Ivermectin under scrutiny: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and possible sources of controversies in COVID-19 patients
Arman Shafiee, Mohammad Mobin Teymouri Athar, Omid Kohandel Gargari, Kyana Jafarabady, Sepehr Siahvoshi, Sayed-Hamidreza Mozhgani
Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8
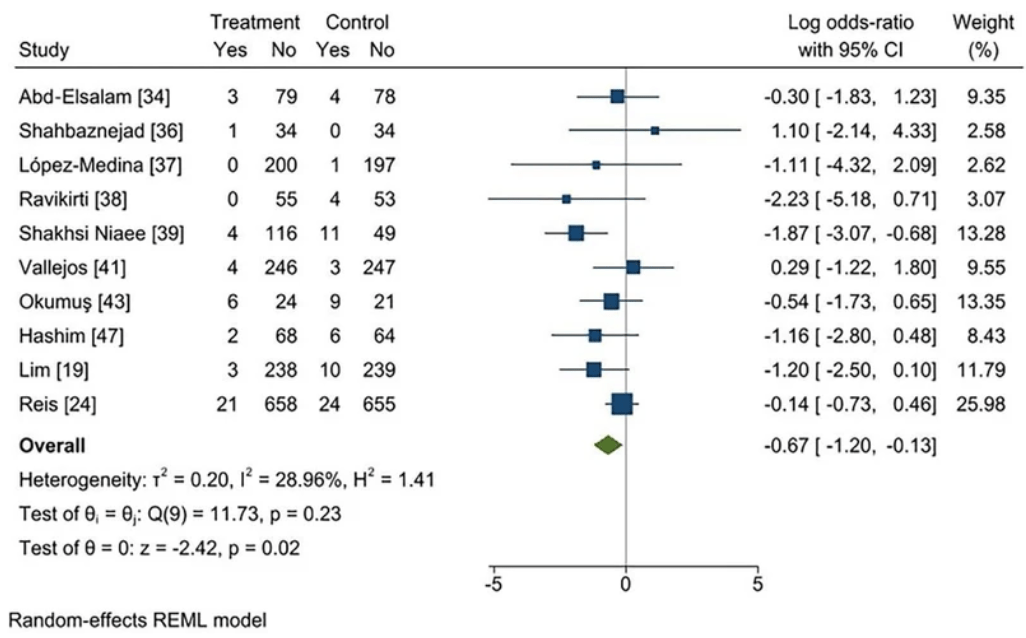
Background: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19 patients based on current peer-reviewed RCTs and to address disputes over the existing evidence. Methods: MEDLINE (Pubmed), Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane library, Google scholar and Clinicaltrials.gov were searched for RCTs assessing the efficacy of Ivermectin up to 20 February 2022. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies was performed based on the PRISMA 2020 statement criteria. Results: 19 and 17 studies were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis, respectively. There was no significant difference in progression to severe disease (log OR − 0.27 [95% CI − 0.61 to 0.08], I2 = 42.29%), negative RT-PCR (log OR 0.25 [95% CI − 0.18-0.68], I2 = 58.73%), recovery (log OR 0.11 [95% CI − 0.22-0.45], I2 = 13.84%), duration of hospitalization (SMD − 0.40 [95% CI − 0.85-0.06], I2 = 88.90%), time to negative RT-PCR (SMD − 0.36 [95% CI − 0.89-0.17], I2 = 46.2%), and viral load (SMD -0.17 [95% CI -0.45 to 0.12], I^2 = 0%). It is worth noting that, based on low-certainty evidence, ivermectin may possibly reduce mortality (log OR − 0.67 [95% CI − 1.20 to − 0.13], I2 = 28.96%). However, studies with a higher risk of bias were more likely to indicate positive effects on the efficacy of this drug, according to our subgroup analyses based on study quality.
Conclusion: Ivermectin did not have any significant effect on outcomes of COVID-19 patients and as WHO recommends, use of ivermectin should be limited to clinical trials.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1186/ s12985-022-01829-8.
