Jun 20 |
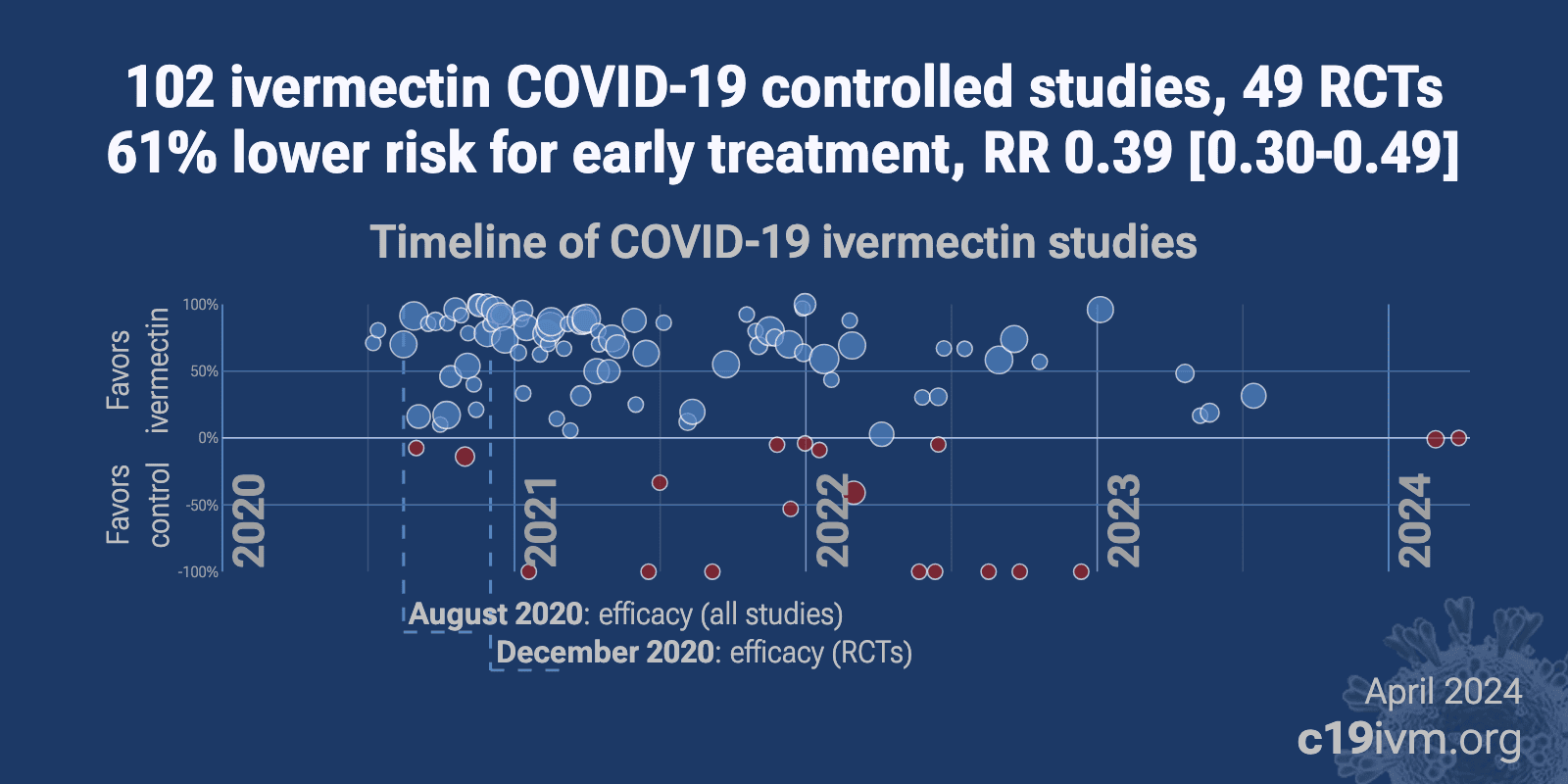
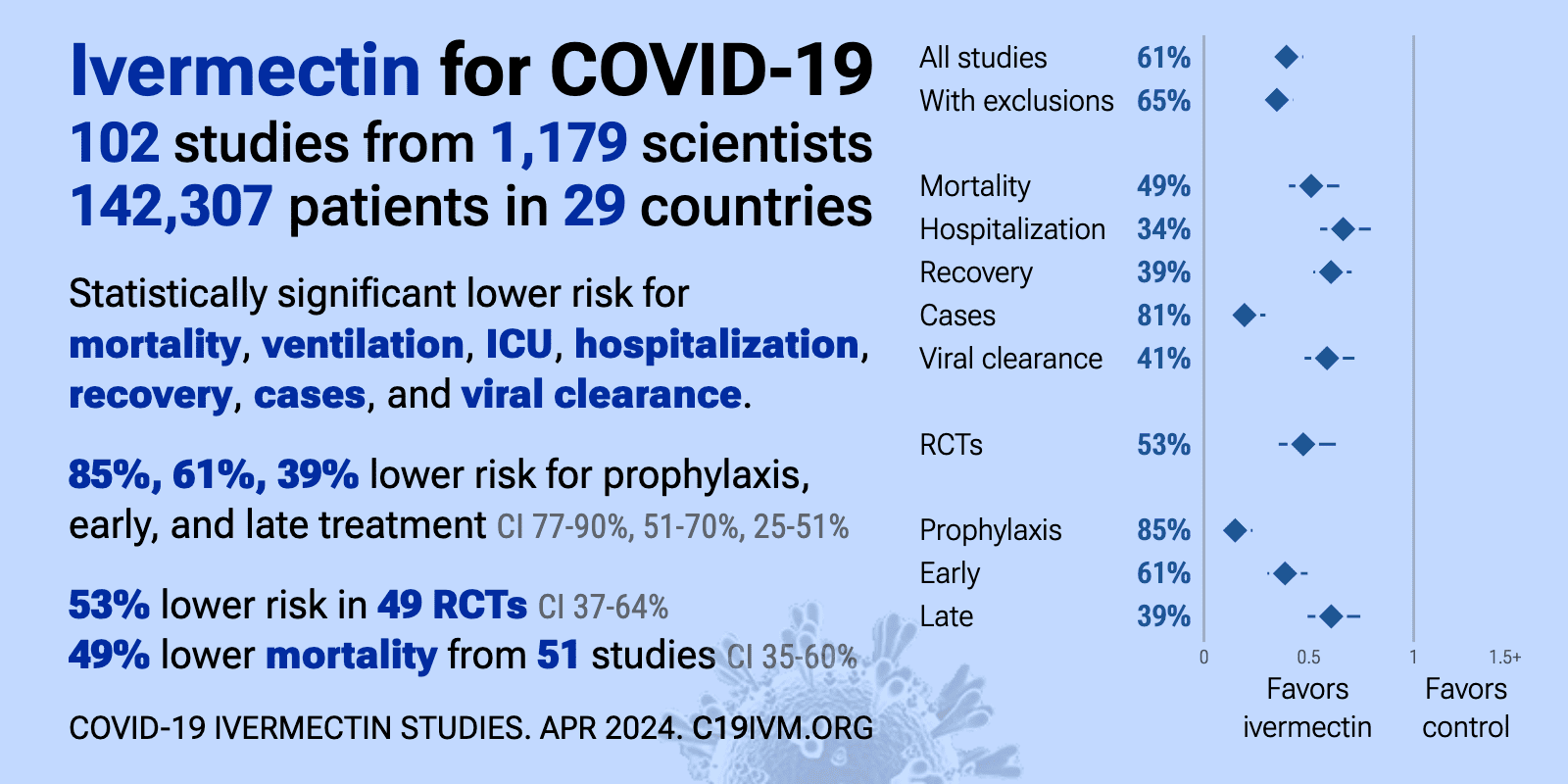
Ivermectin reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 105 studies (ivmmeta) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ventilation, ICU admission, hospitalization, recovery, cases, and viral clearance. All remain significant for higher quality studies. 64 studies from 58 independent teams in 27 different cou.. | ||
Jun 12 |
et al., Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607 | SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis |
| Review of SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactions during viral pathogenesis, focusing on protein-protein interactions that facilitate viral entry, replication, immune evasion, assembly, and release. Authors comprehensively analyze how SARS-.. | ||
May 2 |
et al., AAPS PharmSciTech, doi:10.1208/s12249-025-03113-8 | Enhancing Intracellular Uptake of Ivermectin through Liposomal Encapsulation |
| In Vitro study showing enhanced intracellular uptake of ivermectin through liposomal encapsulation in Vero E6 cells with reduced cytotoxicity. While free ivermectin showed a half-maximal cytotoxic concentration (CC50) of 10 μM, liposomal .. | ||
May 2 |
et al., Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-025-00722-w | Rho-GTPases subfamily: cellular defectors orchestrating viral infection |
| Review of Rho-GTPases as pivotal host factors commandeered by SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses, noting ivermectin as one of many compounds targeting this axis. Authors list ivermectin + atorvastatin as agents that suppress RhoA/CDC42 signalin.. | ||
Apr 18 |
et al., iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.112105 | M-Motif, a potential non-conventional NLS in YAP/TAZ and other cellular and viral proteins that inhibits classic protein import |
| In Vitro study showing that TAZ/YAP proteins contain an M-motif, a novel type of nuclear localization signal that can inhibit classic protein import and may play a role in viral immune evasion. Authors identified that this M-motif consist.. | ||
Apr 18 |
et al., Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2025.106941 | Development and Optimization of Lyophilized Dry Emulsion Tablet for Improved Oral Delivery of Ivermectin |
| In Vitro and rabbit study showing that rapidly disintegrating lyophilized dry‑emulsion tablets (IVM‑LDET) markedly improve oral ivermectin delivery. Authors applied a quality‑by‑design approach to oil‑in‑water emulsions.. | ||
Mar 28 |
et al., Medical Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2025.111613 | Cholinergic eubiosis: A hypothesis on Ivermectin-upregulated Bifidobacterium |
| Hypothesis that ivermectin may increase beneficial Bifidobacterium populations in the gut through a "cholinergic eubiosis" mechanism. Authors theorize that ivermectin acts as a positive allosteric regulator of alpha-7 nicotinic.. | ||
Mar 25 |
et al., The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.78.1_35 | Critical appraisal of multidrug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia Part II: Causal inference using the Bradford Hill criteria |
| Critical appraisal of three case series totaling 119 COVID-19 patients with hypoxemia treated with ivermectin-based multidrug protocols in the United States, Zimbabwe, and Nigeria, showing reduced hospitalization and mortality. Authors ap.. | ||
Mar 13 |
et al., Biotecnia, doi:10.18633/biotecnia.v27.2485 | Binding affinities analysis of ivermectin, nucleocapsid and ORF6 proteins of SARS-CoV-2 to human importins α isoforms: A computational approach |
| In Silico study showing that ivermectin, the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein, and the ORF6 protein share binding sites on human importin α isoforms. Authors used molecular docking to analyze binding affinities between these molecules .. | ||
Feb 12 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17020252 | Inhaled Dry Powder of Antiviral Agents: A Promising Approach to Treating Respiratory Viral Pathogens |
| Review of inhaled dry powder antiviral formulations for treating respiratory viral infections, focusing on COVID-19. Authors explain that traditional antiviral tablets face limitations including systemic side effects and delayed onset of .. | ||
Jan 30 |
et al., International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125302 | Inhalable spray-dried dry powders combining ivermectin and niclosamide to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro |
| In Vitro study showing that inhalable spray-dried dry powders combining ivermectin and niclosamide exhibit enhanced anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity compared to the individual drugs. Authors developed stable, amorphous powders with aerodynamic pr.. | ||
Dec 31 2024 |
et al., Pharmazie, doi:10.1691/ph.2024.4035 | Quantification of ivermectin in veterinary products consumed off-label as a treatment for COVID-19 |
| Analysis of 9 veterinary ivermectin products that were reportedly used off-label as a treatment for COVID-19. All tested products contained ivermectin within acceptable limits of their label claims. In terms of the ivermectin content, thi.. | ||
Nov 27 2024 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121836 | Characterization and Fluctuations of an Ivermectin Binding Site at the Lipid Raft Interface of the N-Terminal Domain (NTD) of the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants |
| In Silico and In Vitro study showing that ivermectin binds to the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variants, potentially inhibiting initial viral attachment to host cell lipid rafts. Authors used molecular modeli.. | ||
Nov 25 2024 |
et al., Revista Cubana de Medicina Militar, 53:4 | Content and characteristics of ivermectin in master formulations |
| Analysis of ivermectin in Peru showing significant variability in quality and concentration, with several formulations falling below the required dosage standards (36.2%-95.8%). Dosage inconsistencies were identified in products from priv.. | ||
Nov 21 2024 |
et al., Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5 | Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study |
| In Silico study showing potential inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 proteins by various compounds including dactinomycin, itraconazole, ivermectin, vitamin D, quercetin, curcumin, montelukast, bromhexine, hesperidin, EGCG and raloxifene. Authors p.. | ||
Nov 15 2024 |
, R., Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.5021494 | Coating of Remdesivir and Ivermectin on Silver Nanoparticles: First Principle Study |
| In Silico study showing that silver nanoparticles could be used as a therapeutic drug delivery mechanism for remdesivir and ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2. Using Density Functional Theory calculations, authors find that both drugs bond str.. | ||
Oct 26 2024 |
et al., Molecular Biology Research Communications, doi:10.22099/mbrc.2024.50245.2001 | Non-spike protein inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by natural products through the key mediator protein ORF8 |
| In Silico study showing that ivermectin, artemisinin, and DEG-168 may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the ORF8 protein's binding sites. Ivermectin showed the highest binding affinity. Authors identified two key binding regions on ORF8 - a.. | ||
Sep 21 2024 |
et al., Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13181591 | The Nucleolus and Its Interactions with Viral Proteins Required for Successful Infection |
| Review of the interaction between viral proteins and the nucleolus during infection. The nucleolus is a crucial site for regulating cellular functions and viral proteins can interact with nucleolar components to facilitate viral replicati.. | ||
Sep 17 2024 |
et al., The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.23-0710 | Circulation of COVID-19-Related Medicines on Japanese Websites during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Their Quality and Authenticity |
| Investigation of the circulation and quality of COVID-19-related medicines sold online in Japan showing poor-quality ivermectin and dexamethasone. Four dexamethasone samples and two ivermectin samples failed quantitative analysis, and thr.. | ||
Aug 24 2024 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm13175013 | Prevalence and Risk Factors of Headache Associated with COVID-19 |
| 98% lower PASC (p=0.37) and 30% worse results (p=0.5). Retrospective 295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Slovakia showing 35% prevalence of headache, of which 41% of patients had persistent headache 12-15 months after infection. Authors' analysis of long COVID headache is only for the subgr.. | ||
Aug 12 2024 |
et al., Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16081061 | Inhaled Ivermectin-Loaded Lipid Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles: Development and Characterization |
| In Vitro study developing ivermectin-loaded lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPHNPs) as a potential dry powder inhalation formulation for pulmonary delivery. | ||
Aug 5 2024 |
et al., Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034 | Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports |
| Review of the successful treatment of COVID-19 using existing medications including HCQ, AZ, ivermectin, famotidine, monoclonal antibodies, and others. Authors note that the typical treatment of severe viral infections with multiple thera.. | ||
Jul 22 2024 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09563-y | Efficacy and safety of oral ivermectin in the treatment of mild to moderate Covid-19 patients: a multi-centre double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial |
| 51% improved viral clearance (p=0.03). RCT 249 hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 in Sri Lanka, showing statistically significant lower viral load. There was no significant difference in clinical outcomes. Only one patient had a serious outcome. Mid-recovery .. | ||
Jul 17 2024 |
, S., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691 | Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity |
| Review showing reduced efficacy of interventions with new variants and suggesting that regulators and health organizations should consider approval and strategic use of cost-effective adjunct therapies such as vitamin D and ivermectin tha.. | ||
Jul 4 2024 |
et al., Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3 | SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147 |
| Review of possible mechanisms for lymphopenia in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Authors describe several indirect and direct mechanisms that may contribute to the T-cell depletion observed in COVID-19, including inflammatory cytokine storms, hyperl.. | ||
Jun 13 2024 |
et al., Critical Care Reviews, CCR24 | Ivermectin for patients admitted to an ICU with COVID-19: REMAP-CAP randomized controlled trial |
| Early terminated REMAP-CAP results showing a trend towards benefit for non-critical patients despite very low dose, poor administration, and very... Early terminated REMAP-CAP results delayed >600 days, showing no significant differences with very low dose, poor administration, very late treatment of ICU patients. Results trend towards benefit for non-critical patients, with 32% lower.. | ||
May 31 2024 |
et al., Integrative Medicine, 23:2 | Global COVID-19 Pandemic Outcomes: A Cross-Country Comparison Study of Policy Strategies |
| Retrospective study of 108 countries showing negative correlations between hydroxychloroquine/ivermectin use and mortality. Higher ivermectin index scores (r=-0.23, p=0.018) and hydroxychloroquine index scores (r=-0.15, p=0.125) were corr.. | ||
May 25 2024 |
et al., International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1055/s-0044-1786046 | Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review |
| Review of treatments for olfactory dysfunction (OD) in COVID-19. Authors report that the prevalence of OD varies among populations and is highest in Europe and North America, ranging from 50-85%. The mechanism may involve inflammation, ob.. | ||
May 16 2024 |
, S., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2024.8723 | Error in the Exclusion of Participants From Analysis in the ACTIV-6 Platform Randomized Clinical Trial |
| Partial correction to ACTIV-6 600 confirming that 16% of patients were missing in the analysis. It's not clear how the trial could have such a large error for the number of patients randomized, why the correction took over a year, or why .. | ||
Apr 30 2024 |
et al., Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences, doi:10.5812/jjhs-146703 | Ivermectin as a Potential Addition to the Limited Anti-COVID-19 Arsenal: A Double-Blinded Clinical Trial |
| 82% lower ventilation (p=0.02), 83% lower ICU admission (p=0.0004), 33% shorter hospitalization (p=0.001), and 28% faster recovery (p<0.0001). Double-blind RCT 110 hospitalized moderate to severe COVID-19 patients showing significantly reduced ICU admission, shorter hospitalization, faster resolution of symptoms, and improved CRP and LDH levels with ivermectin treatment compared.. | ||
Apr 29 2024 |
et al., Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16050601 | Enhanced In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Ivermectin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus via Improved Intracellular Delivery |
| Non-COVID-19 In Vitro study showing enhanced antiviral activity of ivermectin against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus when loaded into nanostructured lipid carriers. Ivermectin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (IVM-NLCs) inhibited vir.. | ||
Apr 28 2024 |
et al., Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202404.1825.v1 | In Silico Comparative Analysis of Ivermectin and Nirmatrelvir Inhibitors Interacting with the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease |
| In Silico study showing that ivermectin and nirmatrelvir interact with the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Authors used molecular docking and 100ns molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the binding interactions. Nirmatrelvir form.. | ||
Apr 22 2024 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647 | Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses |
| Review of the biochemical underpinnings of the severe morbidities of COVID-19, focusing on the binding of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (SP) to sialylated glycans on host cell surfaces. Authors highlight how the SP attaches particularly ti.. | ||
Apr 18 2024 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4180797/v1 | The selective effect of Ivermectin on different human coronaviruses; in-vitro study |
| In Vitro study showing dose-dependent inhibition of wildtype and omicron SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5-5μM ivermectin. Authors found no significant effect for alphacoronavirus NL63 and a moderate effect for betacoronavirus OC43. In contrast, iverme.. | ||
Apr 17 2024 |
et al., International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112073 | Ivermectin ameliorates acute myocarditis via the inhibition of importin-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65 |
| Mouse study showing that ivermectin improves cardiac function and reduces inflammation in models of viral and autoimmune myocarditis. Authors found that ivermectin inhibited the nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65 in macrophages by targeti.. | ||
Apr 16 2024 |
et al., ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1 | Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases |
| In Silico study identifying potential drugs beneficial for COVID-19 by integrating transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, lipidomics, and drug data. Authors explore interactions between drugs, molecular features, and disease severity... | ||
Apr 12 2024 |
et al., Global Journal of Aging & Geriatric Research, doi:10.33552/GJAGR.2024.03.000557 | Early Treatment Outcomes of SARS-Cov-2 with Ivermectin, Nitazoxanide and Acetylsalicylic Acid in 2 Nursing Homes During The COVID-19 Pandemic in Cali, Colombia |
| Retrospective 475 nursing home residents showing low mortality with early treatment using ivermectin, nitazoxanide, and acetylsalicylic acid. All residents were treated when the first positive cases were identified. 87 residents tested po.. | ||
Mar 29 2024 |
et al., Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2024.03.030 | A Randomized Trial to Assess the Acceleration of Viral Clearance by the Combination Favipiravir/Ivermectin/Niclosamide in Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 Adult Patients (FINCOV) |
| 39% improved recovery (p=0.19) and 6% improved viral clearance (p=0.75). RCT 60 low-risk outpatients, median age 31, with mild to moderate COVID-19 showing no significant differences with combined favipiravir/ivermectin/niclosamide treatment compared to favipiravir alone. There was limited room for improvement.. | ||
Mar 25 2024 |
et al., The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.77.1_45 | Global trends in clinical trials of ivermectin for COVID-19—Part 2 |
| Review of global trends in clinical trials of ivermectin for COVID-19. The review summarizes and analyzes the results of trials to date. Authors report that 27 systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been conducted, with 15 demonstratin.. | ||
Mar 21 2024 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29552 | Identification of inositol monophosphatase as a broad‐spectrum antiviral target of ivermectin |
| In vitro study showing that ivermectin inhibits dengue, Zika, and SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the host protein inositol monophosphatase (IMPase). Authors used thermal proteomic profiling to identify IMPase as a target of ivermectin in human c.. | ||
Mar 12 2024 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.56025 | Ivermectin: A Multifaceted Drug With a Potential Beyond Anti-parasitic Therapy |
| Review of the multifaceted effects and potential clinical applications of ivermectin beyond its traditional use as an anthelmintic agent. Authors discuss ivermectin's established antiparasitic activity against infections like scabies and .. | ||
Feb 29 2024 |
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106130 | Ivermectin for COVID-19 in adults in the community (PRINCIPLE): an open, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial of short- and longer-term outcomes |
| Significantly improved recovery and significantly lower risk of long COVID with ivermectin (PRINCIPLE trial).. Significantly improved recovery and significantly lower risk of long COVID with ivermectin, despite very late treatment, low-risk patients, and poor administration. 36% lower ongoing persistent COVID-19 specific symptoms, p 0.999), missin.. | ||
Jan 30 2024 |
et al., GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030 | Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against SARS-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation |
| In Silico study showing that ivermectin and moxidectin bind strongly to SARS-CoV-2 viral targets including the main protease, helicase, and RNA polymerase. Binding was further validated through molecular dynamics simulations indicating st.. | ||
Jan 30 2024 |
et al., European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106714 | A remodeled ivermectin polycaprolactone-based nanoparticles for inhalation as a promising treatment of pulmonary inflammatory diseases |
| In Vitro and rat study showing that an optimized polycaprolactone-based nanoparticle formulation of ivermectin for inhalation had improved lung deposition, bioavailability, and anti-inflammatory effects compared to oral ivermectin. Author.. | ||
Dec 13 2023 |
et al., Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248072 | Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing Applied to the Study of Natural Products and Extracts That Modulate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/ACE2 Interaction |
| In Vitro study showing that ivermectin modulated SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD-ACE2 interaction, suggesting efficacy for COVID-19, at a concentration of 1nM, well below concentrations achieved in practice. Authors use microfluidic diffusional sizi.. | ||
