Safety and Efficacy of the Combined Use of Ivermectin, Dexamethasone, Enoxaparin and Aspirina against COVID-19 the I.D.E.A. Protocol
Carvallo Hector, Hirsch Roberto
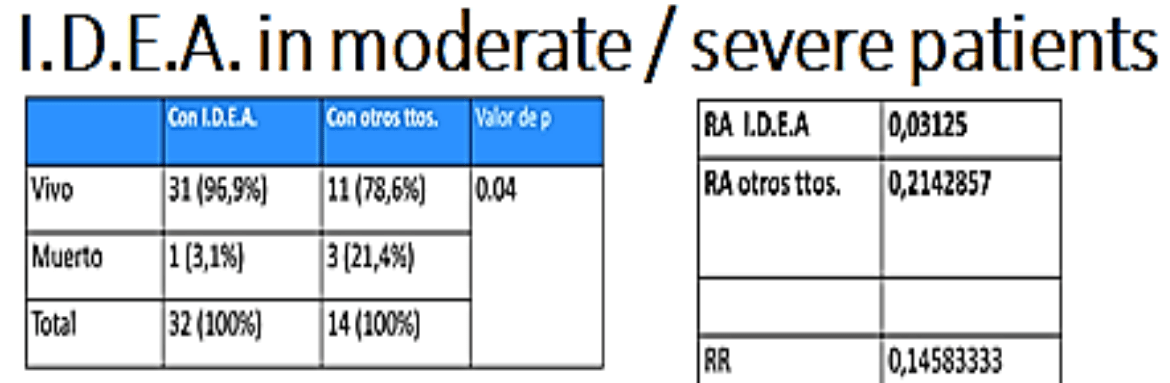
From the first outbreak in Wuhan (China) in December 2019, until today (05/28/2020), the number of deaths worldwide due to the coronavirus pandemic exceeded 2.5 millions. Only in Argentina, 50,000 deaths have been confirmed so far. There haven't been so far any clear diagnostic pattern for this exceptional entity except unilateral skin involvement, early onset of symptoms, positive ANA and negative tests for Borrelia burgdorferi. Hence, we report a new case of a young Moroccan man. No treatment tested worldwide has shown unquestionable efficacy in the fight against COVID-19, according to W.H.O, NIH and NICE reports and accumulated data. Our proposal consists of the combination of drugs, based on the pathophysiology of the virus. We have designed a treatment called I.D.E.A., based on four affordable drugs already available on the pharmacopoeia in Argentina, on the following rationale: -Ivermectin (IVM) solution to lower the viral load in all stages of COVID-19. -Dexamethasone 4 mg injection, as anti-inflammatory drug to treat hyperinflammatory reaction to COVID-infection. -Enoxaparin injection as anticoagulant to treat hypercoagulation in severe cases. -Aspirin 250 mg tablets to prevent hypercoagulation in mild and moderate cases. Except for Ivermection oral solution, which was used in a higher dose than approved for parasitosis, all other drugs were used in the already approved dose and indication. Regarding Ivermectin safety, several oral studies have shown it to be safe even when used at daily doses much higher than those approved already. A clinical study has been conducted on COVID-19 patients at Eurnekian Hospital in the Province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. The study protocol and its final outcomes are described in this article. Results were compared with published data and data from patients admitted to the hospital receiving other treatments. None of the patient presenting mild symptoms needed to be hospitalized. Only one patient died (0.59% of all included patients vs. 2.1% overall mortality for the disease in Argentina today, 3.1% of hospitalized patients vs. 26.8% mortality in published data). I.D.E.A. protocol has proved to be a very effective alternative to prevent disease progression of COVID-19 when applied to mild cases, and to decrease mortality in patients at all stages of the disease with a favorable risk-benefit ratio.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The Authors manifest no conflict of interests.
References
Baraka, Mahmoud, Marschke, Geary, Homeida et al., Ivermectin distribution in the plasma and tissues of patients infected with onchocerca volvulus, Eur J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1007/s002280050131Batya, More evidence hydroxychloroquine is ineffective, harmful in COVID-19
Bin, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Bunyavanich, Do, Vicencio, Nasal gene expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in children and adults, JAMA
Carvallo, Hirsch, Fajardo, Ciruzzi, Ivermectin, corticosteroids, aspirin and enoxaparin in COVID 19, Rev Educándonos Arch Arg Derm
Castro, Duarte, Carvalho, Preliminary study on the clinical effects of the treatment of acute Chikungunya fever using Ivermectin as an antiviral drug,
doi:10.1186/isrctn90437126Ceccotti, COVID 19 saliva and lingual mucosa
Cynthia, Safety, Tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1177/009127002401382731Edwards, Dingsdale, Helsby, Orme, Breckenridge, The relative systemic availability of ivermectin after administration as capsule, Tablet, and oral solution, Eur J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1007/bf00637608Giovannoni, Intrinsic antiviral role of PML in flavivirus infection
Guang, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest,
doi:10.1172/jci137244Gubler, The continuing spread of West Nile virus in the western hemisphere, Clin Infect Dis,
doi:10.1086/521911Hirsch, Nacucchio, Cassará, Ghirardi, Carvallo, Ivermectin its usefulness in prophylaxis, therapy and immunity against COVID 19
Hirsch, Potential benefits of aspirin and enoxaparin in COVID-19 cases
Héctor, Roberto, Francisco, Ciruzzi, Martín et al., Ivermectin, corticosteroids, aspirin and enoxaparin in the treatment of COVID 19
Jean, Hl, Thromboinflammation and the hypercoagulability of COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Kwto, Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an observational cohort study,
doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30196-1Neil, Lopinavir-ritonavir was not effective for COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Nguyen, Evaluation of a novel West Nile virus transmission control strategy that targets Culex tarsalis with endectocide-containing blood meals,
doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007210Ning, Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J Thromb Haemost,
doi:10.1111/jth.14851Ogawa, The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, J Thromb Haemost,
doi:10.1111/jth.14854Orantes, NS2B-NS3-Zika, therapeutic white for zika infection EC, Microbiol
Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Travel Med Infect Dis,
doi:10.22354/in.v25i2.922Santosh, Parmar, Anand, A review of salivary diagnostics and its potential implication in detection of COVID-19, Cureus
Silverman, Feuerstein, Herper, New data on Gilead's remdesivir show no benefit for coronavirus patients
Ziegler, SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is an interferonstimulated gene in human airway epithelial cells and is detected in specific cell subsets across tissues, Cell