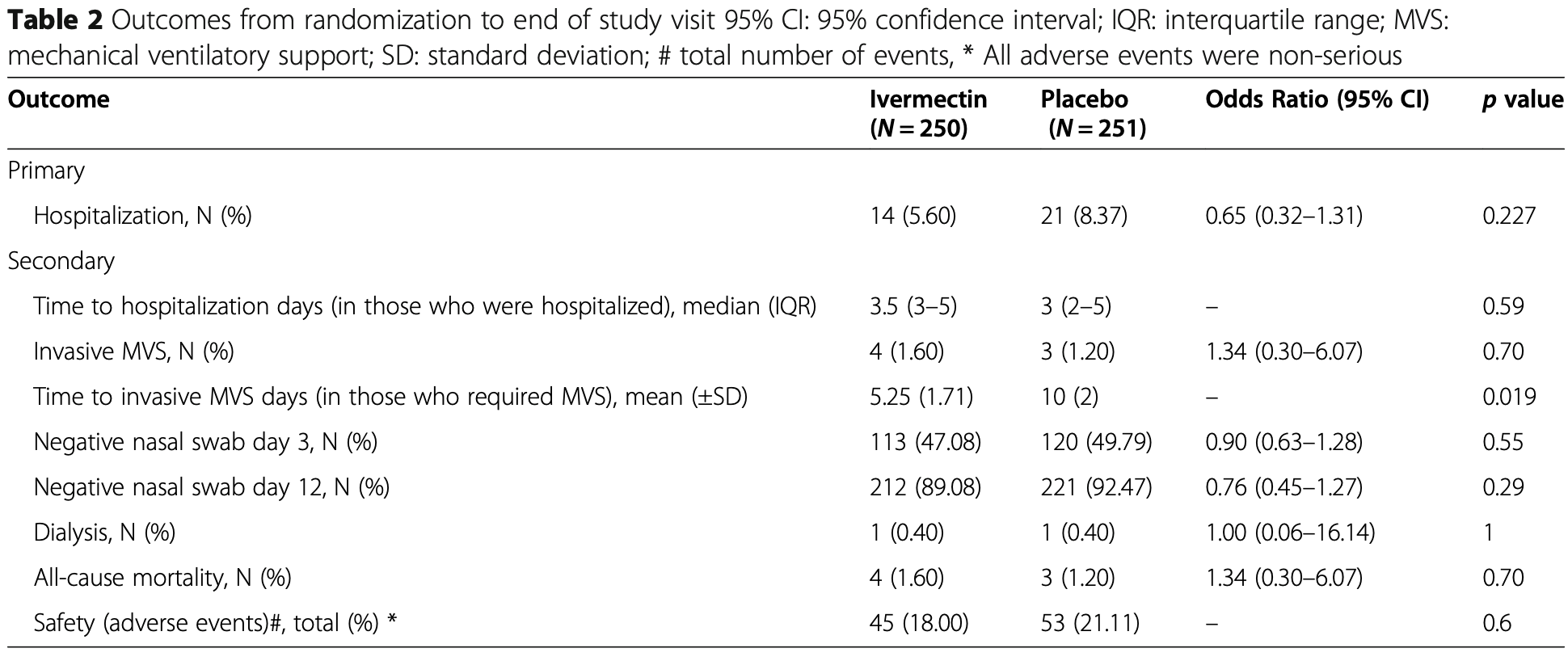
Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Julio Vallejos, Rodrigo Zoni, María Bangher, Silvina Villamandos, Angelina Bobadilla, Fabian Plano, Claudia Campias, Evangelina Chaparro Campias, Maria Fernanda Medina, Fernando Achinelli, Hector Andres Guglielmone, Jorge Ojeda, Diego Farizano Salazar, Gerardo Andino, Pablo Kawerin, Silvana Dellamea, Antonia Cristina Aquino, Victor Flores, Carolina N Martemucci, Silvina Maria Martinez, Juan Emanuel Segovia, Paola Itati Reynoso, Noelia Carolina Sosa, Mariana Elizabeth Robledo, Joaquina Maria Guarrochena, Maria Mercedes Vernengo, Natalia Ruiz Diaz, Elba Meza, María Gabriela Aguirre
BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) has changed our lives. The scientific community has been investigating re-purposed treatments to prevent disease progression in coronavirus disease patients. Objective: To determine whether ivermectin treatment can prevent hospitalization in individuals with early COVID-19. Design, setting and participants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in nonhospitalized individuals with COVID-19 in Corrientes, Argentina. Patients with SARS-CoV-2 positive nasal swabs were contacted within 48 h by telephone to invite them to participate. The trial randomized 501 patients between August 19th 2020 and February 22nd 2021. Intervention: Patients were randomized to ivermectin (N = 250) or placebo (N = 251) arms in a staggered dose, according to the patient's weight, for 2 days. Main outcomes and measures: The efficacy of ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations was evaluated as primary outcome. We evaluated secondary outcomes in relationship to safety and other efficacy end points.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi. org/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5.