Dec 8 2023 |
et al., Preprints | Critical appraisal of multidrug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia |
| Reanalysis of 119 hypoxemic COVID-19 outpatients treated with multidrug regimens that may include ivermectin, doxycycline, zinc, vitamins C/D, hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin. Authors combine case series from the US, Zimbabwe, and Ni.. | ||
Dec 7 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021 | Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury |
| Ivermectin may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by blocking GSDMD and NET formation. Authors review the role of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). Authors discusses the mechanisms of NET.. | ||
Dec 3 2023 |
et al., Drug Testing and Analysis, doi:10.1002/dta.3618 | Substandard and falsified ivermectin tablets obtained for self‐medication during the COVID‐19 pandemic as a source of potential harm |
| Analysis of intercepted ivermectin tablets in Belgium showing 100% of 19 samples were either underdosed or severely contaminated with bacteria. | ||
Dec 1 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039 | Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19 |
| Review of evidence suggesting that binding of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to sialylated glycans on red blood cells, platelets, and endothelial cells plays a key role in COVID-19 morbidity by inducing red blood cell aggregation, microvasc.. | ||
Nov 29 2023 |
, K., Zenodo, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10215620 | Novel non-covalent ivermectin complex Didenectin is revolutionizing healthcare |
| Report on a non-covalent complex of ivermectin called Didenectin, showing improved solubility and lower toxicity in animals, and promising results in early testing for SARS-CoV-2 and Dengue. | ||
Nov 17 2023 |
, E., Do Your Own Research, Nov 17, 2023 | Waiting for PRINCIPLE |
| Discussion of issues in the ivermectin arm of the PRINCIPLE trial [Hayward], including the unsupported supply claim and continuation, design issues favoring finding no effect, changes to include lower risk patients, and the extended delay.. | ||
Nov 16 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242216392 | In Vitro Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Ivermectin Interaction |
| In Vitro analysis showing a definitive interaction between ivermectin and the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2, suggesting therapeutic potential for COVID-19. Using equilibrium dialysis and UV–Vis techniques, the study determined the affin.. | ||
Nov 7 2023 |
et al., Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, doi:10.1017/cts.2023.668 | Strategies used for the COVID-OUT decentralized trial of outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2 |
| Report on the operation of the COVID-OUT trial noting several issues affecting the reliability of the results: - Use of home pulse oximeters for measuring oxygen saturation: authors note that the FDA warned about inaccuracies with home pu.. | ||
Nov 6 2023 |
, E., Do Your Own Research | TOGETHER Files 2: Lawsuit reveals FTX bought effective control of TOGETHER trial, part of SBF's dream of a pharma empire |
| Analysis of legal documents showing that a non-profit controlled by FTX's SBF and a former colleague invested >$50 million in the Together Trial and had the right to potentially control the company. Author notes that incorrect and mislead.. | ||
Oct 31 2023 |
et al., Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, doi:10.1017/cts.2023.644 | ACTIV-6: Operationalizing a decentralized, outpatient randomized platform trial to evaluate efficacy of repurposed medicines for COVID-19 |
| Discussion of the operation of ACTIV-6 [Naggie] revealing participant fraud - authors identified participants that signed up repeatedly, and participants that withdrew when not randomized to their preferred arm. Authors indicate that they.. | ||
Oct 27 2023 |
et al., Do Your Own Research | The TOGETHER Files 1: The Andrew Hill connection - How the principal investigator leaked interim results to a private ivermectin research group |
| Leaked documents show additional misconduct in the Together Trial [Reis]. Blinding was broken, with interim results available not only within the team, but shared externally with a group of 90+ people, many from other ivermectin trials, i.. | ||
Oct 22 2023 |
et al., ACG 2023 | Treatment with Ivermectin Increases the Population of Bifidobacterium in the Gut |
| Analysis of the effect of ivermectin on the gut microbiome, showing a significant increase in Bifidobacterium. Bifidobacterium plays a key role in the immune system, for example enhancing antibody production, facilitating the induction of.. | ||
Sep 13 2023 |
et al., Stem Cell Research & Therapy, doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03485-3 | SARS-CoV-2 viral genes Nsp6, Nsp8, and M compromise cellular ATP levels to impair survival and function of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes |
| In Vitro study showing that ivermectin and meclizine mitigated cardiac cell death and dysfunction caused by SARS-CoV-2 viral genes. Authors found that SARS-CoV-2 viral genes Nsp6, Nsp8, and M had harmful effects on human cardiomyocytes (h.. | ||
Sep 4 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1197752 | Identification of the shared gene signatures between pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension using bioinformatics analysis |
| In Silico study identifying IGF1 as a shared gene between pulmonary fibrosis and hypertension that promotes inflammation, fibrosis, and cell proliferation when overactivated. Molecular docking analysis demonstrated ivermectin directly bin.. | ||
Aug 15 2023 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.08.10.23293924 | Published benefits of ivermectin use in Itajaí, Brazil for COVID-19 infection, hospitalisation, and mortality are entirely explained by statistical artefacts |
| Highly flawed analysis with multiple basic errors, invalid assumptions, highly biased discussion, failure to correct any of the issues for over two months, major changes without explanation, and repeating known major errors. There are maj.. | ||
Aug 8 2023 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.43168 | COVID-19 Excess Deaths in Peru’s 25 States in 2020: Nationwide Trends, Confounding Factors, and Correlations With the Extent of Ivermectin Treatment by State |
| Ecological analysis showing that ivermectin distribution correlated significantly (p<0.002) with the reduction in excess deaths across 25 states in Peru. Ivermectin was authorized for COVID-19 treatment in Peru in May 2020 and distributed.. | ||
Jul 16 2023 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.07.13.23292643 | Clinical manifestations and mortality among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Tanzania, 2021-2022. |
| 32% lower mortality (p=0.02). Retrospective 1,387 hospitalized PCR confirmed COVID-19 patients in Tanzania, showing lower mortality with ivermectin treatment and with steroid treatment in multivariable analysis. | ||
Jul 14 2023 |
et al., Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms241411449 | Computational Prediction of the Interaction of Ivermectin with Fibrinogen |
| In Silico study showing that ivermectin may bind with high affinity to multiple sites on fibrinogen and may interfere with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein – fibrinogen binding, potentially inhibiting the formation of fibrin clots resistant to de.. | ||
Jul 8 2023 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y | Patch-clamp studies and cell viability assays suggest a distinct site for viroporin inhibitors on the E protein of SARS-CoV-2 |
| In Vitro analysis of inhibitors against the SARS-CoV-2 E ion channel. - The E protein of SARS-CoV-2 is a viroporin that forms ion channels important for viral replication. The E proteins from SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 are highly similar. - .. | ||
Jul 1 2023 |
et al., Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B, doi:10.1631/jzus.B2200385 | Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis |
| Animal study showing that ivermectin alleviated pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis induced by bleomycin in a rat model. Authors note this may add to the clinical usefulness of ivermectin for patients with pulmonary fibrosis from COVID-19.. | ||
Jun 24 2023 |
Prophylaxis of COVID-19 Disease With Ivermectin in COVID-19 Contact Persons | |
| Estimated 412 participant ivermectin prophylaxis RCT with results not reported over 3 years after estimated completion. Results were submitted to the NIH on January 24, 2023 and have not been released later. NIH is normally required to p.. | ||
Jun 12 2023 |
et al., Journal of Korean Medical Science, doi:10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e195 | Two Years of Experience and Methodology of Korean COVID-19 Living Clinical Practice Guideline Development |
| Review of the development of COVID-19 treatment guidelines in Korea. Authors claim "continuous evidence updates" and "living recommendations", however the ivermectin recommendation has not been updated si.. | ||
Jun 10 2023 |
et al., Value in Health, doi:10.1016/j.jval.2023.03.2056 | Variation in Demographic Characteristics, Socioeconomic Status, Clinical Presentation and Selected Treatments in Mortality Among Patients with a Diagnosis of COVID-19 in the United States |
| Retrospective analysis of mortality for COVID-19 patients in the USA. Authors do not provide adjusted results, preventing any strong evidence. However it is notable that, despite comparable treatment frequencies, the mortality for patient.. | ||
Jun 8 2023 |
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068923 | Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of medical products in Zimbabwe: a qualitative study based on key informant interviews with health system stakeholders |
| Review of the quality of medical products in Zimbabwe during the pandemic, noting reports of inauthentic ivermectin in South Africa that was tested and found to have low or no active ingredient. | ||
May 29 2023 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16060799 | Phase II, Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Investigating the Efficacy of Mebendazole in the Management of Symptomatic COVID-19 Patients |
| RCT 69 outpatients in Jordan, showing improved viral clearance and CRP with mebendazole. Authors note that mebendazole, like ivermectin, has been shown to have antiviral activity against multiple viruses. | ||
May 27 2023 |
, K., This Scattrd Corn | Schedule A: Statement |
| Dr. Kyle Sheldrick, part of a group of researchers known for false and highly influential claims about ivermectin research, posted a schedule A statement admitting to false claims regarding one of the world's most highly published and res.. | ||
May 24 2023 |
et al., BMJ Global Health, doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2022-010962 | Quality of clinical evidence and political justifications of ivermectin mass distribution of COVID-19 kits in eight Latin American countries |
| Authors' claim the first RCT was in August 2020 and did not show a benefit, however the first two RCTs were actually: [Chowdhury] in July 2020, showing 46% improved recovery with statistical significance. [Shouman], showing over 90% lower.. | ||
May 23 2023 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm12113625 | When Characteristics of Clinical Trials Require Per-Protocol as Well as Intention-to-Treat Outcomes to Draw Reliable Conclusions: Three Examples |
| Analysis of PP vs. ITT results in three RCTs, including discussion of multiple critical issues with the ivermectin arm of the TOGETHER trial [Reis]: - conflicting and inconsistent decreases in PP vs. ITT groups between different tables an.. | ||
May 22 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1139046 | Efficacy and safety of single-dose ivermectin in mild-to-moderate COVID-19: the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled CORVETTE-01 trial |
| 19% lower progression (p=0.46), 14% higher need for oxygen therapy (p=0.46), 23% worse improvement (p=0.61), and 60% improved recovery (p=0.17). Late treatment (6.6 days after onset/PCR+) RCT with 221 low risk (no deaths) COVID-19 patients in Japan, showing no significant difference in viral clearance with a single dose of ivermectin under fasting. Authors note that a single 200 μ.. | ||
May 10 2023 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15051138 | Ivermectin Effect on In-Hospital Mortality and Need for Respiratory Support in COVID-19 Pneumonia: Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Study |
| 17% lower mortality (p=0.82), 18% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.37), 23% lower progression (p=0.52), and 4% higher ICU admission (p=0.92). Retrospective 96 late stage patients receiving a single dose of 200 μg/kg ivermectin for strongyloides and 96 matched controls, showing no significant difference in outcomes. Authors note that this may be due to the low dose used. | ||
May 3 2023 |
, P., International Covid Summit III, European Parliament, Brussels | The Global War on Ivermectin |
| Review of the clinical evidence for ivermectin for COVID-19 and the methods used in many countries to hide the efficacy, covering: extreme financial conflicts of interest, coordinated censorship, refusal of Merck to run a trial requested .. | ||
Apr 25 2023 |
et al., Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778 | The Place of Ivermectin in the Management of Covid-19: State of the Evidence |
| Review of the clinical and epidemiological evidence of efficacy, in vitro and animal studies, and the mechanisms of action of ivermectin for COVID-19. | ||
Apr 25 2023 |
et al., Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03520-1 | Recent Advances in Inhaled Nanoformulations of Vaccines and Therapeutics Targeting Respiratory Viral Infections |
| Review of nanoformulations for inhaled therapeutics for respiratory viral infections including COVID-19. Inhaled formulations can deliver treatment directly to the respiratory tract, enabling higher concentrations while minimising systemi.. | ||
Apr 21 2023 |
et al., Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare11081192 | Clinical Disease Characteristics and Treatment Trajectories Associated with Mortality among COVID-19 Patients in Punjab, Pakistan |
| 48% lower mortality (p=0.13). Retrospective 1,000 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Pakistan, showing lower mortality with ivermectin without statistical significance. | ||
Mar 7 2023 |
et al., GeroScience, doi:10.1007/s11357-023-00756-y | Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis of early studies on ivermectin in SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| Systematic review and meta analysis of trials within the first year of the pandemic, showing significantly faster viral clearance with ivermectin. | ||
Feb 20 2023 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.1650 | Effect of Higher-Dose Ivermectin for 6 Days vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 600µg/kg arm of ACTIV-6. Results of this trial are unreliable, with multiple critical anomalies, and no response from the authors. For details see [c19early]. | ||
Feb 15 2023 |
et al., Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114391 | Ivermectin systemic availability in adult volunteers treated with different oral pharmaceutical formulations |
| Comparison of ivermectin as an oral solution, tablets, or capsules, showing >50% higher systemic exposure for the oral solution compared to tablets or capsules. Authors note that the oral solution improved absorption without risk of exces.. | ||
Jan 16 2023 |
et al., The Gazette of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46766/thegms.pubheal.22120905 | Intravenous high dose vitamin C and ozonated saline effective treatment for Covid-19: The Evolution of Local Standard of Care |
| Retrospective 479 high risk outpatients in the USA treated with a protocol including intravenous vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, quercetin, bromelain, lactoferrin, HCQ, ivermectin, ozonated saline, azithromycin, ceftriaxone, methylprednisolon.. | ||
Jan 5 2023 |
et al., ECCMID 2023 (results released 1/5/2023) | The SAIVE Trial, Post-Exposure use of ivermectin in Covid-19 prevention: Efficacy and Safety Results |
| 96% fewer cases (p<0.0001). PEP RCT 399 patients in Bulgaria showing significantly lower COVID-19 cases with ivermectin prophylaxis, and significantly lower cases with high viral load. No participant had severe symptoms, required oxygen, or was hospitalized. All pat.. | ||
Dec 12 2022 |
et al., Infection & Chemotherapy, doi:10.3947/ic.2022.0127 | An Open Label Randomized Controlled Trial of Ivermectin Plus Favipiravir-Based Standard of Care versus Favipiravir-Based Standard of Care for Treatment of Moderate COVID-19 in Thailand |
| 104% higher ICU admission (p=0.62), 104% worse improvement (p=0.62), and 4% faster recovery (p=0.63). RCT low risk hospitalized patients in Thailand showing no significant difference with the addition of ivermectin to favipiravir based SOC. Only the abstract is currently available. The trial was registered retrospectively [thaiclinicaltri.. | ||
Dec 10 2022 |
et al., Advances in Virology, doi:10.1155/2022/3014686 | The Use of Mebendazole in COVID-19 Patients: An Observational Retrospective Single Center Study |
| Retrospective 157 inpatients and 185 outpatients, showing improved recovery with mebendazole. For outpatients, the treatment group was younger (40 vs. 48). Mebendazole was offered to patients when ivermectin/HCQ were unavailable. | ||
Nov 28 2022 |
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.24.517882 | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Hemagglutination: Implications for COVID-19 Morbidities and Therapeutics and for Vaccine Adverse Effects |
| In Vitro study showing that ivermectin blocked hemagglutination (clumping of red blood cells) when added to red blood cells prior to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and reversed hemagglutination when added afterwards. Spike protein from four li.. | ||
Nov 10 2022 |
et al., PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0276751 | Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients |
| Vero E6 In Vitro study showing ivermectin and remdesivir to be highly synergistic with 6-13 times lower concentration required for 100% inhibition. | ||
Oct 21 2022 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.18590 | Effect of Ivermectin vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
| The ACTIV-6 trial can be found under the original release date [Naggie]. | ||
Oct 21 2022 |
et al., Revista Infectio, doi:10.22354/24223794.1105 | Clinical efficacy and safety of ivermectin (400 μg/kg, single dose) in patients with severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial |
| 57% lower mortality (p=0.35), 34% higher ventilation (p=0.62), and 37% higher ICU admission (p=0.52). RCT 75 very late stage patients in Colombia, showing no significant difference in outcomes with a single dose of 400μg/kg ivermectin. | ||
Oct 17 2022 |
, D., Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2 | From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells |
| Review of how SARS-CoV-2 evolved to agglutinate and clot blood cells without hemagglutinin esterase (HE). Author proposes a "catch and clump" mechanism where SARS-CoV-2 binds and clumps red blood cells (RBCs) and other cells via.. | ||
Sep 27 2022 |
, A., Do Your Own Research | Did Use Of Ivermectin In Latin America Sabotage Clinical Trials and Confuse The World Of Medicine? |
| Meta analysis of ivermectin trials showing community use of ivermectin in Latin America associated with lower observed efficacy in trials, consistent with the side effect profiles, Google Trends analysis, and investigator statements. Auth.. | ||
Sep 26 2022 |
et al., Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2023.12.012 (date from news release) | Efficacy and safety of ivermectin in patients with mild COVID-19 in Japan and Thailand |
