Efficacy of single‐dose and double‐dose ivermectin early treatment in preventing progression to hospitalization in mild COVID‐19: A multi‐arm, parallel‐group randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial
Alireza Mirahmadizadeh, Ali Semati, Alireza Heiran, Mostafa Ebrahimi, Abdolrasool Hemmati, Mohammadreza Karimi, Souzan Basir, Marjan Zare, Antonio Charlys Da Costa, Mohammad Zeinali, Maryam Sargolzaee, Owrang Eilami
Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.14318
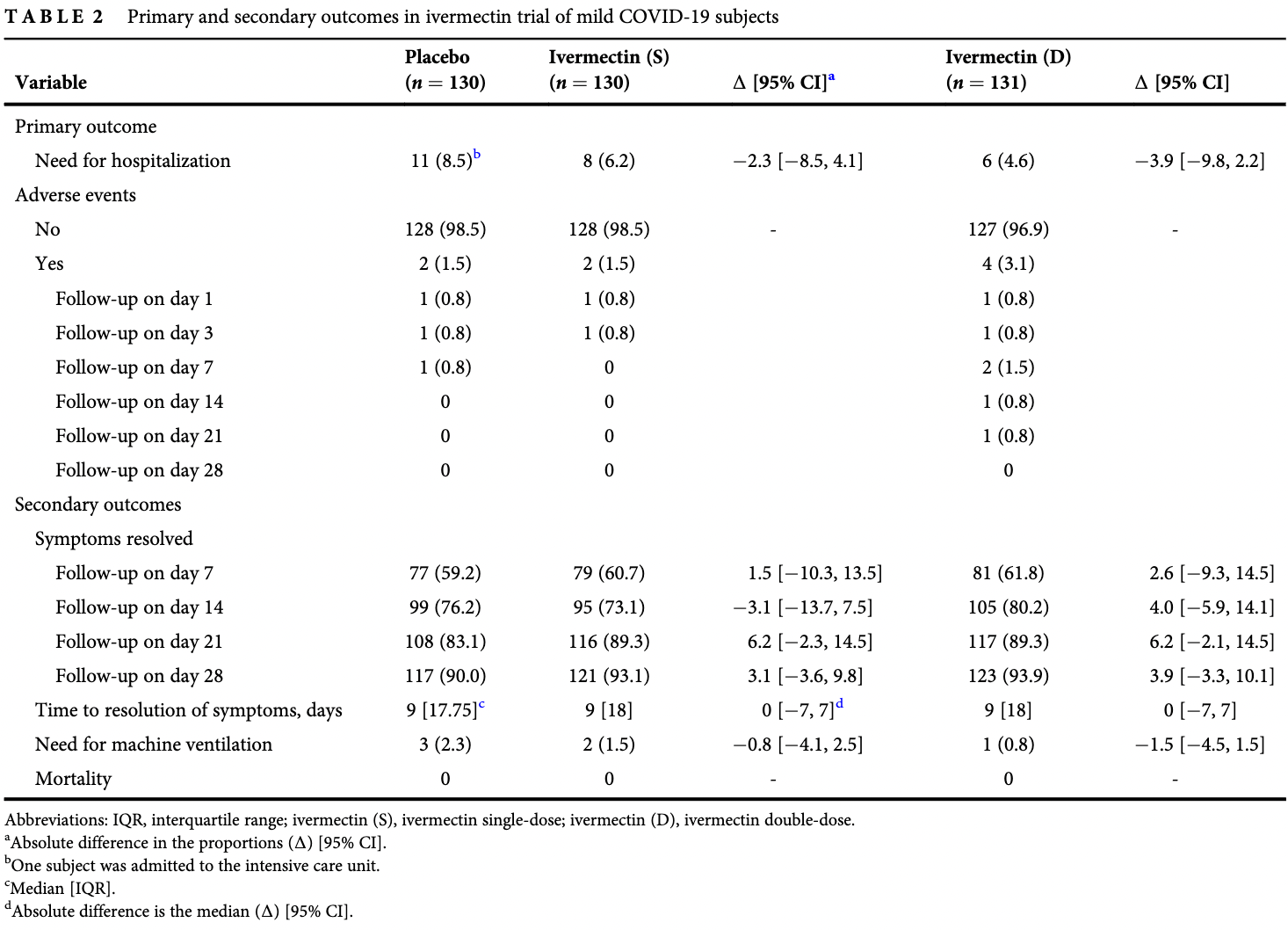
Background and objective: Ivermectin is a known anti-parasitic agent that has been investigated as an antiviral agent against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of ivermectin in mild COVID-19 patients. Methods: In this multi-arm randomized clinical trial conducted between 9 April 2021 and 20 May 2021, a total of 393 patients with reverse transcription-PCR-confirmed COVID-19 infection and mild symptoms were enrolled. Subjects were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive single-dose ivermectin (12 mg), double-dose ivermectin (24 mg) or placebo. The primary outcome was need for hospitalization. Results: There was no significant difference in the proportion of subjects who required hospitalization between the placebo and single-dose ivermectin groups (absolute difference in the proportions: À2.3 [95% CI = À8.5, 4.1]) and between the placebo and double-dose ivermectin groups (absolute difference in the proportions: À3.9 [95% CI = À9.8, 2.2]). The odds of differences in mean change in severity score between single-dose ivermectin and placebo groups (OR difference = 1.005 [95% CI: 0.972, 1.040]; p = 0.762) and double-dose ivermectin and placebo groups (OR difference = 1.010 [95% CI: 0.974, 1.046]; p = 0.598) were not statistically significant. None of the six adverse events (including mild dermatitis, tachycardia and hypertension) were serious and required extra action. Conclusion: Single-dose and double-dose ivermectin early treatment were not superior to the placebo in preventing progression to hospitalization and improving clinical course in mild COVID-19.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST None declared.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section at the end of this article.
How to cite this article:
References
Bloomberg, Remdesivir Averts Hospitalization in Study of High-Risk Patients
Buonfrate, Chesini, Martini, Roncaglioni, Fernandez et al., High dose ivermectin for the early treatment of COVID-19 (COVER study): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase II, dose-finding, proof of concept clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Chowdhury, Shahbaz, Karim, Islam, Dan et al., A comparative study on ivermectin-doxycycline and hydroxychloroquineazithromycin therapy on COVID-19 patients, EJMO
Crump, Omura, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,
doi:10.2183/pjab.87.13Götz, Magar, Dornfeld, Giese, Pohlmann et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci Rep
Kaur, Shekhar, Sharma, Sarma, Prakash et al., Ivermectin as a potential drug for treatment of COVID-19: an in-sync review with clinical and computational attributes, Pharmacol Rep,
doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00195-yKrolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Travacio, Valentini et al., Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959Lundberg, Pinkham, Baer, Amaya, Narayanan et al., Nuclear import and export inhibitors alter capsid protein distribution in mammalian cells and reduce Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus replication, Antiviral Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.10.004Mastrangelo, Pezzullo, Burghgraeve, Kaptein, Pastorino et al., Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug, J Antimicrob Chemother,
doi:10.1093/jac/dks147Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and metaanalysis, J Antimicrob Chemother,
doi:10.1093/jac/dkz524Opez-Medina, Hurtado, Ramirez, Martínez, Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Roy, Pattadar, Raj, Agarwal, Biswas et al., Evaluation of ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19: a double-blind randomized placebo controlled trial in eastern India, J Pharm Pharm Sci,
