Ivermectin Effect on In-Hospital Mortality and Need for Respiratory Support in COVID-19 Pneumonia: Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Study
Jara Llenas-García, Alfonso Del Pozo, Alberto Talaya, Nuria Roig-Sánchez, Noemí Poveda Ruiz, Carlos Devesa García, Emilio Borrajo Brunete, Inmaculada González Cuello, Ana Lucas Dato, Miriam Navarro, Philip Wikman-Jorgensen
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15051138
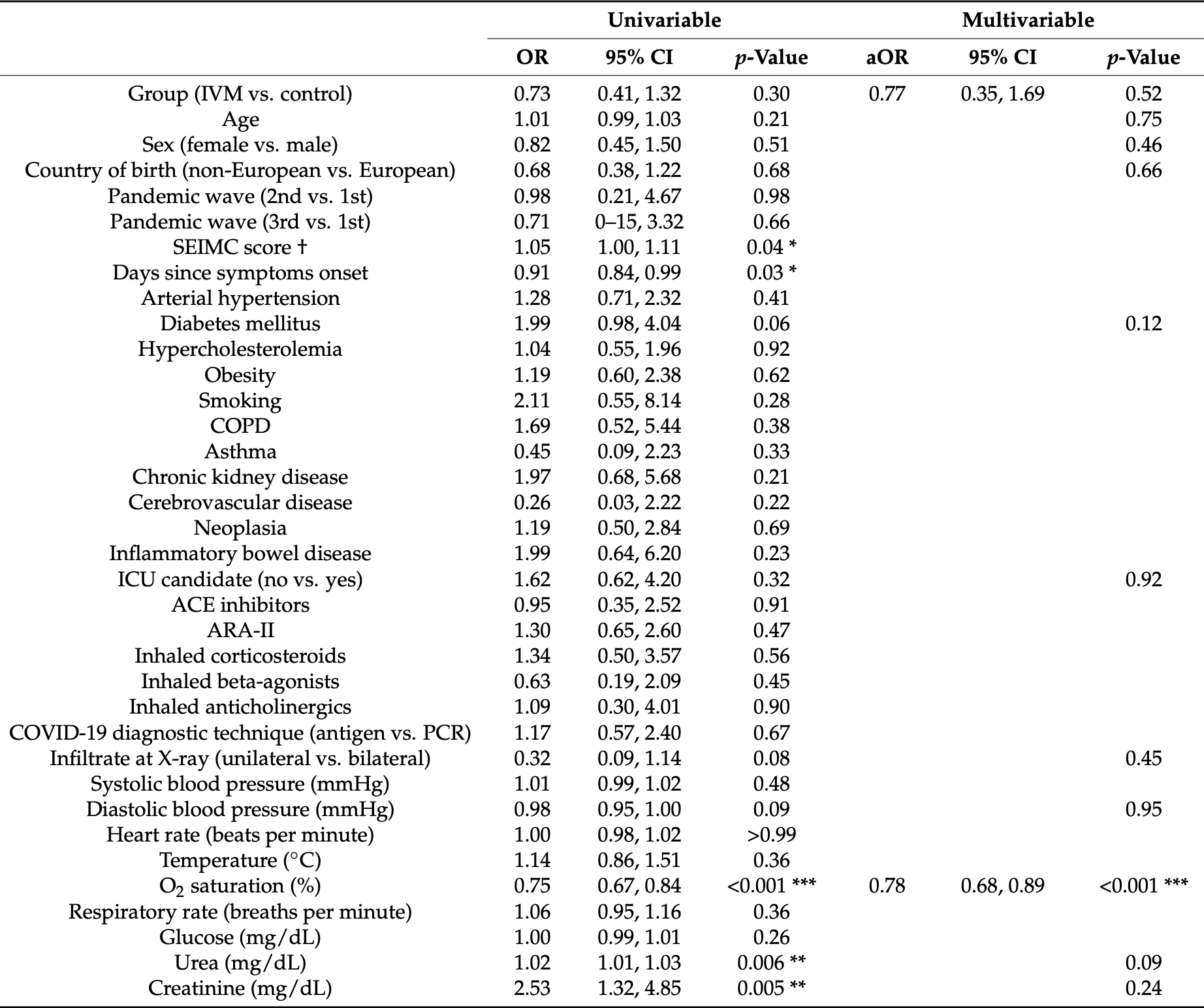
Introduction. There is negligible evidence on the efficacy of ivermectin for treating COVID-19 pneumonia. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of ivermectin for pre-emptively treating Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome in order to reduce mortality and the need for respiratory support in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. Methods. This single-center, observational, retrospective study included patients admitted with COVID-19 pneumonia at Hospital Vega Baja from 23 February 2020 to 14 March 2021. Because strongyloidiasis is endemic to our area, medical criteria support empiric administration of a single, 200 µg/kg dose of ivermectin to prevent Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome. The outcome was a composite of all-cause in-hospital mortality and the need for respiratory support. Results. Of 1167 patients in the cohort, 96 received ivermectin. After propensity score matching, we included 192 patients. The composite outcome of in-hospital mortality or need for respiratory support occurred in 41.7% of the control group (40/96) and 34.4% (33/96) of the ivermectin group. Ivermectin was not associated with the outcome of interest (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.77, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.35, 1.69; p = 0.52). The factors independently associated with this endpoint were oxygen saturation (aOR 0.78, 95% CI 0.68, 0.89, p < 0.001) and C-reactive protein at admission (aOR: 1.09, 95% CI 1.03, 1.16, p < 0.001). Conclusions. In hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, ivermectin at a single dose for pre-emptively treating Strongyloides stercoralis is not effective in reducing mortality or the need for respiratory support measures.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abd-Elsalam, Noor, Badawi, Khalaf, Esmail et al., Clinical Study Evaluating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Study, J. Med. Virol,
doi:10.1002/jmv.27122Ahmed, Karim, Ross, Hossain, Clemens et al., A Five-Day Course of Ivermectin for the Treatment of COVID-19 May Reduce the Duration of Illness, Int. J. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191Berenguer, Borobia, Ryan, Rodríguez-Baño, Bellón et al., Development and Validation of a Prediction Model for 30-Day Mortality in Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19: The COVID-19 SEIMC Score, Thorax,
doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216001Bitterman, Martins, Cices, Nadendla, Comparison of Trials Using Ivermectin for COVID-19 Between Regions With High and Low Prevalence of Strongyloidiasis: A Meta-Analysis, JAMA Netw. Open,
doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.3079Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines, Am. J. Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402Buonfrate, Chesini, Martini, Roncaglioni, Ojeda Fernandez et al., High-Dose Ivermectin for Early Treatment of COVID-19 (COVER Study): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Multicentre, Phase II, Dose-Finding, Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents,
doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106516Colosimo, Caroleo, Caruso, Luciani, Cione et al., Fatal Case of Autochthonous Strongyloides Stercoralis Hyperinfection in an Immunosuppressed Calabrian Patient, Reports
Dato, Pacheco-Tenza, Brunete, López, López et al., Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases,
doi:10.3390/pathogens9080601Dimitroglou, Alexopoulos, Aggeli, Kalantzi, Nouli et al., Eosinophilic Myocarditis in a Patient With Strongyloides Stercoralis Infection. Case Rep,
doi:10.1016/j.jaccas.2021.04.014Galan, Santos, Asato, Araújo, De Lima Moreira et al., Phase 2 Randomized Study on Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine or Ivermectin in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Pathog. Glob. Health,
doi:10.1080/20477724.2021.1890887Jenks, Driscoll, Locke, Strongyloidiasis Hyperinfection Syndrome in COVID-19 Positive Migrants Treated with Corticosteroids, J. Immigr. Minor. Health,
doi:10.1007/s10903-022-01386-wLehrer, Rheinstein, Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Attached to ACE2,
doi:10.21873/invivo.12134Lim, Hor, Tay, Jelani, Tan et al., Efficacy of Ivermectin Treatment on Disease Progression Among Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities: The I-TECH Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Intern. Med,
doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Dávalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults with Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Mahmud, Rahman, Alam, Ahmed, Kabir et al., Ivermectin in Combination with Doxycycline for Treating COVID-19 Symptoms: A Randomized Trial, J. Int. Med. Res,
doi:10.1177/03000605211013550Manu, Bryant A, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Hill et al., Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001482Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Stewart, Gentile et al., Effect of Ivermectin vs. Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2022.18590Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study, Chest
Rayner, Dron, Park, Decloedt, Cotton et al., Accelerating Clinical Evaluation of Repurposed Combination Therapies for COVID-19, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg,
doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0995Stauffer, Alpern, Walker, COVID-19 and Dexamethasone: A Potential Strategy to Avoid Steroid-Related Strongyloides Hyperinfection, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2020.13170Temple, Hoang, Hendrickson, Toxic Effects from Ivermectin Use Associated with Prevention and Treatment of Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMc2114907Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Villamandos, Bobadilla et al., Ivermectin to Prevent Hospitalizations in Patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, BMC Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin Is a Specific Inhibitor of Importin α/β-Mediated Nuclear Import Able to Inhibit Replication of HIV-1 and Dengue Virus, Biochem. J,
doi:10.1042/BJ20120150Wikman-Jorgensen, Llenas-Garcia, Shedrawy, Gascon, Muñoz et al., Cost-Effectiveness of Different Strategies for Screening and Treatment of Strongyloides Stercoralis in Migrants from Endemic Countries to the European Union, BMJ Glob,
doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002321DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15051138",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v15051138",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction. There is negligible evidence on the efficacy of ivermectin for treating COVID-19 pneumonia. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of ivermectin for pre-emptively treating Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome in order to reduce mortality and the need for respiratory support in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. Methods. This single-center, observational, retrospective study included patients admitted with COVID-19 pneumonia at Hospital Vega Baja from 23 February 2020 to 14 March 2021. Because strongyloidiasis is endemic to our area, medical criteria support empiric administration of a single, 200 μg/kg dose of ivermectin to prevent Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome. The outcome was a composite of all-cause in-hospital mortality and the need for respiratory support. Results. Of 1167 patients in the cohort, 96 received ivermectin. After propensity score matching, we included 192 patients. The composite outcome of in-hospital mortality or need for respiratory support occurred in 41.7% of the control group (40/96) and 34.4% (33/96) of the ivermectin group. Ivermectin was not associated with the outcome of interest (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.77, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.35, 1.69; p = 0.52). The factors independently associated with this endpoint were oxygen saturation (aOR 0.78, 95% CI 0.68, 0.89, p < 0.001) and C-reactive protein at admission (aOR: 1.09, 95% CI 1.03, 1.16, p < 0.001). Conclusions. In hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, ivermectin at a single dose for pre-emptively treating Strongyloides stercoralis is not effective in reducing mortality or the need for respiratory support measures.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v15051138"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9125-7706",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Medicine Department, Miguel Hernández University, 03202 Elche, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Llenas-García",
"given": "Jara",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6991-923X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "del Pozo",
"given": "Alfonso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5594-8083",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Talaya",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Roig-Sánchez",
"given": "Nuria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6217-6077",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Unit, Hospital Reina Sofía, 30003 Murcia, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Poveda Ruiz",
