Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review
Esmaeil Mehraeen, Soudabeh Yarmohammadi, Pegah Mirzapour, Seyed Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, Soheil Dehghani, Leila Molaeipour, Ayoob Molla, Elaheh Karimi, Faeze Abbaspour, Seyedahmad Seyedalinaghi
International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1055/s-0044-1786046
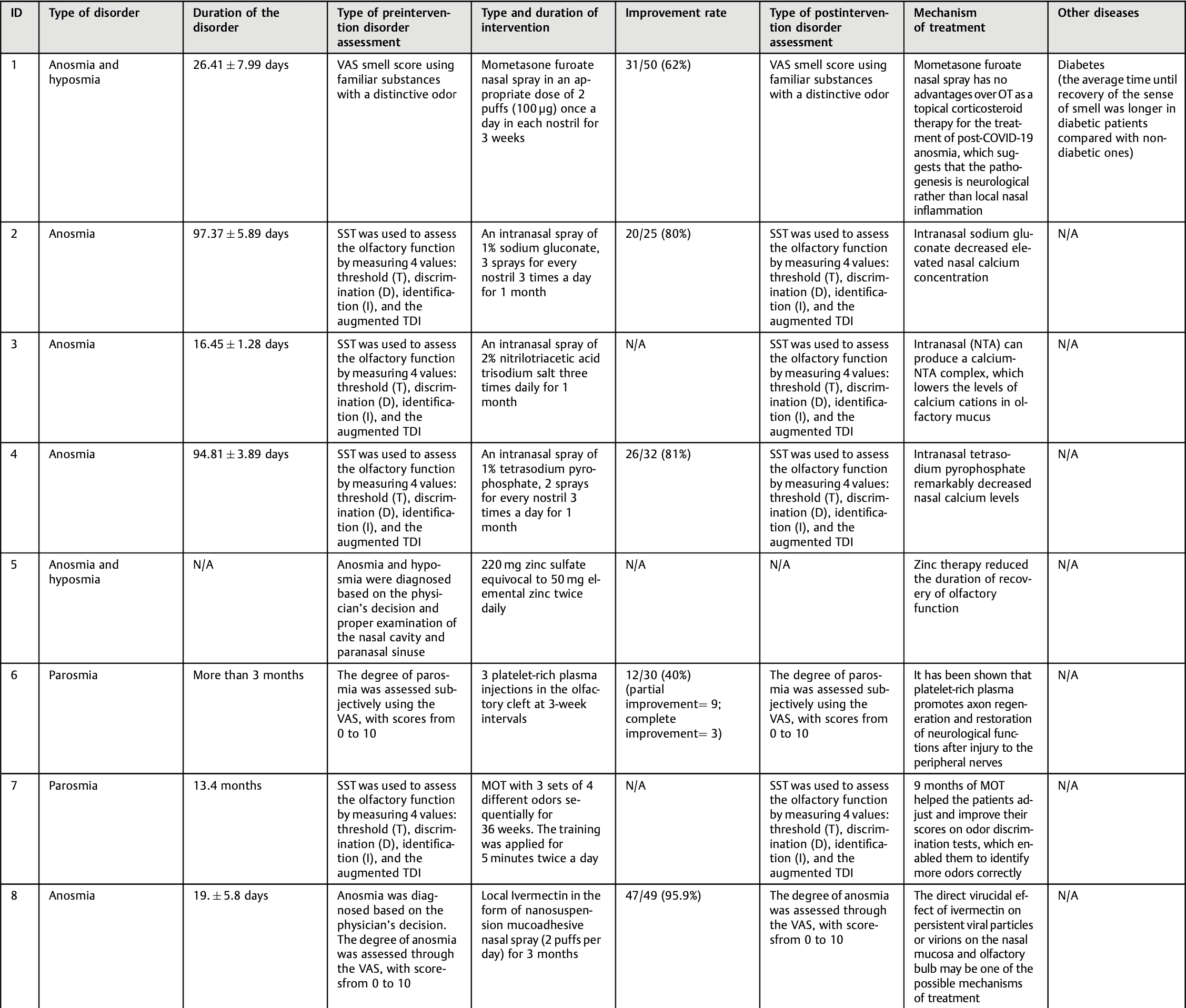
Introduction Olfactory dysfunction (OD) has emerged as a notable symptom among coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, with its prevalence varying among different populations. Recognizing the need to provide therapeutic solutions for these individuals, the present study seeks to comprehensively review the current evidence on potential underlying mechanisms and treatment modalities to manage OD in COVID-19 patients. Objective To review the recent evidence on treatments for OD in COVID-19. From the beginning of the study until August 2nd, 2023, we conducted a systematic search on four electronic databases, PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Web of Science, to find relevant publications. Data Synthesis In the present study, 37 articles were selected for data extraction and included in the final review. The total number of patients was of 3,560 (2,098 female and 1,462 male subjects). The predominant disorders reported were hyposmia, anosmia, and parosmia. In most of the studies, the pre and postintervention assessments were the same, except for one study, in which the pre-intervention assessment of the disorder was through the SST, Sniffin' Sticks Test (SST), and the post-intervention assessment was through the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and the 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22). The findings suggest olfactory training (OT), ivermectin, palmitoylethanolamide, luteolin, and systemic corticosteroids, in combination with topical corticosteroids, are potential therapies for COVID-19 patients with olfactory impairment.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate Not applicable Consent to Publication Not applicable.
Authors' Contributions EM: conception and design of the study, and final approval of the version to be submitted; SS: conception and design of the study, critical review for important intellectual content, and final approval of the version to be submitted; LM: acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; SY, PM, SSTZ, SD, AM, EK and FA: drafting of the article.
Funding The authors declare that they did not receive funding from agencies in the public, private, or not-for-profit sectors for the conduction of the present study.
Conflict of Interests The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
References
Abdelalim, Mohamady, Elsayed, Elawady, Ghallab, Corticosteroid nasal spray for recovery of smell sensation in COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial, Am J Otolaryngol
Abdelazim, Abdelazim, Moneir, The effect of intra-nasal tetra sodium pyrophosphate on decreasing elevated nasal calcium and improving olfactory function post COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial, Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol
Abdelmaksoud, Ghweil, Hassan, Olfactory Disturbances as Presenting Manifestation Among Egyptian Patients with COVID-19: Possible Role of Zinc, Biol Trace Elem Res
Bilinska, Butowt, Anosmia in COVID-19: A Bumpy Road to Establishing a Cellular Mechanism, ACS Chem Neurosci
Boscolo-Rizzo, Borsetto, Fabbris, Evolution of Altered Sense of Smell or Taste in Patients With Mildly Symptomatic COVID-19, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Butowt, Bartheld, Anosmia in COVID-19: Underlying Mechanisms and Assessment of an Olfactory Route to Brain Infection, Neuroscientist
De Luca, Camaioni, Marra, Effect of Ultra-Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin on Olfaction and Memory in Patients with Long COVID: Results of a Longitudinal Study, Cells
Donegani, Miceli, Pardini, Brain metabolic correlates of persistent olfactory dysfunction after SARS-Cov2 infection, Biomedicines
Esposito, Cirillo, Micco, Olfactory loss and brain connectivity after COVID-19, Hum Brain Mapp
Galougahi, Ghorbani, Bakhshayeshkaram, Naeini, Haseli, Olfactory bulb magnetic resonance imaging in SARS-CoV-2-induced anosmia: the first report, Acad Radiol
Gerkin, Ohla, Veldhuizen, The best COVID-19 predictor is recent smell loss: a cross-sectional study, medRxiv
Gracia, Ortiz, Candela, Design and Evaluation of a Potential Non-Invasive Neurostimulation Strategy for Treating Persistent Anosmia in Post-COVID-19 Patients, Sensors
Helman, Adler, Jafari, Treatment strategies for postviral olfactory dysfunction: A systematic review, Allergy Asthma Proc
Hummel, Sekinger, Wolf, Pauli, Kobal, Sniffin' sticks': olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold, Chem Senses