doi:10.18433/jpps32105Samaha, Mouawia, Fawaz, Hassan, Salami et al., Effects of a single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARSCoV-2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v13060989Tay, Fraser, Chan, Moreland, Rathore et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor ivermectin, Antiviral Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Villamandos, Bobadilla et al., Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04813-1Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem J,
doi:10.1042/BJ20120150Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.14318",
"ISSN": [
"1323-7799",
"1440-1843"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/resp.14318",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/resp.14318"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-12-08"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-05-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-06-23"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2259-4984",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Non‐communicable Diseases Research Center Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mirahmadizadeh",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6322-7876",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Non‐communicable Diseases Research Center Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Semati",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6567-5306",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Non‐communicable Diseases Research Center Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Heiran",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2724-039X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Communicable Diseases Control Center Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ebrahimi",
"given": "Mostafa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9951-8341",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Affairs Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hemmati",
"given": "Abdolrasool",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1435-3996",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Affairs Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Karimi",
"given": "Mohammadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8474-8822",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Basir",
"given": "Souzan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0199-3230",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Non‐communicable Diseases Research Center Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zare",
"given": "Marjan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5516-5177",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Tropical Medicine, School of Medicine University of São Paulo São Paulo Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Charlys da Costa",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4233-9275",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Zoonoses Control Department Ministry of Health and Medical Education Tehran Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zeinali",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7689-9866",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Communicable Diseases Control Center Ministry of Health and Medical Education Tehran Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sargolzaee",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5313-1352",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine and Infectious Diseases Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Shiraz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Eilami",
"given": "Owrang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Respirology",
"container-title-short": "Respirology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-24T00:59:40Z",
"timestamp": 1656032380000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-24T01:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656032400000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004320",
"award": [
"99‐7850"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Shiraz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-24T01:41:33Z",
"timestamp": 1656034893495
