SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19
Sabina Semiz
Biomolecular Concepts, doi:10.1515/bmc-2021-0017
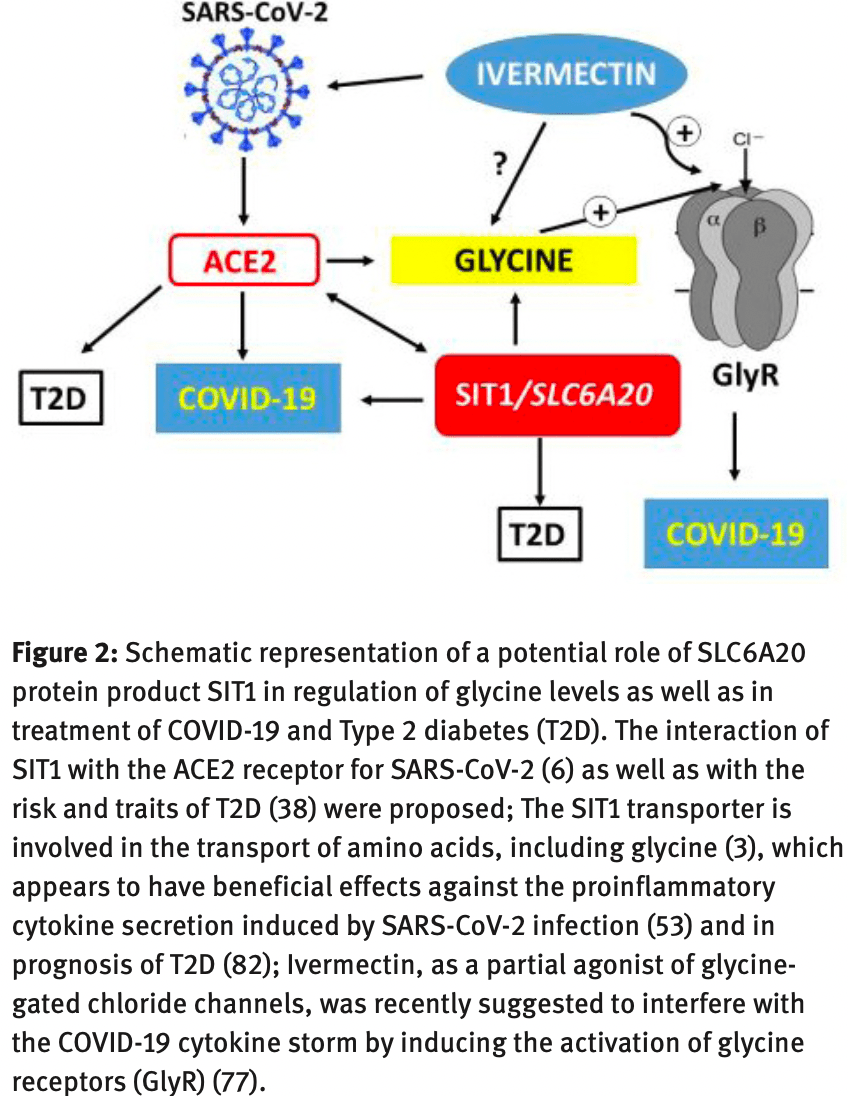
Studies published earlier this year demonstrated the association of the solute carrier SLC6A20 gene with the risk and severity of COVID-19. The SLC6A20 protein product (Sodium-dependent Imino Transporter 1 (SIT1)) is involved in the transport of amino acids, including glycine. Here we summarized the results of recent studies demonstrating the interaction of SIT1 with the ACE2 receptor for SARS-CoV-2 as well as an observed association of SLC6A20 with the risk and traits of Type 2 diabetes (T2D). Recently, it was also proposed that SLC6A20 represents the novel regulator of glycine levels and that glycine has beneficial effects against the proinflammatory cytokine secretion induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ivermectin, as a partial agonist of glycine-gated chloride channels, was also recently suggested to interfere with the COVID-19 cytokine storm by inducing the activation of glycine receptors. Furthermore, plasma glycine levels are found to be decreased in diabetic patients. Thus, further clinical trials are warranted to confirm the potential favorable effects of targeting the SIT1 transporter and glycine levels in the treatment of COVID-19, particularly for the severe case of disease associated with hyperglycemia, inflammation, and T2D. These findings suggest that SIT1 may potentially represent one of the missing pieces in the complex puzzle observed between these two pandemic diseases and the potential novel target for their efficient treatment.
