Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities
Zena Wehbe, Maya Wehbe, Rabah Iratni, Gianfranco Pintus, Hassan Zaraket, Hadi M Yassine, Ali H Eid
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586
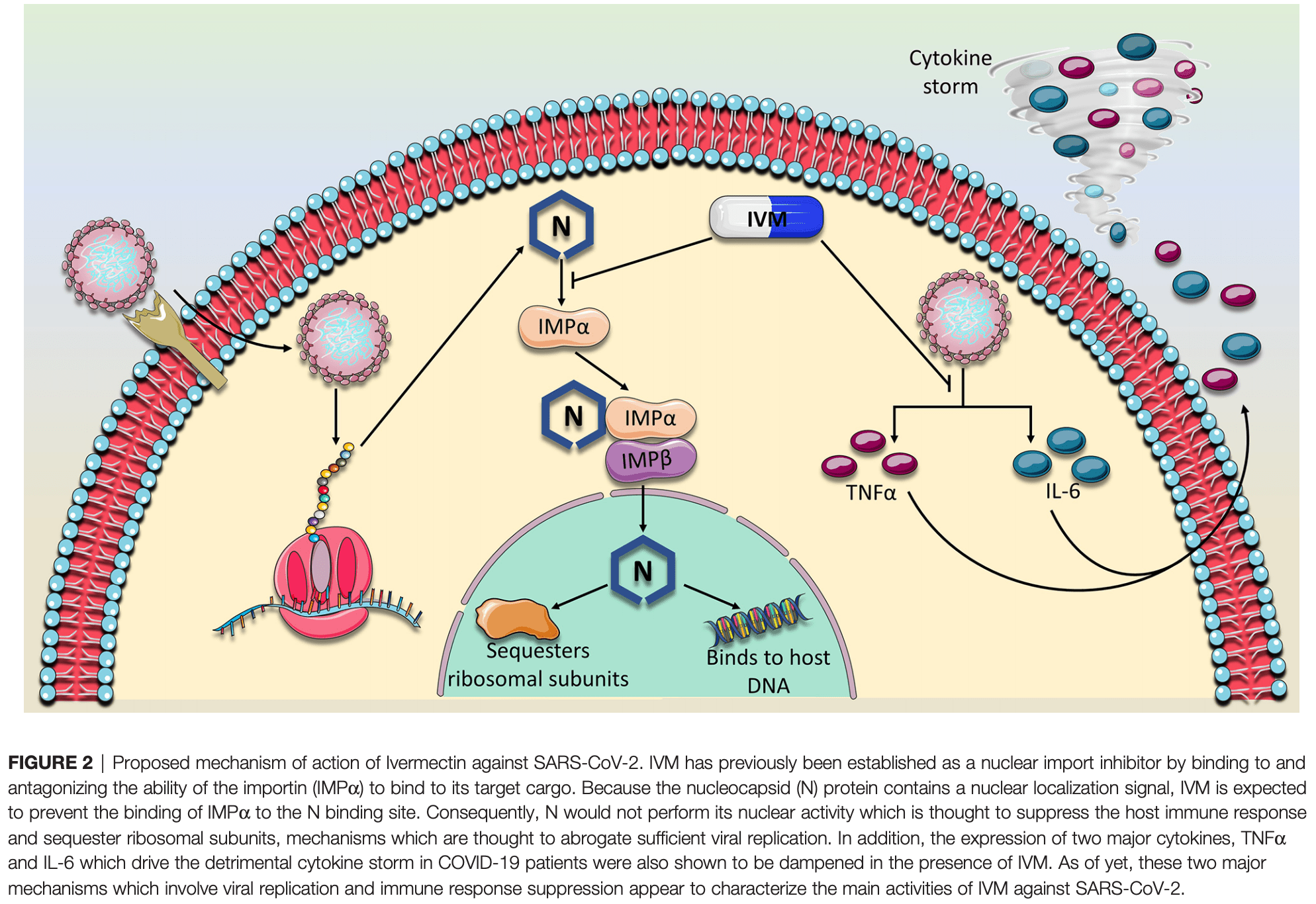
As of January 2021, SARS-CoV-2 has killed over 2 million individuals across the world. As such, there is an urgent need for vaccines and therapeutics to reduce the burden of COVID-19. Several vaccines, including mRNA, vector-based vaccines, and inactivated vaccines, have been approved for emergency use in various countries. However, the slow roll-out of vaccines and insufficient global supply remains a challenge to turn the tide of the pandemic. Moreover, vaccines are important tools for preventing the disease but therapeutic tools to treat patients are also needed. As such, since the beginning of the pandemic, repurposed FDA-approved drugs have been sought as potential therapeutic options for COVID-19 due to their known safety profiles and potential anti-viral effects. One of these drugs is ivermectin (IVM), an antiparasitic drug created in the 1970s. IVM later exerted antiviral activity against various viruses including SARS-CoV-2. In this review, we delineate the story of how this antiparasitic drug was eventually identified as a potential treatment option for COVID-19. We review SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle, the role of the nucleocapsid protein, the turning points in past research that provided initial 'hints' for IVM's antiviral activity and its molecular mechanism of action-and finally, we culminate with the current clinical findings.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS AE generated the concept. ZW and MW wrote the first draft. All authors revised the manuscript and approved it before submission. HY generated funding.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Agostini, Andres, Sims, Graham, Sheahan et al., Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease, mBio,
doi:10.1128/mBio.00221-18Ahmed, Karim, Ross, Hossain, Clemens et al., A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764Camprubı́d, Martı-Soler, Soriano, Hurtado, Subirà, Lack of efficacy of standard doses of ivermectin in severe COVID-19 patients, PloS One,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0242184Chaccour, Ruiz-Castillo, Richardson, Moncunill, Casellas et al., The SARS-CoV-2 Ivermectin Navarra-ISGlobal Trial (SAINT) to Evaluate the Potential of Ivermectin to Reduce COVID-19 Transmission in low risk, non-severe COVID-19 patients in the first 48 hours after symptoms onset: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized control pilot trial, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04421-zChen, Nirula, Heller, Gottlieb, Boscia et al., SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody LY-CoV555 in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7Cong, Ulasli, Schepers, Mauthe, V'kovski et al., Nucleocapsid Protein Recruitment to Replication-Transcription Complexes Plays a Crucial Role in Coronaviral Life Cycle, J Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.01925-19Crump, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,
doi:10.2183/pjab.87.13De Melo, Lazarini, Larrous, Feige, Kergoat et al., Anti-COVD-19 efficacy of ivermectin in the golden hamster, BioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.11.21.392639Fulcher, Jans, Regulation of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of viral proteins: an integral role in pathogenesis?, Biochim Biophys Acta,
doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.019Goldfarb, Corbett, Mason, Harreman, Adam, Importin alpha: a multipurpose nuclear-transport receptor, Trends Cell Biol,
doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.016Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Rowan, Nichol et al., Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19 -Preliminary report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433Gotz, Magar, Dornfeld, Giese, Pohlmann et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci Rep,
doi:10.1038/srep23138Gupta, Biswal, Panda, Ray, Rana, Binding mechanism and structural insights into the identified protein target of COVID-19 and importin-a with, J Biomol Struct Dyn,
doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1839564Gussow, Auslander, Faure, Wolf, Zhang et al., Genomic determinants of pathogenicity in SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses, Proc Natl Acad Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.2008176117Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Chen, Tipping et al., Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1177/009127002401382731Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19 -Preliminary Report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436Hu, Sneyd, Dekant, Wang, Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein: A Highly Conserved Multi-Functional Viral Protein as a Hot Antiviral Drug Target, Curr Top M ed Chem,