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655942400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655942400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/resp.14318",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/resp.14318",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/resp.14318",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_2_1.1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.COVID‐19: Clinical Care. Therapeutics and COVID‐19: Living Guideline. [updated 2021 Sep 25"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_2_1.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2021 Sep 28]. Available from:https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-therapeutics-2021.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-020-02360-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-02783-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-03074-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1",
"unstructured": "Bloomberg.Remdesivir Averts Hospitalization in Study of High‐Risk Patients.2021Sep 22 [cited 2021 Nov 27]. Available from:https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-09-22/remdesivir-averts-hospitalization-in-study-of-high-risk-patients"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-02054-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: 21st List 2019.Geneva:World Health Organization;2019[cited 2021 Sep 19]. Available from:https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/325771/WHO-MVP-EMP-IAU-2019.06-eng.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2017.02.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep23138",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.10.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20120150",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.06.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dks147",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13060989",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04813-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkz524",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00195-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_24_1.1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.COVID‐19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis Draft. [updated 2020 Feb 18"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_24_1.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2021 Sep 19]. Available from:https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/covid-19-therapeutic-trial-synopsis"
},
{
"article-title": "A comparative study on ivermectin‐doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine‐azithromycin therapy on COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Chowdhury A",
"first-page": "63",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "EJMO",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0895-4356(98)00138-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps32105",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106516",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_30_1.1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.WHO Advises that Ivermectin Only Be Used to Treat COVID‐19 Within Clinical Trials. [updated 2021 Mar 31"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_30_1.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2021 Sep 19]. Available from:https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/who-advises-that-ivermectin-only-be-used-to-treat-covid-19-within-clinical-trials"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).Rapid Increase in Ivermectin Prescriptions and Reports of Severe Illness Associated with Use of Products Containing Ivermectin to Prevent or Treat COVID‐19. [updated 2021 Aug 26; cited 2021 Sep 19]. Available from:https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2021/han00449.asp"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_32_1.1",
"unstructured": "Google News.Coronavirus (COVID‐19). [updated 2021 Sep 27"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-e_1_2_10_32_1.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2021 Oct 2]. Available from:https://news.google.com/covid19/map?hl=fa&state=7&mid=%2Fm%2F03shp"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/resp.14318"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of single‐dose and double‐dose ivermectin early treatment in preventing progression to hospitalization in mild\n <scp>COVID</scp>\n ‐19: A multi‐arm, parallel‐group randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}