| 205% higher progression (p=0.49), 4% worse improvement (p=0.62), and 4% improved recovery (p=0.72). RCT very low risk patients (mean age 35.7, SpO2 97.4) showing no significant differences with rapid recovery and almost no progression in both groups. The groups were unbalanced. There were 41% more patients with dyspnea at baseline in th.. | ||
Sep 22 2022 |
et al., Medicina Clínica Práctica, doi:10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346 | Clinical protocol for early treatment of COVID-19 in a real-world scenario: Results of a series of patients |
| Retrospective 116 patients between May and September 2020 in Brazil receiving an early treatment protocol including ivermectin and azithromycin, showing no mortality compared to up to 5.7% CFR in Brazil during the study period. | ||
Sep 19 2022 |
et al., Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S381715 | Possible Role of Ivermectin Mucoadhesive Nanosuspension Nasal Spray in Recovery of Post-COVID-19 Anosmia |
| 74% faster recovery (p=0.0005). 96 patient RCT showing faster resolution of post-COVID anosmia with an ivermectin nanosuspension nasal spray. | ||
Sep 16 2022 |
, P., Pierre Kory’s Medical Musings | The Criminal Censorship of Ivermectin's Efficacy By The High-Impact Medical Journals - Part 1 |
| Review of censorship and negative publication bias for ivermectin research. | ||
Sep 15 2022 |
et al., The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-023-00623-0 (date from preprint) | Prophylactic administration of ivermectin attenuates SARS-CoV-2 induced disease in a Syrian Hamster Model |
| Hamster study showing that prophylactic ivermectin inhibited COVID-19 weight loss, reduced lung viral titer by a factor of 10, inhibited pulmonary inflammatory cytokine expression, and reduced the severity of pathological changes with a s.. | ||
Sep 1 2022 |
et al., The Professional Medical Journal, doi:10.29309/TPMJ/2022.29.09.6634 | Does ivermectin reduce COVID-19 mortality and progression of disease severity? – A retrospective study |
| 90% lower mortality (p<0.0001), 72% lower ICU admission (p=0.0006), 80% higher hospital discharge (p<0.0001), and 59% faster viral clearance (p<0.0001). Retrospective 423 patients in Pakistan, 216 receiving 6 day treatment, showing lower mortality, lower ICU admission, and faster viral clearance with treatment. Limited baseline information per group is provided. There were more severe pat.. | ||
Aug 31 2022 |
et al., Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, doi:10.53350/pjmhs2216824 | Ivermectin A Potential Treatment In Covid-19, Related to Critical Illness |
| 58% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). Prospective convenience sampling study of 210 hospitalized age-matched COVID-19 patients, showing faster viral clearance with ivermectin. Baseline information per group is not provided. | ||
Aug 18 2022 |
et al., COVID, doi:10.3390/covid2080084 | Statistical Analysis Methods Applied to Early Outpatient COVID-19 Treatment Case Series Data |
| Retrospective analysis of case series data from 3,164 high-risk COVID-19 outpatients treated with early multidrug protocols similar to the McCullough protocol, including hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, zinc, azithromycin, vitamin C, vitam.. | ||
Aug 18 2022 |
et al., NEJM, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662 | Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19 |
| COVID-OUT remote RCT, showing no significant differences compared to a combined metformin/placebo "control" group. Results for other treatments are listed separately - metformin , fluvoxamine . Authors include metformin patients in the co.. | ||
Aug 12 2022 |
, P., Pierre Kory’s Medical Musings | The Miracle Not-Heard Around The World: The Success of Uttar Pradesh |
| Detailed review of Uttar Pradesh's use of ivermectin, the dramatically better results compared to states declining ivermectin, and the censorship of ivermectin use. If Uttar Pradesh was a country, it would be the 6th largest in the world. | ||
Aug 10 2022 |
et al., Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277 | Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors |
| In Silico study of SARS-CoV-1&2 endodomains and ezrin docking, identifying ivermectin, quercetin, calcifediol, calcitriol, selamectin, and minocycline as potential therapeutic drugs with strong ezrin binding which may restrict viral endod.. | ||
Aug 10 2022 |
et al., Current Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1389450123666220810102406 | Central effects of Ivermectin in alleviation of Covid-19-induced dysautonomia |
| Review of the potential benefits of ivermectin for mitigating SARS-CoV-2 infection-induced dysautonomia. | ||
Jul 23 2022 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8 | Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype |
| Meta analysis including 25 of studies ( RCTs), with only 10 and 8 reporting mortality and mechanical ventilation results, finding lower mortality and mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. The conclusion is incorrect, d.. | ||
Jul 19 2022 |
et al., eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.83201 (date from preprint) | Pharmacometrics of high dose ivermectin in early COVID-19: an open label, randomized, controlled adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV) |
| 86% lower progression (p=0.24) and 9% worse viral clearance (p=0.36). Very high conflict of interest RCT with design optimized for a null result: very low risk patients, high existing immunity, post-hoc change to exclude patients more likely to benefit. There was no significant difference in viral clearance.. | ||
Jul 11 2022 |
, S., Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.952321 | Microbiome-Based Hypothesis on Ivermectin’s Mechanism in COVID-19: Ivermectin Feeds Bifidobacteria to Boost Immunity |
| Hypothesis for an additional mechanism of action for ivermectin: inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines due to enhanced replication of Bifidobacterium. This article was censored by the journal stating concerns "regarding the scient.. | ||
Jul 8 2022 |
et al., Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14071432 | Manipulation of Spray-Drying Conditions to Develop an Inhalable Ivermectin Dry Powder |
| Development and analysis of an inhalable dry powder formulation of ivermectin. Authors optimized the formulation to have good aerosolization properties for lung delivery. The powder maintained ivermectin's ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 re.. | ||
Jul 4 2022 |
et al., Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy, doi:10.1080/14787210.2022.2098113 | Ivermectin Role in COVID-19 Treatment (IRICT): single center, adaptive, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, clinical trial |
| This study was retracted due to data integrity and validity concerns [tandfonline.com]. Data in this study was anomalous, for example at day 14 ivermectin simultaneously showed 4x greater chance of recovery and 26x greater mortality. Figu.. | ||
Jun 30 2022 |
et al., Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344 | Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach |
| In Silico study of ivermectin, camostat, and nafamostat, showing that ivermectin had the best inhibitory action on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and Nsp10, while nafamostat had the best results for the other non-structural proteins. Author.. | ||
Jun 29 2022 |
et al., Journal of Global Infectious Diseases, doi:10.4103/jgid.jgid_281_21 | A randomized controlled trial of combined ivermectin and zinc sulfate versus combined hydroxychloroquine, darunavir/ritonavir, and zinc sulfate among adult patients with asymptomatic or mild coronavirus-19 infection |
| 33% improved viral clearance (p=0.12). RCT low-risk patients in Thailand comparing HCQ, darunavir/ritonavir, and zinc, with ivermectin and zinc, showing no significant differences. All patients recovered. 65% of patients were asymptomatic at baseline, 26% were PCR- at baseline.. | ||
Jun 23 2022 |
et al., Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.14318 | Efficacy of single-dose and double-dose ivermectin early treatment in preventing progression to hospitalization in mild COVID-19: A multi-arm, parallel-group randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial |
| 67% lower ventilation (p=0.37), 46% lower hospitalization (p=0.22), and 39% improved recovery (p=0.27). RCT with 131 24mg ivermectin, 130 12mg ivermectin, and 130 placebo patients, showing no significant differences in outcomes. Lower ventilation and hospitalization was seen with treatment, in a dose-dependent manner, but not reaching stati.. | ||
Jun 21 2022 |
et al., Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub3 | Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19 |
| Highly biased meta analysis. Authors originally wrote a highly biased meta analysis that avoided statistical significance on individual outcomes with extreme exclusions [ Popp ] , although efficacy was still seen when looking across all o.. | ||
Jun 18 2022 |
et al., BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1186/s40360-022-00580-8 (date from preprint) | Synergistic anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of repurposed anti-parasitic drug combinations |
| In Vitro study showing a strong synergistic effect of combinations of ivermectin, niclosamide, and chloroquine, with >10x reduction in IC50 compared to individual drugs. | ||
Jun 16 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.919708 | Non-effectiveness of Ivermectin on Inpatients and Outpatients With COVID-19; Results of Two Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials |
| 9% higher ICU admission (p=0.95), 36% higher hospitalization (p=0.41), 2% worse recovery (p=0.49), and 23% worse viral clearance (p=0.16). RCT 549 low risk outpatients in Iran. Reported outcomes are very different from the pre-specified outcomes [irct.ir]. The inpatient trial is listed separately. The pre-specified primary clinical outcome was not reported. The reported comp.. | ||
Jun 16 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.919708 | Non-effectiveness of Ivermectin on Inpatients and Outpatients With COVID-19; Results of Two Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials |
| 31% lower mortality (p=0.36), 50% lower ventilation (p=0.07), 16% lower ICU admission (p=0.47), and 11% longer hospitalization (p=0.009). RCT 609 inpatients in Iran. Reported outcomes are very different from the pre-specified outcomes [irct.ir]. The outpatient trial is listed separately. From the pre-specified outcomes, all are either positive or not reported. Pre-specified.. | ||
Jun 14 2022 |
, T., Do Your Own Research | Not All Ivermectin Is Created Equal: Comparing The Quality of 11 Different Ivermectin Sources |
| In Vitro analysis of ivermectin from 11 different sources showing highly variable antiparasitic efficacy. Multiple sources and brands were more effective than the US mass produced Edenbridge brand. | ||
Jun 13 2022 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8 | Ivermectin under scrutiny: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and possible sources of controversies in COVID-19 patients |
| Meta analysis including 17 of studies ( RCTs), finding significantly lower mortality with ivermectin. All seven outcomes favor ivermectin, while statistical significance is reached only for mortality. The conclusion is incorrect, authors.. | ||
Jun 12 2022 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.18590 | Effect of Ivermectin vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 257% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.11), 5% higher hospitalization (p=1), 68% lower progression (p=0.36), and 2% faster recovery (p=0.71). RCT low-risk outpatients with very late treatment (median 6 days, 25% ≥8 days) in the USA, showing 98% probability of efficacy for clinical progression at day 14, a treatment delay-response relationship, and significant efficacy for patie.. | ||
Jun 12 2022 |
et al., Antibiotics, doi:10.3390/antibiotics11060796 | Safety and Efficacy of Ivermectin for the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: A Double-Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study |
| Low-risk RCT in Thailand with zero mortality, reporting no significant differences with the addition of ivermectin to favipiravir treatment, however the study as reported does not make sense as detailed below. All participants were suspec.. | ||
May 27 2022 |
et al., Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, doi:10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w | Single Dose of Ivermectin is not Useful in Patients with Hematological Disorders and COVID-19 Illness: A Phase II B Open Labelled Randomized Controlled Trial |
| 30% lower mortality (p=0.55), 19% faster recovery (p=0.37), 33% lower progression (p=0.41), and 33% worse viral clearance (p=0.5). RCT with 35 single dose 24mg, 38 single dose 12mg, and 39 SOC hospitalized patients with hematological illnesses in India, showing no significant differences. Results were better for 24mg vs. 12mg for all symptomatic outcomes. Viral clear.. | ||
May 27 2022 |
, E., New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2022.100989 | Does ivermectin have a place in the treatment of mild Covid-19? |
| Discussion of ivermectin research compared to paxlovid and molnupiravir. Author includes a meta analysis of low-risk-of-bias studies showing significantly lower hospitalization for outpatient treatment with ivermectin. This efficacy is se.. | ||
May 23 2022 |
et al., Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.258325 | Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols |
| Review of ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19, focusing on 2022 protocols. Authors discuss the long history of safe ivermectin use in humans for parasitic infections, noting its promising in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, .. | ||
May 23 2022 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07890-6 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin compared with placebo in the clinical course in Mexican patients with asymptomatic and mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial |
| 15% worse recovery (p=0.58) and 2% improved viral clearance (p=0.64). Small low-risk patient RCT with 30 low-dose ivermectin and 26 control patients, with no primary outcome events in either arm. Viral load was significantly better with ivermectin on day 5, while there was no significant difference on day 1.. | ||
May 20 2022 |
et al., Epidemiology International Journal, doi:10.23880/eij-16000234 | Repurposing Drugs for Covid-19 by a Developing Country |
| Review of a multiphasic multidrug early treatment protocol for COVID-19 in Honduras, showing one death from 415 patients, which was for a patient not receiving early treatment (presenting on the 5th day in need of hospitalization and supp.. | ||
May 20 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.899702 | Clinical-Epidemiology Aspect of Inpatients With Moderate or Severe COVID-19 in a Brazilian Macroregion: Disease and Countermeasures |
| 32% lower mortality (p=0.57). Retrospective 395 hospitalized patients in Brazil, showing mortality HR 0.59 for antiparasitic use, however there were only 8 patients treated and authors do not distinguish between albendazole and ivermectin. | ||
May 14 2022 |
et al., Computational Biology and Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107692 | Interaction of the New Inhibitor Paxlovid (PF-07321332) and Ivermectin With the Monomer of the Main Protease SARS-CoV-2: A Volumetric Study Based on Molecular Dynamics, Elastic Networks, Classical Thermodynamics and SPT |
| In Silico study comparing ivermectin and paxlovid Mpro interaction, showing similar interaction for paxlovid and the ivermectin B1a homologue, a different mechanism for ivermectin B1b, and interaction at different sites for paxlovid. | ||
May 8 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Biomaterials, doi:10.1155/2016/8043983 | Liposomal Systems as Nanocarriers for the Antiviral Agent Ivermectin |
| In Vitro study of liposomal formulations of ivermectin showing up to 5 times lower cytotoxicity and increased antiviral activity in Dengue strains. | ||
Apr 27 2022 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1576399/v1 | Ivermectin is associated with increase in SPO2 in hypoxemic SARS-CoV-2 patients: pharmacodynamic profile and correlates |
| Extended analysis of [Thairu], showing significantly faster and greater improvement in SpO2 with ivermectin treatment. | ||
Apr 13 2022 |
, A. | The Problem With The TOGETHER Trial |
| Analysis of serious problems with the Together Trial. Also see [Marinos]. | ||
Apr 11 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121719 | Red blood cell-hitchhiking mediated pulmonary delivery of ivermectin: Effects of nanoparticle properties |
| In Vitro and mouse study proposing a method for improving ivermectin pharmacokinetics and bioavailability using delivery via red blood cells. | ||
Apr 6 2022 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1522422/v1 | Association between Ivermectin treatment and mortality in Covid-19: A hospital-based case-control study |
| 3% lower mortality (p=0.82). Retrospective 965 late stage (44% severe, 27% ICU) hospitalized patients in India, showing no significant difference with ivermectin treatment. Overall mortality was very high, suggesting very late treatment. The low non-weight-adjusted d.. | ||
Apr 2 2022 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445 | Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants |
| In Vitro study with 30 COVID-19 strains from 14 variants, showing stronger efficacy with ivermectin compared to CQ and remdesivir, and relatively homogeneous efficacy with ivermectin regardless of strain/variant, in contrast to results fo.. | ||
Mar 25 2022 |
et al., Computation, doi:10.3390/computation10040051 | In Silico Analysis of the Multi-Targeted Mode of Action of Ivermectin and Related Compounds |
| In Silico analysis identifying strong or moderate affinity bindings for ivermectin to multiple sites on the spike protein, CD147 and α7nAChr, which may provide effective competitive binding for all variants of SARS-CoV-2. Ivermectin had t.. | ||
Mar 21 2022 |
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.3079 | Comparison of Trials Using Ivermectin for COVID-19 Between Regions With High and Low Prevalence of Strongyloidiasis |
| Analysis of a small subset of 12 ivermectin trials showing a relationship with efficacy and strongyloides prevalence. This analysis is confounded by treatment delay, dose, conflicts of interest, and other factors, and the effect disappear.. | ||
Mar 18 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121688 | Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Inhaled Ivermectin in Mice as a Potential COVID-19 Treatment |
| Mouse study of an inhaled ivermectin formulation, showing high concentrations in the lung and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, exceeding the required concentration for efficacy based on in vitro studies. | ||
Mar 15 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Health Sciences, doi:10.53730/ijhs.v6nS1.4792 | Effect of Ivermectin mass drug administration on the COVID-19 Pandemic |
| Analysis of mass administration of ivermectin for COVID-19 in Uttarakhand compared to four other states not adopting ivermectin, showing a sharp fall in cases compared to the other states at the time of maximum coverage of ivermectin dist.. | ||
Mar 11 2022 |
et al., Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery, doi:10.1089/jamp.2021.0059 | Preparation and Characterization of Inhalable Ivermectin Powders as a Potential COVID-19 Therapy |
| Creation and analysis of an inhalable dry powder formulation of ivermectin for COVID-19. | ||
Mar 7 2022 |
, P. | Professor tied to altered Andrew Hill paper also prepared 'Ivermectin Evidence' for World Health Organisation |
| Forensic analysis of the Hill meta analysis discovering an unlisted author potentially connected to changes and also related to the WHO ivermectin analysis. Author notes that "the person who allegedly edited the Andrew Hill paper .. | ||
Mar 4 2022 |
, T. | A Letter to Dr. Andrew Hill |
| Documentary about the external forces changing the conclusions of the Hill et al. meta analysis, and the subsequent negative impact around the world. | ||
Mar 3 2022 |
