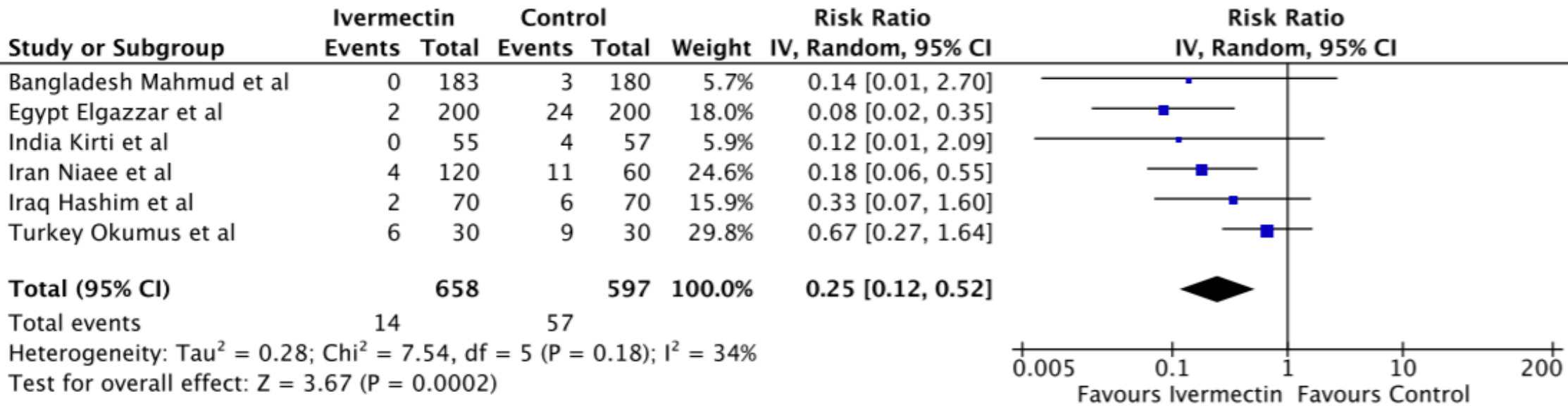
Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection
Dr Andrew Hill, Ahmed S Abdulamir, Sabeena Ahmed, Asma Asghar, Olufemi Emmanuel Babalola, Rabia Basri, Carlos Chaccour, Aijaz Zeeshan Khan Chachar, Abu Tauib Mohammed Chowdhury, Ahmed Elgazzar, Leah Ellis, Jonathan Falconer, Anna Garratt, Basma M Hany, Hashim A Hashim, Wasim Ul Haque, Arshad Hayat, Shuixiang He, Ramin Jamshidian, Wasif Ali Khan, Ravi Kirti, Alejandro Krolewiecki, Carlos Lanusse, Jacob Levi, Reaz Mahmud, Sermand Ahmed Mangat, Kaitlyn Mccann, Anant Mohan, Mortezza Shakshi Niaee, Nurullah Okumus, Victoria Pilkington, Chinmay Saha Podder, Ambar Qavi, Houssam Raad, Mohammaed Sadegh Rezai, Surapaneni Sasank, Veerapaneni Spoorthi, Tejas Suri, Junzheng Wang, Hannah Wentzel
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-148845/v1
Forum Infectious Diseases published a version of this preprint. The authors subsequently learned that one of the studies on which this analysis was based had been withdrawn due to fraudulent data. An expression of concern was issued on August 9, 2021.