References
Abuissa, Jones, Marso, Keefe, Angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers for prevention of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, J Am Coll Cardiol
Adeva-Andany, Souto-Adeva, Ameneiros-Rodríguez, Fernández-Fernández, Donapetry-García et al., Insulin resistance and glycine metabolism in humans, Amino Acids
Analysis, Ivermectin for COVID-19: real-time meta analysis of 64 studies
Anand, Ziebuhr, Wadhwani, Mesters, Hilgenfeld, Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs, Science
Bae, Roh, Kim, Kim, Han et al., SLC6A20 transporter: a novel regulator of brain glycine homeostasis and NMDAR function, EMBO Mol Med
Bonafè, Prattichizzo, Giuliani, Storci, Sabbatinelli et al., Inflamm-aging: why older men are the most susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 complicated outcomes, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., Observational Study of Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19,
doi:10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines, Am J Ther
Bukanova, Solntseva, Kondratenko, Skrebitsky, Antiviral Drug Ivermectin at Nanomolar Concentrations Inhibits Glycine-Induced Chloride Current in Rat Hippocampal Neurons, Bull Exp Biol Med
Burgos-Morón, Abad-Jiménez, Marañón, Iannantuoni, Escribano-López et al., Relationship Between Oxidative Stress, ER Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes: The Battle Continues, J Clin Med
Bălută, Vintilă, Vintilă, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system inhibition in prevention of diabetes mellitus, Rom J Intern Med
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDAapproved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Camargo, Singer, Makrides, Huggel, Pos et al., Tissue-specific amino acid transporter partners ACE2 and collectrin differentially interact with hartnup mutations, Gastroenterology
Camargo, Vuille-Dit-Bille, Meier, Verrey, ACE2 and gut amino acid transport, Clin Sci (Lond)
Cao, Yang, Xin, Xie, Yang, The ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis can inhibit hepatic insulin resistance, Mol Cell Endocrinol
Ceriello, Prattichizzo, Pharmacological management of COVID-19 in type 2 diabetes, J Diabetes Complications
Chen, Wu, Wang, Yu, Sun, The Impact of COVID-19 on Blood Glucose: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Endocrinol
Cheng, Shah, Bröer, Fairweather, Jiang et al., Identification of novel inhibitors of the amino acid transporter B 0 AT1 (SLC6A19), a potential target to induce protein restriction and to treat type 2 diabetes, Br J Pharmacol
Chosidow, Bernigaud, Guillemot, Giraudeau, Lespine et al., Ivermectin as a potential treatment for COVID-19?, PLoS Negl Trop Dis
Cobos-Campos, Apiñaniz, Parraza, Cordero, García et al., Potential use of ivermectin for the treatment and prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Curr Res Transl Med
Cruciani, Pati, Masiello, Malena, Pupella et al., Ivermectin for Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Diagnostics
Crump, Ōmura, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad, Ser B, Phys Biol Sci
Deng, Zhou, Ali, Heybati, Hou et al., Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, QJM,
doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab247Dinicolantonio, Barroso, Mccarty, Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart
Dinicolantonio, Barroso-Aranda, Mccarty, Antiinflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors, Open Heart
Ellinghaus, Degenhardt, Bujanda, Buti, Albillos et al., Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group. Genomewide Association Study of Severe Covid-19 with Respiratory Failure, N Engl J Med
Erener, Diabetes, infection risk and COVID-19, Mol Metab
Felig, Marliss, Cahill, Plasma amino acid levels and insulin secretion in obesity, N Engl J Med
Gemmati, Tisato, Genetic Hypothesis and Pharmacogenetics Side of Renin-Angiotensin-System in COVID-19, Genes
Gheblawi, Wang, Viveiros, Nguyen, Zhong et al., Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2, Circ Res
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Liang, Chen et al., China Medical Treatment Expert Group for COVID-19. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Respir J
Hagiya, Otsuka, Ivermectin for Coronavirus Disease 2019: Yet to Be Well Evaluated Before Clinical Use, Clin Ther
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot
Ilias, Diamantopoulos, Pratikaki, Botoula, Jahaj et al., Glycemia, Beta-Cell Function and Sensitivity to Insulin in Mildly to Critically Ill Covid-19 Patients, Medicina
Ilias, Zabuliene, Hyperglycemia and the novel Covid-19 infection: possible pathophysiologic mechanisms, Med Hypotheses
Irving, Carter, Soop, Weymiller, Syed et al., Effect of insulin sensitizer therapy on amino acids and their metabolites, Metabolism
Jafar, Edriss, Nugent, The Effect of Short-Term Hyperglycemia on the Innate Immune System, Am J Med Sci
Kasela, Daniloski, Bollepalli, Jordan, Tenoever et al., Integrative approach identifies SLC6A20 and CXCR6 as putative causal genes for the COVID-19 GWAS signal in the 3p21.31 locus, Genome Biol
Kaur, Acharya, Mondal, Singh, Saso et al., Should ACE2 be given a chance in COVID-19 therapeutics: A semi-systematic review of strategies enhancing ACE2, Eur J Pharmacol
Kircik, Rosso, Layton, Schauber, Over 25 Years of Clinical Experience With Ivermectin: An Overview of Safety for an Increasing Number of Indications, J Drugs Dermatol
Kory, Meduri, Varon, Iglesias, Marik, Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, Am J Ther
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Goronflot, Wiernsperger et al., CORONADO investigators. Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab
Lazarus, Wangsaputra, Tahapary, High admission blood glucose independently predicts poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Lehrer, Rheinstein, Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2, Vivo
Li, Can Glycine Mitigate COVID-19 Associated Tissue Damage and Cytokine Storm?, Radiat Res
Li, Yang, Yan, Sun, Zeng et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Med
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat Rev Endocrinol
Lim, Reddy, Curtis, Afroz, Billah et al., A Systematic Review of the Incidence and Outcomes of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrests in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019, Crit Care Med
Ling, Van Herpt, Van Hoek, Dehghan, Hofman et al., A genetic variant in SLC6A20 is associated with Type 2 diabetes in white-European and Chinese populations, Diabet Med
