URGENT COVID-19 information: Ivermectin reduces the risk of death from COVID-19 -a rapid review and meta-analysis in support of the recommendation of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance
PhD Tess Lawrie Mbbch
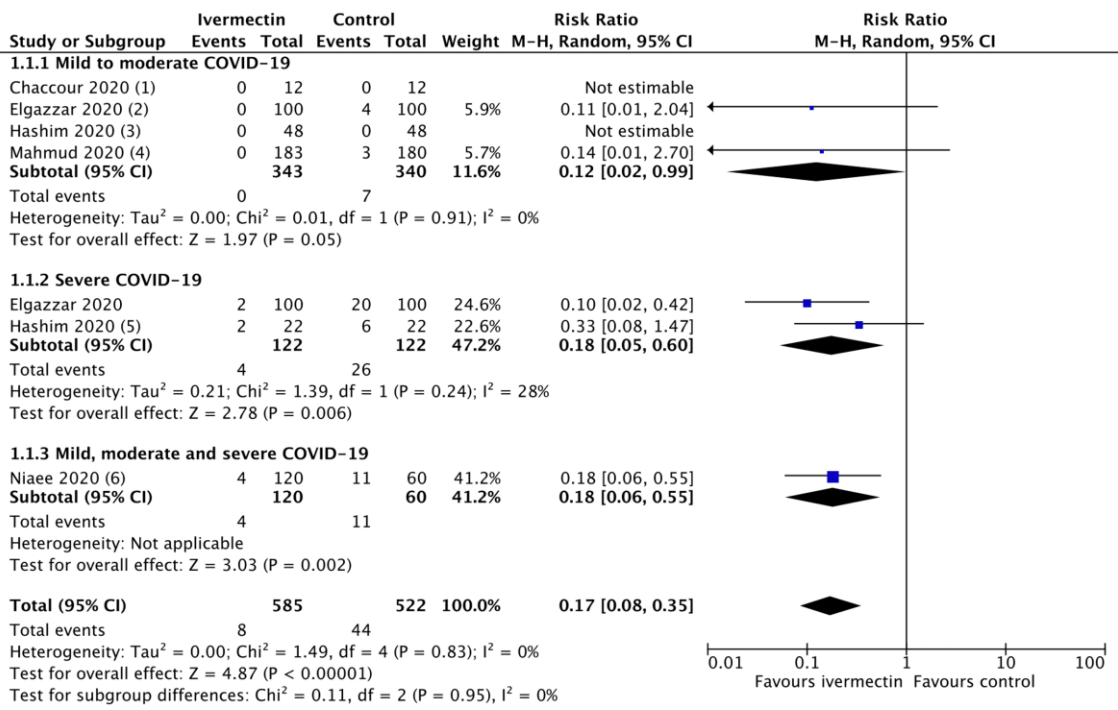
Background to this rapid review Recently a group of expert critical care physicians, called the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC), reviewed the evidence on the effects of ivermectin on SARS-CoV-2 virus and COVID-19 infections. 1 They concluded that the evidence on ivermectin "demonstrates a strong signal of therapeutic efficacy" and recommended that ivermectin is adopted globally and systematically for the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19. 1 Ivermectin is an anti-parasitic medication widely used in low-and middle-income countries to treat parasitic worm infections in adults and children. 1, 2 Having been used for decades for this purpose, it is considered extremely safe and effective 2,3 and has an increasing list of indications due to its antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. 4 On the WHO's Model List of Essential Medicines it is retained in the form of a 3 mg tablet. 5 For parasitic infections in adults, ivermectin is commonly administered as a single 12 mg oral dose (0.2mg/kg). The FLCCC review summarizes the findings of 27 studies evaluating ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19 infection; however, it does not include metaanalyses for the majority of outcomes. The FLCCC has called upon national and international
Author statement I take full responsibility for the scientific integrity of this urgent evidence synthesis. The evidence derived from the studies included in the FLCCC review is sufficient to support a strong recommendation on ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19. Due to the urgency and imperative to communicate this critical information to health professionals, and in the context of the probable effect size of ivermectin on COVID-19 deaths revealed by this meta-analysis, additional exploratory analyses (for example looking at the effect of co-administration of doxycycline) have not been conducted. Neither have I sought unpublished data from the numerous ongoing trials of ivermectin on clinical trial registries. It is my hope that both health professionals and policy makers now respond to this information with the required urgency, so that critical time in saving lives is not wasted. Forest plot for the primary outcome (deaths) including RCTs and OCTs with accompanying funnel plot.
References
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, Hossain, Clemens et al., A five day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int. J. Infect. Disease
Alam, Murshed, Gomes, Masud, Saber et al., Ivermectin as Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 among Healthcare Providers in a Selected Tertiary Hospital in Dhaka -An Observational Study
Barrow, Campos, Powell, A screen of FDA-approved drugs for inhibitors of Zika virus infection, Cell Host & Microbe
Carvallo, Hircsh, Alkis, Contreras, Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Topical Ivermectin + IotaCarrageenan in the Prophylaxis against COVID-19 in Health Personnel, J. Biomed. Res
Chachar, Khan, Asif, Tanveer, Khaqan et al., Effectiveness of Ivermectin in SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Patients, Int. J. Sciences
Chowdhury, Shahbaz, Karim, Islam, Guo et al., SA Randomized Trial of Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin therapy on COVID19 patients, Res. Square
Cochrane, Available from
Elgazzar, Eltaweel, Youssef, Hany, Hafez et al., Efficacy and Safety of ivermectin for Treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 Pandemic, Res. Square
Gorial, Mashhadani, Sayaly, Dakhil, Almashhadani et al., Effectiveness of Ivermectin as add-on Therapy in COVID-19 Management, Pilot Trial,
doi:10.1101/2020.07.07.20145979Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Fatak, Kabah et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345Higgins, Thompson, Deeks, Altman, Measuring inconsistency in metaanalyses, BMJ
Khan, Khan, Debnath, Nath, Mahtab et al., Ivermectin Treatment May Improve the Prognosis of Patients With COVID-19, Archivos de Bronconeumología,
doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007Kircik, Rosso, Layton, Schauber, Over 25 Years of Clinical Experience With Ivermectin: An Overview of Safety for an Increasing Number of Indications, J Drugs Derm
Kory, Meduri, Iglesias, Review of the emerging evidence demonstrating the efficacy of ivermectin in the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19. 18
Niaee, Gheibi, Namdar, Allami, Zolghadr et al., Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multicentre clinical trial, Res. Square
Podder, Chowdhury, Is, Haque, Outcome of ivermectin treated mild to moderate COVID-19 cases: a single-centre, open-label, randomised controlled study, IMC Journal of Medical Science
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease, J. Chest
Shouman, Use of Ivermectin as a Prophylactic Option in Asymptomatic Family Close Contact for Patient with COVID-19, Clinical Trials
Spoorthi, Sasank, Utility of ivermectin and doxycycline combination for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2, International Archives of Integrated Medicine
Sterne, Hernán, Reeves, Savovíc, Berkman et al., ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions, BMJ