Hummel, Whitcroft, Andrews, Position paper on olfactory dysfunction, Rhinol Suppl
Hura, Xie, Choby, Treatment of post-viral olfactory dysfunction: an evidence-based review with recommendations, International forum of allergy & rhinology
Kandemirli, Altundag, Yildirim, Sanli, Saatci, Olfactory Bulb MRI and Paranasal Sinus CT Findings in Persistent COVID-19 Anosmia, Acad Radiol
Kattar, Do, Unis, Migneron, Thomas et al., Olfactory training for postviral olfactory dysfunction: systematic review and meta-analysis, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Keshavarz, Haseli, Yazdanpanah, Bagheri, Raygani et al., A systematic review of imaging studies in olfactory dysfunction secondary to COVID-19, Acad Radiol
Kim, Kim, Kang, Hwang, Efficacy of topical steroids for the treatment of olfactory disorders caused by COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Otolaryngol
Korber, Fischer, Gnanakaran, Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus, Cell
Lechien, Chiesa-Estomba, Siati, Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Marinosci, Landis, Calmy, Possible link between anosmia and COVID-19: sniffing out the truth. European archives of otorhino-laryngology: official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies (EUFOS): affiliated with the German Society for Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Head Neck Surg
Mehraeen, Behnezhad, Salehi, Noori, Harandi et al., Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions due to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a review of current evidence, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Menni, Valdes, Polidori, Symptom prevalence, duration, and risk of hospital admission in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 during periods of omicron and delta variant dominance: a prospective observational study from the ZOE COVID Study, Lancet
Niesen, Trotta, Noel, Structural and metabolic brain abnormalities in COVID-19 patients with sudden loss of smell, Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging
Ono, Arita, Takayama, Kampo medicine promotes early recovery from coronavirus disease 2019-related olfactory dysfunction: a retrospective observational study, Front Pharmacol
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ
Parma, Ohla, Veldhuizen, More Than Smell-COVID-19 Is Associated With Severe Impairment of Smell, Taste, and Chemesthesis, Chem Senses
Pendolino, Ottaviano, Nijim, A multicenter real-life study to determine the efficacy of corticosteroids and olfactory training in improving persistent COVID-19-related olfactory dysfunction, Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol
Peterson, Welch, Losos, Tugwell, The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses, Ottawa:Ottawa Hospital Research Institute
Pires, Steffens, Mocelin, Intensive olfactory training in post-COVID-19 patients: a multicenter randomized clinical trial, Am J Rhinol Allergy
Politi, Salsano, Grimaldi, Magnetic resonance imaging alteration of the brain in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and anosmia, JAMA Neurol
Rashid, Zgair, Rm, Effect of nasal corticosteroid in the treatment of anosmia due to COVID-19: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study, Am J Otolaryngol
Rashid, Zgair, Rm, Effect of nasal corticosteroid in the treatment of anosmia due to COVID-19: A randomised doubleblind placebo-controlled study, Am J Otolaryngol
Rocke, Hopkins, Philpott, Kumar, Is loss of sense of smell a diagnostic marker in COVID-19: A systematic review and metaanalysis, Clin Otolaryngol
Rydzewski, Pruszewicz, Sulkowski, Assessment of smell and taste in patients with allergic rhinitis, Acta Otolaryngol
Saussez, Vaira, Chiesa-Estomba, Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Oral and Nasal Corticosteroids in COVID-19 Patients with Olfactory Dysfunction: A European Multicenter Study, Pathogens
Saussez, Vaira, Chiesa-Estomba, Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Oral and Nasal Corticosteroids in COVID-19 Patients with Olfactory Dysfunction: A European Multicenter Study, Pathogens
Schepens, Blijleven, Boek, Prednisolone does not improve olfactory function after COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Med
Schepens, Blijleven, Boek, Prednisolone does not improve olfactory function after COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Med
Schirinzi, Landi, Liguori, COVID-19: dealing with a potential risk factor for chronic neurological disorders, J Neurol
Schmidt, Azar, Goektas, Treatment of Olfactory Disorders After SARS -CoViD 2 Virus Infection, Ear Nose Throat J
Seiden, Postviral olfactory loss, Otolaryngol Clin North Am
Singh, Jain, Parveen, The outcome of fluticasone nasal spray on anosmia and triamcinolone oral paste in dysgeusia in COVID-19 patients, Am J Otolaryngol