References
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, Hossain, Clemens et al., A five day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191Arshad, Pertinez, Box, Tatham, Rajoli et al., Prioritization of Anti-SARS-Cov-2 Drug Repurposing Opportunities Based on Plasma and Target Site Concentrations Derived from their Established Human Pharmacokinetics, Clin Pharmacol Ther,
doi:10.1002/cpt.1909Asghar, Efficacy of Ivermectin in COVID-19
Babaloa, Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: A randomised controlled double blind dose response study in Lagos,
doi:10.1186/ISRCTN40302986Canga, Prieto, Liébana, Martínez, Vega et al., The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin in humans--a mini-review, AAPS J,
doi:10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, Pineda, Fernandez-Montero et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral
Chachar, Khan, Asif, Khaqan, Basri, Effectiveness of ivermectin in SARS-CoV-2 / COVID-19 patients, International Journal of Sciences,
doi:10.18483/ijSci.2378Chowdhury, A randomised trial of Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin therapy on COVID19 patients,
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-38896/v1Ci, Li, Yu, Zhang, Yu et al., Avermectin exerts anti-inflammatory effect by downregulating the nuclear transcription factor kappa-B and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation pathway, Fundam Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00684.xClinicaltrials, Gov, Prophylaxis Covid-19 In Healthcare Agents By Intensive Treatment With Ivermectin And Iota-Carrageenan
Cottam, Maier, Manifava, Vaux, Chandra-Schoenfelder et al., Coronavirus nsp6 proteins generate autophagosomes from the endoplasmic reticulum via an omegasome intermediate, Autophagy,
doi:10.4161/auto.7.11.16642De Melo, Lazarini, Larrous, Feige, Kergoat et al., Anti-COVID-19 efficacy of ivermectin in the golden hamster, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.11.21.392639Elgazzar, Hany, Youssef, Hafez, Moussa et al., Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 pandemic
Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Fatak, Kabah et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq
Henry, De Oliveira, Benoit, Plebani, Lippi, Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, Clin Chem Lab Med,
doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0369Jermain, Hanafin, Cao, Lifschitz, Lanusse et al., Development of a Minimal Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Simulate Lung Exposure in Humans Following Oral Administration of Ivermectin for COVID-19 Drug Repurposing, J Pharm Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2020.08.024Kirti, Low Low Low Low Low Low Good
Kirti, Roy, Pattadar, Raj, Agarwal et al., Ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19: A double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial,
doi:10.1101/2021.01.05.21249310Kramer, Grandi, Passeri, Gianelli, Genchi et al., Evaluation of lung pathology in Dirofilaria immitis-experimentally infected dogs treated with doxycycline or a combination of doxycycline and ivermectin before administration of melarsomine dihydrochloride, Veterinary parasitology
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Travacio, Valentini et al., Antiviral Effect of High-Dose Ivermectin in Adults with COVID-19: A Pilot Randomised, Controlled, Open Label, Multicentre Trial
Liu, Liang, Chen, Wang, Qu et al., Ivermectin induces autophagymediated cell death through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioma cells, Biosci Rep,
doi:10.1042/BSR20192489Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Niaee, Gheibi, Namdar, Allami, Zolghadr et al., Invermctin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: a randomized, multi-center clinical trial
Okumus, Ivermectin for Severe COVID-19 management
Podder, Chowdhury, Sina, Haque, Outcome of ivermectin treated mild to moderate COVID-19 cases: a single-centre, open-label, randomized controlled study, IMC J Med Sci
Raad, In vivo use of ivermectin (IVR) for treatment for corona virus infected patients (COVID-19): a randomized controlled trial
Rezai, Effect of Ivermectin on COVID-19: A multicenter double-blind randomized clinical trial
Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The Approved Dose of Ivermectin Alone is not the Ideal Dose for the Treatment of COVID-19, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Singh, Mittal, Gollapudi, Butzmann, Kumar et al., A meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 patients identifies the combinatorial significance of D-dimer, C-reactive protein, lymphocyte, and neutrophil values as a predictor of disease severity, International journal of laboratory hematology
Spoorthi, Utiilty of Ivermectin and Doxycycline combination for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2, IAIM
Stolberg, Lafraniere, Warning of Shortages, Researchers Look to Stretch Vaccine Supply
Tzou, Tao, Nouhin, Coronavirus Antiviral Research Database (CoV-RDB): An Online Database Designed to Facilitate Comparisons between Candidate Anti-Coronavirus Compounds, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v12091006Van Nguyen, Ferrand, Cohen-Boulakia, Martinez, Kapp et al., RCT studies on preventive measures and treatments for COVID-19
Ventre, Rozières, Lenief, Albert, Rossio et al., Topical ivermectin improves allergic skin inflammation, Allergy,
doi:10.1111/all.13118Who, WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard
Yan, Ci, Chen, Chen, Li et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflamm Res,
doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8Zhang, Song, Ci, Ju, Li, Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflamm Res,
doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8Zhang, Song, Xiong, Ci, Li et al., Inhibitory effects of ivermectin on nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, Int Immunopharmacol,
doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2008.12.016Zhu, Cong, Yu, Bresnahan, Shenk, Inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 blocks human cytomegalovirus replication, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
doi:10.1073/pnas.052713799DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-148845/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-148845/v1",
"abstract": "<title>Abstract</title>\n <p>Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug being investigated for repurposing to SARS-CoV-2. In-vitro, ivermectin showed limited antiviral activity and a COVID-19 animal model demonstrated pathological benefits but no effect on viral RNA. This meta-analysis investigated ivermectin in 18 randomized clinical trials (2282 patients) identified through systematic searches of PUBMED, EMBASE, MedRxiv and trial registries. Ivermectin was associated with reduced inflammatory markers (C-Reactive Protein, d-dimer and ferritin) and faster viral clearance by PCR. Viral clearance was treatment dose- and duration-dependent. In six randomized trials of moderate or severe infection, there was a 75% reduction in mortality (Relative Risk=0.25 [95%CI 0.12-0.52]; p=0.0002); 14/650 (2.1%) deaths on ivermectin; 57/597 (9.5%) deaths in controls) with favorable clinical recovery and reduced hospitalization. Many studies included were not peer reviewed and meta-analyses are prone to confounding issues. Ivermectin should be validated in larger, appropriately controlled randomized trials before the results are sufficient for review by regulatory authorities.</p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool"