Additional file 1.
Authors' contributions
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate study authorized by Health Sciences Research Bioethics Committee (HSRBC) of the National University of the Northeast (UNNE) Faculty of Medicine, Argentina (Resolution 21/20 on August 17th, 2020). The consent to participate in the trial was approved by HSRBC of the UNNE. The study was performance in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the study. The study has been supervised by a Steering Committee and Safety Committee.
Consent for publication Not Applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Ahmed, Hany, Youssef, Hany, Hafez et al., Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 pandemic,
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-100956/v1Al-Abdouh, Bizanti, Barbarawi, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Contemp Clin Trials,
doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106272Babalola, Bode, Ajayi, Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double blind dose response study in Lagos. medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.01.05.21249131Bartoli, Gabrielli, Alicandro, Nascimbeni, Andreoni, COVID-19 treatment options: a difficult journey between failed attempts and experimental drugs, Intern Emerg Med,
doi:10.1007/s11739-020-02569-9Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -final report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764Camprubí, Almuedo-Riera, Martí-Soler, Lack of efficacy of standard doses of ivermectin in severe COVID-19 patients, PLoS One
Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebocontrolled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720Gotz, Magar, Dornfeld, Influenza a viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci Rep,
doi:10.1038/srep23138Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Dhurgham, Fatak et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq medRxiv Preprint,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345Khan, Khan, Debnath, Nath, Mahtab et al., Ivermectin treatment may improve the prognosis of patients with COVID
Lai, Liu, Wang, Wang, Hsueh et al., Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): facts and myths, J Microbiol Immunol Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012Libster, Marc, Wappner, Coviello, Bianchi et al., Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033700López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Dávalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Mahmud, Rahman, Alam, Ahmed, Kabir et al., Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial, J Int Med Res,
doi:10.1177/03000605211013550Mega, Latin America's embrace of an unproven COVID treatment is hindering drug trials, Nature
Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and metaanalysis, J Antimicrob Chemother,
doi:10.1093/jac/dkz524Padhy, Mohanty, Das, Meher, Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Pharm Pharm Sci,
doi:10.18433/jpps31457Ross, Clemens, Sumiya, A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191Salama, Han, Yau, Reiss, Kramer et al., Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2030340Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Beruto, Vallone et al., A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031304Tay, Fraser, Chan, Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antivir Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Villamandos, Bobadilla et al., Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04813-1Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin alpha/betamediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem J,
doi:10.1042/BJ20120150Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 inWuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2334"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) has changed our lives. The scientific community has been investigating re-purposed treatments to prevent disease progression in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To determine whether ivermectin treatment can prevent hospitalization in individuals with early COVID-19.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Design, setting and participants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in non-hospitalized individuals with COVID-19 in Corrientes, Argentina. Patients with SARS-CoV-2 positive nasal swabs were contacted within 48 h by telephone to invite them to participate. The trial randomized 501 patients between August 19th 2020 and February 22nd 2021.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Intervention</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Patients were randomized to ivermectin (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic> = 250) or placebo (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic> = 251) arms in a staggered dose, according to the patient’s weight, for 2 days.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Main outcomes and measures</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The efficacy of ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations was evaluated as primary outcome. We evaluated secondary outcomes in relationship to safety and other efficacy end points.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The mean age was 42 years (SD ± 15.5) and the median time since symptom onset to the inclusion was 4 days [interquartile range 3–6]. The primary outcome of hospitalization was met in 14/250 (5.6%) individuals in ivermectin group and 21/251 (8.4%) in placebo group (odds ratio 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.32–1.31; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.227). Time to hospitalization was not statistically different between groups. The mean time from study enrollment to invasive mechanical ventilatory support (MVS) was 5.25 days (SD ± 1.71) in ivermectin group and 10 days (SD ± 2) in placebo group, (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.019). There were no statistically significant differences in the other secondary outcomes including polymerase chain reaction test negativity and safety outcomes.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Limitations</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Low percentage of hospitalization events, dose of ivermectin and not including only high-risk population.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Ivermectin had no significant effect on preventing hospitalization of patients with COVID-19. Patients who received ivermectin required invasive MVS earlier in their treatment. No significant differences were observed in any of the other secondary outcomes.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>ClinicalTrials.gov <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04529525\">NCT04529525</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"6348"
],
"article-number": "635",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "6 May 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "17 June 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "2 July 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study was authorized by the Health Sciences Research Bioethics Committee (HSRBC) of the National University of the Northeast (UNNE) Faculty of Medicine, Argentina (Resolution 21/20 on August 17th, 2020). The consent to participate in the trial was approved by HSRBC of the UNNE. The study was performance in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the study. The study has been supervised by a Steering Committee and Safety Committee."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not Applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vallejos",