Stadio, Bernitsas, Mantia, Targeting Neuroinflammation to Alleviate Chronic Olfactory Dysfunction in Long COVID: A Role for Investigating Disease-Modifying Therapy (DMT)? Life
Stadio, Severini, Colizza, Vincentiis, Mantia, Investigational drugs for the treatment of olfactory dysfunction, Expert Opin Investig Drugs
Sterne, Savović, Page, RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Tan, Han, Zhao, Prognosis and persistence of smell and taste dysfunction in patients with covid-19: meta-analysis with parametric cure modelling of recovery curves, BMJ
Vaira, Hopkins, Petrocelli, Efficacy of corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of long-lasting olfactory disorders in COVID-19 patients, Rhinology
Vaira, Hopkins, Petrocelli, Efficacy of corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of long-lasting olfactory disorders in COVID-19 patients, Rhinology
Vandersteen, Payne, Dumas, Olfactory training in post-COVID-19 persistent olfactory disorders: value normalization for threshold but not identification, J Clin Med
Von Bartheld, Hagen, Butowt, Prevalence of Chemosensory Dysfunction in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Reveals Significant Ethnic Differences, ACS Chem Neurosci
Von Bartheld, Hagen, Butowt, The D614G virus mutation enhances anosmia in COVID-19 patients: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies from South Asia, ACS Chem Neurosci
Welge-Lüssen, Wolfensberger, Olfactory disorders following upper respiratory tract infections, Adv Otorhinolaryngol
Whitaker, Elliott, Bodinier, Variant-specific symptoms of COVID-19 among 1
Wu, Yu, Lee, Management of post-COVID-19 olfactory dysfunction, Curr Treat Options Allergy
Yaylacı, Azak, Önal, Aktürk, Karadenizli, Effects of classical olfactory training in patients with COVID-19-related persistent loss of smell, International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology
Zhang, Lee, Chu, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infects and Damages the Mature and Immature Olfactory Sensory Neurons of Hamsters, Clin Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0044-1786046",
"ISSN": [
"1809-9777",
"1809-4864"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0044-1786046",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>\n Introduction Olfactory dysfunction (OD) has emerged as a notable symptom among coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, with its prevalence varying among different populations. Recognizing the need to provide therapeutic solutions for these individuals, the present study seeks to comprehensively review the current evidence on potential underlying mechanisms and treatment modalities to manage OD in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p><jats:p>\n Objective To review the recent evidence on treatments for OD in COVID-19. From the beginning of the study until August 2nd, 2023, we conducted a systematic search on four electronic databases, PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Web of Science, to find relevant publications.</jats:p><jats:p>\n Data Synthesis In the present study, 37 articles were selected for data extraction and included in the final review. The total number of patients was of 3,560 (2,098 female and 1,462 male subjects). The predominant disorders reported were hyposmia, anosmia, and parosmia. In most of the studies, the pre and postintervention assessments were the same, except for one study, in which the pre-intervention assessment of the disorder was through the SST, Sniffin' Sticks Test (SST), and the post-intervention assessment was through the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and the 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22). The findings suggest olfactory training (OT), ivermectin, palmitoylethanolamide, luteolin, and systemic corticosteroids, in combination with topical corticosteroids, are potential therapies for COVID-19 patients with olfactory impairment.</jats:p><jats:p>\n Conclusion Although the review suggested several medications for OD treatment, further research must delve into the specific impact of OT, a non-pharmacological modality, regarding the mitigation of OD. By continuing to investigate and refine these therapeutic approaches, we can better support COVID-19 patients and improve their quality of life while navigating the challenges posed by OD.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4108-2973",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Information Technology, Khalkhal University of Medical Sciences, Khalkhal, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mehraeen",
"given": "Esmaeil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Trauma Research Center, Kashan University of Medical Sciences, Kashan, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Yarmohammadi",