Additional file1
Funding The authors declare no funding information.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no Competing interests. • fast, convenient online submission • thorough peer review by experienced researchers in your field
• rapid publication on acceptance • support for research data, including and complex data types • gold Open Access which fosters wider collaboration and increased citations maximum visibility for your research: over 100M website views per year
• At BMC, research is always in progress.
Learn more biomedcentral.com/submissions Ready to submit your research Ready to submit your research ? Choose BMC and benefit from: ? Choose BMC and benefit from:
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Abd-Elsalam, Noor, Badawi, Khalaf, Esmail et al., Clinical study evaluating the efficacy of ivermectin in COVID-19 treatment: a randomized controlled study, J Med Virol
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, Hossain, Clemens et al., A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis
Alvarez-Moreno, Cassell, Donkor, Head, Middleton et al., Long-term consequences of the misuse of ivermectin data, Lancet Infect Dis
Babalola, Bode, Ajayi, Alakaloko, Akase et al., Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos, Qjm
Barnett, Gaye, Jena, Mehrotra, Association of County-Level Prescriptions for Hydroxychloroquine and Ivermectin With County-Level Political Voting Patterns in the 2020 US Presidential Election, JAMA Intern Med
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther
Buonfrate, Chesini, Martini, Roncaglioni, Fernandez et al., High dose ivermectin for the early treatment of COVID-19 (COVER study): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase II, dose-finding, proof of concept clinical trial, Int Antimicrob Agents
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir Res
Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, Pineda, Fernandez-Montero et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, Eclinicalmedicine
Chaudhry, Zubair, Zubairi, Irfan, Role of ivermectin in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a systematic review of literature, Adv Respir Med
Chopra, Industry funding of clinical trials: benefit or bias?, JAMA
Chua, Conti, Becker, us insurer spending on ivermectin prescriptions for COVID-19, JAMA
Cruciani, Pati, Masiello, Malena, Pupella et al., Correction: Cruciani et al. Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of covid-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diagnostics
Cruciani, Pati, Masiello, Malena, Pupella et al., Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diagnostics
Davidson, Source of funding and outcome of clinical trials, J Gen Intern Med
Deng, Zhou, Ali, Heybati, Hou et al., Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, QJM Int J Med
Garegnani, Madrid, Meza, Misleading clinical evidence and systematic reviews on ivermectin for COVID-19, BMJ Evid Based Med
Guyatt, Oxman, Vist, Kunz, Falck-Ytter et al., GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, Bmj
Götz, Magar, Dornfeld, Giese, Pohlmann et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci Rep
Hashim, Maulood, Ali, Rasheed, Fatak et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad. Iraq Iraqi JMS
Higgins, Thomas, Chandler, Cumpston, Li et al., Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions
Hill, Garratt, Levi, Falconer, Ellis et al., Retracted: meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab358Hill, Mirchandani, Ellis, Pilkington, Ivermectin for the prevention of COVID-19: addressing potential bias and medical fraud, J Antimicrob Chemother
Hill, Mirchandani, Pilkington, Ivermectin for COVID-19: addressing potential bias and medical fraud, Open Forum Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab645Izcovich, Peiris, Ragusa, Tortosa, Rada et al., Bias as a source of inconsistency in ivermectin trials for COVID-19: A systematic review. Ivermectin's suggested benefits are mainly based on potentially biased results, J Clin Epidemiol,
doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.12.018Kakodkar, Kaka, Baig, A comprehensive literature review on the clinical presentation, and management of the pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Cureus
Kow, Merchant, Mustafa, Hasan, The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a metaanalysis, Pharmacol Rep
Kow, Merchant, Mustafa, Hasan, The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a metaanalysis, Pharmacol Rep PR
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Travacio, Valentini et al., Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine
Krumm, Lloyd, Francis, Nasif, Mitchell et al., Precision therapeutic targets for COVID-19, Virol J
Lawrence, Meyerowitz-Katz, Heathers, Brown, Sheldrick, The lesson of ivermectin: meta-analyses based on summary data alone are inherently unreliable, Nat Med
Lim, Hor, Tay, Jelani, Tan et al., Efficacy of ivermectin treatment on disease progression among adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 and comorbidities: the I-TECH randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med