"given": "Julio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zoni",
"given": "Rodrigo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bangher",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Villamandos",
"given": "Silvina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bobadilla",
"given": "Angelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plano",
"given": "Fabian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campias",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaparro Campias",
"given": "Evangelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Medina",
"given": "Maria Fernanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Achinelli",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guglielmone",
"given": "Hector Andres",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ojeda",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farizano Salazar",
"given": "Diego",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andino",
"given": "Gerardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kawerin",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dellamea",
"given": "Silvana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aquino",
"given": "Antonia Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flores",
"given": "Victor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martemucci",
"given": "Carolina N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martinez",
"given": "Silvina Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Segovia",
"given": "Juan Emanuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reynoso",
"given": "Paola Itati",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sosa",
"given": "Noelia Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robledo",
"given": "Mariana Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guarrochena",
"given": "Joaquina Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vernengo",
"given": "Maria Mercedes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruiz Diaz",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meza",
"given": "Elba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aguirre",
"given": "María Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "BMC Infect Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-02T10:03:52Z",
"timestamp": 1625220232000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-02T10:04:14Z",
"timestamp": 1625220254000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T17:20:42Z",
"timestamp": 1712596842315
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 70,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625184000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625184000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "6348_CR1",
"unstructured": "Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. Coronavirus resource center. Accessed 22 Mar 2021. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "China Lancet",
"key": "6348_CR2",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "6348_CR3",
"unstructured": "Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 inWuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012",
"author": "CC Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "404",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "6348_CR4",
"unstructured": "Lai CC, Liu YH, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Yen MY, et al. Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): facts and myths. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020;53(3):404–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02569-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6348_CR5",
"unstructured": "Bartoli A, Gabrielli F, Alicandro T, Nascimbeni F and Andreoni P. COVID-19 treatment options: a difficult journey between failed attempts and experimental drugs. Intern Emerg Med (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-020-02569-9, 16, 2, 281, 308."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "P Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "6348_CR6",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson J, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):693–704. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2021436.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "6348_CR7",
"unstructured": "Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 —final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19):1813–26. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cct.2021.106272",
"author": "A Al-Abdouh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106272",
"journal-title": "Contemp Clin Trials",
"key": "6348_CR8",
"unstructured": "Al-Abdouh A, Bizanti A, Barbarawi M, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021 Jan 7;101:106272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cct.2021.106272.",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2030340",
"author": "C Salama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "6348_CR9",
"unstructured": "Salama C, Han J, Yau L, Reiss WG, Kramer B, Neidhart JD, et al. Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):20–30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2030340.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"author": "R Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "610",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "6348_CR10",
"unstructured": "Libster R, Pérez Marc G, Wappner D, Coviello S, Bianchi A, Braem V, et al. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(7):610–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2033700.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"author": "VA Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "619",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "6348_CR11",
"unstructured": "Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, Beruto MV, Vallone MG, Vázquez C, et al. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(7):619–29. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2031304.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "6348_CR12",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.",
"volume-title": "World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep23138",
"author": "V Gotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "23138",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "6348_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gotz V, Magar L, Dornfeld D, et al. Influenza a viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):23138. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23138.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002",
"author": "MY Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "301",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "6348_CR14",
"unstructured": "Tay MY, Fraser JE, Chan WKK, et al. Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1– non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin. Antivir Res. 2013;99(3):301–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002.",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20120150",