"given": "Soudabeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Iranian Research Center for HIV/AIDS, Iranian Institute for Reduction of High-Risk Behaviors, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mirzapour",
"given": "Pegah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Prevention of Metabolic Disorders Research Center, Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Zadeh",
"given": "Seyed Saeed Tamehri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Dehghani",
"given": "Soheil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Molaeipour",
"given": "Leila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Bushehr University of Medical Sciences, Bushehr, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Molla",
"given": "Ayoob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Karimi",
"given": "Elaheh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Abbaspour",
"given": "Faeze",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Iranian Research Center for HIV/AIDS, Iranian Institute for Reduction of High-Risk Behaviors, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "SeyedAlinaghi",
"given": "SeyedAhmad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology",
"container-title-short": "Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-25T22:30:20Z",
"timestamp": 1716676220000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-25T22:32:34Z",
"timestamp": 1729895554000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-25T23:10:16Z",
"timestamp": 1729897816250,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "04",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "04",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
25
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1716595200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.thieme-connect.de/products/ejournals/pdf/10.1055/s-0044-1786046.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "194",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e728-e743",
"prefix": "10.1055",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Georg Thieme Verlag KG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.otc.2004.06.007",
"article-title": "Postviral olfactory loss",
"author": "A M Seiden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1159",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Otolaryngol Clin North Am",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"article-title": "Olfactory disorders following upper respiratory tract infections",
"author": "A Welge-Lüssen",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Adv Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-020-06120-6",
"article-title": "Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions due to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a review of current evidence",
"author": "E Mehraeen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1073858420956905",
"article-title": "Anosmia in COVID-19: Underlying Mechanisms and Assessment of an Olfactory Route to Brain Infection",
"author": "R Butowt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "582",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Neuroscientist",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hbm.25741",
"article-title": "Olfactory loss and brain connectivity after COVID-19",
"author": "F Esposito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1548",
"issue": "05",
"journal-title": "Hum Brain Mapp",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13543784.2022.2113054",
"article-title": "Investigational drugs for the treatment of olfactory dysfunction",
"author": "A Di Stadio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "945",
"issue": "09",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Investig Drugs",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00415-020-10131-y",
"article-title": "COVID-19: dealing with a potential risk factor for chronic neurological disorders",
"author": "T Schirinzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1171",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "J Neurol",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "268",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prognosis and persistence of smell and taste dysfunction in patients with covid-19: meta-analysis with parametric cure modelling of recovery curves",
"author": "B KJ Tan",
"first-page": "e069503",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acra.2020.04.002",
"article-title": "Olfactory bulb magnetic resonance imaging in SARS-CoV-2-induced anosmia: the first report",
"author": "M K Galougahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "892",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Acad Radiol",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acra.2021.08.010",
