Comparative Analytical Study of Two Different Drug Regimens in Treatment of Covid 19 Positive Patients in Index Medical College Hospital and Research Center, Indore, India
Sudhir Mourya, Ajay Singh Thakur, Deepti Singh Hada, Vibhu Sagar Kulshreshtha, Yash Sharma
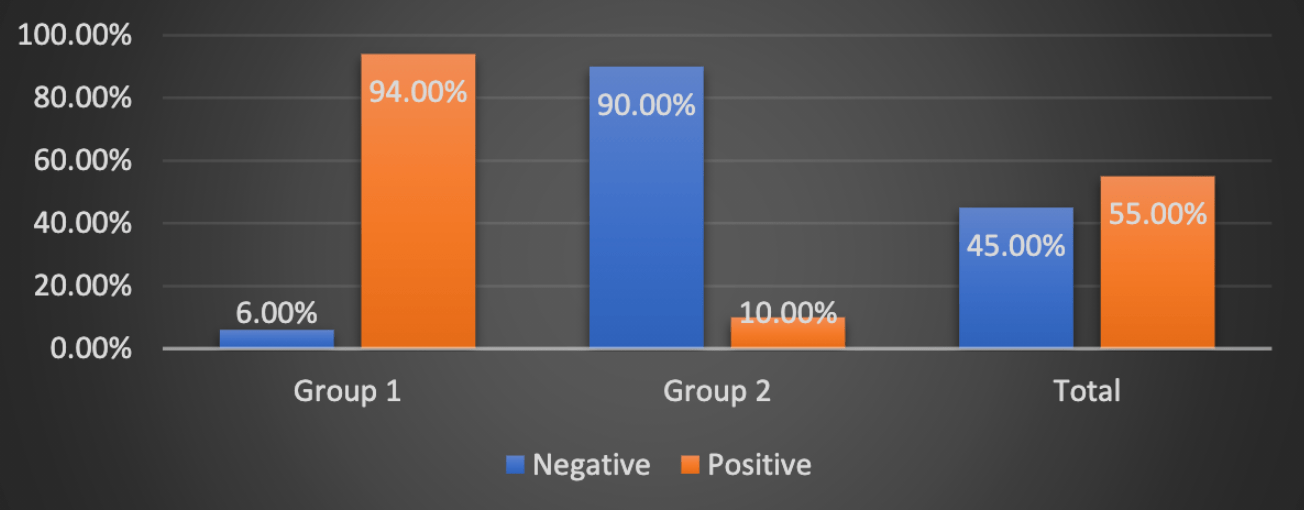
Background: SARS-CoV-2 is a novel virus that first emerged in Wuhan, China. Considering the novel nature of the coronavirus, there are not yet any proven treatment strategies. In this emergency, there is no specific pharmacologic treatment that specifically targets and kill the virus or control the infection and improve the clinical outcomes. Several drugs were repurposed for this illness based on in-vitro studies or minimal evidence to combat the rapid spread of the COVID-19 pandemic.Aims and objectives: To compare efficacy of two regimens', Regimen 1 (hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) and Regimen 2 (hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin and ivermectin) in Covid-19 positive patients. Materials and methods: An observation study on 100 Covid 19 positive patients having age between 20-60 years of either sex was conducted from April to May 2020. Patients below 20 years of and above 60 years of age and having chronic conditions like hypertension, diabetes and others were excluded. Group 1 received oral hydroxychloroquine 400 mg twice a day with azithromycin 500 mg once a day. Both medications were given by per oral route for a period of 7 days. Group 2 received hydroxychloroquine 400 mg twice a day with azithromycin 500 mg once a day and ivermectin 12 mg once a day. All medications were given by per oral route for a period of 7 days.Results: Mean age of patients in Group 1 and Group 2 was 37.62 ± 11.609 years and 38.20±11.73 years respectively (p=0.804). No significant difference was obtained between the SpO2 concentration (p=0.778). When we did final the COVID-19 testing, it showed that majority of the patients were found negative in the group 2, whereas 94% were found to be positive in the group 1. This difference was statistically significant with the p value of <0.001.
Conclusion: The treatment with HCQ, azithromycin, and ivermectin had a better success rate compared to HCQ and azithromycin. Based on the results, ivermectin could be the potential therapeutic agents for the COVID-19 disease. The study had various limitations; so further randomized controlled trial is required for the results to be implemented on the larger population.
Conflict of Interest: Nil Source of support:Nil
References
Baby, Maity, Mehta, Suresh, Nayak et al., Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Computational Drug Repurposing Study, Arch Med Res
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hoang, Meddeb et al., Clinical and microbiological effect of a combination of Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin in 80 COVID-19 patients with at least a six-day follow up: an observational study, Mediterr-Infect
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Gorial, Mashhadani, Sayaly, Dakhil, Mashhadani et al., Effectiveness of Ivermectin as add-on Therapy in COVID-19 Management, Pilot Trial
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot
Juul, Nielsen, Feinberg, Siddiqui, Jørgensen et al., Interventions for treatment of COVID-19: A living systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses (The LIVING Project), PLOS Medicine
Richman, Antiviral Drug Discovery to Address the COVID-19 Pandemic, mBio
Sohag, Hannan, Rahman, Hossain, Hasan et al., Revisiting potential druggable targets against SARS-CoV-2 and repurposing therapeutics under preclinical study and clinical trials: A comprehensive review, Drug Dev Res
Yu, Li, Wang, Duan, Yang et al., Techniques and strategies for the potential protein-targets discovery and active pharmaceutical molecules screening in Pandemic, Journal of Proteome Research
Õmura, Ivermectin: 25 years and still going strong, Int J Antimicrob Agents