Lu, Wang, Yuan, Li, Li, The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin (1-7)/Mas axis protects the function of pancreatic β cells by improving the function of islet microvascular endothelial cells, Int J Mol Med
Lumpuy-Castillo, Lorenzo-Almorós, Pello-Lázaro, Sánchez-Ferrer, Egido et al., Cardiovascular Damage in COVID-19: Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, Int J Mol Sci
Lynagh, Webb, Dixon, Cromer, Lynch, Molecular determinants of ivermectin sensitivity at the glycine receptor chloride channel, J Biol Chem
Mizuiri, Hemmi, Arita, Ohashi, Tanaka et al., Expression of ACE and ACE2 in individuals with diabetic kidney disease and healthy controls, Am J Kidney Dis
Mody, Ho, Wills, Mawri, Lawson et al., Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, Commun Biol
Niklason, Hedner, Niskanen, Lanke, Prevention, Project Study Group. Development of diabetes is retarded by ACE inhibition in hypertensive patients-a subanalysis of the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP), J Hypertens
O'loughlin, Toledo, Budrie, Waechter, Rayner, A Systematic Review of Severe Neurological Manifestations in Pediatric Patients with Coexisting SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Neurol Int
Omura, Ivermectin: 25 years and still going strong, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Pal, Bhadada, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: an unholy interaction of two pandemics, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Palmer, Stevens, Antinozzi, Anderson, Bergman et al., Metabolomic profile associated with insulin resistance and conversion to diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Patterson, Bonzo, Li, Krausz, Eichler et al., Metabolomics reveals attenuation of the SLC6A20 kidney transporter in nonhuman primate and mouse models of type 2 diabetes mellitus, J Biol Chem
Penlioglou, Papachristou, Papanas, COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus: May Old Anti-diabetic Agents Become the New Philosopher's Stone?, Diabetes Ther
Perlot, Penninger, ACE2 -from the renin-angiotensin system to gut microbiota and malnutrition, Microbes Infect
Popp, Stegemann, Metzendorf, Gould, Kranke et al., Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Prattichizzo, De Candia, Nicolucci, Ceriello, Elevated HbA1c levels in pre-Covid-19 infection increases the risk of mortality: A sistematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Res Rev
Prattichizzo, Giuliani, Mensà, Sabbatinelli, Nigris et al., Pleiotropic effects of metformin: shaping the microbiome to manage type 2 diabetes and postpone ageing, Ageing Res Rev
Prattichizzo, Sabbatinelli, De Candia, Olivieri, Ceriello, Tackling the pillars of ageing to fight COVID-19, Lancet Healthy Longev
Qi, Clark, Suvorov, Park, Ivermectin decreases triglyceride accumulation by inhibiting adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, Food Chem Toxicol
Reich, Oudit, Penninger, Scholey, Herzenberg, Decreased glomerular and tubular expression of ACE2 in patients with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease, Kidney Int
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area, JAMA
Sachdeva, Desai, Gupta, Prakash, Jain et al., Admission Hyperglycemia in Non-diabetics Predicts Mortality and Disease Severity in COVID-19: a Pooled Analysis and Metasummary of Literature, SN Compr Clin Med
Santin, Scheim, Mccullough, Yagisawa, Borody, Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honoured distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect
Schlesinger, Neuenschwander, Lang, Pafili, Kuss et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia
Shan, Haddrill, Lynch, Ivermectin, an unconventional agonist of the glycine receptor chloride channel, J Biol Chem
Shao, Xu, Ma, Xu, Lyu et al., In-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes among patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Resuscitation
Shao, Yang, Pan, Yu, Chen, Interaction of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 and Diabetes, Front Endocrinol
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: A possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Singer, Camargo, Ramadan, Schäfer, Mariotta et al., Defective intestinal amino acid absorption in Ace2 null mice, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol
Takanaga, Mackenzie, Suzuki, Hediger, Identification of mammalian proline transporter SIT1 (SLC6A20) with characteristics of classical system imino, J Biol Chem
Teuwen, Geldhof, Pasut, Carmeliet, COVID-19: the vasculature unleashed, Nat Rev Immunol
Tufano, Rendina, Abate, Casoria, Marra et al., Venous Thromboembolism in COVID-19 Compared to Non-COVID-19 Cohorts: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis, J Clin Med
Vuille-Dit-Bille, Camargo, Emmenegger, Sasse, Kummer et al., Human intestine luminal ACE2 and amino acid transporter expression increased by ACE-inhibitors, Amino Acids
Wang, Chiou, Poirion, Buchanan, Valdez et al., NHLBI LungMap Consortium. Single-cell multiomic profiling of human lungs reveals cell-type-specific and agedynamic control of SARS-CoV2 host genes, eLife
White, Mcgarrah, Herman, Bain, Shah et al., Insulin action, type 2 diabetes, and branched-chain amino acids: A two-way street, Mol Metab
Whittaker, Anson, Harky, Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review and current update, Acta Neurol Scand
Yagisawa, Fpj, Hanaki, Omura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, Japanese J Antib
Yang, Cai, Zhang, Hyperglycemia at admission is a strong predictor of mortality and severe/critical complications in COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis, Biosci Rep,
doi:10.1042/BSR20203584Yao, Ye, Li, Xu, Tan et al., Genome and epigenome editing identify CCR9 and SLC6A20 as target genes at the 3p21.31 locus associated with severe COVID-19, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Yusuf, Gerstein, Hoogwerf, Pogue, Bosch et al., HOPE Study Investigators. Ramipril and the development of diabetes, JAMA
Zhong, Yu, Lin, Li, Huang et al., Enhanced angiotensin converting enzyme 2 regulates the insulin/Akt signalling pathway by blockade of macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression, Br J Pharmacol
Zhu, Mao, Chen, Predictive value of HbA1c for in-hospital adverse prognosis in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Prim Care Diabetes,
doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.07.013DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1515/bmc-2021-0017",
"ISSN": [
"1868-503X",
"1868-5021"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2021-0017",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Studies published earlier this year demonstrated the association of the solute carrier <jats:italic>SLC6A20</jats:italic> gene with the risk and severity of COVID-19. The <jats:italic>SLC6A20</jats:italic> protein product (Sodium-dependent Imino Transporter 1 (SIT1)) is involved in the transport of amino acids, including glycine. Here we summarized the results of recent studies demonstrating the interaction of SIT1 with the ACE2 receptor for SARS-CoV-2 as well as an observed association of <jats:italic>SLC6A20</jats:italic> with the risk and traits of Type 2 diabetes (T2D). Recently, it was also proposed that <jats:italic>SLC6A20</jats:italic> represents the novel regulator of glycine levels and that glycine has beneficial effects against the proinflammatory cytokine secretion induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ivermectin, as a partial agonist of glycine-gated chloride channels, was also recently suggested to interfere with the COVID-19 cytokine storm by inducing the activation of glycine receptors. Furthermore, plasma glycine levels are found to be decreased in diabetic patients. Thus, further clinical trials are warranted to confirm the potential favorable effects of targeting the SIT1 transporter and glycine levels in the treatment of COVID-19, particularly for the severe case of disease associated with hyperglycemia, inflammation, and T2D. These findings suggest that SIT1 may potentially represent one of the missing pieces in the complex puzzle observed between these two pandemic diseases and the potential novel target for their efficient treatment.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1515/bmc-2021-0017"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Medicine and Health Sciences , Khalifa University , Abu Dhabi , United Arab Emirates ; Association South East European Network for Medical Research-SOVE , E-mail: sabina.semiz@ku.ac.ae"
}
],
"family": "Semiz",
"given": "Sabina",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Biomolecular Concepts"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-30T13:00:50Z",
"timestamp": 1640869250000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-30T18:41:53Z",
"timestamp": 1640889713000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-31T05:57:42Z",
"timestamp": 1640930262401
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1868-503X"
},
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1868-5021"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/bmc-2021-0017/xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/bmc-2021-0017/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "374",
"original-title": [],
"page": "156-163",
"prefix": "10.1515",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Walter de Gruyter GmbH",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13059-021-02454-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_001",
"unstructured": "Kasela S, Daniloski Z, Bollepalli S, Jordan TX, tenOever BR, Sanjana NE, et al. Integrative approach identifies SLC6A20 and CXCR6 as putative causal genes for the COVID-19 GWAS signal in the 3p21.31 locus. Genome Biol. 2021 Aug;22(1):242."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00519-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_002",
"unstructured": "Yao Y, Ye F, Li K, Xu P, Tan W, Feng Q, et al. Genome and epigenome editing identify CCR9 and SLC6A20 as target genes at the 3p21.31 locus associated with severe COVID-19. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb;6(1):85."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202012632",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_003",
"unstructured": "Bae M, Roh JD, Kim Y, Kim SS, Han HM, Yang E, et al. SLC6A20 transporter: a novel regulator of brain glycine homeostasis and NMDAR function. EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Feb;13(2):e12632."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M413027200",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_004",
"unstructured": "Takanaga H, Mackenzie B, Suzuki Y, Hediger MA. Identification of mammalian proline transporter SIT1 (SLC6A20) with characteristics of classical system imino. J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar;280(10):8974–84."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2013.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_005",
"unstructured": "Perlot T, Penninger JM. ACE2 - from the renin-angiotensin system to gut microbiota and malnutrition. Microbes Infect. 2013 Nov;15(13):866–73."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-014-1889-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_006",
"unstructured": "Vuille-dit-Bille RN, Camargo SM, Emmenegger L, Sasse T, Kummer E, Jando J, et al. Human intestine luminal ACE2 and amino acid transporter expression increased by ACE-inhibitors. Amino Acids. 2015 Apr;47(4):693–705."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20200477",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_007",
"unstructured": "Camargo SM, Vuille-Dit-Bille RN, Meier CF, Verrey F. ACE2 and gut amino acid transport. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Nov;134(21):2823–33."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2020283",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_008",
"unstructured": "Ellinghaus D, Degenhardt F, Bujanda L, Buti M, Albillos A, Invernizzi P, et al.; Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group. Genomewide Association Study of Severe Covid-19 with Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct;383(16):1522–34."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.62522",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_009",
"unstructured": "Wang A, Chiou J, Poirion OB, Buchanan J, Valdez MJ, Verheyden JM, et al.; NHLBI LungMap Consortium. Single-cell multiomic profiling of human lungs reveals cell-type-specific and age-dynamic control of SARS-CoV2 host genes. eLife. 2020 Nov;9:9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.055",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_010",
"unstructured": "Camargo SM, Singer D, Makrides V, Huggel K, Pos KM, Wagner CA, et al. Tissue-specific amino acid transporter partners ACE2 and collectrin differentially interact with hartnup mutations. Gastroenterology. 2009 Mar;136(3):872–82."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173545",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_011",