, News Release, March 2022 | TGA cautions consumers over counterfeit ivermectin |
| News release from the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration warning about counterfeit ivermectin tablets. | ||
Mar 2 2022 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0264789 | Mortality and associated risk factors in patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 in a Peruvian reference hospital |
| 41% higher mortality (p=0.001). Retrospective 1,418 very late stage (46% mortality) patients in Peru, showing higher mortality with ivermectin. There is strong confounding by indication, for example 48% of patients with baseline SpO2 <70% were treated compared with 22% .. | ||
Feb 28 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.096 | Treatment with Ivermectin Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: Analysis of a National Federated Database |
| 69% lower mortality (p<0.0001). PSM retrospective 41,608 patients in the USA, 1,072 treated with ivermectin and 40,536 treated with remdesivir, showing lower mortality with ivermectin treatment. This study was presented at a conference (IMED 2021). Submissions were peer.. | ||
Feb 25 2022 |
et al., Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, doi:10.9734/jpri/2022/v34i44A36328 (date from preprint) | A Comparison of Ivermectin and Non Ivermectin Based Regimen for COVID-19 in Abuja: Effects on Virus Clearance, Days-to-discharge and Mortality |
| 88% lower mortality (p=0.12), 55% higher hospital discharge (p=0.0001), and 95% improved viral clearance (p=0.001). PSM retrospective 87 patients in Nigeria, 61 treated with ivermectin, showing lower mortality, faster recovery, and faster viral clearance with ivermectin treatment. All patients received zinc and vitamin C. A synergistic effect was seen .. | ||
Feb 18 2022 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189 (data 11/3/21) | Efficacy of Ivermectin Treatment on Disease Progression Among Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities: The I-TECH Randomized Clinical Trial |
| The I-TECH RCT can be found at [c19ivm.org]. Studies are listed under the date they first became available (November 3, 2021 for this study). | ||
Feb 6 2022 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.28624 (date from preprint) | Regular Use of Ivermectin as Prophylaxis for COVID-19 Led Up to a 92% Reduction in COVID-19 Mortality Rate in a Dose-Response Manner: Results of a Prospective Observational Study of a Strictly Controlled Population of 88,012 Subjects |
| 92% lower mortality (p=0.0008). PSM multivariable analysis of the Itajaí trial showing significantly lower mortality with regular use of ivermectin prophylaxis. Immortal time bias may significantly affect these results. See [Mills] regarding [medrxiv.org]. | ||
Feb 2 2022 |
et al., Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06649-3 (date from preprint) | Efficacy and safety of ivermectin in the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 infection: A randomized, double blind, placebo, controlled trial |
| 43% improved recovery (p=0.26) and 5% improved viral clearance (p=1). Small RCT with 72 low-risk patients in Thailand, showing improved recovery with ivermectin, without statistical significance. All patients recovered and there was no escalation of care in either group. There were no adverse events. | ||
Jan 31 2022 |
, Press Release | Antiviral effect of ivermectin confirmed for omicron |
| Kowa reports that ivermectin is effective for omicron in In Vitro research. | ||
Jan 25 2022 |
et al., Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, doi:10.4103/1995-7645.364007 | Efficacy and safety of ivermectin in patients with mild and moderate COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial |
| Small trial with 50% of patients missing without explanation. The protocol and registration show both outpatient and inpatient inclusion, with 60 patients in each group, a total of 120 patients, and enrollment completed as of July 11, 202.. | ||
Jan 24 2022 |
et al., Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.01.002 | A Multimodal Strategy to Reduce the Risk of Hospitalization/death in Ambulatory Patients with COVID-19 |
| 59% lower combined mortality/hospitalization (p<0.0001), 15% lower mortality (p=0.16), 9% lower ventilation (p=0.51), and 48% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001). Retrospective 28,048 COVID+ patients in Mexico, 7,898 receiving a treatment kit including low dose ivermectin, AZ, aspirin, and acetaminophen, shower lower mortality/hospitalization for those receiving the kit. Delivery of the treatment k.. | ||
Jan 23 2022 |
et al., Stem Cell Reports, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.01.014 (date from preprint) | Genome-wide analyses reveal the detrimental impacts of SARS-CoV-2 viral gene Orf9c on human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes |
| In Vitro study showing that ivermectin and meclizine treatment may minimize SARS-CoV-2-induced cardiac damage by reducing Orf9c-induced apoptosis and dysfunction. Using human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, authors show that.. | ||
Jan 20 2022 |
et al., Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.639 (date from preprint) | Insights from a computational analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Host–pathogen interaction, pathogenicity, and possible drug therapeutics |
| In Silico analysis of the omicron variant and 10 treatments reported effective for previous variants, predicting that all will be effective for omicron, with ivermectin showing the best results. | ||
Jan 18 2022 |
et al., Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease, doi:10.4081/monaldi.2022.2062 | The effect of ivermectin on non-severe and severe COVID-19 disease and gender-based difference of its effectiveness |
| 9% higher mortality (p=1) and 8% longer hospitalization (p=0.4). Retrospective 188 hospitalized patients in Pakistan, 90 treated with ivermectin, showing no significant differences with treatment. The ivermectin group had more severe disease (66% vs 58%, with 6x higher risk for severe disease patients).. | ||
Jan 13 2022 |
et al., Rounding the Earth, Preprint | Low Rates of Hospitalization and Death in 4,376 COVID-19 Patients Given Early Ambulatory Medical and Supportive Care. A Case Series and Observational Study. |
| 100% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 100% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001). Retrospective 4,376 patients with mild/moderate COVID-19 in the USA treated with multiple medications including HCQ/ivermectin, favipiravir, vitamin C, D, quercetin, zinc, mAbs, budesonide, dexamethasone, prednisone, and colchicine (exact.. | ||
Dec 31 2021 |
et al., Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.36468/pharmaceutical-sciences.spl.416 | The Effect of Ivermectin on Reducing Viral Symptoms in Patients with Mild COVID-19 |
| 41% lower progression (p=0.54) and 36% improved recovery (p=0.04). RCT 99 ivermectin and 103 control low risk patients in China, up to 7 days from symptom onset, showing statistically significant improvement in recovery with treatment, and non-statistically significant improvements in recovery time and.. | ||
Dec 31 2021 |
et al., ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.26793.52327 | COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality Rate is Reduced by Prophylactic Use of Ivermectin: Findings From a City-Wide, Prospective Observational Study Using Propensity Score Matching (PSM) |
| 45% lower mortality (p=0.05). PSM retrospective 378 hospitalized patients in Brazil, showing lower mortality for patients that were on ivermectin prophylaxis before admission (not taking into account the lower risk of being hospitalized shown in the related larger stu.. | ||
Dec 31 2021 |
et al., Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2021.12.024 | Ivermectin administration is associated with lower gastrointestinal complications and greater ventilator-free days in ventilated patients with COVID-19: A propensity score analysis |
| 100% lower mortality (p=0.001), 48% lower ventilation (p=0.03), 43% lower ICU admission (p=0.06), and 78% lower progression (p=0.03). Retrospective 88 ventilated COVID-19 patients in Japan, 39 treated with ivermectin within 3 days of admission, showing significantly reduced incidence of GI complications and mortality, and increased ventilator-free days with treatment. | ||
Dec 30 2021 |
, S., Biomolecular Concepts, doi:10.1515/bmc-2021-0017 | SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19 |
| Review of the potential connections between SLC6A20/SIT1, ACE2, Type 2 Diabetes, and COVID-19 severity. This provides another potential mechanism of action for ivermectin as a partial agonist of glycine-gated chloride channels, interferin.. | ||
Dec 29 2021 |
et al., Exploratory Research in Clinical and Social Pharmacy, doi:10.1016/j.rcsop.2021.100101 | Pattern of medication utilization in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in three District Headquarters Hospitals in the Punjab province of Pakistan |
| 64% lower mortality (p=0.09). Retrospective 444 hospitalized patients in Pakistan, showing lower mortality with ivermectin treatment in unadjusted results, not reaching statistical significance. Ivermectin was mostly used with patients in severe condition. Dose ranged.. | ||
Dec 28 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1193578/v1 | Characteristics of the COVID-19 patients treated at Gulu Regional Referral Hospital, Northern Uganda: A cross-sectional study |
| 97% lower mortality (p=0.31). Retrospective COVID+ hospitalized patients in Uganda, showing no statistically significant difference in mortality with ivermectin, however there were only 7 patients receiving ivermectin. | ||
Dec 21 2021 |
et al., The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6 | The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review |
| Extensive review of 20 mechanisms of action of ivermectin for SARS-CoV-2. | ||
Dec 14 2021 |
, News Release, December 2021 | TGA warns about imports of ivermectin |
| News release from the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration warning about counterfeit ivermectin tablets. | ||
Dec 13 2021 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.20394 | Determinants of Outcome Among Critically Ill Police Personnel With COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Study From Andhra Pradesh, India |
| 53% higher mortality (p=0.13). Retrospective 266 COVID-19 ICU patients in India, showing significantly lower mortality with PVP-I oral gargling and topical nasal use, and non-statistically significant higher mortality with ivermectin and lower mortality with remdesivir. | ||
Dec 11 2021 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.21272 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin Prophylaxis Used for COVID-19: A Citywide, Prospective, Observational Study of 223,128 Subjects Using Propensity Score Matching |
| 70% lower mortality (p<0.0001), 67% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001), and 44% fewer cases (p<0.0001). PSM retrospective 220,517 patients in Brazil,133,051 taking ivermectin as part of a citywide prophylaxis program, showing significantly lower hospitalization and mortality with treatment. Additional results are presented here: [odysee.com.. | ||
Dec 4 2021 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab466.728 | Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Ivermectin Safety Profile in COVID-19 Trials |
| Systematic review and meta-analysis of safety in ivermectin COVID-19 trials, showing no significant difference in adverse events between treatment and control arms. Authors conclude that ivermectin is safe and well-tolerated. | ||
Dec 1 2021 |
et al., Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072 | CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target |
| Review of the cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147) transmembrane protein as an entry route for SARS-CoV-2, correlation with observed characteristics of COVID-19, and relevant potential therapeutics including azithromycin, melatonin, sta.. | ||
Nov 26 2021 |
et al., Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira, doi:10.1590/1806-9282.20210661 | Outcomes associated with Hydroxychloroquine and Ivermectin in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a single-center experience |
| 54% higher combined mortality/intubation (p=0.37). Retrospective 230 hospitalized patients in Brazil showing no significant difference with ivermectin treatment. Authors note that the treatments were more likely to be offered to sicker patients. Authors note that they do not know if treat.. | ||
Nov 23 2021 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27469 | Effectiveness and Safety of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Study at A Safety-Net Hospital |
| 75% lower mortality (p=0.09), 13% lower ventilation (p=0.2), and 9% longer hospitalization (p=0.09). Small prospective PSM study in the USA, showing 75% lower mortality with ivermectin treatment, without reaching statistical significance, significantly shorter ventilation and ICU time, and longer hospitalization time. Authors leave the s.. | ||
Nov 17 2021 |
et al., Journal of the Association of Physicians India, 69:11 | Ivermectin and Hydroxychloroquine for Chemo-Prophylaxis of COVID-19: A Questionnaire Survey of Perception and Prescribing Practice of Physicians vis-a-vis Outcomes |
| 80% fewer cases (p<0.0001). Physician survey in India with 164 ivermectin prophylaxis, 129 HCQ prophylaxis, and 81 control patients, showing significantly lower COVID-19 cases with treatment. Details of the treatment and control groups and the definition of cases ar.. | ||
Nov 9 2021 |
et al., Biologics, doi:10.3390/biologics2030015 (date from preprint) | Changes in SpO2 on Room Air for 34 Severe COVID-19 Patients after Ivermectin-Based Combination Treatment: 62% Normalization within 24 Hours |
| Retrospective severe COVID-19 patients in Zimbabwe treated with ivermectin, doxycycline, and zinc. For 34 with SpO2 tracking, there was rapid improvement in SpO2, with 55% recovery towards SpO2 97 within 12 hours. The preprint shows furth.. | ||
Nov 3 2021 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189 (data 11/3/21) | Efficacy of Ivermectin Treatment on Disease Progression Among Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities: The I-TECH Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 69% lower mortality (p=0.09), 59% lower ventilation (p=0.17), 22% lower ICU admission (p=0.79), and 31% lower progression (p=0.29). RCT 490 late stage (>65% lung change chest radiography at baseline) hospitalized patients in Malaysia, showing no significant differences. Mortality was 1.2% for ivermectin vs. 4% for control. If the same event rates continue, the trial w.. | ||
Oct 30 2021 |
et al., Zagazig University Medical Journal, doi:10.21608/zumj.2021.92746.2329 | miRNA-223-3p, miRNA- 2909 and Cytokines Expression in COVID-19 Patients Treated with Ivermectin |
| 56% lower progression (p=0.06), 33% improved recovery (p=0.27), and 27% faster viral clearance (p=0.01). Prospective 320 hospitalized moderate COVID-19+ patients in Egypt, 160 treated with ivermectin, showing lower mortality, improved recovery, and decreased cytokine expression with treatment. All patients were treated with HCQ. 7890/26-8-20.. | ||
Oct 28 2021 |
et al., Indian Journal of Community Health, 33:3 | Assessing Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices towards Ivermectin Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 among Health Care Workers |
| Survey of 306 healthcare workers involved in the medication of COVID-19 patients in India. 71% indicated that ivermectin had a protective effect for COVID-19. | ||
Oct 20 2021 |
et al., Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294 | Repositioning Ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication |
| Review of the antiviral characteristics of ivermectin and mechanisms of action. Authors note that ivermectin has proven effective for HIV-1, Adenovirus, flu, SARS-CoV, and more; due to genomic similarity between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, t.. | ||
Oct 19 2021 |
et al., TrialSite News | Combination Therapy For COVID-19 Based on Ivermectin in an Australian Population |
| 92% lower mortality (p=0.03) and 93% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001). Retrospective 600 PCR+ outpatients in Australia treated with ivermectin, zinc, and doxycycline, showing significantly lower mortality and hospitalization with treatment. This trial uses a synthetic control group, and the preliminary repor.. | ||
Oct 15 2021 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13102084 | Effect of Ivermectin and Atorvastatin on Nuclear Localization of Importin Alpha and Drug Target Expression Profiling in Host Cells from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2- Positive Patients |
| Gene expression analysis of nasopharyngeal swabs of COVID-19 positive and negative patients, and in vitro study supporting the use of ivermectin and atorvastatin for COVID-19, and the efficacy of ivermectin at clinically relevant dosages... | ||
Oct 14 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-941811/v1 | Favipiravir and Ivermectin Showed in Vitro Synergistic Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2 |
| In Vitro study showing a strong synergistic effect of ivermectin and favipiravir. Combining multiple antiviral drugs with different mechanisms of action helps to minimize drug resistance and toxicity. For ivermectin alone, IC50 for Calu-3.. | ||
Oct 14 2021 |
, M. | Are Major Ivermectin Studies Designed for Failure? |
| Discussion of flaws in ivermectin trials creating a bias towards not finding an effect. | ||
Oct 7 2021 |
et al., OSF Preprints, doi:10.31219/osf.io/mp4f2 | The uses and abuses of systematic reviews |
| Analysis of defects in the Popp et al. meta analysis. | ||
Oct 5 2021 |
et al., Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, doi:10.1039/D1CP02967C | Microscopic interactions between ivermectin and key human and viral proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| In Silico molecular dynamics study showing that ACE2 and ACE2/RBD aggregates form persistent interactions with ivermectin. | ||
Oct 2 2021 |
Committed to Medical Evidence, a Prominent Ivermectin Group is Eradicated from the Memories of Cyberspace | |
| Report on Twitter's censorship of the British Ivermectin Recommendation Development group. | ||
Oct 1 2021 |
et al., Journal of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, doi:10.23937/2474-3658/1510233 (date from preprint) | A Randomized Controlled Trial of Ivermectin Monotherapy versus Hydroxychloroquine, Ivermectin, and Azithromycin Combination Therapy in COVID-19 Patients in Nigeria |
| Small RCT with 61 patients in Nigeria, all patients treated with ivermectin, zinc, and vitamin C, showing no significant improvements in recovery with the addition of HCQ+AZ. | ||
Sep 23 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.813378 (date from preprint) | Safety and Efficacy of a MEURI Program for the Use of High Dose Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients |
| 55% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 66% lower ICU admission (p<0.0001). Retrospective 21,232 patients in Argentina, 3,266 assigned to ivermectin treatment, showing lower mortality with treatment. Greater benefits were seen for patients >40, and a dose dependent response was found. For more discussion see [twi.. | ||
Sep 7 2021 |
, D., TrialsSite News | Merck’s deadly Vioxx playbook, redux: a debunked smear campaign against its competing drug—the FDA-approved, Nobel prize-honored ivermectin |
| Discussion of Merck's ivermectin statements and past actions related to Vioxx raising significant concerns. | ||
Sep 6 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106516 (date from preprint) | High dose ivermectin for the early treatment of COVID-19 (COVER study): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase II, dose-finding, proof of concept trial |
| 20% improved viral clearance (p=0.59). Early terminated 89 patient RCT with 29 high dose and 32 very high dose ivermectin patients, showing dose dependent viral load reduction, although not reaching statistical significance due to early termination. Since most patients have lo.. | ||