"article-title": "A systematic review of imaging studies in olfactory dysfunction secondary to COVID-19",
"author": "P Keshavarz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1530",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Acad Radiol",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2125",
"article-title": "Magnetic resonance imaging alteration of the brain in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and anosmia",
"author": "L S Politi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1028",
"issue": "08",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00259-020-05154-6",
"article-title": "Structural and metabolic brain abnormalities in COVID-19 patients with sudden loss of smell",
"author": "M Niesen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1890",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9030287",
"article-title": "Brain metabolic correlates of persistent olfactory dysfunction after SARS-Cov2 infection",
"author": "M I Donegani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "287",
"issue": "03",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043",
"article-title": "Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus",
"author": "B Korber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00542",
"article-title": "The D614G virus mutation enhances anosmia in COVID-19 patients: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies from South Asia",
"author": "C S von Bartheld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3535",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem Neurosci",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00327-0",
"article-title": "Symptom prevalence, duration, and risk of hospital admission in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 during periods of omicron and delta variant dominance: a prospective observational study from the ZOE COVID Study",
"author": "C Menni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1618",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Variant-specific symptoms of COVID-19 among 1,542,510 people in England",
"author": "M Whitaker",
"first-page": "2022.05",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40521-021-00297-9",
"article-title": "Management of post-COVID-19 olfactory dysfunction",
"author": "T J Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Curr Treat Options Allergy",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "N Hura",
"key": "ref19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0194599820943550",
"article-title": "Olfactory training for postviral olfactory dysfunction: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "N Kattar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "244",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"article-title": "The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "M J Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n71",
"issue": "71",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"article-title": "RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials",
"author": "J AC Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "l4898",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses",
"author": "J Peterson",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Ottawa:Ottawa Hospital Research Institute",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/lio2.989",
"article-title": "A multicenter real-life study to determine the efficacy of corticosteroids and olfactory training in improving persistent COVID-19-related olfactory dysfunction",
"author": "A L Pendolino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02625-5",
"article-title": "Prednisolone does not improve olfactory function after COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "E JA Schepens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102884",
"article-title": "Corticosteroid nasal spray for recovery of smell sensation in COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial",
"author": "A A Abdelalim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102884",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Am J Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/chemse/22.1.39",
"article-title": "‘Sniffin’ sticks': olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold",
"author": "T Hummel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Chem Senses",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "22",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/coa.13620",
"article-title": "Is loss of sense of smell a diagnostic marker in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "J Rocke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "914",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Clin Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00460",
"article-title": "Prevalence of Chemosensory Dysfunction in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Reveals Significant Ethnic Differences",