"unstructured": "Kaur U, Acharya K, Mondal R, Singh A, Saso L, Chakrabarti S, et al. Should ACE2 be given a chance in COVID-19 therapeutics: A semi-systematic review of strategies enhancing ACE2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;887:173545."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101044",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_012",
"unstructured": "Erener S. Diabetes, infection risk and COVID-19. Mol Metab. 2020 Sep;39:101044."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01227-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_013",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Liang WH, Zhao Y, Liang HR, Chen ZS, Li YM, et al.; China Medical Treatment Expert Group for COVID-19. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Respir J. 2020 May;55(5):2000547."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_014",
"unstructured": "Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, et al.; the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 2020 May;323(20):2052–9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resuscitation.2020.04.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_015",
"unstructured": "Shao F, Xu S, Ma X, Xu Z, Lyu J, Ng M, et al. In-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes among patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Resuscitation. 2020 Jun;151:18–23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004950",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_016",
"unstructured": "Lim ZJ, Ponnapa Reddy M, Curtis JR, Afroz A, Billah B, Sheth V, et al. A Systematic Review of the Incidence and Outcomes of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrests in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Crit Care Med. 2021 Jun;49(6):901–11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ane.13266",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_017",
"unstructured": "Whittaker A, Anson M, Harky A. Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review and current update. Acta Neurol Scand. 2020 Jul;142(1):14–22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/neurolint13030041",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_018",
"unstructured": "O’Loughlin L, Alvarez Toledo N, Budrie L, Waechter R, Rayner J. A Systematic Review of Severe Neurological Manifestations in Pediatric Patients with Coexisting SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Neurol Int. 2021 Aug;13(3):410–27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10214925",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_019",
"unstructured": "Tufano A, Rendina D, Abate V, Casoria A, Marra A, Buonanno P, et al. Venous Thromboembolism in COVID-19 Compared to Non-COVID-19 Cohorts: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med. 2021 Oct;10(21):4925."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_020",
"unstructured": "Lim S, Bae JH, Kwon HS, Nauck MA. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021 Jan;17(1):11–30."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.04.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_021",
"unstructured": "Bonafè M, Prattichizzo F, Giuliani A, Storci G, Sabbatinelli J, Olivieri F. Inflamm-aging: why older men are the most susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 complicated outcomes. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Jun;53:33–7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00053-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_022",
"unstructured": "Prattichizzo F, Sabbatinelli J, de Candia P, Olivieri F, Ceriello A. Tackling the pillars of ageing to fight COVID-19. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021 Apr;2(4):e191."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-021-05458-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_023",
"unstructured": "Schlesinger S, Neuenschwander M, Lang A, Pafili K, Kuss O, Herder C, et al. Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2021 Jul;64(7):1480–91."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcd.2021.07.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_024",
"unstructured": "Zhu Z, Mao Y, Chen G. Predictive value of HbA1c for in-hospital adverse prognosis in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021 Aug;15(6):S1751-9918(21)00130-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcd.2021.07.013."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20203584",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_025",
"unstructured": "Yang Y, Cai Z, Zhang J. Hyperglycemia at admission is a strong predictor of mortality and severe/critical complications in COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis. Biosci Rep. 2021 Feb;41(2):BSR20203584. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20203584."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108561",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_026",
"unstructured": "Lazarus G, Audrey J, Wangsaputra VK, Tamara A, Tahapary DL. High admission blood glucose independently predicts poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021 Jan;171:108561."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.574541",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_027",
"unstructured": "Chen J, Wu C, Wang X, Yu J, Sun Z. The Impact of COVID-19 on Blood Glucose: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Oct;11:574541."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3476",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_028",
"unstructured": "Prattichizzo F, de Candia P, Nicolucci A, Ceriello A. Elevated HbA1c levels in pre-Covid-19 infection increases the risk of mortality: A sistematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 May;•••:e3476."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.107927",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_029",
"unstructured": "Ceriello A, Prattichizzo F. Pharmacological management of COVID-19 in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2021 Jul;35(7):107927."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_030",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Ingraham NE, Murray TA, Marmor S, Hovertsen S, Gronski J, et al. Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021 Jan;2(1):e34–41."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_031",
