Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients with Mild to Moderate Disease
Karamat Hussain Shah Bukhari, Dr Asma Asghar, Najma Perveen, Dr Arshad Hayat, Dr Sermad Ahmad Mangat, Kamil Rehman Butt, Dr Mohammad Abdullah, Tehreem Fatima, Ahmad Mustafa, Talal Iqbal
doi:10.1101/2021.02.02.21250840
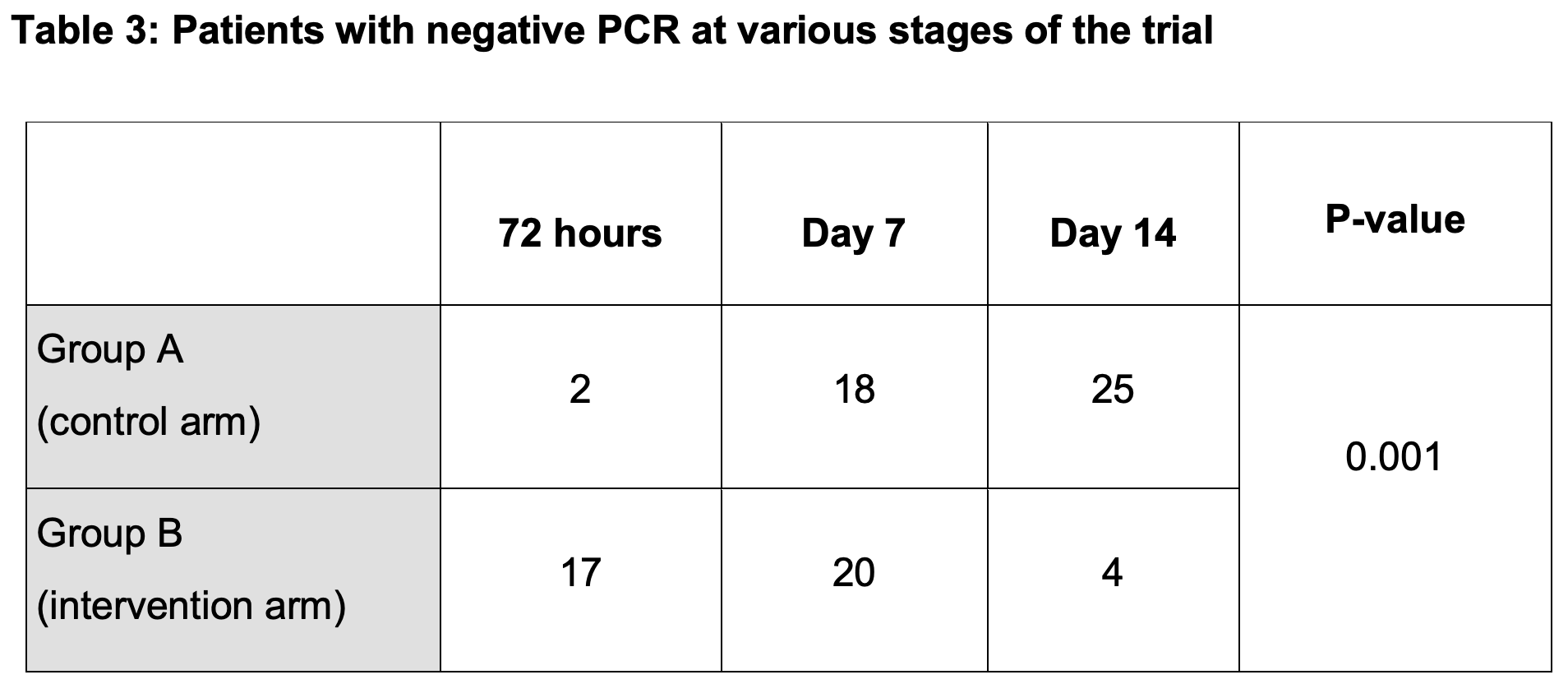
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of ivermectin (IVM) as an addition to the standard of care (SOC) treatment in COVID-19 patients with mild and moderate disease Materials and Methods: A randomized clinical trial (Trial registration # NCT04392713) was carried out at Combined Military Hospital Lahore from March 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020. Eighty-six patients with reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) proven SARS-CoV-2 infection completed the trial protocol. Patients were stratified via the lottery method into two groups. Group A was administered standard of care (SOC) treatment as per existing hospital guidelines whereas group B was given ivermectin (single dose of 12 milligrams) along with SOC treatment. PCR was repeated at 72 hours, 7 th day, and at 14 th day of admission for both the groups and the point at which the PCR became negative was noted. Complete blood counts, liver function tests and renal function tests were done at recruitment, 7 th day, and 14 th day. The primary outcome was the viral clearance, measured as days to achieve PCR negativity. The secondary outcome was the development of any adverse side effects pertinent to ivermectin or derangement in baseline laboratory parameters. Results: In group A, 36 (80%) participants were males, and 9 (20%) were females, whereas in group B, 37 (90.2%) were males and 4 (9.8%) were females. Mean age was 39.0 ± 12.6 and 42.2 ± 12.0 years for groups A and B, respectively (p= 0.394). There was early viral clearance in group B as compared to group A (p=0.001). No adverse reaction or derangements in laboratory parameters was noted in the intervention arm during the trial period.