"given": "Noemí",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8350-5124",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital Pharmacy Department, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Devesa García",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiology Department, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Borrajo Brunete",
"given": "Emilio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8519-7823",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "González Cuello",
"given": "Inmaculada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Vega Baja, 03314 Orihuela, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Lucas Dato",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7727-1587",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Epidemiology Unit, Public Health Centre, 03202 Elche, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Navarro",
"given": "Miriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Foundation for the Promotion of Health and Biomedical Research of the Valencia Region (FISABIO), 46020 Valencia, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Internal Medicine Service, Elda General University Hospital, 03600 Elda, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Wikman-Jorgensen",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-11T05:37:09Z",
"timestamp": 1683783429000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-11T05:39:51Z",
"timestamp": 1683783591000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"UGP-21-410"
],
"name": "Consellería de Sanitat Universal i Salut Pública"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-12T04:38:50Z",
"timestamp": 1683866330491
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1683676800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/15/5/1138/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1138",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard (2022, November 02). WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Clinical Spectrum (2022, November 02). COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines, Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0995",
"article-title": "Accelerating Clinical Evaluation of Repurposed Combination Therapies for COVID-19",
"author": "Rayner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1364",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20120150",
"article-title": "Ivermectin Is a Specific Inhibitor of Importin α/β-Mediated Nuclear Import Able to Inhibit Replication of HIV-1 and Dengue Virus",
"author": "Wagstaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "851",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "443",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-Approved Drug Ivermectin Inhibits the Replication of SARS-CoV-2 in Vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/invivo.12134",
"article-title": "Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Attached to ACE2",
"author": "Lehrer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3023",
"journal-title": "In Vivo",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2114907",
"article-title": "Toxic Effects from Ivermectin Use Associated with Prevention and Treatment of Covid-19",
"author": "Temple",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2197",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines",
"author": "Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e434",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Ther.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001482",
"article-title": "Expression of Concern for Bryant a, Lawrie TA, Dowswell T, Fordham EJ, Mitchell S., Hill SR, Tham TC. Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines. Am J Ther. 2021;28(4): E434-E460",
"author": "Manu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E232",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Ther.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Popp, M., Stegemann, M., Metzendorf, M.I., Gould, S., Kranke, P., Meybohm, P., Skoetz, N., and Weibel, S. (2021). Ivermectin for Preventing and Treating COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.3079",
"article-title": "Comparison of Trials Using Ivermectin for COVID-19 Between Regions With High and Low Prevalence of Strongyloidiasis: A Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Bitterman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E223079",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/reports5040047",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Colosimo, M., Caroleo, M.C., Caruso, A., Luciani, F., Cione, E., Talarico, G., Vescio, V., Sarro, G.D., Minchella, P., and Nisticò, S. (2022). Fatal Case of Autochthonous Strongyloides Stercoralis Hyperinfection in an Immunosuppressed Calabrian Patient. Reports, 5."
