Analysis of Mexico City's use of an ivermectin-based medical kit, showing significantly lower hospitalization with use. Authors use logistic-regression models with matched observations, including adjustments for age, sex, COVID severity, and comorbidities.
This preprint was censored by the original preprint host. Censors claim that the government treatment program, which used approved medications and saved over 500 people from hospitalization, was unethical. In part they also indicate that studies of "the effects of a medication on a disease outcome" are outside the scope of their site, however retroactively censoring a paper for this reason is not appropriate.
The author's response (not provided by the censors) can be found here:.
Author's provide the data and code for the study, and the results have been independently verified.
52 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with
p=0.00000021.
|
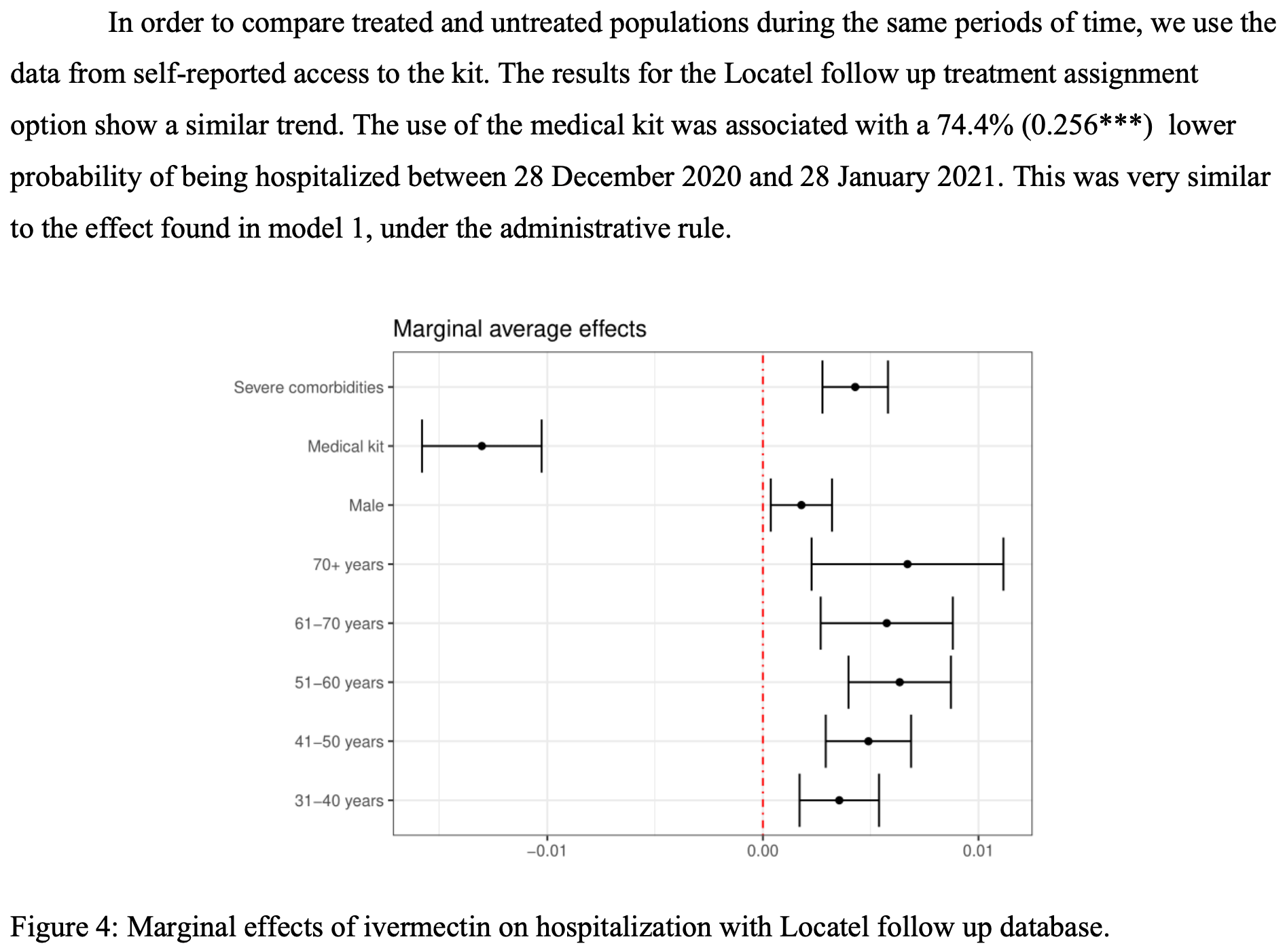
risk of hospitalization, 74.4% lower, RR 0.26, p < 0.001, model 7, same time period, patients receiving kit.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 68.4% lower, RR 0.32, p < 0.001, model 1, different time periods, administrative rule.
|
|
Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates
|
Merino et al., 3 May 2021, retrospective quasi-randomized (patients receiving kit), population-based cohort, Mexico, preprint, 7 authors, dosage 6mg bid days 1-2.
Ivermectin and the odds of hospitalization due to COVID-19: evidence from a quasi-experimental analysis based on a public intervention in Mexico City José Merino i (i Digital Agency for Public Innovation, Mexico City) Victor Hugo Borja ii (ii, Mexican Social Security Institute) Oliva López, José Alfredo Ochoa iii (iii, Ministry of Health, Mexico City)
Eduardo Clark, Lila Petersen, Saul Caballero
Objective To measure the effect of Mexico City's population-level intervention -an ivermectin-based Medical Kit --in hospitalizations during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods A quasi-experimental research design with a Coarsened Exact Matching method using administrative data from hospitals and phone-call monitoring. We estimated logistic-regression models with matched observations adjusting by age, sex, COVID severity, and comorbidities. For robustness checks separated the effect of the kit from phone medical monitoring; changed the comparison period; and subsetted the sample by hospitalization occupancy,
Results We found a significant reduction in hospitalizations among patients who received the ivermectin-based medical kit; the range of the effect is 52%-76% depending on model specification.
Conclusions The study supports ivermectin-based interventions to assuage the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the health system. 1 Priority zones: total active cases, deaths, hospitalized patients, outpatients, positivity rate, and active cases per 100,000 inhabitants, population density, establishments with requests for disability, average number of households per dwelling, average number of persons per household, people with symptoms detected in the house-to-house program, and the proportion of the sample of follow-up patients.
References
Akbar, Navarro, Krolewiecki, Ivermectin treatment may improve the prognosis of patients with COVID-19, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Bibliography ; Athey, Imbens, Recursive partitioning for heterogeneous causal effects, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Blackwell, Iacus, King, Porro, cem: Coarsened exact matching in Stata, The Stata Journal
Brignardello-Petersen, Drug treatments for COVID-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis, Bmj
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff et al., Sharp Reductions in COVID-19 Case Fatalities and Excess Deaths in Peru in Close Time Conjunction, State-By-State, with Ivermectin Treatments, By-State, with Ivermectin Treatments
Castillo, Fernández-Alonso, Hill, Abdulamir, Ahmed et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial
Chaccour, Hammann, Ramón-García, Rabinovich, Chaccour et al., Ivermectin and COVID-19: keeping rigor in times of urgency, The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene
Chang, Inclusión de la ivermectina en La primera línea de acción terapéutica para COVID
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study, Chest