Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial
Reaz Mahmud, Md. Mujibur Rahman, Iftikher Alam, Kazi Gias Uddin Ahmed, A K M Humayon Kabir, S K Jakaria Been Sayeed, Mohammad Aftab Rassel, Farhana Binte Monayem, Md Shahidul Islam, Mohammad Monirul Islam, Anindita Das Barshan, Mohammad Mahfuzul Hoque, MD Md. Uzzal Mallik, Mohammad Abdullah Yusuf, Mohammad Zaid Hossain
Journal of International Medical Research, doi:10.1177/03000605211013550
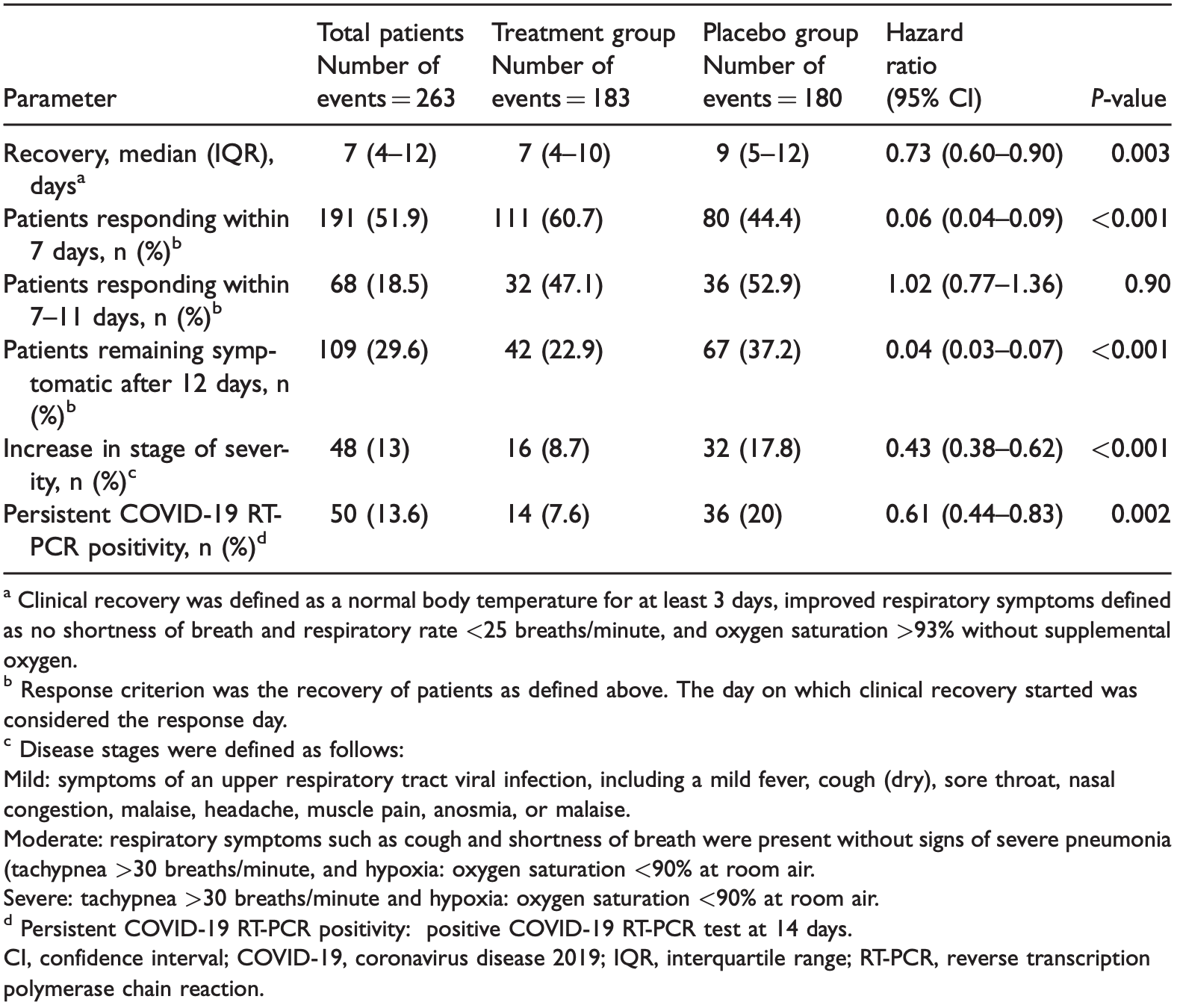
Objective: We evaluated whether ivermectin combined with doxycycline reduced the clinical recovery time in adults with COVID-19 infection. Methods: This was a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial in patients with mild-tomoderate COVID-19 symptoms randomly assigned to treatment (n ¼ 200) and placebo (n ¼ 200) groups. The primary outcome was duration from treatment to clinical recovery. Secondary outcomes were disease progression and persistent COVID-19 positivity by RT-PCR.
Declaration of conflicting interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. Popular Pharmaceuticals Limited, Bangladesh provided ivermectin, doxycycline, and placebo. The company was not involved in the planning or design of the study and had no role in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data.