},
{
"article-title": "Eosinophilic Myocarditis in a Patient With Strongyloides Stercoralis Infection",
"author": "Dimitroglou",
"first-page": "954",
"journal-title": "Case Rep.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens9080601",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "Dato, A.L., Pacheco-Tenza, M.I., Brunete, E.B., López, B.M., López, M.G., Cuello, I.G., Colomé, J.G., Cots, M.N., Saugar, J.M., and García-Vazquez, E. (2020). Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases. Pathogens, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216001",
"article-title": "Development and Validation of a Prediction Model for 30-Day Mortality in Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19: The COVID-19 SEIMC Score",
"author": "Berenguer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "920",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"article-title": "Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study",
"author": "Rajter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Ivermectin Treatment on Disease Progression Among Adults With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities: The I-TECH Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "426",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.18590",
"article-title": "Effect of Ivermectin vs. Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Naggie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1595",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "328",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Vallejos, J., Zoni, R., Bangher, M., Villamandos, S., Bobadilla, A., Plano, F., Campias, C., Chaparro Campias, E., Medina, M.F., and Achinelli, F. (2021). Ivermectin to Prevent Hospitalizations in Patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. BMC Infect. Dis., 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"article-title": "Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults with Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Hurtado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106516",
"article-title": "High-Dose Ivermectin for Early Treatment of COVID-19 (COVER Study): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Multicentre, Phase II, Dose-Finding, Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial",
"author": "Buonfrate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106516",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"article-title": "A Five-Day Course of Ivermectin for the Treatment of COVID-19 May Reduce the Duration of Illness",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/20477724.2021.1890887",
"article-title": "Phase 2 Randomized Study on Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine or Ivermectin in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Galan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"journal-title": "Pathog. Glob. Health",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211013550",
"article-title": "Ivermectin in Combination with Doxycycline for Treating COVID-19 Symptoms: A Randomized Trial",
"author": "Mahmud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "03000605211013550",
"journal-title": "J. Int. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27122",
"article-title": "Clinical Study Evaluating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Study",
"author": "Noor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5833",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Popp, M., Reis, S., Schießer, S., Hausinger, R.I., Stegemann, M., Metzendorf, M.I., Kranke, P., Meybohm, P., Skoetz, N., and Weibel, S. (2022). Ivermectin for Preventing and Treating COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2021.03.003",
"article-title": "Standard Dose Ivermectin for COVID-19",
"author": "Buonfrate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2111",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10903-022-01386-w",
"article-title": "Strongyloidiasis Hyperinfection Syndrome in COVID-19 Positive Migrants Treated with Corticosteroids",
"author": "Jenks",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1431",
"journal-title": "J. Immigr. Minor. Health",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.13170",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Dexamethasone: A Potential Strategy to Avoid Steroid-Related Strongyloides Hyperinfection",
"author": "Stauffer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "623",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002321",
"article-title": "Cost-Effectiveness of Different Strategies for Screening and Treatment of Strongyloides Stercoralis in Migrants from Endemic Countries to the European Union",
"author": "Shedrawy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e002321",
"journal-title": "BMJ Glob. Health",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/15/5/1138"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin Effect on In-Hospital Mortality and Need for Respiratory Support in COVID-19 Pneumonia: Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}