doi:10.2174/1568026617666170224122508Hurst, Koetzner, Masters, Characterization of a critical interaction between the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein 3 of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex, J Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.01275-13Ikeda, Canga, Prieto, Liebana, Martıńez et al., Pharmacological effects of ivermectin, an antiparasitic agent for intestinal strongyloidiasis: its mode of action and clinical efficacy, Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi,
doi:10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9Jeffreys, Pennington, Duggan, Breen, Jinks et al., Remdesivir-Ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2,
doi:10.1101/2020.12.23.424232Juarez, Schcolnik-Cabrera, Dueñas-Gonzalez, The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug, Am J Cancer Res
Kaddoura, Alibrahim, Hijazi, Soudani, Alkalamouni, COVID-19 Therapeutic Options Under Investigation, Front Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01196Kaur, Shekhar, Sharma, Sarma, Prakash et al., Ivermectin as a potential drug for treatment of COVID-19: an in-sync review with clinical and computational attributes, Pharmacol Rep,
doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00195-yKosyna, Nagel, Kluxen, Kraushaar, Depping, The importin a/ b-specific inhibitor Ivermectin affects HIF-dependent hypoxia response pathways, Biol Chem,
doi:10.1515/hsz-2015-0171Lin, Lin, Hsu, Chang, Chien et al., Structure-Based Stabilization of Non-native Protein-Protein Interactions of Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Proteins in Antiviral Drug Design, J Med Chem,
doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01913Lu, Wang, Gao, Bat-to-human: spike features determining 'host jump' of coronaviruses SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and beyond, Trends Microbiol,
doi:10.1016/j.tim.2015.06.003Mathew, Faheem, Hassain, Benslimane, Thani et al., Platforms Exploited for SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Development, Vaccines,
doi:10.3390/vaccines9010011Mcbride, Van Zyl, Fielding, The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v6082991Moriyama, Nagai, Oka, Ikawa, Okabe et al., Targeted disruption of one of the importin a family members leads to female functional incompetence in delivery, FEBS J,
doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08079.xNjoo, Hack, Oosting, Luyendijk, Stilma et al., C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 are elevated in onchocerciasis patients after ivermectin treatment, J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/infdis/170.3.663Oka, Yoneda, Importin a: functions as a nuclear transport factor and beyond, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,
doi:10.2183/pjab.94.018Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Preziosi, Sathiyamoorthy et al., Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 -Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023184Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study, Chest,
doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009Romano, Ruggiero, Squeglia, Maga, Berisio, A Structural View of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Replication Machinery: RNA Synthesis, Proofreading and Final Capping, Cells,
doi:10.3390/cells9051267Rout, Aitchison, Pore relations: nuclear pore complexes and nucleocytoplasmic exchange, Essays Biochem,
doi:10.1042/bse0360075Santos, Grosche, Bergamini, Sabino-Silva, Jardim, Antivirals Against Coronaviruses: Candidate Drugs for SARS-CoV-2 Treatment?, Front Microbiol,
doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01818Savastano, De Opakua, Rankovic, Zweckstetter, Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates, Nat Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19843-1Schröder, Swan, Soll, Hotson, Efficacy of ivermectin against ectoparasites of cattle in South Africa, J S Afr Vet Assoc
Seward, Reactions in dogs given ivermectin, J Am Vet Med Assoc
Singh, Kulsum, Rufai, Mudliar, Singh, Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Leading to Antigenic Variations in Spike Protein: A Challenge in Vaccine Development, J Lab Physicians,
doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715790Tablets, STROMECTOL ® (IVERMECTIN
Tay, Fraser, Chan, Moreland, Rathore et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antiviral Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002Wagstaff, Rawlinson, Hearps, Jans, An AlphaScreen ® -based assay for high-throughput screening for specific inhibitors of nuclear import, J Biomol Screen,
doi:10.1177/1087057110390360Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin a/b-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem J,