Sep 3 2021 |
et al., Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal, doi:10.4103/npmj.npmj_532_21 | Clinical characteristics, treatment modalities and outcome of coronavirus disease 2019 patients treated at thisday dome isolation and treatment centre, federal capital territory Abuja, Nigeria |
| Retrospective 300 COVID-19 patients in Nigeria treated with ivermectin, zinc, vitamin C, and azithromycin, reporting no deaths. Authors conclude that early treatment is critical. | ||
Sep 2 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001443 | Ivermectin, A Reanalysis of the Data |
| Updated meta analysis showing no significant change if Elgazzar et al. is excluded. | ||
Sep 2 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001450 | Bayesian Hypothesis Testing and Hierarchical Modeling of Ivermectin Effectiveness |
| Updated Bayesian analysis of a subset of ivermectin trials showing that there is strong evidence to support a causal link between ivermectin and COVID-19 severity and mortality, and that the result is robust in sensitivity analysis, inclu.. | ||
Aug 19 2021 |
et al., Biophysical Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677 | Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach |
| In Silico analysis of the components of ivermectin (avermectin-B1a and avermectin-B1b), suggesting different and complementary inhibitory activity of each component, with an affinity of avermectin-B1b for viral structures, and of avermect.. | ||
Aug 17 2021 |
et al., Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284 | Structural Deformability Induced in Proteins of Potential Interest Associated with COVID-19 by binding of Homologues present in Ivermectin: Comparative Study Based in Elastic Networks Models |
| In Silico elastic network model analysis of ivermectin components (avermectin-B1a and avermectin-B1b) providing a biophysical and computational perspective of proposed multi-target activity of ivermectin for COVID-19. | ||
Aug 16 2021 |
, P., Substack | Summary of the Evidence for Ivermectin in COVID-19 |
| Summary of the evidence base for ivermectin and COVID-19 including in vitro and in silico studies, animal studies, pharmacologic studies, clinical observation and experience, observational controlled trials, randomized controlled trials, .. | ||
Aug 12 2021 |
et al., Lung India, doi:10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_493_21 | Clinical features, demography, and predictors of outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection at a tertiary care hospital in India: A cohort study |
| 20% lower mortality (p=0.12). Retrospective 2017 hospitalized patients in India, showing lower mortality with ivermectin treatment in unadjusted results. No group details are provided and this result is subject to confounding by indication. | ||
Aug 12 2021 |
et al., The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.bjid.2021.101603 | Self-prescribed Ivermectin use is associated with a lower rate of seroconversion in health care workers diagnosed with COVID, in a dose-dependent response |
| Retrospective 45 healthcare workers in Brazil, showing lower creation of antibodies with multiple doses of ivermectin, which may be expected due to the antiviral activity as demonstrated in multiple studies. Authors appear unaware of thes.. | ||
Aug 10 2021 |
, Argentina | La Pampa expondrá a la comunidad científica los resultados del Programa de Intervención Monitoreado de Ivermectina |
| 27% lower mortality and 38% lower combined mortality/ICU admission. News report on the use of ivermectin in La Pampa, Argentina, showing lower mortality with treatment. | ||
Aug 6 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441 | Pitfalls in Reporting Sample Size Calculation Across Randomized Controlled Trials Involving Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 |
| Review of sample size calculations in ivermectin RCTs, showing that existing RCTs are very underpowered. | ||
Aug 6 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2115869 (results released 8/6/2021) | Effect of Early Treatment with Ivermectin among Patients with Covid-19 |
| 12% lower mortality (p=0.68), 23% lower ventilation (p=0.38), 17% lower hospitalization (p=0.19), and 10% fewer combined hospitalization/ER visits (p=0.42). Many major issues including multiple impossible numbers, blinding broken, randomization failure, and many protocol violations , as detailed below. We provide more detailed analysis of this study due to widespread incorrect press. Submit U.. | ||
Aug 5 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-755838/v1 | A Computational Study of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Combination Drug Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection |
| In silico study showing strong binding affinity of ivermectin and doxycycline for SARS-CoV-2 main protease 3CLpro, and increased binding affinity for the combination of both. | ||
Aug 3 2021 |
et al., New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924 | Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honored distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19 |
| Review concluding that the evidence supports worldwide use of ivermectin for COVID-19, complementary to immunization. Authors note that it is likely non-epitope specific, possibly retaining efficacy with new viral strains. They note that .. | ||
Jul 31 2021 |
et al., Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186 | Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials |
| 61% lower mortality (p=0.005). Systematic review and meta analysis showing lower mortality with ivermectin. | ||
Jul 31 2021 |
et al., Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Research, doi:10.31838/jcdr.2021.12.05.11 | Clinical Effect of the Combination Therapy of Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin and Ivermectin in Patients with COVID-19 |
| Prospective study of 85 COVID-19 patients including 8 ICU patients treated with ivermectin, HCQ, and AZ, showing all patients improving except for one patient that died 3 days after admission. Authors recommend early treatment. There was .. | ||
Jul 30 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.700502 | Combination Treatment With Remdesivir and Ivermectin Exerts Highly Synergistic and Potent Antiviral Activity Against Murine Coronavirus Infection |
| In Vitro study showing highly synergistic antiviral activity of the combination of ivermectin and remdesivir against murine coronavirus (MHV) infection in RAW264.7 macrophages. Authors found that while remdesivir monotherapy (6 μM) achiev.. | ||
Jul 28 2021 |
et al., Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub2 | Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19 |
| This meta analysis is designed to exclude most studies. Authors select a small subset of studies, with a majority of results based on only 1 or 2 studies. Authors split up studies which dilutes the effects and results in a lack of statist.. | ||
Jul 25 2021 |
et al., Epidemiology International Journal, doi:10.23880/eij-16000217 | Early multidrug treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and decreased case fatality rates in Honduras |
| Report on the nationwide implementation of multi-drug COVID-19 inpatient and outpatient treatment protocols in Honduras, showing a case fatality rate decrease from 9.33% to 2.97%. No decrease was seen in Mexico, a similar Latin American c.. | ||
Jul 24 2021 |
World Ivermectin Day | |
| Joint event by 22 worldwide organizations. | ||
Jul 23 2021 |
et al., International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108004 | Safety of inhaled ivermectin as a repurposed direct drug for treatment of COVID-19: A preclinical tolerance study |
| Safety analysis of an inhaled lyophilized ivermectin formulation, showing 127-fold increase in drug solubility, and identifying safe dosage levels in rats. | ||
Jul 16 2021 |
Alliance and British Ivermectin Recommendation Development Group | Joint Statement of the FLCCC Alliance and British Ivermectin Recommendation Development Group on Retraction of Early Research on Ivermectin |
| News release noting that ivermectin remains effective after excluding Elgazzar et al. Given the large magnitude effects and 61 studies, excluding one study with ~3% of patients does not significantly change the evidence base. | ||
Jul 12 2021 |
et al., ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.31800.88323 | Bayesian Meta Analysis of Ivermectin Effectiveness in Treating Covid-19 Disease |
| Bayesian analysis of a subset of ivermectin trial data concluding that there is overwhelming evidence to support a causal link between ivermectin, COVID-19 severity, and mortality. | ||
Jul 8 2021 |
et al., Journal of Virology & Antiviral Research | Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Anti-Parasitic Drugs Inhibiting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein |
| In Silico study identifying 32 anti-parisitic compounds effectively inhibiting the RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, showing ivermectin and atovaquone among the top compounds. | ||
Jul 8 2021 |
Together Trial removes sublingual administration mid-trial | |
| Together Trial removes sublingual administration mid-trial. | ||
Jul 7 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.07.06.21259924 | Effectiveness of ivermectin-based multidrug therapy in severely hypoxic, ambulatory COVID-19 patients |
| 86% lower mortality (p=0.04) and 93% lower hospitalization (p=0.001). Small study of 24 consecutive patients in serious condition (9 days post symptoms, mean SpO2 87.4) using combined treatment with ivermectin, doxycycline, zinc, vitamin D, and vitamin C, showing no mortality or hospitalization with treatme.. | ||
Jul 3 2021 |
, Statement of Concern and Request for Retraction, re: Roman et al. | Open Letter, Statement of Concern and Request for Retraction |
| Open letter signed by 40 physicians detailing errors and flaws in the Roman et al. meta analysis, and requesting retraction. | ||
Jul 2 2021 |
et al., African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2 | A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin |
| Review of the antiviral effects of ivermectin. | ||
Jul 2 2021 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5 | Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial |
| 33% lower hospitalization (p=0.23) and 5% worse viral clearance (p=0.55). RCT with 501 relatively low-risk outpatients in Argentina showing hospitalization OR 0.65 [0.32-1.31]. With only 7% hospitalization, this trial is underpowered. The trial primarily includes low-risk patients that recover quickly without t.. | ||
Jun 30 2021 |
, M., ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.16973.36326 | A Continuation of a Timeline of Ivermectin-Related Events in the COVID-19 Pandemic [June 30, 2021] |
| An extension of the ivermectin timeline covering April - June 2021, including WHO's role and funding, Gavi, COVAX, Trusted News Initiative, International Fact-Checking Network, the role of private philantrophy, Frontiers, comparison to th.. | ||
Jun 28 2021 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab591 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials |
| This is a severely flawed meta analysis. An open letter signed by 40 physicians detailing errors and flaws, and requesting retraction, can be found at [ trialsitenews.com ] . See also [ bird-group.org ] . Authors cherry-pick to include on.. | ||
Jun 25 2021 |
et al., The International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14574 | Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID-19 in India- A nationwide cross-sectional survey |
| Survey of medication use for severe COVID-19 in India, showing 33% adoption of ivermectin as of January 2021. | ||
Jun 22 2021 |
Results from ivermectin use from the Misiones Ministry of Public Health | |
| News report on ivermectin use in Misiones, Argentina, showing significantly lower hospitalization and mortality, and a dose-dependent effect with improved results for those taking 0.6mg/kg. | ||
Jun 18 2021 |
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046799 | Platform Randomised trial of INterventions against COVID-19 In older peoPLE (PRINCIPLE): protocol for a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform, trial of community treatment of COVID-19 syndromic illness in people at higher risk |
| Protocol paper for the PRINCIPLE trial. For the colchicine arm see [Dorward], for budesonide see [Yu], and for ivermectin see [Hayward]. | ||
Jun 18 2021 |
et al., Journal of General Internal Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06948-6 | Increase in Outpatient Ivermectin Dispensing in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Analysis |
| CDC analysis of ivermectin prescriptions in the US suggesting that, while national health authority recognition is delayed in that country, many physicians are aware of the efficacy demonstrated in clinical trials. | ||
Jun 18 2021 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959 | Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial |
| 66% improved viral load (p=0.09). Proof of concept RCT with 30 ivermectin patients and 15 control patients, showing a concentration dependent antiviral activity, but no significant difference in clinical outcomes. There was no significant difference in viral load reductio.. | ||
Jun 17 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines |
| 62% lower mortality (p=0.005). Systematic review, meta analysis, and trial sequential analysis of 24 RCTs finding mortality RR 0.38 [0.19-0.73]. An update notes potentially inaccurate data collection and/or reporting in some sources [journals.lww.com]. | ||
Jun 16 2021 |
et al., British Society For Nanomedicine Early Career Researcher Summer Meeting, 2021 | Niclosamide and ivermectin modulate caspase-1 activity and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a monocytic cell line |
| In Vitro study showing potential therapeutic effects of ivermectin and niclosamide on the immune system by reducing inflammation and modulating key proteins involved in the inflammatory response. Ivermectin and niclosamide reduced proinfl.. | ||
Jun 15 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S313093 | Clinical, Biochemical and Molecular Evaluations of Ivermectin Mucoadhesive Nanosuspension Nasal Spray in Reducing Upper Respiratory Symptoms of Mild COVID-19 |
| 63% improved recovery (p=0.0001) and 79% improved viral clearance (p=0.004). RCT 114 patients in Egypt, 57 treated with ivermectin mucoadhesive nanosuspension intranasal spray, showing faster recovery and viral clearance with treatment. NCT04716569. | ||
Jun 6 2021 |
et al., Reviews In Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2265 | Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid-19 pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trial studies |
| 69% lower mortality (p=0.001). Systematic review and meta analysis of 19 RCTs showing mortality RR 0.31 [0.15-0.62]. | ||
Jun 3 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.01.21258147 | Minimum manufacturing costs, national prices and estimated global availability of new repurposed therapies for COVID-19 |
| Analysis of the manufacturing cost of several COVID-19 medications, showing a cost of $0.55 per course of ivermectin, including excipients, formulation, tax, and profit. | ||
Jun 2 2021 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27122 | Clinical Study Evaluating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Study |
| 20% shorter hospitalization (p=0.09). RCT 164 hospitalized patients in Egypt showing lower mortality and shorter hospitalization, but without statistical significance. There were no serious adverse effects. Authors suggest the low dosage may have resulted in lower efficacy th.. | ||
May 31 2021 |
et al., Journal of the Indian Medical Association, 119:5 | Prevalence of COVID-19 Infection and Identification of Risk Factors among Asymptomatic Healthcare Workers: A Serosurvey Involving Multiple Hospitals in West Bengal |
| 88% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.006). Retrospective 1,470 healthcare workers in India, showing significantly lower risk of symptomatic COVID-19 with ivermectin prophylaxis. | ||
May 18 2021 |
Mountain Valley MD Receives Successful Results From BSL-4 COVID-19 Clearance Trial on Three Variants Tested With Ivectosol™ | |
| In Vitro and mouse study with human ACE2 cells, using solubilized ivermectin with Ivectosol™, showing antiviral effect with B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1 variants of SARS-CoV-2. The ability to inject ivermectin potentially reduces the onset o.. | ||
May 12 2021 |
Public Statement | FLCCC Alliance Statement on the Irregular Actions of Public Health Agencies and the Widespread Disinformation Campaign Against Ivermectin |
| Analysis of the ivermectin recommendations from WHO and others, and a call to action for all citizens, scientists, and media to counter false information. Whistleblowers can submit anonymous reports and images at the bottom of this page. | ||
May 10 2021 |
et al., The Professional Medical Journal, doi:10.29309/TPMJ/2021.28.05.5867 | Potential use of azithromycin alone and in combination with ivermectin in fighting against the symptoms of COVID-19 |
| 68% improved recovery (p=0.005). RCT 100 outpatients in Pakistan, 50 treated with ivermectin, showing faster recovery with ivermectin. All patients received AZ, zinc, vitamin C, vitamin D, and paracetemol. Details of randomization were not provided. No mortality or hospi.. | ||
May 5 2021 |
et al. | News report on In Vitro results from the research institute of Prof. Zatloukal |
| News report on In Vitro results from the research institute of Prof. Zatloukal, showing that "ivermectin was able to reduce virus replication by a factor of 1,000 even at low concentrations". | ||
May 5 2021 |
et al., Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1906750 | Mechanistic insights into the inhibitory activity of FDA approved ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: old drug with new implications |
| In Silico study showing inhibition of importin-α1 by ivermectin, which disrupts SARS-CoV-2 replication. | ||
May 4 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.04.30.21256415 | A Meta-analysis of Mortality, Need for ICU admission, Use of Mechanical Ventilation and Adverse Effects with Ivermectin Use in COVID-19 Patients |
| Systematic review and meta analysis with 30 studies included in quantitative analysis, showing mortality OR 0.39 [0.22-0.70]. Subgroup analysis of trials with severity data showed mortality OR 0.10 [0.03-0.33] for mild/moderate cases. | ||
May 3 2021 |
et al., Preprint | Ivermectin and the odds of hospitalization due to COVID-19: evidence from a quasi-experimental analysis based on a public intervention in Mexico City |
| 74% lower hospitalization (p=0.001). Analysis of Mexico City's use of an ivermectin-based medical kit, showing significantly lower hospitalization with use. Authors use logistic-regression models with matched observations, including adjustments for age, sex, COVID severity, .. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., NCT04384458 | Comparative Study of Hydroxychloroquine and Ivermectin in COVID-19 Prophylaxis |
| Estimated 400 participant ivermectin vs. HCQ prophylaxis RCT with results not reported over 4 years after estimated completion. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377 | Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19 |
| Review of ivermectin trials and epidemiological data, concluding that ivermectin is effective for prophylaxis and treatment, and should be globally and systematically deployed in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. An update notes p.. | ||
Apr 29 2021 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.14761 | Clinical Variants, Characteristics, and Outcomes Among COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series Analysis at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Karachi, Pakistan |
| 50% lower mortality (p=0.03). Retrospective 165 hospitalized patients in Pakistan showing unadjusted lower mortality with combined ivermectin and doxycycline treatment. Details of the ivermectin group compared to other patients are not provided, however ivermectin was.. | ||
Apr 19 2021 |