Lopez-Medina, Lopez, Hurtado, Davalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19 a randomized clinical trial, Jama-J Am Med Assoc
Lu, Stratton, Tang, Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: the mystery and the miracle, J Med Virol
Luo, Wan, Liu, Tong, Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range, Stat Methods Med Res
Mahmud, Rahman, Alam, Ahmed, Kabir et al., Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial, J Int Med Res
Manu, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther
Mohan, Tiwari, Suri, Mittal, Patel et al., Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): A single-centre randomized, placebocontrolled trial, J Infect Chemother,
doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021Molnar, Lau, Berges, Masa, Solano et al., Ivermectin in COVID-19: the case for a moratorium on prescriptions, Ther Innov Regul Sci
Mouffak, Shubbar, Saleh, El-Awady, Recent advances in management of COVID-19: a review, Biomed Pharmacother
Niaee, Namdar, Allami, Zolghadr, Javadi et al., Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: a randomized multicenter clinical trial, Asian Pac J Trop Med
Okumuş, Demirtürk, Çetinkaya, Güner, Avcı et al., Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID-19 patients, BMC Infect Diseases
Padhy, Mohanty, Das, Meher, Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Pharm Pharm Sci
Padhy, Mohanty, Das, Meher, Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis: ivermectin in COVID-19: a meta-analysis, J Pharm Pharm Sci
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, Int J Surg
Pott-Junior, Paoliello, Miguel, Da Cunha, De et al., Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: a pilot trial, Toxicol Rep
Rakedzon, Neuberger, Domb, Petersiel, Schwartz, From hydroxychloroquine to ivermectin: what are the anti-viral properties of anti-parasitic drugs to combat SARS-CoV-2?, J Travel Med,
doi:10.1093/jtm/taab005Ravikirti, Pattadar, Raj, Agarwal, Biswas et al., Evaluation of ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate covid-19: a double-blind randomized placebo controlled trial in eastern India, J Pharm Pharm Sci
Reardon, Flawed ivermectin preprint highlights challenges of COVID drug studies, Nature
Reis, Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with ivermectin among patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Riaz, Raza, Khan, Riaz, Krasuski, Impact of funding source on clinical trial results including cardiovascular outcome trials, Am J Cardiol
Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Piscoya, Vidal et al., Ivermectin for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Infect Dis
Rothrock, Weber, Giordano, Barneck, Meta-analyses do not establish improved mortality with ivermectin use in COVID-19, Am J Ther
Samaha, Mouawia, Fawaz, Hassan, Salami et al., Effects of a Single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon, Viruses
Samaha, Mouawia, Fawaz, Hassan, Salami et al., Effects of a single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon, Viruses
Saxena, Rajanagam, Jhamb, Manchanda, Saxena, Efficacy of single-dose ivermectin on virologic and clinical recovery in COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial, MAMC J Med Sci
Schraer, Ivermectin: How false science created a Covid 'miracle' drug
Shahbaznejad, Davoudi, Eslami, Markowitz, Navaeifar et al., Effects of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, Controll Clin Trial Clin Ther
Sheldrick, Data from Niaee et al is not consistent with a genuine randomised controlled trial
Shi, Luo, Wan, Liu, Liu et al., Detecting the skewness of data from the sample size and the five-number summary
Sterne, Savović, Page, Elbers, Blencowe et al., RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Temple, Hoang, Hendrickson, Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Villamandos, Bobadilla et al., Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Infect Dis,
doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem J
Wan, Wang, Liu, Tong, Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range, BMC Med Res Methodol
Zein, Sulistiyana, Raffaelo, Pranata, Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials, Diabetes Metab Syndr
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8",
"ISSN": [
"1743-422X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19 patients based on current peer-reviewed RCTs and to address disputes over the existing evidence.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>MEDLINE (Pubmed), Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane library, Google scholar and Clinicaltrials.gov were searched for RCTs assessing the efficacy of Ivermectin up to 20 February 2022. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies was performed based on the PRISMA 2020 statement criteria.