"author": "C S von Bartheld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2944",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem Neurosci",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1",
"article-title": "Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study",
"author": "J R Lechien",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2251",
"issue": "08",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "277",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10060698",
"article-title": "Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Oral and Nasal Corticosteroids in COVID-19 Patients with Olfactory Dysfunction: A European Multicenter Study",
"author": "S Saussez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "698",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/chemse/bjaa041",
"article-title": "More Than Smell-COVID-19 Is Associated With Severe Impairment of Smell, Taste, and Chemesthesis",
"author": "V Parma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "609",
"issue": "07",
"journal-title": "Chem Senses",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Possible link between anosmia and COVID-19: sniffing out the truth. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology: official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies (EUFOS): affiliated with the German Society for Oto-Rhino-Laryngology -",
"author": "A Marinosci",
"first-page": "2149",
"issue": "07",
"journal-title": "Head Neck Surg",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "277",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00406",
"article-title": "Anosmia in COVID-19: A Bumpy Road to Establishing a Cellular Mechanism",
"author": "K Bilinska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2152",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem Neurosci",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1379",
"article-title": "Evolution of Altered Sense of Smell or Taste in Patients With Mildly Symptomatic COVID-19",
"author": "P Boscolo-Rizzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "729",
"issue": "08",
"journal-title": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of long- lasting olfactory disorders in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "L A Vaira",
"first-page": "21",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Rhinology",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2500/aap.2022.43.210107",
"article-title": "Treatment strategies for postviral olfactory dysfunction: A systematic review",
"author": "S N Helman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "96",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Allergy Asthma Proc",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/coa.13933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of topical steroids for the treatment of olfactory disorders caused by COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "D H Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "Clin Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11162552",
"article-title": "Effect of Ultra-Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin on Olfaction and Memory in Patients with Long COVID: Results of a Longitudinal Study",
"author": "P De Luca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2552",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/s23135880",
"article-title": "Design and Evaluation of a Potential Non-Invasive Neurostimulation Strategy for Treating Persistent Anosmia in Post-COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "D I Gracia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5880",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Sensors (Basel)",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13223-022-00711-0",
"article-title": "The effect of intra-nasal tetra sodium pyrophosphate on decreasing elevated nasal calcium and improving olfactory function post COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "M H Abdelazim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02546-5",
"article-title": "Olfactory Disturbances as Presenting Manifestation Among Egyptian Patients with COVID-19: Possible Role of Zinc",
"author": "A A Abdelmaksoud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4101",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Targeting Neuroinflammation to Alleviate Chronic Olfactory Dysfunction in Long COVID: A Role for Investigating Disease-Modifying Therapy (DMT)?",
"author": "A Di Stadio",
"first-page": "226",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Life (Basel)",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103033",
"article-title": "Effect of nasal corticosteroid in the treatment of anosmia due to COVID-19: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study",