doi:10.1042/BJ20120150Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody CocktailOutpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002Wurm, Chen, Hodgson, Britton, Brooks et al., Localization to the nucleolus is a common feature of coronavirus nucleoproteins, and the protein may disrupt host cell division, J Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.75.19.9345-9356.2001Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin a/b1 heterodimer, Antiviral Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760Zeng, Liu, Ma, Zhao, Yang et al., Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.136Zhang, Song, Ci, Ju, Li, Ivermectin inhibits LPSinduced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflamm Res,
doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586",
"abstract": "<jats:p>As of January 2021, SARS-CoV-2 has killed over 2 million individuals across the world. As such, there is an urgent need for vaccines and therapeutics to reduce the burden of COVID-19. Several vaccines, including mRNA, vector-based vaccines, and inactivated vaccines, have been approved for emergency use in various countries. However, the slow roll-out of vaccines and insufficient global supply remains a challenge to turn the tide of the pandemic. Moreover, vaccines are important tools for preventing the disease but therapeutic tools to treat patients are also needed. As such, since the beginning of the pandemic, repurposed FDA-approved drugs have been sought as potential therapeutic options for COVID-19 due to their known safety profiles and potential anti-viral effects. One of these drugs is ivermectin (IVM), an antiparasitic drug created in the 1970s. IVM later exerted antiviral activity against various viruses including SARS-CoV-2. In this review, we delineate the story of how this antiparasitic drug was eventually identified as a potential treatment option for COVID-19. We review SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle, the role of the nucleocapsid protein, the turning points in past research that provided initial ‘hints’ for IVM’s antiviral activity and its molecular mechanism of action- and finally, we culminate with the current clinical findings.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wehbe",
"given": "Zena",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wehbe",
"given": "Maya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iratni",
"given": "Rabah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pintus",
"given": "Gianfranco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zaraket",
"given": "Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yassine",
"given": "Hadi M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eid",
"given": "Ali H.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-30T13:12:05Z",
"timestamp": 1617109925000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-30T13:12:14Z",
"timestamp": 1617109934000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Qatar University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-17T11:59:40Z",
"timestamp": 1713355180707
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 23,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
30
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1617062400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-0716-0900-2_1",
"article-title": "Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "2203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2015.06.003",
"article-title": "Bat-to-human: spike features determining ‘host jump’ of coronaviruses SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and beyond",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines9010011",
"article-title": "Platforms Exploited for SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Development",
"author": "Mathew",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2020.07.009",
"article-title": "Mutations Strengthened SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Mol Biol",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "432",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0040-1715790",
"article-title": "Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Leading to Antigenic Variations in Spike Protein: A Challenge in Vaccine Development",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Lab Physicians",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, ‘wonder drug’ from Japan: the human use perspective",
"author": "Crump",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9051267",
"article-title": "A Structural View of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Replication Machinery: RNA Synthesis, Proofreading and Final Capping",
"author": "Romano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1267",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/0022-1317-81-4-853",
"article-title": "Virus-encoded proteinases and proteolytic processing in the Nidovirales",
"author": "Ziebuhr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01925-19",
"article-title": "Nucleocapsid Protein Recruitment to Replication-Transcription Complexes Plays a Crucial Role in Coronaviral Life Cycle",
"author": "Cong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4615-5331-1_26",
