Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID‐19 in India: A nationwide cross‐sectional survey
Bharat Jagiasi, Prashant Nasa, Gunjan Chanchalani, Ahsan Ahmed, Ajith Kumar Ak, Kanwalpreet Sodhi, Kishore Mangal, Manoj K Singh, Nitesh Gupta, Prasanna U Bidkar, Ranvir S Tyagi, Reshu G Khanikar, Swagata Tripathy, Swapna Khanzode, Kesavarapu Subba Reddy, Saurabh Saigal, Vijay Anand Sivakumar, Yash Javeri, Seema S Tekwani
International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14574
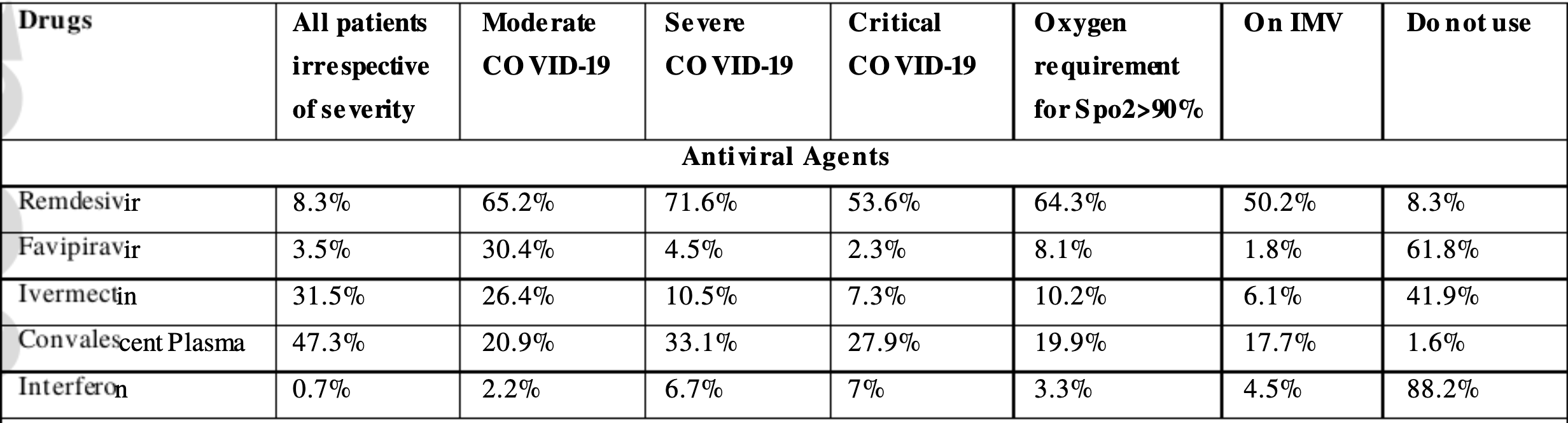
Aim: During the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the physicians are using various off-label therapeutics to manage COVID-19. We undertook a crosssectional survey to study the current variation in therapeutic strategies for managing severe COVID-19 in India. Methods: From January 4 to January 18, 2021, an online cross-sectional survey was conducted among physicians involved in the management of severe COVID-19. The survey had three sections: 1. Antiviral agents, 2. Immunomodulators, and 3. Adjuvant therapies. Results: 1055 respondents (from 24 states and five union territories), of which 64.2% were consultants, 54.3% working in private hospitals, and 39.1% were from critical care medicine completed the survey. Remdesivir (95.2%), antithrombotics (94.2%),
prescribed antibiotics with severity of COVID-19 (58.3%) or increased inflammatory markers (56.4%) were preferred indications. There was significant variation in the use of adjuvant therapies with specialists from critical care medicine preferred use of antibiotics in severe and critical COVID-19, while anaesthesiologists preferred vitamins in all patients of COVID-19. Bacterial co-infections are uncommon in COVID-19 and vary from 3.5% at the time of admission to 15% among hospitalised patients. 28 A recent guideline on antimicrobials in COVID-19, recommended a restrictive approach and empirical antibiotics to be considered only if clinical, imaging and biochemical markers suggest a bacterial co-infection. The de-escalation of antibiotics within 48 hours is suggested if representative cultures or antigen tests excluded bacterial co-infection. 29 The authors did not recommend any empirical antibiotic regimen and advised to use community or hospital-acquired pneumonia guidelines while starting antibiotics and using local antimicrobial surveillance. 29 Recently, the RECOVERY trial found no role of azithromycin in the treatment of hospitalised COVID-19 patients. 30 The prepublication release from the PRINCIPAL trial using azithromycin or doxycycline for 14 days showed no significant benefit in time to recovery or hospitalisation. 31 NIH does not recommend vitamin C in COVID-19 because of insufficient data. 32 There are ongoing trials on intravenous vitamin C in..