"unstructured": "Lalau JD, Al-Salameh A, Hadjadj S, Goronflot T, Wiernsperger N, Pichelin M, et al.; CORONADO investigators. Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. 2021 Sep;47(5):101216."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.704666",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_032",
"unstructured": "Li Y, Yang X, Yan P, Sun T, Zeng Z, Li S. Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Aug;8:704666."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13300-020-00830-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_033",
"unstructured": "Penlioglou T, Papachristou S, Papanas N. COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus: May Old Anti-diabetic Agents Become the New Philosopher's Stone? Diabetes Ther. 2020 May;11(6):1–3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_034",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Ingraham NE, Murray TA, Marmor S, Hovertsen S, Gronski J, et al. Observational Study of Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19. medRxiv. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_035",
"unstructured": "Sharma S, Ray A, Sadasivam B. Metformin in COVID-19: A possible role beyond diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Jun;164:108183."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_036",
"unstructured": "Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q, Zhong JC, Turner AJ, et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2. Circ Res. 2020 May;126(10):1456–74."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2018.10.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_037",
"unstructured": "Prattichizzo F, Giuliani A, Mensà E, Sabbatinelli J, De Nigris V, Rippo MR, et al. Pleiotropic effects of metformin: shaping the microbiome to manage type 2 diabetes and postpone ageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2018 Dec;48:87–98."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dme.12528",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_038",
"unstructured": "Ling Y, van Herpt TT, van Hoek M, Dehghan A, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, et al. A genetic variant in SLC6A20 is associated with Type 2 diabetes in white-European and Chinese populations. Diabet Med. 2014 Nov;31(11):1350–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes11091044",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_039",
"unstructured": "Gemmati D, Tisato V. Genetic Hypothesis and Pharmacogenetics Side of Renin-Angiotensin-System in COVID-19. Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep;11(9):E1044."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.051",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_040",
"unstructured": "Abuissa H, Jones PG, Marso SP, O’Keefe JH Jr. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers for prevention of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005 Sep;46(5):821–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00004872-200403000-00029",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_041",
"unstructured": "Niklason A, Hedner T, Niskanen L, Lanke J; Captopril Prevention Project Study Group. Development of diabetes is retarded by ACE inhibition in hypertensive patients—a subanalysis of the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP). J Hypertens. 2004 Mar;22(3):645–52."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.286.15.1882",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_042",
"unstructured": "Yusuf S, Gerstein H, Hoogwerf B, Pogue J, Bosch J, Wolffenbuttel BH, et al.; HOPE Study Investigators. Ramipril and the development of diabetes. JAMA. 2001 Oct;286(15):1882–5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.13711",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_043",
"unstructured": "Cheng Q, Shah N, Bröer A, Fairweather S, Jiang Y, Schmoll D, et al. Identification of novel inhibitors of the amino acid transporter B0 AT1 (SLC6A19), a potential target to induce protein restriction and to treat type 2 diabetes. Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;174(6):468–82."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.221739",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_044",
"unstructured": "Patterson AD, Bonzo JA, Li F, Krausz KW, Eichler GS, Aslam S, et al. Metabolomics reveals attenuation of the SLC6A20 kidney transporter in nonhuman primate and mouse models of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun;286(22):19511–22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ki.2008.497",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_045",
"unstructured": "Reich HN, Oudit GY, Penninger JM, Scholey JW, Herzenberg AM. Decreased glomerular and tubular expression of ACE2 in patients with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008 Dec;74(12):1610–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.11.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_046",
"unstructured": "Mizuiri S, Hemmi H, Arita M, Ohashi Y, Tanaka Y, Miyagi M, et al. Expression of ACE and ACE2 in individuals with diabetic kidney disease and healthy controls. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008 Apr;51(4):613–23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.049",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_047",
"unstructured": "Pal R, Bhadada SK. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: an unholy interaction of two pandemics. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Jul–Aug;14(4):513–7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2014.1917",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_048",
"unstructured": "Lu CL, Wang Y, Yuan L, Li Y, Li XY. The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin (1–7)/Mas axis protects the function of pancreatic β cells by improving the function of islet microvascular endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 2014 Nov;34(5):1293–300."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2014.05.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_049",
"unstructured": "Cao X, Yang FY, Xin Z, Xie RR, Yang JK. The ACE2/Ang-(1–7)/Mas axis can inhibit hepatic insulin resistance. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Aug;393(1–2):30–8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0707482",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_050",