"article-title": "A new model for coronavirus transcription",
"author": "Sawicki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "440",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v6082991",
"article-title": "The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein",
"author": "McBride",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2991",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19843-1",
"article-title": "Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates",
"author": "Savastano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6041",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.019",
"article-title": "Regulation of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of viral proteins: an integral role in pathogenesis",
"author": "Fulcher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "1813",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bse0360075",
"article-title": "Pore relations: nuclear pore complexes and nucleocytoplasmic exchange",
"author": "Rout",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Essays Biochem",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-003-3070-3",
"article-title": "Nucleocytoplasmic transport: taking an inventory",
"author": "Fried",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Life Sci",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.016",
"article-title": "Importin alpha: a multipurpose nuclear-transport receptor",
"author": "Goldfarb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trends Cell Biol",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00082-5",
"article-title": "Regulating access to the genome: nucleocytoplasmic transport throughout the cell cycle",
"author": "Weis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1087057110390360",
"article-title": "An AlphaScreen®-based assay for high-throughput screening for specific inhibitors of nuclear import",
"author": "Wagstaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "192",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Screen",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2008176117",
"article-title": "Genomic determinants of pathogenicity in SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses",
"author": "Gussow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/embo-reports/kvd092",
"article-title": "Finding nuclear localization signals",
"author": "Cokol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.75.19.9345-9356.2001",
"article-title": "Localization to the nucleolus is a common feature of coronavirus nucleoproteins, and the protein may disrupt host cell division",
"author": "Wurm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep23138",
"article-title": "Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import",
"author": "Gotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.136",
"article-title": "Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "527",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.036",
"article-title": "Trafficking motifs in the SARS-coronavirus nucleocapsid protein",
"author": "You",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "358",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01275-13",
"article-title": "Characterization of a critical interaction between the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein 3 of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex",
"author": "Hurst",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1568026617666170224122508",
"article-title": "Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein: A Highly Conserved Multi-Functional Viral Protein as a Hot Antiviral Drug Target",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Top Med Chem",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01913",
"article-title": "Structure-Based Stabilization of Non-native Protein-Protein Interactions of Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Proteins in Antiviral Drug Design",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1254/fpj.122.527",
"article-title": "Pharmacological effects of ivermectin, an antiparasitic agent for intestinal strongyloidiasis: its mode of action and clinical efficacy",
"author": "Ikeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9",
"article-title": "The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin in humans–a mini-review",
"author": "González Canga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "AAPS J",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of ivermectin against ectoparasites of cattle in South Africa",
"author": "Schröder",
"journal-title": "J S Afr Vet Assoc",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "56",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"article-title": "The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug",
"author": "Juarez",
"journal-title": "Am J Cancer Res",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00195-y",
"article-title": "Ivermectin as a potential drug for treatment of COVID-19: an in-sync review with clinical and computational attributes",
