved antifilarial activity of ivermectin in chitosan-alginate nanoparticles against human lymphatic filarial parasite, Brugia malayi, Parasitol. Res,
doi:10.1007/s00436-013-3466-4Barrows, Campos, Powell, Prasanth, Schott-Lerner et al., A screen of FDA-approved drugs for inhibitors of Zika virus infection, Cell Host Microbe,
doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004Camargo, Sapin, Daloz, Maincent, Ivermectin-loaded microparticles for parenteral sustained release: in vitro characterization and effect of some formulation variables, J. Microencapsul,
doi:10.3109/02652048.2010.501397Chaccour, Ruiz-Castillo, Richardson, Moncunill, Casellas et al., The SARS-CoV-2 Ivermectin Navarra-ISGlobal trial (SAINT) to evaluate the potential of ivermectin to reduce COVID-19 transmission in low risk, non-severe COVID-19 patients in the first 48 hours after symptoms onset: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized control pilot trial, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04421-zCojocaru, Botezat, Gardikiotis, Uritu, Dodi et al., Nanomaterials designed for antiviral drug delivery transport across biological barriers, Pharmaceutics,
doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12020171Croci, Bottaro, Chan, Watanabe, Pezzullo et al., Liposomal systems as nanocarriers for the antiviral agent Ivermectin, Int. J. Biomater,
doi:10.1155/2016/8043983Ebbelaar, Venema, Van Dijk, Topical ivermectin in the treatment of Papulopustular rosacea: a systematic review of evidence and clinical guideline recommendations, Dermatol. Ther. (Heidelb),
doi:10.1007/s13555-018-0249-yHo, Nichols, Edgar, Murgia, Loretz et al., Challenges and strategies in drug delivery systems for treatment of pulmonary infections, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm,
doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.002Ketkar, Yang, Wormser, Wang, Lack of efficacy of ivermectin for prevention of a lethal Zika virus infection in a murine system, Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.03.012Liu, Guan, Qin, Zhang, Mao, Physicochemical properties affecting the fate of nanoparticles in pulmonary drug delivery, Drug Discov. Today,
doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2019.09.023Lv, Liu, Wang, Dang, Qiu et al., Ivermectin inhibits DNA polymerase UL42 of pseudorabies virus entrance into the nucleus and proliferation of the virus in vitro and vivo, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.09.010Ono, Tatsuo, Hidaka, Aoki, Minagawa et al., Measles viruses on throat swabs from measles patients use signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (CDw150) but not CD46 as a cellular receptor, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.75.9.4399-4401.2001Paranjpe, Müller-Goymann, Nanoparticle-mediated pulmonary drug delivery: a review, Int. J. Mol. Sci,
doi:10.3390/ijms15045852Rizzo, Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action, Naunyn Schmiedeberg's, Arch. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1007/s00210-020-01902-5Sandler, Firpo, Omoba, Vu, Menachery et al., Novel ionophores active against La Crosse virus identified through rapid antiviral screening, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother,
doi:10.1128/AAC.00086-20Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the Ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther,
doi:10.1002/cpt.1889Surnar, Kamran, Shah, Basu, Kolishetti et al., Orally administrable therapeutic synthetic nanoparticle for Zika virus, ACS Nano,
doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b02807Takano, Sugano, Higashida, Hayashi, Machida et al., Oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs: computer simulation of fraction absorbed in humans from a miniscale dissolution test, Pharm. Res,
doi:10.1007/s11095-006-0162-4Ullio-Gamboa, Palma, Benoit, Allemandi, Picollo et al., Ivermectin lipid-based nanocarriers as novel formulations against head lice, Parasitol. Res,
doi:10.1007/s00436-017-5510-2Varghese, Kaukinen, Glasker, Bespalov, Hanski et al., Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.012Wang, Lv, Ji, Wang, Qiu et al., Ivermectin treatment inhibits the replication of porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) in vitro and mitigates the impact of viral infection in piglets, Virus Res,
doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2019.01.010Xu, Han, Liu, Pang, Zheng et al., Antivirus effectiveness of ivermectin on dengue virus type 2 in Aedes albopictus, PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis,
doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0006934Yan, Ci, Chen, Chen, Li et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflamm. Res,
doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin alpha/beta1 heterodimer, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760Zhang, Song, Ci, An, Ju et al., Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflamm. Res,
doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8Zhang, Zhou, Wei, Yue, Wang et al., Histopathologic changes and SARS-CoV-2 imunostaining in the lung of a patient with COVID-19, Ann. Intern. Med,
doi:10.7326/M20-0533Zheng, Fan, Yu, Feng, Lou et al., Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang Province, China, BMJ,
doi:10.1136/bmj.m1443Zhou, Leung, Tang, Parumasivam, Loh et al., Inhaled formulations and pulmonary drug delivery systems for respiratory infections, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev,
doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.022Zou, Ruan, Huang, Liang, Huang et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMc2001737DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009",
"ISSN": [
"0168-3659"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009",
"alternative-id": [
"S0168365920305800"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Controlled Release"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1553-0533",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Formiga",
"given": "Fabio Rocha",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leblanc",
"given": "Roger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Souza Rebouças",
"given": "Juliana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farias",
"given": "Leonardo Paiva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Oliveira",
"given": "Ronaldo Nascimento",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pena",
"given": "Lindomar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Controlled Release",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Controlled Release",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-07T15:10:29Z",
"timestamp": 1602083429000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-26T11:46:04Z",
"timestamp": 1656243964000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003593",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000193",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "International Development Research Centre"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002322",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100006162",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100006507",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação Oswaldo Cruz"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-14T02:35:27Z",
"timestamp": 1715654127631
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 50,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0168365920305800?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0168365920305800?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "758-761",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature.2015.18507",
"article-title": "Anti-parasite drugs sweep Nobel prize in medicine 2015",
"author": "Callaway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "174",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0005",
"volume": "526",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.09.010",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits DNA polymerase UL42 of pseudorabies virus entrance into the nucleus and proliferation of the virus in vitro and vivo",
"author": "Lv",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0010",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2019.01.010",
"article-title": "Ivermectin treatment inhibits the replication of porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) in vitro and mitigates the impact of viral infection in piglets",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "80",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0015",
"volume": "263",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0006934",
"article-title": "Antivirus effectiveness of ivermectin on dengue virus type 2 in Aedes albopictus",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0020",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.012",
"article-title": "Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses",