"unstructured": "Zhong JC, Yu XY, Lin QX, Li XH, Huang XZ, Xiao DZ, et al. Enhanced angiotensin converting enzyme 2 regulates the insulin/Akt signalling pathway by blockade of macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression. Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;153(1):66–74."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109699",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_051",
"unstructured": "Ilias I, Zabuliene L. Hyperglycemia and the novel Covid-19 infection: possible pathophysiologic mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2020 Jun;139:109699."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpgi.00140.2012",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_052",
"unstructured": "Singer D, Camargo SM, Ramadan T, Schäfer M, Mariotta L, Herzog B, et al. Defective intestinal amino acid absorption in Ace2 null mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Sep;303(6):G686–95."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1667/RADE-20-00146.1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_053",
"unstructured": "Li CY. Can Glycine Mitigate COVID-19 Associated Tissue Damage and Cytokine Storm? Radiat Res. 2020 Sep;194(3):199–201."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M011264200",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_054",
"unstructured": "Shan Q, Haddrill JL, Lynch JW. Ivermectin, an unconventional agonist of the glycine receptor chloride channel. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr;276(16):12556–64."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.262634",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_055",
"unstructured": "Lynagh T, Webb TI, Dixon CL, Cromer BA, Lynch JW. Molecular determinants of ivermectin sensitivity at the glycine receptor chloride channel. J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec;286(51):43913–24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0009446",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_056",
"unstructured": "Chosidow O, Bernigaud C, Guillemot D, Giraudeau B, Lespine A, Changeux JP, et al. Ivermectin as a potential treatment for COVID-19? PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jun;15(6):e0009446."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_057",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2020 Jun;178:104787."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001442",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_058",
"unstructured": "Bryant A, Lawrie TA, Dowswell T, Fordham EJ, Mitchell S, Hill SR, et al. Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines. Am J Ther. 2021 Jun;28(4):e434–60."
},
{
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_059",
"unstructured": "Analysis C. Ivermectin for COVID-19: real-time meta analysis of 64 studies. 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_060",
"unstructured": "Kory P, Meduri GU, Varon J, Iglesias J, Marik PE. Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19. Am J Ther. 2021 Apr;28(3):e299–318."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_061",
"unstructured": "Santin AD, Scheim DE, McCullough PA, Yagisawa M, Borody TJ. Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honoured distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19. New Microbes New Infect. 2021 Aug;43:100924."
},
{
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_062",
"unstructured": "Yagisawa M. FPJ, Hanaki H., Omura S. . Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19. Japanese J Antib. 2021;74(1)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.retram.2021.103309",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_063",
"unstructured": "Cobos-Campos R, Apiñaniz A, Parraza N, Cordero J, García S, Orruño E. Potential use of ivermectin for the treatment and prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Curr Res Transl Med. 2021 Oct;69(4):103309."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics11091645",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_064",
"unstructured": "Cruciani M, Pati I, Masiello F, Malena M, Pupella S, De Angelis V. Ivermectin for Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Sep;11(9):1645."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab247",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_065",
"unstructured": "Deng J, Zhou F, Ali S, Heybati K, Hou W, Huang E, et al. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM. 2021 Sep;hcab247. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcab247."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.07.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_066",
"unstructured": "Hagiya H, Otsuka F. Ivermectin for Coronavirus Disease 2019: Yet to Be Well Evaluated Before Clinical Use. Clin Ther. 2021 Sep;43(9):1622–3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_067",
"unstructured": "Popp M, Stegemann M, Metzendorf MI, Gould S, Kranke P, Meybohm P, et al. Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul;7:CD015017."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_068",
"unstructured": "Heidary F, Gharebaghi R. Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020 Sep;73(9):593–602."
},
{
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_069",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Geneva S. 22nd Model List of Essential Medicines. 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_070",
"unstructured": "Crump A, Ōmura S. Ivermectin, ‘wonder drug’ from Japan: the human use perspective. Proc Jpn Acad, Ser B, Phys Biol Sci. 2011;87(2):13–28."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.08.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_071",
"unstructured": "Omura S. Ivermectin: 25 years and still going strong. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008 Feb;31(2):91–8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1085658",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_072",
"unstructured": "Anand K, Ziebuhr J, Wadhwani P, Mesters JR, Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 2003 Jun;300(5626):1763–7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_073",
"unstructured": "Mody V, Ho J, Wills S, Mawri A, Lawson L, Ebert MC, et al. Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. Commun Biol. 2021 Jan;4(1):93."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/invivo.12134",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_074",
"unstructured": "Lehrer S, Rheinstein PH. Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2. In Vivo. 2020 Sep–Oct;34(5):3023–6."