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>19 and 17 studies were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis, respectively. There was no significant difference in progression to severe disease (log OR − 0.27 [95% CI − 0.61 to 0.08], I2 = 42.29%), negative RT-PCR (log OR 0.25 [95% CI − 0.18–0.68], I2 = 58.73%), recovery (log OR 0.11 [95% CI − 0.22–0.45], I2 = 13.84%), duration of hospitalization (SMD − 0.40 [95% CI − 0.85–0.06], I2 = 88.90%), time to negative RT-PCR (SMD − 0.36 [95% CI − 0.89–0.17], I2 = 46.2%), and viral load (SMD -0.17 [95% CI -0.45 to 0.12], I^2 = 0%). It is worth noting that, based on low-certainty evidence, ivermectin may possibly reduce mortality (log OR − 0.67 [95% CI − 1.20 to − 0.13], I2 = 28.96%). However, studies with a higher risk of bias were more likely to indicate positive effects on the efficacy of this drug, according to our subgroup analyses based on study quality.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Ivermectin did not have any significant effect on outcomes of COVID-19 patients and as WHO recommends, use of ivermectin should be limited to clinical trials.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"1829"
],
"article-number": "102",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "24 March 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "13 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no Competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shafiee",
"given": "Arman",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teymouri Athar",
"given": "Mohammad Mobin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kohandel Gargari",
"given": "Omid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafarabady",
"given": "Kyana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siahvoshi",
"given": "Sepehr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mozhgani",
"given": "Sayed-Hamidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Virology Journal",
"container-title-short": "Virol J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-13T17:03:52Z",
"timestamp": 1655139832000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-14T01:07:58Z",
"timestamp": 1668388078000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-07T11:27:41Z",
"timestamp": 1670412461615
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655078400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655078400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25678",
"author": "H Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "401",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1829_CR1",
"unstructured": "Lu H, Stratton CW, Tang Y-W. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: the mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol. 2020;92:401–2.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "P Kakodkar",
"first-page": "e7560",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "1829_CR2",
"unstructured": "Kakodkar P, Kaka N, Baig MN. A comprehensive literature review on the clinical presentation, and management of the pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Cureus. 2020;12:e7560–e7560.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "1829_CR3",
"unstructured": "WHO COVID-19 Dashboard [https://covid19.who.int/]"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-021-01526-y",
"author": "ZA Krumm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "1829_CR4",
"unstructured": "Krumm ZA, Lloyd GM, Francis CP, Nasif LH, Mitchell DA, Golde TE, Giasson BI, Xia Y. Precision therapeutic targets for COVID-19. Virol J. 2021;18:66.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112107",
"author": "S Mouffak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112107",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "1829_CR5",
"unstructured": "Mouffak S, Shubbar Q, Saleh E, El-Awady R. Recent advances in management of COVID-19: a review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112107.",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taab005",
"author": "S Rakedzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Travel Med",
"key": "1829_CR6",
"unstructured": "Rakedzon S, Neuberger A, Domb AJ, Petersiel N, Schwartz E. From hydroxychloroquine to ivermectin: what are the anti-viral properties of anti-parasitic drugs to combat SARS-CoV-2? J Travel Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taab005.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac052",
"author": "A Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1413",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob. Chemother.",
"key": "1829_CR7",
"unstructured": "Hill A, Mirchandani M, Ellis L, Pilkington V. Ivermectin for the prevention of COVID-19: addressing potential bias and medical fraud. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022;77:1413–6.",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001461",
"author": "SG Rothrock",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e87",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "1829_CR8",
"unstructured": "Rothrock SG, Weber KD, Giordano PA, Barneck MD. Meta-analyses do not establish improved mortality with ivermectin use in COVID-19. Am J Ther. 2022;29:e237–44.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43441-022-00378-0",