References
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India:open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ
Alhazzani, Evans, Alshamsi, Surviving sepsis campaign guidelines on the management of adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the ICU: first update, Crit Care Med
Armstrong, Kane, Cook, Outcomes from intensive care in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Anaesthesia
Asch, Sheils, Islam, Variation in US hospital mortality rates for patients admitted with COVID-19 during the first 6 months of the pandemic, JAMA Intern Med
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of covid-19 -final report, N Engl J Med
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe covid-19, N Engl J Med
Borczuk, Salvatore, Seshan, COVID-19 pulmonary pathology: a multi-institutional autopsy cohort from Italy and New York City, Mod Pathol
Charan, Kaur, Bhardwaj, Snapshot of COVID-19 related clinical trials in India, Indian J Clin Biochem
Chatterjee, Is India missing COVID-19 deaths?, Lancet
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and inhospital mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Anesth Analg
Dong, Du, Gardner, An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time, Lancet Infect Dis
Gopalan, Misra, COVID-19 pandemic and challenges for socio-economic issues, healthcare and National Health Programs in India, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern Med
He, Yi, Zhu, Estimation of the basic reproduction number, average incubation time, asymptomatic infection rate, and case fatality rate for COVID-19: meta-analysis and sensitivity analysis, J Med Virol
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Janiaud, Axfors, Schmitt, Association of convalescent plasma treatment with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA
Joshi, Parkar, Ansari, Role of favipiravir in the treatment of COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis
Lim, Subramaniam, Reddy, Case fatality rates for patients with COVID-19 requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. a meta-analysis, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Murdaca, Pioggia, Negrini, Vitamin D and Covid-19: an update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications, Clin Mol Allergy
News, PRINCIPLE trial finds antibiotics azithromycin and doxycycline not generally effective treatments for COVID-19
Nice, COVID-19 rapid evidence summary: Tocilizumab for COVID-19
Nih, The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel's Statement on the Use of Ivermectin for the Treatment of COVID-19
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Repurposed antiviral drugs for covid-19 -Interim WHO Solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Parr, Time to Reassess Tocilizumab's Role in COVID-19 Pneumonia, JAMA Intern Med
Sieswerda, De Boer, Bonten, Recommendations for antibacterial therapy in adults with COVID-19 -an evidence based guideline, Clin Microbiol Infect
Sterne, Murthy, Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically Ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA
Wise, Covid-19: Arthritis drugs improve survival in intensive care patients, shows study, BMJ
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14574",
"ISSN": [
"1368-5031",
"1742-1241"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.14574",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/ijcp.14574"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-03-01"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-06-24"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-07-18"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Department Reliance Hospital Navi Mumbai Maharashtra India"
}
],
"family": "Jagiasi",
"given": "Bharat",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1948-4060",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine NMC Specialty Hospital Dubai United Arab Emirates"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nasa",
"given": "Prashant",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Cumballa Hill Hospital Mumbai Maharashtra India"
}
],
"family": "Chanchalani",
"given": "Gunjan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Anesthesiology and Critical Care KPC Medical College and Hospital Kolkata West Bengal India"
}
],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Ahsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Manipal Hospitals Bengaluru Karnataka India"
}
],
"family": "AK",
"given": "Ajith Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical CareDeep Hospital Ludhiana Punjab India"
}
],
"family": "Sodhi",
"given": "Kanwalpreet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Eternal Hospital Jaipur Rajasthan India"
}
],
"family": "Mangal",
"given": "Kishore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care & Sleep Medicine Apollo Hospital Ahmedabad Gujarat India"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Manoj K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Critical Care and Sleep Medicine VMMC and Safdarjung Hospital New Delhi India"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Nitesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4497-6772",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology and Critical Care Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER) Puducherry India"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bidkar",
"given": "Prasanna U.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesia and Critical Care Medicine Synergy Plus Hospital Agra Uttar Pradesh India"
}
],
"family": "Tyagi",