et al., Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2021-001655 | Anti-inflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors |
| Review suggesting that the effectiveness of ivermectin in the cytokine storm phase of COVID-19 may be, at least in part, an anti-inflammatory effect mediated by increased activation of glycine receptors on leukocytes and possibly vascular.. | ||
Apr 17 2021 |
et al., J. Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, doi:10.23937/2474-3658/1510202 | Ivermectin and COVID-19 in Care Home: Case Report |
| 70% lower mortality (p=0.34) and 55% lower severe cases (p=0.11). Small quasi-randomized (patient choice) study with 25 PCR+ patients in a nursing home offered ivermectin, of which 10 chose to be treated. The mean age was 83.5 in the treatment group and 81.8 in the control group. There was lower mortali.. | ||
Apr 16 2021 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.17455 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin as a SARS-CoV-2 Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis Method in Healthcare Workers: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 74% fewer cases (p=0.008). Propensity matched retrospective prophylaxis study of healthcare workers in the Dominican Republic showing significantly lower cases with treatment, and no hospitalization with treatment (versus 2 in the PSM matched control group). The ca.. | ||
Apr 15 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-379291/v1 | Highly-transmissible Variants of SARS-CoV-2 May Be More Susceptible to Drug Therapy Than Wild Type Strains |
| In Silico study of ivermectin treatment predicting greater efficacy for variants with higher R0. | ||
Apr 14 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.035 | Positive impact of oral hydroxychloroquine and povidone-iodine throat spray for COVID-19 prophylaxis: an open-label randomized trial |
| 50% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.0009) and 6% fewer cases (p=0.61). Prophylaxis RCT in Singapore with 3,037 low risk patients, showing lower serious cases, lower symptomatic cases, and lower confirmed cases of COVID-19 with all treatments (ivermectin, HCQ, PVP-I, and Zinc + vitamin C) compared to vitamin .. | ||
Apr 10 2021 |
et al., Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1911857 | Elucidation of the inhibitory activity of ivermectin with host nuclear importin α and several SARS-CoV-2 targets |
| In Silico analysis finding that the in vitro activity of ivermectin may explained by acting as an inhibitor of importin-α, dimeric 3CLpro, and Nsp9. | ||
Apr 3 2021 |
, M., Research Gate | A timeline of ivermectin-related events in the COVID-19 pandemic |
| An extensive timeline of ivermectin-related events from April 2020 to March 2021 including studies, news, health authority decisions, biased news coverage, and censorship. The author concludes that in a broader historical perspective, the.. | ||
Apr 1 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Health and Clinical Research, 4:6 | Comparative Analytical Study of Two Different Drug Regimens in Treatment of Covid 19 Positive Patients in Index Medical College Hospital and Research Center, Indore, India |
| 89% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). Retrospective 100 patients in India with 50 treated with ivermectin, and SOC for all patients including HCQ+AZ, showing much higher viral clearance with ivermectin. Baseline clinical status was worse in the control group. Time of testing .. | ||
Mar 30 2021 |
et al., Front. Immunol., doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586 | Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities |
| Review of how ivermectin was identified for use in COVID-19, mechanisms of action, and selected clinical trials. | ||
Mar 30 2021 |
et al., Research, Society and Development, doi:10.33448/rsd-v11i8.30844 (date from preprint) | Randomized trials - Ivermectin repurposing for COVID-19 treatment of outpatients with mild disease in primary health care centers |
| 87% higher hospital discharge (p=0.004). Cluster RCT outpatients in Argentina showing significantly faster recovery with ivermectin. There were no deaths. Outpatients in Tucumán were assigned to the ivermectin group and outpatients from San Miguel de Tucumán and Gran San Miguel .. | ||
Mar 29 2021 |
et al., Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z | The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis |
| Small meta analysis of 6 RCTs showing mortality OR 0.21 [0.11-0.42]. Authors do not include two more recent RCTs with mortality results, 10 other studies with mortality results, and a total of 42 other studies including other outcomes. Au.. | ||
Mar 26 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.26.21254377 | Why COVID-19 is not so spread in Africa: How does Ivermectin affect it? |
| 88% lower mortality (p=0.002). Retrospective study of the 31 onchocerciasis-endemic countries using the community-directed treatment with ivermectin (CDTI) and the 22 non-endemic countries in Africa, showing significantly lower mortality per capita in the countries us.. | ||
Mar 25 2021 |
et al., Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, doi:10.1007/s13721-021-00299-2 | In silico studies of selected multi-drug targeting against 3CLpro and nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV |
| In Silico analysis finding that ivermectin had the highest binding energy against the 3CLpro of SARS-CoV-2 and RdRps of both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. | ||
Mar 25 2021 |
et al., Future Medicine, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0342 | Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach |
| In Silico analysis finding that ivermectin has high binding affinity for the SARS-CoV-2 viral spike protein, main protease, replicase, and human TMPRSS2 receptors. | ||
Mar 25 2021 |
, Press Release | Kovid-19 - Huvemek® Phase 2 clinical trial |
| 32% greater improvement (p=0.28). Multicenter double-blind RCT with 100 hospitalized patients in Bulgaria showing faster viral clearance, greater clinical improvement, and improved biomarkers with treatment. Limited data has been reported currently. No serious adverse eve.. | ||
Mar 24 2021 |
et al., The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, 74-1, Mar 2021 | Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19 |
| Review of ivermectin for COVID-19. Authors note that Kitasato University's project was expanded in response to the results of Caly et al. which had left questions regarding in vivo therapeutic levels, and the results of those studies were.. | ||
Mar 21 2021 |
et al., Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18073371 | Comparisons between the Neighboring States of Amazonas and Pará in Brazil in the Second Wave of COVID-19 Outbreak and a Possible Role of Early Ambulatory Treatment |
| Comparison between the two largest neighboring states in Brazil, Amazonas and Pará, showing more than 5 times lower mortality in Pará during the second wave when the Pará government supported early treatment and Amazonas did not, compared.. | ||
Mar 18 2021 |
et al., Journal of Biomedical Research and Clinical Investigation, doi:10.31546/2633-8653.1008 | Ivermectin in Long-Covid Patients: A Retrospective Study |
| Retrospective 856 patients previously admitted to hospital for COVID-19 in Argentina, finding that ivermectin improved recovery from "long covid" symptoms. | ||
Mar 17 2021 |
et al., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/AAC.01543-21 (date from preprint) | Moxidectin and ivermectin inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero E6 cells but not in human primary airway epithelium cells |
| In Vitro study showing moxidectin and ivermectin exhibited antiviral activity in Vero E6 cells. Authors indicate that no statistically significant effect was seen in Calu-3/PBEC cells, however Figure 3 shows a dose dependent reduction wit.. | ||
Mar 12 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.08.21252883 | Outcome of Different Therapeutic Interventions in Mild COVID-19 Patients in a Single OPD Clinic of West Bengal: A Retrospective study |
| 6% faster recovery (p=0.87). Retrospective database analysis of 56 mild COVID-19 patients, all treated with vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc, comparing ivermectin + doxycycline (n=14), AZ (n=13), HCQ (n=14), and SOC (n=15), finding that all groups recover quickly, and .. | ||
Mar 11 2021 |
et al., Signa Vitae, doi:10.22514/sv.2021.043 | Crying wolf in time of Corona: the strange case of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine. Is the fear of failure withholding potential life-saving treatment from clinical use? |
| 79% lower mortality (p<0.0001). Meta analysis of RCT mortality results showing RR 0.19, p < 0.00001. | ||
Mar 11 2021 |
et al., OSF Preprints | Ivermectin sales in Valle del Cauca, Colombia, patterns of AEs, and other background re López-Medina et al. 2021 |
| Analysis of several issues with López-Medina et al. including the atypical adverse effects in the control arm and population use of ivermectin. | ||
Mar 11 2021 |
et al., OSF Preprints | Protocol violations in López-Medina et al.: 38 switched ivermectin (IVM) and placebo doses, failure of blinding, widespread IVM sales OTC in Cali, and nearly identical AEs for the IVM and control groups |
| Report on protocol violations in López-Medina et al. | ||
Mar 10 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.625678 | Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Treatment Effects for Informed Drug Repurposing |
| Modeling study analyzing timing and dosing regimens of hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir/ritonavir, ivermectin, artemisinin, and nitazoxanide. The greatest benefits were seen when treatments were given immediately at the time of diagnosis. Au.. | ||
Mar 10 2021 |
et al., Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384 | Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro |
| In Vitro study showing that ivermectin can inhibit infection of bovine respiratory disease viral agents BCoV, BPIV-3, BVDV, BRSV and BoHV-1 at the concentrations of 2.5 and 5 μM and in a dose-dependent manner. | ||
Mar 9 2021 |
et al., Toxicology Reports, doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003 | Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: a pilot trial |
| 85% lower ventilation (p=0.25), 85% lower ICU admission (p=0.25), and 1% improved viral clearance (p=1). Very small RCT with 4 control patients and 28 ivermectin patients split across 3 different dosage levels, showing lower (non-statistically significant) ICU admission with treatment. Authors suggest that ivermectin for SARS-CoV-2 is safe a.. | ||
Mar 8 2021 |
et al., OSF Preprints | Ivermectin for COVID-19 in Peru: 14-fold reduction in nationwide excess deaths, p=.002 for effect by state, then 13-fold increase after ivermectin use restricted |
| Analysis of ivermectin use in Peru concluding that ivermectin most likely caused a 14 times reduction in excess deaths in Peru, prior to a 13 times increase after reversal of ivermectin use. Authors conclude that the results strongly sugg.. | ||
Mar 8 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.04.21252084 | Factors associated with increased mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients in a Mexican public hospital: the other faces of health system oversaturation |
| 19% lower mortality (p=0.35). Retrospective 196 critically ill patients in Mexico. Patients overlap with the existing RCT by Beltran-Gonzalez (NCT04391127). This preprint shows a larger treated population and greater (non-statistically significant) improvement with iv.. | ||
Mar 8 2021 |
et al., Pathogens and Global Health, doi:10.1080/20477724.2021.1890887 | Phase 2 randomized study on chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine or ivermectin in hospitalized patients with severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| RCT 168 very late stage severe condition hospitalized patients comparing CQ, HCQ, and ivermectin not showing significant differences. Authors indicate that it would have been unethical to include an untreated control group. However, autho.. | ||
Mar 5 2021 |
, J., ImmunoSafe Consultance | Medical Safety of Ivermectin |
| Safety analysis of >350 articles showing that ivermectin has an excellent safety profile. The author notes that "no severe adverse event has been reported in dozens of completed or ongoing studies involving thousands of participants.. | ||
Mar 4 2021 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071 | Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults With Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 61% lower progression (p=0.11) and 15% improved recovery (p=0.53). Phone survey based RCT with low risk patients, 200 ivermectin and 198 control, showing lower mortality, lower disease progression, lower treatment escalation, and faster resolution of symptoms with treatment, without reaching statistical .. | ||
Mar 1 2021 |
et al., Structural Chemistry, doi:10.1007/s11224-021-01776-0 (date from preprint) | The Binding mechanism of ivermectin and levosalbutamol with spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 |
| In Silico analysis predicting that ivermectin has a large binding affinity for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Three different computer modeling techniques show that ivermectin can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 entrance via hACE2. | ||
Feb 23 2021 |
et al., Infectious Disease Reports, doi:10.3390/idr14020020 (date from preprint) | Efficacy and Safety of Ivermectin and Hydroxychloroquine in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial |
| 14% lower mortality (p=1), 9% lower progression (p=1), 37% lower hospital discharge (p=0.71), and 20% longer hospitalization (p=0.43). RCT late stage severe condition (93% SOFA ≥ 2, 96% APACHE ≥ 8) high comorbidity hospitalized patients in Mexico with 36 low dose ivermectin and 37 control patients not finding significant differences. NCT04391127. Another study reports re.. | ||
Feb 20 2021 |
Meeting 20th February 2021 | BIRD Meeting 20th February 2021 |
| The British Ivermectin Recommendation Development (BIRD) panel, with dozens of multi-national scientists & doctors, issued sweeping recommendations for the immediate global use of ivermectin. | ||
Feb 16 2021 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26880 | Effect of a combination of Nitazoxanide, Ribavirin and Ivermectin plus zinc supplement (MANS.NRIZ study) on the clearance of mild COVID-1 |
| 87% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). Non-randomized controlled trial with 62 mild and early moderate patients with home treatment with ivermectin + nitazoxanide + ribavirin + zinc, showing significantly faster viral clearance. | ||
Feb 15 2021 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.16897 (date from preprint) | Prophylactic Role of Ivermectin in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection Among Healthcare Workers |
| 83% fewer cases (p=0.001). Prospective prophylaxis study with 3,532 healthcare workers, 2,199 receiving two-dose ivermectin prophylaxis, showing adjusted relative risk of confirmed COVID-19 with treatment 0.17 [0.12-0.23] p<0.001. 186 patients took only the first d.. | ||
Feb 12 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.07.003 (results 2/12/21) | The effect of ivermectin on the viral load and culture viability in early treatment of non-hospitalized patients with mild COVID-19 – A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial |
| 70% lower hospitalization (p=0.34) and 62% improved viral clearance (p=0.02). Double blind RCT for mild-moderate COVID-19 outpatients in Israel showing significantly faster reduction in viral load with treatment, and lower hospitalization with treatment. The one treatment hospitalization was a few hours after treat.. | ||
Feb 10 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.014 | Effectiveness of a multidrug therapy consisting of ivermectin, azithromycin, montelukast and acetylsalicylic acid to prevent hospitalization and death among ambulatory COVID-19 cases in Tlaxcala, Mexico |
| 78% lower mortality (p=0.001), 52% lower ventilation (p=0.15), 67% lower hospitalization (p=0.001), and 59% improved recovery (p=0.001). Prospective trial of 768 COVID-19 outpatients in Mexico, 481 treated with ivermectin, AZ, montelukast, and aspirin, and 287 control patients with various treatments, showing significantly lower mortality and hospitalization, and significa.. | ||
Feb 2 2021 |
et al., Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021 (date from preprint) | Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): a single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial |
| 62% improved recovery (p=0.27) and 24% improved viral clearance (p=0.18). RCT in India with low risk patients, comparing 24mg ivermectin, 12mg ivermectin, and placebo showing non-statistically significant improvements in recovery and PCR+ status (day 5 both arms, day 7 24mg only) with treatment, and showing gre.. | ||
Jan 31 2021 |
et al., Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042 | The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ? |
| Review of the potential of ivermectin as an antiviral against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport protein importin alpha, which many RNA viruses hijack to enhance infection. Authors review evidence that .. | ||
Jan 29 2021 |
et al., Clin. Res. Trials, 2021, doi:10.15761/CRT.1000333 | Potential use of ivermectin for the treatment and profilaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Efficacy of ivermectin for SARS-CoV-2 |
| Review finding that there appears to be sufficient evidence to recommend ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19, especially in the early stages of the disease. | ||
Jan 27 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.26.21250420 | Outcomes of Ivermectin in the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis |
| Meta analysis of a very small subset of studies exhibiting very high bias and significant flaws. Some of the problems: - As of the publication date, there are 35 studies, authors include only 4. (They list 5, but two are the same study, p.. | ||
Jan 25 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908 | Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2 |
| Molecular docking analysis showing that ivermectin efficiently binds to the viral S protein as well as the human cell surface receptors ACE-2 and TMPRSS2; therefore, it might be involved in inhibiting the entry of the virus into the host .. | ||
Jan 23 2021 |
et al., Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2021.01.017 | Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assessments of a Novel Ivermectin Nasal Spray Formulation in a Pig Model |
| Animal study of a novel spray formulation of ivermectin, showing an advantage of the spray formulation in terms of fast attainment of high and persistent ivermectin concentrations in nasopharyngeal tissue. | ||
Jan 21 2021 |
et al., Preprint, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3765018 | Sharp Reductions in COVID-19 Case Fatalities and Excess Deaths in Peru in Close Time Conjunction, State-By-State, with Ivermectin Treatments |
| Analysis of ivermectin usage within states in Peru showing sharp reductions in COVID-19 deaths corresponding to the usage of ivermectin treatment. | ||
Jan 20 2021 |
et al., Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x | Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents |
| Computational molecular modeling screening and in vitro analysis for inhibitory effects on SARS-CoV-2 specific 3CLpro enzyme, showing that ivermectin blocked more than 85% of 3CLpro activity of SARS-CoV-2. Antiviral activity of ivermectin.. | ||
Jan 19 2021 |
et al., Clinical Therapeutics, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.007 (partial results available 1/19) | Effects of Ivermectin in Patients With COVID-19: A Multicenter, Double-blind, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial |
| 32% faster recovery (p=0.05) and 15% shorter hospitalization (p=0.02). RCT in Iran showing shorter time to recovery and shorter hospitalization time with ivermectin. There were no adverse effects. There was one death in the treatment group, the patient was in critical condition at baseline and died within 24.. | ||