"author": "A Molnar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "Ther Innov Regul Sci",
"key": "1829_CR9",
"unstructured": "Molnar A, Lau S, Berges M, Masa RB, Solano JJ, Alter SM, Clayton LM, Shih RD, DeMets DL, Maki DG, Hennekens CH. Ivermectin in COVID-19: the case for a moratorium on prescriptions. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022;56:382–5.",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.24352",
"author": "K-P Chua",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "584",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1829_CR10",
"unstructured": "Chua K-P, Conti RM, Becker NV. us insurer spending on ivermectin prescriptions for COVID-19. JAMA. 2022;327:584–7.",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"author": "L Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "1829_CR11",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antivir Res. 2020;178:104787.",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep23138",
"author": "V Götz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "23138",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "1829_CR12",
"unstructured": "Götz V, Magar L, Dornfeld D, Giese S, Pohlmann A, Höper D, Kong B-W, Jans DA, Beer M, Haller O, Schwemmle M. Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23138.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20120150",
"author": "KM Wagstaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "851",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "1829_CR13",
"unstructured": "Wagstaff KM, Sivakumaran H, Heaton SM, Harrich D, Jans DA. Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus. Biochem J. 2012;443:851–6.",
"volume": "443",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjebm-2021-111678",
"author": "LI Garegnani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "156",
"journal-title": "BMJ Evid Based Med",
"key": "1829_CR14",
"unstructured": "Garegnani LI, Madrid E, Meza N. Misleading clinical evidence and systematic reviews on ivermectin for COVID-19. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2021;27:156–8.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01535-y",
"author": "JM Lawrence",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1853",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "1829_CR15",
"unstructured": "Lawrence JM, Meyerowitz-Katz G, Heathers JAJ, Brown NJL, Sheldrick KA. The lesson of ivermectin: meta-analyses based on summary data alone are inherently unreliable. Nat Med. 2021;27:1853–4.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186",
"author": "A Zein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102186",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "1829_CR16",
"unstructured": "Zein A, Sulistiyana CS, Raffaelo WM, Pranata R. Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021;15:102186.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z",
"author": "CS Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "1829_CR17",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Merchant HA, Mustafa ZU, Hasan SS. The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Pharmacol Rep. 2021;73:1473–9.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5603/ARM.a2021.0088",
"author": "MW Chaudhry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Adv Respir Med",
"key": "1829_CR18",
"unstructured": "Chaudhry MW, Zubair SM, Zubairi ABS, Irfan M. Role of ivermectin in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a systematic review of literature. Adv Respir Med. 2021;89:413–8.",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189",
"author": "SCL Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "426",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "1829_CR19",
"unstructured": "Lim SCL, Hor CP, Tay KH, Mat Jelani A, Tan WH, Ker HB, Chow TS, Zaid M, Cheah WK, Lim HH, et al. Efficacy of ivermectin treatment on disease progression among adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 and comorbidities: the I-TECH randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(4):426–35.",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106516",
"author": "D Buonfrate",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106516",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "1829_CR20",
"unstructured": "Buonfrate D, Chesini F, Martini D, Roncaglioni MC, Fernandez MLO, Alvisi MF, De Simone I, Rulli E, Nobili A, Casalini G, et al. High dose ivermectin for the early treatment of COVID-19 (COVER study): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase II, dose-finding, proof of concept clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2022;59:106516.",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13112154",
"author": "AA Samaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2154",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "1829_CR21",
"unstructured": "Samaha AA, Mouawia H, Fawaz M, Hassan H, Salami A, Bazzal AA, Saab HB, Al-Wakeel M, Alsaabi A, Chouman M, et al. Retraction: Samaha et al. Effects of a Single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon . Viruses 2021. Viruses. 2021;13:2154.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"author": "P Manu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e434",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "1829_CR22",