Author contributions
Appendix
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, ACTT-1 Study Group Members. Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19 -Preliminary Report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764Canga, Prieto, Li Ebana Mjd, The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin in humans-a mini-review, AAPS J
Canga, Sahag Un Prieto, Li Ebana, The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin in humans-a mini-review, AAPS J,
doi:10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9Charan, Biswas, How to calculate sample size for different study designs in medical research?, Indian J Psychol Med,
doi:10.4103/0253-7176.116232Corona Virus, COVID-19
Fiolet, Guihur, Rebeaud, Effect of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin on the mortality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Microbiol Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.022Gralinski, Baric, Molecular pathology of emerging coronavirus infections, J Pathol,
doi:10.1002/path.4454Griffin, Fricovsky, Ceballos, Tetracycline: a pleiotropic family of compounds with promising therapeutic properties. Review of the literature, Am J Physiol Cell Physiol
Henehan, Montuno, Benedetto, Doxycycline as an anti-inflammatory agent: updates in dermatology, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Mahmud, Rahman Had, Mahmud, Rahman, Alam et al., access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis
Mckellar, Benchaoui, Avermectins and milbemycins, J Vet Pharmacol Ther
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Metlay, Waterer, Long, Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults with Community-acquired Pneumonia. An Official Clinical Practice Guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America, Am J Respir Crit Care Med,
doi:10.1164/rccm.201908-1581STPhillips, Gallagher, Weiss, Neurovirulent Murine Coronavirus JHM. SD uses cellular zinc metalloproteases for virus entry and cell-cell fusion, J Virol,
doi:10.1128/jvi.01564-16Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Errez-Ocampo, Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Travel Med Infect Dis
Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The Approved Dose of Ivermectin Alone is not the Ideal Dose for the Treatment of COVID-19, Clin Pharmacol Ther,
doi:10.1002/cpt.1889Siddiqi, Mehra, COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transplant,
doi:10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012Skipper, Pastick, Engen, Hydroxychloroquine in Nonhospitalized Adults With Early COVID-19: A Randomized Trial, Ann Intern Med,
doi:10.7326/M20-4207Sodhi, Etminan, Therapeutic potential for tetracycline in the treatment of COVID-19, Pharmacotherapy,
doi:10.1002/phar.2395Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Effect of remdesivir vs. standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA. Published online,
doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16349Stone, Frigault, Boyd, Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028836Sundy, Sarah, Chunxiao, The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport import in a/b1heterodimer, J Antiviral
Vanlaere, Libert, Matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets in infections caused by gram-negative bacteria and in septic shock, Clin Microbiol Rev,
doi:10.1128/CMR.00047-08Who Director, s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 -11
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5061/DRYAD.QJQ2BVQF6",
"URL": "https://datadryad.org/stash/dataset/doi:10.5061/dryad.qjq2bvqf6",
"abstract": "Objective: We evaluated whether ivermectin combined with doxycycline\n reduced the time to clinical recovery in adults with COVID-19 infection.\n Methods: This was a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial in\n patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 symptoms randomly assigned to\n treatment (n = 200) and placebo groups (n = 200). The primary outcome was\n duration from treatment to clinical recovery. Secondary outcomes included\n disease progression and persistent COVID-19 positivity by RT-PCR. Results:\n Among 556 screened patients, 400 were enrolled and 363 completed\n follow-up. The mean patient age was 40 years, and 59% were men. The median\n recovery time was 7 (4–10) and 9 (5–12) days in the treatment and placebo\n groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval,\n 0.60–0.90). The number of patients who recovered within 7 days was 61% and\n 44% in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.06;\n 95% confidence interval, 0.04–0.09). The proportion of patients who\n remained RT-PCR positive on day 14 and whose disease did not progress was\n significantly lower in the treatment group than in the placebo group.\n Conclusions: Patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 infection treated\n with ivermectin plus doxycycline recovered earlier, were less likely to\n progress to more serious disease, and were more likely to be COVID-19\n negative by RT-PCR on day 14.",
"author": [
{
"family": "Reaz",
"given": "Mahmud"
},
{
"family": "Rahman",
"given": "Mujibur"
},
{
"family": "Iftikher",
"given": "Alam"
},
{
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Kazi Gias Uddin"
},
{
"family": "Kabir",
"given": "A. K. M. Humayon"
},
{
"family": "S. K. Jakaria Been",
"given": "Sayeed"
},
{
"family": "Mohammad Aftab",
"given": "Rassel"
},
{
"family": "Monayem",
"given": "Farhana"
},
{
"family": "Shahidul",
"given": "Islam"
},
{
"family": "Mohammad Monirul",
"given": "Islam"
},
{
"family": "Anindita Das",
"given": "Barshan"
},
{
"family": "Mohammad Mahfuzul",
"given": "Hoque"
},
{
"family": "Uzzal",
"given": "Mallik"
},
{
"family": "Mohammad Abdullah",
"given": "Yusuf"
},
{
"family": "Hossain",
"given": "Mohammad Zaid"
}
],
"categories": [
"FOS: Health sciences",
"FOS: Health sciences"
],
"copyright": "Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal",
"id": "https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.qjq2bvqf6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
25
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"publisher": "Dryad",
"title": "Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial",
"type": "dataset",
"version": "3"
}