"author": "Kaur",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "B35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20120150",
"article-title": "Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus",
"author": "Wagstaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "443",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002",
"article-title": "Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"article-title": "The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.94.018",
"article-title": "Importin α: functions as a nuclear transport factor and beyond",
"author": "Oka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08079.x",
"article-title": "Targeted disruption of one of the importin α family members leads to female functional incompetence in delivery",
"author": "Moriyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hsz-2015-0171",
"article-title": "The importin α/β-specific inhibitor Ivermectin affects HIF-dependent hypoxia response pathways",
"author": "Kosyna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biol Chem",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "B42",
"unstructured": "TABLETS; STROMECTOL®(IVERMECTIN) (MERCK)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1839564",
"article-title": "Binding mechanism and structural insights into the identified protein target of COVID-19 and importin-α with",
"author": "Sen Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "B43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.11.21.392639",
"article-title": "Anti-COVD-19 efficacy of ivermectin in the golden hamster",
"author": "de Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BioRxiv",
"key": "B45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0242184",
"article-title": "Lack of efficacy of standard doses of ivermectin in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Camprubí",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01196",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Therapeutic Options Under Investigation",
"author": "Kaddoura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/170.3.663",
"article-title": "C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 are elevated in onchocerciasis patients after ivermectin treatment",
"author": "Njoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "170",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/009127002401382731",
"article-title": "Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects",
"author": "Guzzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"article-title": "Reactions in dogs given ivermectin",
"author": "Seward",
"first-page": "493",
"journal-title": "J Am Vet Med Assoc",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "183",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0035-9203(98)91035-5",
"article-title": "Absence of ivermectin-associated excess deaths",
"author": "Alexander",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "92",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"article-title": "A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"article-title": "Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study",
"author": "Rajter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04421-z",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 Ivermectin Navarra-ISGlobal Trial (SAINT) to Evaluate the Potential of Ivermectin to Reduce COVID-19 Transmission in low risk, non-severe COVID-19 patients in the first 48 hours after symptoms onset: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized control pilot trial",
"author": "Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00221-18",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease",
"author": "Agostini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 - Final Report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 - Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.12.23.424232",
"article-title": "Remdesivir-Ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Jeffreys",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19 - Preliminary Report",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B60",
"volume-title": "Recovery Trial Closes Recruitment to Convalescent Plasma Treatment for Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody CocktailOutpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody LY-CoV555 in Outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19 –Preliminary report",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B63",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00042560-199510001-00007",
"article-title": "Viral resistance and the selection of antiretroviral combinations",
"author": "Larder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.01818",
"article-title": "Antivirals Against Coronaviruses: Candidate Drugs for SARS-CoV-2 Treatment",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 65,
"references-count": 65,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}