"unstructured": "Manu P. Expression of concern for Bryant a, Lawrie TA, Dowswell T, Fordham EJ, Mitchell S, Hill SR, Tham TC. Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines. Am J Ther. 2021;28(4):e434–60.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"author": "A Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1829_CR23",
"unstructured": "Hill A, Garratt A, Levi J, Falconer J, Ellis L, McCann K, Pilkington V, Qavi A, Wang J, Wentzel H. Retracted: meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab358.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2115869",
"author": "G Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1721",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1829_CR24",
"unstructured": "Reis G, Silva EASM, Silva DCM, Thabane L, Milagres AC, Ferreira TS, dos Santos CVQ, Campos VHS, Nogueira AMR, de Almeida APFG, et al. Effect of early treatment with ivermectin among patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1721–31.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9781119536604",
"author": "JPT Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1829_CR25",
"unstructured": "Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons; 2019.",
"volume-title": "Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906",
"author": "MJ Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105906",
"journal-title": "Int J Surg",
"key": "1829_CR26",
"unstructured": "Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SEJB. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. 2021;88:105906.",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "1829_CR27",
"unstructured": "Shi J, Luo D, Wan X, Liu Y, Liu J, Bian Z, Tong T. Detecting the skewness of data from the sample size and the five-number summary. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.05749. 2020 Oct 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280216669183",
"author": "D Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1785",
"journal-title": "Stat Methods Med Res",
"key": "1829_CR28",
"unstructured": "Luo D, Wan X, Liu J, Tong T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res. 2018;27:1785–805.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-14-135",
"author": "X Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med Res Methodol",
"key": "1829_CR29",
"unstructured": "Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong TJ. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:1–13.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"author": "JAC Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "l4898",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1829_CR30",
"unstructured": "Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng HY, Corbett MS, Eldridge SM, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898.",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD",
"author": "GH Guyatt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "924",
"journal-title": "Bmj",
"key": "1829_CR31",
"unstructured": "Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJJB. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Bmj. 2008;336:924–6.",
"volume": "336",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959",
"author": "A Krolewiecki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100959",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "1829_CR32",
"unstructured": "Krolewiecki A, Lifschitz A, Moragas M, Travacio M, Valentini R, Alonso DF, Solari R, Tinelli MA, Cimino RO, Álvarez LJE. Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;37:100959.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003",
"author": "H Pott-Junior",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Rep",
"key": "1829_CR33",
"unstructured": "Pott-Junior H, Bastos Paoliello MM, Miguel ADQC, da Cunha AF, de Melo Freire CC, Neves FF, Silva Avó da de LR, Roscani MG, dos Santos SDS, Chachá SGF. Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: a pilot trial. Toxicol Rep. 2021;8:505–10.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27122",
"author": "S Abd-Elsalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5833",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1829_CR34",
"unstructured": "Abd-Elsalam S, Noor RA, Badawi R, Khalaf M, Esmail ES, Soliman S, Abd El Ghafar MS, Elbahnasawy M, Moustafa EF, Hassany SM, et al. Clinical study evaluating the efficacy of ivermectin in COVID-19 treatment: a randomized controlled study. J Med Virol. 2021;93:5833–8.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"author": "C Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Eclinicalmedicine",
"key": "1829_CR35",
"unstructured": "Chaccour C, Casellas A, Blanco-Di Matteo A, Pineda I, Fernandez-Montero A, Ruiz-Castillo P, Richardson MA, Rodriguez-Mateos M, Jordan-Iborra C, Brew J, et al. The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Eclinicalmedicine. 2021;32:9.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "L Shahbaznejad",