}
],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Medicine, Alnahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq"
}
],
"family": "Abdulamir",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Dhaka, Bangladesh,"
}
],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Sabeena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Combined Military Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Asghar",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Bingham University / Lagos University, Nigeria"
}
],
"family": "Babalola",
"given": "Olufemi Emmanuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fatima Memorial Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Basri",
"given": "Rabia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Barcelona Institute for Global Health, Clinica Universidad de Navarra, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Chaccour",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fatima Memorial Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Chachar",
"given": "Aijaz Zeeshan Khan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Xi'an Jiaotong University Medical College First Affiliated Hospital, Shaannxi, China"
}
],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Abu Tauib Mohammed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Benha, Egypt"
}
],
"family": "Elgazzar",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Leah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Falconer",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff and Vale University Health Board, UK"
}
],
"family": "Garratt",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Benha, Egypt"
}
],
"family": "Hany",
"given": "Basma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Alkarkh Hospital, Alatefiya, Baghdad, Iraq"
}
],
"family": "Hashim",
"given": "Hashim A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology, BIRDEM General Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Haque",
"given": "Wasim Ul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Combined Military Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Hayat",
"given": "Arshad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Xi'an Jiaotong University Medical College First Affiliated Hospital, Shaanxi, China"
}
],
"family": "He",
"given": "Shuixiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jundishapur University School of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Jamshidian",
"given": "Ramin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Dhaka, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Wasif Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of General Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, India"
}
],
"family": "Kirti",
"given": "Ravi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Instituto de Investigatiaciones de Enferedades Tropicales, Sede Regional Oran, Universidad National de Salta, Argentina"
}
],
"family": "Krolewiecki",
"given": "Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratorio de Farmacologia, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina"
}
],
"family": "Lanusse",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Intensive Care, University College London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Levi",
"given": "Jacob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Dhaka Medical College, Dhaka, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Mahmud",
"given": "Reaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Combined Military Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Mangat",
"given": "Sermand Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "McCann",
"given": "Kaitlyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India"
}
],
"family": "Mohan",
"given": "Anant",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qazvin Science and Technology Park, Qazvin, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Niaee",
"given": "Mortezza Shakshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neonatology, Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University, Afkonkarahisar, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "Okumus",
"given": "Nurullah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oxford University, Clinical Academic Graduate School, University of Oxford, UK"
}
],
"family": "Pilkington",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Debidwar Upazila Health Complex, Debidwar, Comilla, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Podder",
"given": "Chinmay Saha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Qavi",
"given": "Ambar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biotherapies e Maladies Genetiques et Cancer, Universite Bordeaux, Segalen, France"
}
],
"family": "Raad",
"given": "Houssam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pediatric Infectious Diseases Research Centre, Communicable Diseases Institute, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, India"
}
],
"family": "Rezai",
"given": "Mohammaed Sadegh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gandhi University, Andhra Pradesh, India"
}
],
"family": "Sasank",
"given": "Surapaneni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Apollo Medical College, Hyderabad, India"
}
],
"family": "Spoorthi",
"given": "Veerapaneni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qazvin Science and Technology Park, Qazvin, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Suri",
"given": "Tejas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Junzheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College, London"
}
],
"family": "Wentzel",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-19T19:56:12Z",
"timestamp": 1611086172000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T00:58:38Z",
"timestamp": 1715302718000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T01:40:08Z",
"timestamp": 1715305208506
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
19
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1611014400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-148845/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-148845/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
19
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {
"is-preprint-of": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-148845/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"type": "posted-content"
}