"author": "R A Rashid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103033",
"issue": "05",
"journal-title": "Am J Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref46",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/000164800750001189",
"article-title": "Assessment of smell and taste in patients with allergic rhinitis",
"author": "B Rydzewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "323",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Acta Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref47",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4193/Rhino16.248",
"article-title": "Position paper on olfactory dysfunction",
"author": "T Hummel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "Rhinol Suppl",
"key": "ref48",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acra.2020.10.006",
"article-title": "Olfactory Bulb MRI and Paranasal Sinus CT Findings in Persistent COVID-19 Anosmia",
"author": "S G Kandemirli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Acad Radiol",
"key": "ref49",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa995",
"article-title": "Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infects and Damages the Mature and Immature Olfactory Sensory Neurons of Hamsters",
"author": "A J Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e503",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "ref50",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.844072",
"article-title": "Kampo medicine promotes early recovery from coronavirus disease 2019-related olfactory dysfunction: a retrospective observational study",
"author": "R Ono",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "844072",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref51",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/19458924221113124",
"article-title": "Intensive olfactory training in post-COVID-19 patients: a multicenter randomized clinical trial",
"author": "ÍAT Pires",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "780",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Am J Rhinol Allergy",
"key": "ref52",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103033",
"article-title": "Effect of nasal corticosteroid in the treatment of anosmia due to COVID-19: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study",
"author": "R A Rashid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103033",
"issue": "05",
"journal-title": "Am J Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref53",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10060698",
"article-title": "Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Oral and Nasal Corticosteroids in COVID-19 Patients with Olfactory Dysfunction: A European Multicenter Study",
"author": "S Saussez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "698",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02625-5",
"article-title": "Prednisolone does not improve olfactory function after COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "E JA Schepens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "ref55",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Treatment of Olfactory Disorders After SARS - CoViD 2 Virus Infection",
"author": "F Schmidt",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"key": "ref56",
"volume": "•••",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102892",
"article-title": "The outcome of fluticasone nasal spray on anosmia and triamcinolone oral paste in dysgeusia in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "C V Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102892",
"issue": "03",
"journal-title": "Am J Otolaryngol",
"key": "ref57",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of long- lasting olfactory disorders in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "L A Vaira",
"first-page": "21",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Rhinology",
"key": "ref58",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11123275",
"article-title": "Olfactory training in post-COVID-19 persistent olfactory disorders: value normalization for threshold but not identification",
"author": "C Vandersteen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3275",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "ref59",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-022-07570-w",
"article-title": "Effects of classical olfactory training in patients with COVID-19-related persistent loss of smell",
"author": "A Yaylacı",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "757",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "ref60",
"volume": "280",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 58,
"references-count": 58,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0044-1786046"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "28"
}