"first-page": "1007",
"journal-title": "Controll. Clin. Trial Clin. Ther.",
"key": "1829_CR36",
"unstructured": "Shahbaznejad L, Davoudi A, Eslami G, Markowitz JS, Navaeifar MR, Hosseinzadeh F, Movahedi FS, Rezai MS. Effects of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized. Controll Clin Trial Clin Ther. 2021;43:1007–19.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"author": "E Lopez-Medina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "Jama-J Am Med Assoc",
"key": "1829_CR37",
"unstructured": "Lopez-Medina E, Lopez P, Hurtado IC, Davalos DM, Ramirez O, Martinez E, Diazgranados JA, Onate JM, Chavarriaga H, Herrera S, et al. Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19 a randomized clinical trial. Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 2021;325:1426–35.",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps32105",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1829_CR38",
"unstructured": "Ravikirti, Roy R, Pattadar C, Raj R, Agarwal N, Biswas B, Manjhi PK, Rai DK, Shyama, Kumar A, Sarfaraz A. Evaluation of ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate covid-19: a double-blind randomized placebo controlled trial in eastern India. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2021; 24:343-350."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1995-7645.318304",
"author": "M Shakhsi Niaee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Trop Med",
"key": "1829_CR39",
"unstructured": "Shakhsi Niaee M, Namdar P, Allami A, Zolghadr L, Javadi A, Karampour A, Varnaseri M, Bijani B, Cheraghi F, Naderi Y, et al. Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: a randomized multi-center clinical trial. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2021;14:266–73.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab035",
"author": "OE Babalola",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "780",
"journal-title": "Qjm",
"key": "1829_CR40",
"unstructured": "Babalola OE, Bode CO, Ajayi AA, Alakaloko FM, Akase IE, Otrofanowei E, Salu OB, Adeyemo WL, Ademuyiwa AO, Omilabu S. Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos. Qjm. 2021;114:780–8.",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"author": "J Vallejos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "1829_CR41",
"unstructured": "Vallejos J, Zoni R, Bangher M, Villamandos S, Bobadilla A, Plano F, Campias C, Chaparro Campias E, Medina MF, Achinelli F, et al. Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021",
"author": "A Mohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Chemother",
"key": "1829_CR42",
"unstructured": "Mohan A, Tiwari P, Suri TM, Mittal S, Patel A, Jain A, Velpandian T, Das US, Boppana TK, Pandey RM, et al. Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): A single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Infect Chemother. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06104-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1829_CR43",
"unstructured": "Okumuş N, Demirtürk N, Çetinkaya RA, Güner R, Avcı İY, Orhan S, Konya P, Şaylan B, Karalezli A, Yamanel L, Kayaaslan B. Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID-19 patients. BMC Infect Diseases. 2021;21(1):1-1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211013550",
"author": "R Mahmud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "300060521101355",
"journal-title": "J Int Med Res",
"key": "1829_CR44",
"unstructured": "Mahmud R, Rahman MM, Alam I, Ahmed KGU, Kabir A, Sayeed S, Rassel MA, Monayem FB, Islam MS, Islam MM, et al. Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial. J Int Med Res. 2021;49:3000605211013550.",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"author": "S Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "1829_CR45",
"unstructured": "Ahmed S, Karim MM, Ross AG, Hossain MS, Clemens JD, Sumiya MK, Phru CS, Rahman M, Zaman K, Somani J, et al. A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;103:214–6.",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "R Saxena",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "MAMC J Med Sci",
"key": "1829_CR46",
"unstructured": "Saxena R, Rajanagam M, Jhamb U, Manchanda V, Saxena S. Efficacy of single-dose ivermectin on virologic and clinical recovery in COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial. MAMC J Med Sci. 2021;7:109–14.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "H Hashim",
"first-page": "107",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Iraq Iraqi JMS",
"key": "1829_CR47",
"unstructured": "Hashim H, Maulood M, Ali C, Rasheed A, Fatak D, Kabah K, Abdulamir AJI. Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad. Iraq Iraqi JMS. 2021;19(1):107–15.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "1829_CR48",
"unstructured": "M-K G. Is ivermectin for Covid-19 based on fraudulent research? Accessed Oct 9, 2021."
},
{
"key": "1829_CR49",
"unstructured": "Sheldrick K. Data from Niaee et al is not consistent with a genuine randomised controlled trial. Accessed 8 October 2021."