Declarations Ethical approval and consent to participate -the approval was sought from Combined Military Hospital Lahore Ethics Review Board (ERC # 169/2020) and the trial was registered before initiation (Trial registration # NCT04392713).
Consent for publication -not applicable Competing interests -The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding -not applicable
References
Banerjee, Nandy, Dalai, Ahmed, The Battle against COVID 19 Pandemic: What we Need to Know Before we "Test Fire" Ivermectin, Drug Res (Stuttg,
doi:10.1055/a-1185-8913Bray, Rayner, Noël, Jans, Wagstaff, Ivermectin and COVID-19: A report in Antiviral Research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors' responses, Antiviral Res,
doi:.10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Chen, Kubo, Ivermectin and its target molecules: shared and unique modulation mechanisms of ion channels and receptors by ivermectin, J Physiol,
doi:10.1113/JP275236Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1177/009127002401382731Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot,
doi:10.1038/s41429-020-0336-zJans, Wagstaff, The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectinas an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2?, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
Omrani, Saad, Baig, Ribavirin and interferon alfa-2a for severe Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a retrospective cohort study [published correction appears in, Lancet Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70920-XRajter, Sherman, Fatteh, ICON (Ivermectin in COvid Nineteen) study: Use of Ivermectin is Associated with Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID19, medRxiv, doi:,10.1101/2020.06.06.20124461
Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The Approved Dose of Ivermectin Alone is not the Ideal Dose for the Treatment of COVID-19, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther
Sharun, Dhama, Patel, Ivermectin, a new candidate therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob,
doi:10.1186/s12941-020-00368-wYang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Res,
doi:.10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.02.21250840",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.02.21250840",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To evaluate the efficacy of ivermectin (IVM) as an addition to the standard of care (SOC) treatment in COVID-19 patients with mild and moderate disease</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Materials and Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A randomized clinical trial (Trial registration # <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04392713\">NCT04392713</jats:ext-link>) was carried out at Combined Military Hospital Lahore from March 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020. Eighty-six patients with reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) proven SARS-CoV-2 infection completed the trial protocol. Patients were stratified via the lottery method into two groups. Group A was administered standard of care (SOC) treatment as per existing hospital guidelines whereas group B was given ivermectin (single dose of 12 milligrams) along with SOC treatment. PCR was repeated at 72 hours, 7<jats:sup>th</jats:sup> day, and at 14<jats:sup>th</jats:sup> day of admission for both the groups and the point at which the PCR became negative was noted. Complete blood counts, liver function tests and renal function tests were done at recruitment, 7<jats:sup>th</jats:sup> day, and 14<jats:sup>th</jats:sup> day. The primary outcome was the viral clearance, measured as days to achieve PCR negativity. The secondary outcome was the development of any adverse side effects pertinent to ivermectin or derangement in baseline laboratory parameters.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In group A, 36 (80%) participants were males, and 9 (20%) were females, whereas in group B, 37 (90.2%) were males and 4 (9.8%) were females. Mean age was 39.0± 12.6 and 42.2 ± 12.0 years for groups A and B, respectively (p= 0.394). There was early viral clearance in group B as compared to group A (p=0.001). No adverse reaction or derangements in laboratory parameters was noted in the intervention arm during the trial period.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>In the intervention arm, early viral clearance was observed and no side effects were documented. Therefore ivermectin is a potential addition to the standard care of treatment in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah Bukhari",
"given": "Karamat Hussain",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asghar",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perveen",
"given": "Najma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayat",
"given": "Arshad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mangat",
"given": "Sermad Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butt",
"given": "Kamil Rehman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdullah",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatima",
"given": "Tehreem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustafa",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "Talal",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-05T21:15:48Z",
"timestamp": 1612559748000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-07T16:20:37Z",
"timestamp": 1612714837000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-08T12:28:48Z",
"timestamp": 1709900928275
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.02.02.21250840",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2885.1984.tb00872.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1113/JP275236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1185-8913",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70920-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.06.20124461",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.12",
"unstructured": "Rajter JC , Sherman M , Fatteh N , et al.: ICON (Ivermectin in COvid Nineteen) study: Use of Ivermectin is Associated with Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID19. medRxiv. 2020. DOI, 10.1101/2020.06.06.20124461"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12941-020-00368-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/009127002401382731",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1889",
"article-title": "The Approved Dose of Ivermectin Alone is not the Ideal Dose for the Treatment of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol. Ther",
"key": "2021020708200613000_2021.02.02.21250840v1.15",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.02.02.21250840"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Patients with Mild to Moderate Disease",
"type": "posted-content"
}