"given": "Ranvir S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine Health City Hospital Guwahati Assam India"
}
],
"family": "Khanikar",
"given": "Reshu G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Anesthesia & Intensive Care All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhubaneswar Odisha India"
}
],
"family": "Tripathy",
"given": "Swagata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medicine and Critical Care Wockhardt Multispecialty Hospital Nagpur Maharashtra India"
}
],
"family": "Khanzode",
"given": "Swapna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department Of Critical Care Medicine Apollo Health City Hyderabad Telangana India"
}
],
"family": "Subba Reddy",
"given": "Kesavarapu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Anaesthesia and Intensive Care All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhopal Madhya Pradesh India"
}
],
"family": "Saigal",
"given": "Saurabh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Velammal Medical college and Research Centre Madurai Tamil Nadu India"
}
],
"family": "Sivakumar",
"given": "Vijay Anand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine and Emergency Medicine Regency Super Specialty Hospital Lucknow Uttar Pradesh India"
}
],
"family": "Javeri",
"given": "Yash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta GA USA"
}
],
"family": "Tekwani",
"given": "Seema S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Clinical Practice",
"container-title-short": "Int J Clin Pract",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-25T19:35:17Z",
"timestamp": 1624649717000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-28T06:08:39Z",
"timestamp": 1643350119000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-23T17:34:36Z",
"timestamp": 1692812076672
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1626566400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1626566400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.14574",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/ijcp.14574",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.14574",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "98",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1155",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Hindawi Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Case‐fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID‐19 in Italy",
"author": "Onder G",
"first-page": "1775",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31857-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/anae.15201",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202006-2405OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Variation in US hospital mortality rates for patients admitted with COVID‐19 during the first 6 months of the pandemic",
"author": "Asch DA",
"first-page": "e208193",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1",
"unstructured": "Government of India Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Directorate General of Health Services.Clinical management protocol: COVID‐19.https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/UpdatedClinicalManagementProtocolforCOVID19dated03072020.pdf. Accessed February 12 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation.Clinical management of COVID‐19. Interim guidance;2020.https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/clinical‐management‐of‐covid‐19. Accessed February 11 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41379-020-00661-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1",
"unstructured": "NIH.The COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines Panel’s Statement on the Use of Ivermectin for the Treatment of COVID‐19.https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/statement‐on‐ivermectin/. Accessed February 9 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.069",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.2747",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004899",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n61",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1",
"unstructured": "NICE.COVID‐19 rapid evidence summary: Tocilizumab for COVID‐19.https://www.nice.org.uk/advice/es33/chapter/Product‐overview. Accessed February 9 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-020-00918-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00149-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1",
"unstructured": "News.PRINCIPLE trial finds antibiotics azithromycin and doxycycline not generally effective treatments for COVID‐19.https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2021‐01‐25‐principle‐trial‐finds‐antibiotics‐azithromycin‐and‐doxycycline‐not‐generally. Accessed February 10 2021."
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1",
"unstructured": "NIH.COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines. Vitamin C.https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/adjunctive‐therapy/vitamin‐c/. Accessed on February 10 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1",
"unstructured": "NIH.COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines. Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with COVID‐19.https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.NIH.gov/adjunctive‐therapy/antithrombotic‐therapy/. Accessed February 10 2021."
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ijcp.14574"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID‐19 in India: A nationwide cross‐sectional survey",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "75"
}