"author": "KM Wagstaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "851",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "6348_CR15",
"unstructured": "Wagstaff KM, Sivakumaran H, Heaton SM, Harrich D, Jans DA. Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin alpha/betamediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus. Biochem J. 2012;443(3):851–6. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20120150.",
"volume": "443",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"author": "L Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "6348_CR16",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antivir Res. 2020;178:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787.",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "6348_CR17",
"unstructured": "Ministerio de Salud, Republica del Peru. Resolucion ministerial No. 270–2020-MINSA. Accessed March 8, 2021. https://cdn.www.gob.pe/uploads/document/file/694719/RM_270-2020-MINSA.PDF"
},
{
"key": "6348_CR18",
"unstructured": "Rodriguez Mega E. Latin America’s embrace of an unproven COVID treatment is hindering drug trials. Nature. Accessed March 8, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-02958-2"
},
{
"key": "6348_CR19",
"unstructured": "Ministerio de Salud, Gobierno del Estado de Bolivia. Resolucion ministerial No. 0259. Accessed March 8, 2021. https://www.minsalud.gob.bo/component/jdownloads/?task=download.send&id=425&catid=27&m=0&Itemid=646"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkz524",
"author": "M Navarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "827",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "6348_CR20",
"unstructured": "Navarro M, Camprubí D, Requena-Méndez A, Buonfrate D, Giorli G, Kamgno J, et al. Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(4):827–34. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkz524.",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211013550",
"author": "R Mahmud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "300060521101355",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Int Med Res",
"key": "6348_CR21",
"unstructured": "Mahmud R, Rahman MM, Alam I, Ahmed KGU, Kabir AKMH, Sayeed SKJB, et al. Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial. J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211013550. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211013550.",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"author": "E López-Medina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "6348_CR22",
"unstructured": "López-Medina E, López P, Hurtado IC, Dávalos DM, Ramirez O, Martínez E, et al. Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021;325(14):1426–35. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.3071. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33662102.",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "6348_CR23",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO advises that ivermectin only be used to treat COVID-19 within clinical trials. Accessed 7 June 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/who-advises-that-ivermectin-only-be-used-to-treat-covid-19-within-clinical-trials."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04813-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6348_CR24",
"unstructured": "Vallejos J, Zoni R, Bangher M, Villamandos S, Bobadilla A, Plano F, Campias C, Chaparro Campias E, Achinelli F, Guglielmone HA, Ojeda J, Medina F, Farizano Salazar D, Andino G, Ruiz Diaz NE, Kawerin P, Meza E, Dellamea S, Aquino A, Flores V, Martemucci CN, Vernengo MM, Martinez SM, Segovia JE, Aguirre MG Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 21, 965 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-020-04813-1, 1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6348_CR25",
"unstructured": "Hashim HA, Maulood MF, Rasheed AM, Dhurgham F. Fatak, Khulood K. Kabah and Ahmed S. Abdulamir. Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq medRxiv Preprint posted October 27, 2020. doi:https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-100956/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6348_CR26",
"unstructured": "Ahmed E, Hany B, Abo Youssef S, Basma Hany, Mohy Hafez and Hany Moussa. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 pandemic. Research Square. Preprint posted November 17, 2020. doi:https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-100956/v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.05.21249131",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6348_CR27",
"unstructured": "Babalola OE, Bode CO, Ajayi AA, et al. Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double blind dose response study in Lagos. medRxiv. Preprint posted January 6, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.05.21249131"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps31457",
"author": "BM Padhy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "462",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Pharm Sci",
"key": "6348_CR28",
"unstructured": "Padhy BM, Mohanty RR, Das S, Meher BR. Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2020;23:462–9. https://doi.org/10.18433/jpps31457.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "6348_CR29",
"unstructured": "Pan American Health Organization. Ongoing living update of COVID-19 therapeutic options. Summary of evidence. Rapid review, 27 May 2021. Accessed 7 June 2021. https://iris.paho.org/bitstream/handle/10665.2/52719/PAHOIMSEIHCOVID-1921017.pdf?sequence=42&isAllowed=y."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arbr.2020.08.011",
"author": "MSI Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "828",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Arch Bronconeumol",
"key": "6348_CR30",
"unstructured": "Khan MSI, Khan MSI, Debnath CR, Nath PN, Mahtab MA, Nabeka H, et al. Ivermectin treatment may improve the prognosis of patients with COVID-19. Arch Bronconeumol. 2020;56(12):828–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbr.2020.08.011.",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"author": "S Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "6348_CR31",
"unstructured": "Ahmed S, Karim MM, Ross AG, Hossain MS, Clemens JD, Sumiya MK, et al. A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;103:214–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191.",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"author": "C Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100720",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine.",
"key": "6348_CR32",
"unstructured": "Chaccour C, Casellas A, Blanco-Di Matteo A, et al. The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;32:100720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0242184",
"author": "D Camprubí",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0242184",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "6348_CR33",
"unstructured": "Camprubí D, Almuedo-Riera A, Martí-Soler H, et al. Lack of efficacy of standard doses of ivermectin in severe COVID-19 patients. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0242184.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "21"
}