Jan 19 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-148845/v1 | Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| 75% lower mortality (p=0.0002). Meta analysis of 18 ivermectin RCTs with 2,282 patients showing faster viral clearance (dose and duration dependent), improved clinical recovery, and lower hospitalization and mortality. In six RCTs of moderate or severe infection, there .. | ||
Jan 16 2021 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13060989 (results 1/16) | Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon |
| This study was retracted. | ||
Jan 16 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.02.02.21250840 (results 1/16) | Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients with Mild to Moderate Disease |
| 82% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). RCT of relatively low risk hospitalized patients with 50 ivermectin and 50 control patients showing significantly faster viral clearance with treatment. 9 patients in the treatment arm were lost to followup compared with 5 in the control .. | ||
Jan 13 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.643369 | Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19 |
| Meta analysis of ivermectin clinical studies and natural experiments where ivermectin has been widely used, showing efficacy of ivermectin in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19. This paper was censored by the journal after acceptance.. | ||
Jan 12 2021 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06104-9 (date from preprint) | Evaluation of the Effectiveness and Safety of Adding Ivermectin to Treatment in Severe COVID-19 Patients |
| 33% lower mortality (p=0.55), 43% greater improvement (p=0.18), and 80% improved viral clearance (p=0.02). Small RCT for severe COVID-19 comparing the addition of ivermectin to SOC (low dose HCQ+AZ+favipiravir), with 30 treatment and 30 control patients in Turkey, showing lower mortality and faster clinical recovery. Authors also investigate t.. | ||
Jan 11 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001433 | Intensive Treatment With Ivermectin and Iota-Carrageenan as Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 in Health Care Workers From Tucuman, Argentina |
| 95% fewer moderate/severe cases (p=0.002) and 84% fewer cases (p=0.004). Prophylaxis RCT for ivermectin and iota-carrageenan in Argentina, 117 healthcare workers treated with ivermectin and iota-carrageenan, and 117 controls, showing significantly lower cases with treatment. There were no moderate/severe cases.. | ||
Jan 11 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.666348 (date from preprint) | A Large Impact of Obesity on the Disposition of Ivermectin, Moxidectin and Eprinomectin in a Canine Model: Relevance for COVID-19 Patients |
| Animal dosing study with an obese dog model concluding that ivermectin maintenance doses should be based on lean body weight and not the total body weight in obese subjects, while the loading dose should be based on the total body weight. | ||
Jan 10 2021 |
et al., J. Control Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009 | Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19 |
| Review hypothesizing that micro- and nanotechnology-based formulations of ivermectin for the pulmonary delivery of ivermectin may be beneficial for use with COVID-19. | ||
Jan 9 2021 |
et al., Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.18433/jpps32105 | Ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19: A double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial |
| 89% lower mortality (p=0.12), 79% lower ventilation (p=0.1), 14% lower ICU admission (p=0.8), and 89% higher hospital discharge (p=0.12). RCT with 112 mild and moderate COVID-19 patients in India, showing lower mortality, ventilation, and ICU admission, although not statistically significant due to the small number of events. There was no mortality in the treatment arm (55 .. | ||
Jan 8 2021 |
, J. | COVID-19 in Mexico |
| Comparison of COVID-19 death rates in Mexico showing that the only state using ivermectin has a dramatically lower rate. | ||
Jan 6 2021 |
et al., QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab035 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: A randomised controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos |
| 64% improved viral clearance (p=0.11) and 41% improved recovery (p=0.07). Small RCT comparing ivermectin 6mg & 12mg q84hr with lopinavir/ritonavir, showing a statistically significant and dose dependent effect of ivermectin on reducing the time to PCR-. The study does not report mortality, hospitalization, prog.. | ||
Jan 6 2021 |
et al., Microbiology & Infectious Diseases | Ivermectin as Prophylaxis Against COVID-19 Retrospective Cases Evaluation |
| Report on ivermectin prophylaxis for healthcare workers in a hospital in Argentina, showing 0 cases in the 162 participants. Dosage was 0.2mg/kg weekly for eight weeks, followed by 4 months rest. | ||
Jan 3 2021 |
et al., Preprint | Ivermectin reduces the risk of death from COVID-19 – a rapid review and meta-analysis in support of the recommendation of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance |
| 83% lower mortality (p<0.0001). Meta analysis confirming the effectiveness of ivermectin for COVID-19, showing ivermectin treatment mortality relative risk RR 0.17 [0.18-0.35] and prophylaxis cases RR 0.12 [0.08-0.18]. | ||
Dec 31 2020 |
et al., Cermin Dunia Kedokteran, 47:7 | Ivermectin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for COVID-19 – case studies |
| Case report on 3 confirmed cases of COVID-19 with significant clinical and radiological improvement after a single dose of ivermectin. | ||
Dec 31 2020 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05820 | Safety of oral administration of high doses of ivermectin by means of biocompatible polyelectrolytes formulation |
| In vivo analysis of the safety of high dose ivermectin with a Corydoras fish animal model. | ||
Dec 31 2020 |
, D., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557 | Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion |
| Review of ivermectin for COVID-19 treatment and a hypothesized mechanism of action. Author proposes that ivermectin's antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 may be mediated by competitive binding to the CD147 receptor, which is densely dis.. | ||
Dec 30 2020 |
et al., Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, doi:10.31083/j.rcm.2020.04.264 | Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multidrug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19) |
| Review urging early treatment of COVID-19 with sequential multidrug treatment that has been shown to be safe and effective. Proposed treatment includes zinc, vitamin D & C, quercetin, and depending on age, comorbidities, and symptoms may .. | ||
Dec 30 2020 |
et al., Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, doi:10.31083/j.rcm.2020.04.260 | Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for high-risk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection |
| Retrospective 922 outpatients, with 320 treated early due to age>50 or comorbidities, showing 2.2% hospitalization and 0.3% death, which authors note is considerably lower than reported in other studies in their region. At least two of zi.. | ||
Dec 27 2020 |
, A., Preprint | Meta-analysis of clinical trials of ivermectin to treat COVID-19 infection |
| WHO-funded meta analysis showing ivermectin treatment mortality relative risk RR 0.17 [0.08-0.35] for RCTs and RR 0.28 [0.13-0.62] for RCTs and observational studies, and confirming a dose-response effect. | ||
Dec 24 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106542 (date from preprint) | Remdesivir-ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2 |
| In Vitro study showing enhanced antiviral activity of ivermectin and remdesivir in combination. | ||
Dec 20 2020 |
, Preliminary Results | Ivermectina en agentes de salud e IVERCOR COVID19 |
| 73% fewer cases (p<0.0001). Report on ivermectin prophylaxis in a hospital in Argentina showing lower cases for healthcare workers taking ivermectin. Results have been published in the press [lanacion.com.ar] (interim results), and a presentation posted online:.. | ||
Dec 18 2020 |
et al., FLCCC Alliance | Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19 |
| 69% lower mortality (p<0.0001). Meta analysis of ivermectin clinical studies and natural experiments where ivermectin has been widely used, showing efficacy of ivermectin in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19. There is potentially inaccurate data collection and/or re.. | ||
Dec 15 2020 |
et al., European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, doi:10.24018/ejmed.2020.2.6.599 | Ivermectin as Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 among Healthcare Providers in a Selected Tertiary Hospital in Dhaka – An Observational Study |
| 91% fewer cases (p<0.0001). 91% reduction in COVID-19 cases with ivermectin prophylaxis. 118 healthcare workers in Bangladesh, 58 receiving ivermectin 12mg monthly, showing RR 0.094, p < 0.0001. | ||
Dec 15 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Clinical Studies & Medical Case Reports, doi:10.46998/IJCMCR.2021.13.000320 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin Use Associated with Reduced Duration of Covid-19 Febrile Illness in a Community Setting |
| 92% improved recovery (p=0.04). Retrospective 95 outpatients in Pakistan with strong clinical suspicion of COVID-19 (testing was not widely available), with 40 patients treated with ivermectin, showing significantly shorter duration of febrile illness with treatment. Mo.. | ||
Dec 11 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular and Immuno Oncology, doi:10.25259/IJMIO_30_2020 | Outcome of ivermectin and doxycycline in cancer patients with COVID-19: A positive experience in Bangladesh |
| Small case study of ivermectin + doxycycline with 8 cancer patients, with all patients becoming PCR- by day 6 when tested again. | ||
Dec 7 2020 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720 (date from preprint) | The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial |
| 96% improved symptoms (p=0.05), 95% improved viral load (p=0.01), and 8% improved viral clearance (p=1). Tiny RCT for early treatment of mild COVID-19 in low risk patients, with 12 400mcg/kg single dose ivermectin patients and 12 control patients, showing significantly faster viral load reduction and symptom improvement with ivermectin. Aver.. | ||
Dec 4 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.11.30.20236570 | The therapeutic potential of ivermectin for COVID-19: a systematic review of mechanisms and evidence |
| Review of ivermectin mechanisms and 8 trials, showing positive mortality benefit, reduced time to clinical recovery, reduced incidence of disease progression, and decreased duration of hospital admission in patients across all stages of c.. | ||
Dec 4 2020 |
et al., ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci., doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00179 | Clinically Approved Antiviral Drug in an Orally Administrable Nanoparticle for COVID-19 |
| In Vitro analysis of ivermectin with orally administrable nanoparticles showing efficacy for decreasing expression of the viral spike protein and ACE2. Inhibition of nuclear transport activities mediated through proteins such as importin .. | ||
Dec 2 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191 | A five day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness |
| 85% improved symptoms (p=0.09), 76% improved viral clearance (p=0.03), and 1% shorter hospitalization. Small 72 patient RCT of ivermectin and ivermectin + doxycycline showing faster recovery with ivermectin. The ivermectin + doxycycline group uses only a single dose of ivermectin vs. 5 daily doses for the ivermectin group. PCR testing was .. | ||
Dec 2 2020 |
, J. | The effect of using ivermectin to control COVID-19 in Chiapas |
| Report showing that after starting to distribute ivermectin in drug kits in July, the Mexican state of Chiapas has seen a dramatic divergence from other states with much lower mortality [sie7edechiapas.com, web.archive.org]. | ||
Dec 1 2020 |
et al., Correa Radiovisión | COVID-19: Uso de ivermectina |
| 92% lower mortality (p=0.009). Observational study in Argentina showing significantly lower mortality in the 60 days after adopting ivermectin compared to the 60 days before, relative risk RR 0.082, p=0.003. | ||
Nov 30 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.098 | Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach |
| In Silico study showing that ivermectin, rifabutin, rifapentine, fidaxomicin, and 7-methyl-guanosine-5′-triphosphate-5′-guanosine could be potential inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Authors used molecular .. | ||
Nov 30 2022 |
et al., Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113706 | Ivermectin contributes to attenuating the severity of acute lung injury in mice |
| Animal study showing dose dependent inhibition of lung injury with ivermectin. In lipopolysaccharide and bleomycin-induced mouse models of acute lung injury, treatment with ivermectin improved survival rates, body weight loss, lung injury.. | ||
Nov 28 2020 |
et al., Annals of Dermatology and Venereology, doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.09.231 | Ivermectin benefit: from scabies to COVID-19, an example of serendipity |
| 99% lower mortality (p=0.08) and 55% fewer cases (p=0.01). 69 residents of a French care home, median age 90, were treated with ivermectin for a scabies outbreak. 3,062 residents in 45 nearby comparable homes were used as controls. 7 of 69 treated patients had probable or certain COVID-19, with n.. | ||
Nov 28 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106248 | A COVID-19 Prophylaxis? Lower incidence associated with prophylactic administration of Ivermectin |
| 78% fewer cases (p=0.02). Analysis of COVID-19 cases vs. widespread prophylactic use of ivermectin for parasitic infections showing significantly lower incidence of COVID-19 cases. | ||
Nov 24 2020 |
et al., Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, doi:10.4103/1995-7645.318304 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multi-center clinical trial |
| 82% lower mortality (p=0.001). 82% lower mortality with ivermectin. RCT with 180 hospitalized patients showing reduced mortality and hospital stay with ivermectin, with a wide margin of safety. All patients received SOC including low dose HCQ. Analysis suggests randomi.. | ||
Nov 22 2020 |
et al., EMBO Mol. Med., doi:10.15252/emmm.202114122 (date from preprint) | Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin |
| Animal study showing that standard doses of ivermectin prevented clinical deterioration, reduced olfactory deficit, and limited inflammation in the upper and lower respiratory tracts of SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters. | ||
Nov 18 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.11.16.20232223 | Clinical Profile of First 1000 COVID-19 Cases Admitted at Tertiary Care Hospitals and the Correlates of their Mortality: An Indian Experience |
| 99% lower mortality (p=0.04). Retrospective 976 hospitalized patients with 34 treated with ivermectin showing lower mortality with ivermectin in unadjusted results. | ||
Nov 17 2020 |
et al., Journal of Biomedical Research and Clinical Investigation, doi:10.31546/2633-8653.1007 | Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Topical Ivermectin + Iota-Carrageenan in the Prophylaxis against COVID-19 in Health Personnel |
| 100% fewer cases (p<0.0001). Prophylaxis study using ivermectin and iota-carrageenan showing 0 of 788 cases from treated healthcare workers, compared to 237 of 407 control. See [doyourownresearch.substack.com] for discussion of issues with this trial. | ||
Nov 14 2020 |
et al., IAIM, 2020, 7:10, 177-182 | Utility of Ivermectin and Doxycycline combination for the treatment of SARSCoV-2 |
| 21% faster recovery (p=0.03) and 16% shorter hospitalization (p=0.01). 100 patient prospective trial of ivermectin + doxycycline showing reduced time to symptom resolution and shorter hospital stay with treatment. | ||
Nov 13 2020 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-100956/v2 | Efficacy and Safety of Ivermectin for Treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 Pandemic |
| This study was withdrawn. | ||
Nov 11 2020 |
et al., PLoS ONE, 15:11, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0242184 | Lack of efficacy of standard doses of ivermectin in severe COVID-19 patients |
| 40% lower ventilation (p=0.67), 33% lower ICU admission (p=1), 33% worse improvement (p=1), and 25% worse viral clearance (p=1). Tiny 26 patient retrospective study of very late treatment with ivermectin 200 μg/kg, median 12 days after symptoms, not showing significant differences. Authors suggest the dose is too low and recommend evaluation of higher doses. All pa.. | ||
Nov 10 2020 |
, M., ResearchGate | FLCCC Alliance MATH+ ascorbic acid and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocols for COVID-19 — a brief review |
| Review suggesting that ivermectin should be used based on existing data suggesting significant benefits, and that waiting for additional data may result in significant harm. | ||
Nov 4 2020 |
et al., New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915 (date from preprint) | Early COVID-19 Therapy with azithromycin plus nitazoxanide, ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine in Outpatient Settings Significantly Improved COVID-19 outcomes compared to Known outcomes in untreated patients |
| 94% lower ventilation (p=0.005) and 98% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001). Comparison of HCQ, nitazoxanide, and ivermectin showing similar effectiveness for overall clinical outcomes in COVID-19 when used before seven days of symptoms, and overwhelmingly superior compared to the untreated COVID-19 population, ev.. | ||
Nov 3 2020 |
et al., J. Clinical Trials (date from preprint) | The Use of Compassionate Ivermectin in the Management of Symptomatic Outpatients and Hospitalized Patients with Clinical Diagnosis of Covid-19 at the Centro Medico Bournigal and at the Centro Medico Punta Cana, Grupo Rescue, Dominican Republic, from May 1 to August 10, 2020 |
| Retrospective 3,099 outpatients treated with ivermectin in an ER. Of 2,706 treated on an outpatient basis, 18 were subsequently hospitalized, 2 in the ICU, and there was one death (0.04%). The average treatment delay for patients treated .. | ||
Nov 3 2020 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247163 (date from preprint) | Role of ivermectin in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers in India: A matched case-control study |
| 54% fewer cases (p=0.0007). Retrospective matched case-control prophylaxis study for HCQ, ivermectin, and vitamin C with 372 healthcare workers, showing lower COVID-19 incidence for all treatments, with statistical significance reached for ivermectin. HCQ OR 0.56, p.. | ||
Nov 2 2020 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86679-0 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model |
| Mouse study showing ivermectin reducing MHV viral load and disease. MHV is a type 2 family RNA coronavirus similar to SARS-CoV2. | ||
Oct 31 2020 |
et al., ResearchGate | COVID-19: Effectiveness of pre-exposure prophylaxis with ivermectin in exposed persons |
| Pre-exposure prophylaxis study with 129 people split into high/low exposure groups, with each group split into different dosing regimens, showing higher effectivess with more frequent doses. High-exposure group: every 7 days dosing: 0 of .. | ||
Oct 31 2020 |
et al., Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101906 | Risk of Hospitalization for Covid-19 Outpatients Treated with Various Drug Regimens in Brazil: Comparative Analysis |
| 14% higher hospitalization (p=0.53). Retrospective 717 patients in Brazil showing OR 1.17 [0.72-1.90] for ivermectin. This paper focuses on HCQ, event counts for ivermectin are not provided. With significant correlation between the variables used, including overlap in the pr.. | ||
Oct 26 2020 |
et al., Iraqi Journal of Medical Science, 19:1 | Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq |
| 92% lower mortality (p=0.03), 83% lower progression (p=0.07), and 41% faster recovery (p=0.0001). RCT 70 ivermectin+doxycycline patients and 70 control patients showing reduced time to recovery and reduced mortality with treatment. Earlier treatment was more successful. For ethical reasons, critical patients were all in the treatment .. | ||
Oct 22 2020 |
et al., Colombia Médica, doi:10.25100/cm.v51i4.4613 | COVID-19: The Ivermectin African Enigma |
| Study of African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control (APOC) countries, which used ivermectin, with non-APOC countries in Africa, showing 28% lower mortality for APOC countries, relative risk RR = 0.72 [0.67-0.78]. See also.. | ||
Oct 19 2020 |
et al., NCT04425850 | Usefulness of Topic Ivermectin and Carrageenan to Prevent Contagion of Covid 19 (IVERCAR) |
| 96% fewer cases (p<0.0001). Prophylaxis study using ivermectin and carrageenan showing 0 of 131 cases from treated healthcare workers, compared to 11 of 98 control. The effect is likely to be primarily due to ivermectin - the author has later reported that carrageen.. | ||
Oct 13 2020 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74084-y | Nebulized ivermectin for COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases, a proof of concept, dose-ranging study in rats |
| Study showing that nebulized ivermectin can reach pharmacodynamic concentrations in the lung tissue of rats. Authors note that additional experiments are required to assess the safety of this formulation in larger animals. | ||
Oct 13 2020 |
et al., Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009 | Use of Ivermectin is Associated with Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 (ICON study) |
| 46% lower mortality (p=0.05) and 64% lower ventilation (p=0.1). Retrospective 280 hospitalized patients showing lower mortality with ivermectin (13.3% vs 24.5%), propensity matched odds ratio OR 0.47 [0.22-0.99], p=0.045. | ||
Oct 9 2020 |
et al., Journal of International Medical Research, doi:10.5061/dryad.qjq2bvqf6 (date from preprint) | Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial |
| 86% lower mortality (p=0.25), 57% lower progression (p=0.001), 94% improved recovery (p<0.0001), and 39% improved viral clearance (p=0.002). RCT for ivermectin+doxycycline showing improvements in mortality, recovery, progression, and virological cure. 183 treatment and 183 control patients with no deaths in the treatment arm vs. 3 in the control arm (the 3 control deaths are n.. | ||
Oct 8 2020 |
et al., ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12782258.v1 | Has Ivermectin Virus-Directed Effects against SARS-CoV-2? Rationalizing the Action of a Potential Multitarget Antiviral Agent |
| In silico study showing that ivermectin is capable of interfering in different key steps of the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle. | ||
Oct 8 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.06.20208066 | Real-World Effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and ivermectin among hospitalized COVID-19 patients: Results of a target trial emulation using observational data from a nationwide Healthcare System in Peru |
| 17% lower mortality (p=0.01). Retrospective database study of 5683 patients, 692 received HCQ/CQ+AZ, 200 received HCQ/CQ, 203 received ivermectin, 1600 received AZ, 358 received ivermectin+AZ, and 2630 received standard of care. This study includes anyone with ICD-10 .. | ||
Sep 30 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Sciences, 9:31-35, doi:10.18483/ijSci.2378 | Effectiveness of Ivermectin in SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Patients |
| 10% improved recovery (p=0.5). Small RCT with 25 ivermectin and 25 control patients, not finding a significant difference in recovery at day 7. | ||
Sep 24 2020 |
et al., Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1824816 | Repurposing of the approved small molecule drugs in order to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 S protein and human ACE2 interaction through virtual screening approaches |
| In Silico study showing favorable binding of several FDA-approved drugs to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD). Authors performed structure-based virtual screening of FDA drug libraries and identified ivermectin, di.. | ||
Sep 24 2020 |
et al., Archivos de Bronconeumología, doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007 | Ivermectin treatment may improve the prognosis of patients with COVID-19 |
| 87% lower mortality (p=0.02), 89% lower ICU admission (p=0.007), 83% lower progression (p=0.0004), and 87% improved recovery (p=0.02). Retrospective 115 ivermectin patients and 133 control patients showing significantly lower death and faster viral clearance. Some potential issues and the authors' response can be found in [sciencedirect.com, sciencedirect.com]. | ||
Sep 22 2020 |
et al., J. Cellular Physiology, doi:10.1002/jcp.30055 | Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment |
| In Vitro study showing Ivermectin is a safe wide-spectrum antiviral against SARS-CoV-2, human papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), and HIV. Authors note that the combination of ivermectin and other drugs might result in more fa.. | ||
Sep 15 2020 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Trials, 11:459 (date from preprint) | Safety and Efficacy of the Combined Use of Ivermectin, Dexamethasone, Enoxaparin and Aspirina against COVID-19 the I.D.E.A. Protocol |
| 85% lower mortality (p=0.08). Prospective trial of ivermectin, dexamethasone, enoxaparin, and aspirin, showing no hospitalization for mild cases, and lower mortality for moderate/severe patients. | ||
Sep 15 2020 |
et al., Cells 2020, 9:9, 2100, doi:10.3390/cells9092100 | Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal? |
| Review of ivermectin as a host-directed broad-spectrum antiviral agent for a range of viruses, including SARS-CoV-2. Cell culture experiments show robust antiviral action towards HIV-1, dengue virus (DENV), Zika virus, West Nile virus, Ve.. | ||
Sep 11 2020 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10378 | Ivermectin: A Closer Look at a Potential Remedy |
| Proposal to use inhaled ivermectin for COVID-19. Author notes that ivermectin may have broad-spectrum antiviral properties and research in this area may also be beneficial for other emerging viral outbreaks in the future. | ||
Sep 9 2020 |
, A., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1 | Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: Evidence from in silico studies |
| In Silico study showing high binding affinity of ivermectin with SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, suggesting ivermectin as an inhibitor of RdRp. | ||
Sep 6 2020 |
et al., Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350 | Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19 |
| Review suggesting that ivermectin may be useful for late stage COVID-19. Authors note that ivermectin, in doses at or modestly above the standard clinical dose, may have important clinical potential for managing disorders associated with.. | ||
Sep 3 2020 |
et al., IMC J. Med. Science, doi:10.3329/imcjms.v14i2.52826 | Outcome of ivermectin treated mild to moderate COVID-19 cases: a single-centre, open-label, randomised controlled study |
| 16% faster recovery (p=0.34). Small RCT with 32 ivermectin patients and 30 control patients. The mean recovery time after enrolment in the intervention arm was 5.31 ± 2.48 days vs. 6.33 ± 4.23 days in the control arm, p > 0.05. Negative PCR results were not significan.. | ||
Sep 1 2020 |
et al., NCT04425707 | Ivermectin In Treatment of COVID 19 Patients |
| Estimated 100 patient ivermectin early treatment RCT with results not reported over 4 years after estimated completion. | ||
Aug 31 2020 |
et al., Paripex - Indian Journal of Research, doi:10.36106/paripex/4801859 | Ivermectin as adjuvant to hydroxychloroquine in patients resistant to standard treatment for SARS-CoV-2: results of an open-label randomized clinical study |
| 8% lower hospital discharge (p=1) and 8% worse viral clearance (p=1). Small RCT of hospitalized patients in India with 19 ivermectin patients and 13 control patients, with all receiving SOC including HCQ, showing no significant differences. The patient population is biased because the study recruited patien.. | ||
Aug 28 2020 |
et al., Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, doi:10.7860/JCDR/2021/46795.14529 | Use of Ivermectin as a Potential Chemoprophylaxis for COVID-19 in Egypt: A Randomised Clinical Trial |
| 91% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.001) and 93% lower severe cases (p=0.002). PEP trial for asymptomatic close contacts of COVID-19 patients, 203 ivermectin patients and 101 control patients. 7.4% of contacts developed COVID-19 in the ivermectin group vs. 58.4% in the control group. Efficacy for symptomatic cases a.. | ||
Aug 15 2020 |
et al., Biomedical Research, 31:5 | Effects of Ivermectin-azithromycin-cholecalciferol combined therapy on COVID-19 infected patients: A proof of concept study |
| 70% faster recovery (p=0.0001) and 97% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). Small study with 28 patients treated with ivermectin + AZ + cholecalciferol and 7 control patients. All treated patients were PCR- at day 10 while all control patients remained PCR+. The mean duration of symptoms was 3 days in the treatme.. | ||
Aug 14 2020 |
et al., Int. J. Scientific Research, doi:10.36106/ijsr/7232245 | Observational Study on Clinical Features, Treatment and Outcome of COVID 19 in a tertiary care Centre in India- a retrospective case series |
| Retrospective 148 hospitalized patients showing triple therapy with ivermectin + atorvastatin + N-acetylcysteine resulted in a 1.35% case fatality rate which was well below the national average. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.07.031 | White paper on Ivermectin as a potential therapy for COVID-19 |
| Panel review of ivermectin reporting that "ivermectin in the dose of 12mg BD alone or in combination with other therapy for 5–7 days may be considered as safe therapeutic option for mild moderate or severe cases of Covid-19 infection.. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., ResearchGate | Post-acute or prolonged COVID-19: ivermectin treatment for patients with persistent symptoms or post-acute symptoms |
| Report on 33 patients with persistent or post-acute symptoms treated with ivermectin, showing a high rate of clinical improvement. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.34561.48483/2 | COVID-19: Post-exposure prophylaxis with ivermectin in contacts. At Homes, Places of Work, Nursing Homes, Prisons, and Others |
| Proposed PEP protocol based on ivermectin. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons, doi:10.3329/jbcps.v38i0.47512 | A Case Series of 100 COVID-19 Positive Patients Treated with Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline |
| Case study of 100 patients treated with ivermectin and doxycycline, with no ICU admission, deaths, or serious side effects reported. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., J. Bangladesh Coll. Phys. Surg. 38, 5-9, doi:10.3329/jbcps.v38i0 | Comparison of Viral Clearance between Ivermectin with Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine with Azithromycin in COVID-19 Patients |
| Comparison of 200 patients treated with ivermectin + doxycycline and 200 treated with HCQ + AZ. The HCQ + AZ group had more severe cases at baseline. Viral clearance was faster with ivermectin + doxycycline, however ivermectin clearance r.. | ||
Jul 21 2020 |
et al., Research Gate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.11985.35680/3 | COVID-19: Ivermectin Prophylaxis in Adult Contacts: First Report on Health Personnel and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis |
| Report on ivermectin post-exposure prophylaxis with 33 patients, showing no cases over 21 days followup. | ||
Jul 14 2020 |
et al., Eurasian Journal of Medicine and Oncology, doi:10.14744/ejmo.2021.16263 | A Comparative Study on Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin Therapy on COVID-19 Patients |
| 81% lower hospitalization (p=0.23), 46% improved recovery (p<0.0001), and 81% improved viral clearance (p=0.23). Small 116 patient RCT with low-risk patients comparing ivermectin+doxycycline and HCQ+AZ, showing lower hospitalization, higher viral clearance, and faster symptom resolution and viral clearance with ivermectin+doxycycline. Mid-recovery r.. | ||
Jul 9 2020 |
, D., American Chemical Society (ACS), doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12630539.v1 | A Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Possibly Blocks the Viral Entry and Modulate the Innate Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients |
| In Silico study showing that a combination of ivermectin and doxycycline may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection through binding to multiple viral proteins as well as the host ACE2 receptor. Authors suggest that ivermectin may block viral entry .. | ||
Jul 8 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.07.20145979 | Effectiveness of Ivermectin as add-on Therapy in COVID-19 Management (Pilot Trial) |
| 42% shorter hospitalization (p<0.0001). Small trial of hospitalized patients with 16 of 87 patients being treated with ivermectin, showing a significantly lower mean hospital stay with ivermectin: 7.62 vs. 13.22 days, p=0.00005. 0 of 16 ivermectin patients died vs. 2 of 71 cont.. | ||
Jun 19 2020 |
et al., In Vivo, 34:5, 3023-3026, doi:10.21873/invivo.12134 | Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2 |
| In silico analysis showing ivermectin may interfere with the attachment of the spike to the human cell membrane. | ||
Jun 16 2020 |
et al., Preprint | Intervención de la Ivermectina Pre-Hospitalaria para la Modificación de la Evolución del Covid19. Estudio realizado en Perú |
| Prospective study of 63 outpatients in Peru treated with ivermectin, reporting significant improvement within 24 hours. | ||
Jun 12 2020 |
et al., The Journal of Antibiotics, 73, 593–602, doi:10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z | Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen |
| Review of the antimicrobial, antiviral, and anti-cancer properties of ivermectin. Antiviral effects have been reported for Zika, dengue, yellow fever, West Nile, Hendra, Newcastle, Venezuelan equine encephalitis, chikungunya, Semliki Fore.. | ||
Jun 7 2020 |
et al., Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3 | Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins |
| In Silico study reporting that ivermectin had the best affinity towards all targeted proteins and showed efficient binding to non-structural proteins. | ||
May 20 2020 |
et al., Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.1909 | Prioritization of Anti-SARS-Cov-2 Drug Repurposing Opportunities Based on Plasma and Target Site Concentrations Derived from their Established Human Pharmacokinetics |
| Pharmacokinetic analysis predicting that ivermectin, HCQ, CQ, and azithromycin will achieve lung concentrations well over 10 times higher than the reported EC50. Nitazoxanide had a lung tissue Cmax/EC50 of 7.8. | ||
May 2 2020 |
, G., Research Gate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.34689.48482/7 | Inclusión de la ivermectina en la primera línea de acción terapéutica para COVID-19 |
| Peru observational case study of 7 patients treated with ivermectin, showing improvement and resolution of fever within 48 hours, and 100% recovery. | ||
Apr 21 2020 |
et al., Antiviral Res., doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805 | Ivermectin and COVID-19: A report in Antiviral Research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors' responses |
| Responses to Caly et al., and the author's reply. The original authors note that "ivermectin's key direct target in mammalian cells is a not a viral component, but a host protein important in intracellular transport; the fact that it.. | ||
Apr 3 2020 |
et al., Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787 | The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro |
| In Vitro study showing that ivermectin is an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2, with a single addition to Vero-hSLAM cells 2h post infection with SARS-CoV-2 able to effect ~5000-fold reduction in viral RNA at 48h. There are claims that this study s.. | ||
Dec 31 2012 |
et al., Veterinary Parasitology, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011 | Dexamethasone treatment interferes with the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin in young cattle |
| Analysis of ivermectin and dexamethasone treatment in cattle, showing that dexamethasone interfered with the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin and reduced the efficacy of ivermectin. | ||
Jan 29 2011 |
et al., Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8 | Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma |
| Mouse study showing ivermectin significantly reduced airway inflammation, Th2 cytokine production, mucus hypersecretion, and airway hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Ivermectin lessened lung inflammation by decreasi.. | ||
Nov 13 2008 |
et al., Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8 | Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice |
| Analysis of ivermectin's effects in mouse models of lethal endotoxemia, which mimics key pathological features seen in severe and critical COVID-19 cases. Pretreatment with ivermectin significantly improved survival rates in mice given a .. | ||
Mar 31 2005 |
et al., Veterinary Parasitology, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.11.028 | Influence of the route of administration on efficacy and tissue distribution of ivermectin in goat |
| Pharmacokinetic analysis of ivermectin in goats, showing that tissue concentration can be several times higher than plasma concentration. | ||
Oct 1 2002 |
et al., J. Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1177/009127002237994 | Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Escalating High Doses of Ivermectin in Healthy Adult Subjects |
| Safety study concluding that ivermectin was generally well tolerated, with no indication of associated CNS toxicity for doses up to 10 times the highest FDA-approved dose. Adverse effects were similar between ivermectin and placebo and di.. | ||
Feb 29 2000 |
et al., Veterinary Parasitology, doi:10.1016/s0304-4017(99)00175-2 | Comparative distribution of ivermectin and doramectin to parasite location tissues in cattle |
| Pharmacokinetic analysis of ivermectin in cattle, showing that tissue concentration can be several times higher than plasma concentration. | ||
Nov 1 1990 |
et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., doi:10.1021/jf00101a015 | Absorption, tissue distribution, and excretion of tritium-labeled ivermectin in cattle, sheep, and rat |
| Animal study showing that lung tissue concentration of ivermectin may be ~20 times higher than plasma concentration. | ||
For search methods, inclusion criteria, effect extraction
criteria (more serious outcomes have priority), PRISMA answers, and
statistical methods see methods.
Studies with preprints and journal versions are listed under the earlier
preprint date.
References
Hayward et al., Ivermectin for COVID-19 in adults in the community (PRINCIPLE): an open, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial of short- and longer-term outcomes, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106130.
Please send us corrections, updates, or comments.
c19early involves the extraction of 200,000+ datapoints from
thousands of papers. Community updates
help ensure high accuracy.
Treatments and other interventions are complementary.
All practical, effective, and safe
means should be used based on risk/benefit analysis.
No treatment or intervention is 100% available and effective for all current
and future variants.
We do not provide medical advice. Before taking any medication,
consult a qualified physician who can provide personalized advice and details
of risks and benefits based on your medical history and situation. IMA and WCH
provide treatment protocols.
Thanks for your feedback! Please search before submitting papers and note
that studies are listed under the date they were first available, which may be
the date of an earlier preprint.