"author": "Varghese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0025",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"article-title": "The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin alpha/beta1 heterodimer",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104760",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0030",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004",
"article-title": "A screen of FDA-approved drugs for inhibitors of Zika virus infection",
"author": "Barrows",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0035",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.03.012",
"article-title": "Lack of efficacy of ivermectin for prevention of a lethal Zika virus infection in a murine system",
"author": "Ketkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0040",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0045",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.75.9.4399-4401.2001",
"article-title": "Measles viruses on throat swabs from measles patients use signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (CDw150) but not CD46 as a cellular receptor",
"author": "Ono",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4399",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0050",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "Histopathologic changes and SARS-CoV-2 imunostaining in the lung of a patient with COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"first-page": "M20",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0055",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1889",
"article-title": "The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the Ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Schmith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0060",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01902-5",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action",
"author": "Rizzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1153",
"journal-title": "Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0065",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00086-20",
"article-title": "Novel ionophores active against La Crosse virus identified through rapid antiviral screening",
"author": "Sandler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0070",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137647",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2: a storm is raging",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2202",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0075",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0080",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x",
"article-title": "Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019",
"author": "Wölfel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0085",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001737",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1177",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0090",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1443",
"article-title": "Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang Province, China, January-march 2020: retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1443",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0095",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13555-018-0249-y",
"article-title": "Topical ivermectin in the treatment of Papulopustular rosacea: a systematic review of evidence and clinical guideline recommendations",
"author": "Ebbelaar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "Dermatol. Ther. (Heidelb).",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0100",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "589",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0105",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "524",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0110",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04421-z",
"author": "Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Trials.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0115",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.002",
"article-title": "Challenges and strategies in drug delivery systems for treatment of pulmonary infections",
"author": "Ho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0120",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.022",
"article-title": "Inhaled formulations and pulmonary drug delivery systems for respiratory infections",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0125",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics11030113",
"article-title": "Strategies to enhance drug absorption via nasal and pulmonary routes",
"author": "Ghadiri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0130",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11095-006-0162-4",
"article-title": "Oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs: computer simulation of fraction absorbed in humans from a miniscale dissolution test",
"author": "Takano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1144",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0140",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.9b02807",
"article-title": "Orally administrable therapeutic synthetic nanoparticle for Zika virus",
"author": "Surnar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11034",
"journal-title": "ACS Nano",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0145",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S38378",
"article-title": "Nanodrugs: pharmacokinetics and safety",
"author": "Onoue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Nanomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0150",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00436-017-5510-2",
"article-title": "Ivermectin lipid-based nanocarriers as novel formulations against head lice",
"author": "Ullio-Gamboa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2111",
"journal-title": "Parasitol. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0155",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00436-013-3466-4",
"article-title": "Improved antifilarial activity of ivermectin in chitosan-alginate nanoparticles against human lymphatic filarial parasite, Brugia malayi",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2933",
"journal-title": "Parasitol. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0160",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00436-013-3696-5",
"article-title": "Therapeutic efficacy of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles encapsulated ivermectin (nano-ivermectin) against brugian filariasis in experimental rodent model",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Parasitol. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0165",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/02652048.2010.501397",
"article-title": "Ivermectin-loaded microparticles for parenteral sustained release: in vitro characterization and effect of some formulation variables",
"author": "Camargo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "609",
"journal-title": "J. Microencapsul.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0170",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Liposomal systems as nanocarriers for the antiviral agent Ivermectin",
"author": "Croci",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biomater.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0175",
"volume": "8043983",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2019.09.023",
"article-title": "Physicochemical properties affecting the fate of nanoparticles in pulmonary drug delivery",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov. Today",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0180",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4155/tde-2017-0037",
"article-title": "Drug delivery to the lungs: challenges and opportunities",
"author": "Newman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Ther. Deliv.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0185",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms15045852",
"article-title": "Nanoparticle-mediated pulmonary drug delivery: a review",
"author": "Paranjpe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5852",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0190",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics12020171",
"article-title": "Nanomaterials designed for antiviral drug delivery transport across biological barriers",
"author": "Cojocaru",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0195",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.0c02540",
"article-title": "Nano research for COVID-19",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3719",
"journal-title": "ACS Nano",
"key": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009_bb0200",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168365920305800"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "329"
}