},
{
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_075",
"unstructured": "Kircik LH, Del Rosso JQ, Layton AM, Schauber J. Over 25 Years of Clinical Experience With Ivermectin: An Overview of Safety for an Increasing Number of Indications. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016 Mar;15(3):325–32."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_076",
"unstructured": "DiNicolantonio JJ, Barroso J, McCarty M. Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19. Open Heart. 2020 Sep;7(2):e001350."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/openhrt-2021-001655",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_077",
"unstructured": "DiNicolantonio JJ, Barroso-Aranda J, McCarty MF. Anti-inflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors. Open Heart. 2021 Apr;8(1):e001655."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10517-021-05125-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_078",
"unstructured": "Bukanova JV, Solntseva EI, Kondratenko RV, Skrebitsky VG. Antiviral Drug Ivermectin at Nanomolar Concentrations Inhibits Glycine-Induced Chloride Current in Rat Hippocampal Neurons. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2021 Mar;170(5):649–53."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101261",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_079",
"unstructured": "White PJ, McGarrah RW, Herman MA, Bain JR, Shah SH, Newgard CB. Insulin action, type 2 diabetes, and branched-chain amino acids: A two-way street. Mol Metab. 2021 Oct;52:101261."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM196910092811503",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_080",
"unstructured": "Felig P, Marliss E, Cahill GF Jr. Plasma amino acid levels and insulin secretion in obesity. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct;281(15):811–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2014-2357",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_081",
"unstructured": "Palmer ND, Stevens RD, Antinozzi PA, Anderson A, Bergman RN, Wagenknecht LE, et al. Metabolomic profile associated with insulin resistance and conversion to diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Mar;100(3):E463–8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-017-2508-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_082",
"unstructured": "Adeva-Andany M, Souto-Adeva G, Ameneiros-Rodríguez E, Fernández-Fernández C, Donapetry-García C, Domínguez-Montero A. Insulin resistance and glycine metabolism in humans. Amino Acids. 2018 Jan;50(1):11–27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2015.01.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_083",
"unstructured": "Irving BA, Carter RE, Soop M, Weymiller A, Syed H, Karakelides H, et al. Effect of insulin sensitizer therapy on amino acids and their metabolites. Metabolism. 2015 Jun;64(6):720–8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2019.110576",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_084",
"unstructured": "Qi W, Clark JM, Suvorov A, Park Y. Ivermectin decreases triglyceride accumulation by inhibiting adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Sep;131:110576."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00575-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_085",
"unstructured": "Sachdeva S, Desai R, Gupta U, Prakash A, Jain A, Aggarwal A. Admission Hyperglycemia in Non-diabetics Predicts Mortality and Disease Severity in COVID-19: a Pooled Analysis and Meta-summary of Literature. SN Compr Clin Med. 2020 Oct;2(11):1–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina57010068",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_086",
"unstructured": "Ilias I, Diamantopoulos A, Pratikaki M, Botoula E, Jahaj E, Athanasiou N, et al. Glycemia, Beta-Cell Function and Sensitivity to Insulin in Mildly to Critically Ill Covid-19 Patients. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Jan;57(1):68."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2015.11.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_087",
"unstructured": "Jafar N, Edriss H, Nugent K. The Effect of Short-Term Hyperglycemia on the Innate Immune System. Am J Med Sci. 2016 Feb;351(2):201–11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.731974",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_088",
"unstructured": "Shao S, Yang Q, Pan R, Yu X, Chen Y. Interaction of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 and Diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct;12:731974."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0343-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_089",
"unstructured": "Teuwen LA, Geldhof V, Pasut A, Carmeliet P. COVID-19: the vasculature unleashed. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Jul;20(7):389–91."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm8091385",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_090",
"unstructured": "Burgos-Morón E, Abad-Jiménez Z, Marañón AM, Iannantuoni F, Escribano-López I, López-Domènech S, et al. Relationship Between Oxidative Stress, ER Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes: The Battle Continues. J Clin Med. 2019 Sep;8(9):E1385."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21186471",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_091",
"unstructured": "Lumpuy-Castillo J, Lorenzo-Almorós A, Pello-Lázaro AM, Sánchez-Ferrer C, Egido J, Tuñón J, et al. Cardiovascular Damage in COVID-19: Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep;21(18):E6471."
},
{
"key": "2021123018400923816_j_bmc-2021-0017_ref_092",
"unstructured": "Bălută M, Vintilă V, Vintilă M. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system inhibition in prevention of diabetes mellitus. Rom J Intern Med. 2004;42(2):277–88."
}
],
"reference-count": 92,
"references-count": 92,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}