},
{
"key": "1829_CR50",
"unstructured": "Schraer R. Ivermectin: How false science created a Covid 'miracle' drug. Accessed 6 October 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps31457",
"author": "BM Padhy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "462",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Pharm Sci",
"key": "1829_CR51",
"unstructured": "Padhy BM, Mohanty RR, Das S, Meher BR. Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis: ivermectin in COVID-19: a meta-analysis. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2020;23:462–9.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics11122359",
"author": "M Cruciani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2359",
"journal-title": "Diagnostics",
"key": "1829_CR52",
"unstructured": "Cruciani M, Pati I, Masiello F, Malena M, Pupella S, De Angelis V. Correction: Cruciani et al. Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of covid-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics. 2021;11:2359.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z",
"author": "CS Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep PR",
"key": "1829_CR53",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Merchant HA, Mustafa ZU, Hasan SS. The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Pharmacol Rep PR. 2021;73:1473–9.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab591",
"author": "YM Roman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1022",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis.",
"key": "1829_CR54",
"unstructured": "Roman YM, Burela PA, Pasupuleti V, Piscoya A, Vidal JE, Hernandez AV. Ivermectin for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;74(6):1022–9.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab247",
"author": "J Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "721",
"journal-title": "QJM Int J Med",
"key": "1829_CR55",
"unstructured": "Deng J, Zhou F, Ali S, Heybati K, Hou W, Huang E, Wong CY. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM Int J Med. 2021;114:721–32.",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab645",
"author": "A Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1829_CR56",
"unstructured": "Hill A, Mirchandani M, Pilkington V. Ivermectin for COVID-19: addressing potential bias and medical fraud. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab645.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2114907",
"author": "C Temple",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2197",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1829_CR57",
"unstructured": "Temple C, Hoang R, Hendrickson RG. Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2197–8.",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00630-7",
"author": "C Alvarez-Moreno",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1624",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "1829_CR58",
"unstructured": "Alvarez-Moreno C, Cassell JA, Donkor CM, Head MG, Middleton J, Pomat W, Saka B, Yirgu R. Long-term consequences of the misuse of ivermectin data. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:1624–6.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-02081-w",
"author": "S Reardon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1829_CR59",
"unstructured": "Reardon S. Flawed ivermectin preprint highlights challenges of COVID drug studies. Nature. 2021;596:173–4.",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13060989",
"author": "AA Samaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "989",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "1829_CR60",
"unstructured": "Samaha AA, Mouawia H, Fawaz M, Hassan H, Salami A, Bazzal AA, Saab HB, Al-Wakeel M, Alsaabi A, Chouman MJV. Effects of a single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon. Viruses. 2021;13:989.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"author": "A Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e434",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "1829_CR61",
"unstructured": "Bryant A, Lawrie TA, Dowswell T, Fordham EJ, Mitchell S, Hill SR, Tham TC. Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines. Am J Ther. 2021;28:e434–60.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics11091645",
"author": "M Cruciani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1645",
"journal-title": "Diagnostics (Basel)",
"key": "1829_CR62",
"unstructured": "Cruciani M, Pati I, Masiello F, Malena M, Pupella S, De Angelis V. Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11:1645.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.12.018",
"author": "A Izcovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol.",
"key": "1829_CR63",
"unstructured": "Izcovich A, Peiris S, Ragusa M, Tortosa F, Rada G, Aldighieri S, Reveiz L. Bias as a source of inconsistency in ivermectin trials for COVID-19: A systematic review. Ivermectin's suggested benefits are mainly based on potentially biased results. J Clin Epidemiol. 2022;144:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.12.018.",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps31457",
"author": "BM Padhy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "462",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Pharm Sci",
"key": "1829_CR64",
"unstructured": "Padhy BM, Mohanty RR, Das S, Meher BR. Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2020;23:462–9.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF02602327",
"author": "RA Davidson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "J Gen Intern Med",
"key": "1829_CR65",
"unstructured": "Davidson RA. Source of funding and outcome of clinical trials. J Gen Intern Med. 1986;1:155–8.",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.09.034",
"author": "H Riaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1944",
"journal-title": "Am J Cardiol",
"key": "1829_CR66",
"unstructured": "Riaz H, Raza S, Khan MS, Riaz IB, Krasuski RA. Impact of funding source on clinical trial results including cardiovascular outcome trials. Am J Cardiol. 2015;116:1944–7.",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.290.1.113",
"author": "SS Chopra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1829_CR67",
"unstructured": "Chopra SS. Industry funding of clinical trials: benefit or bias? JAMA. 2003;290:113–4.",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0200",
"author": "ML Barnett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "452",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "1829_CR68",
"unstructured": "Barnett ML, Gaye M, Jena AB, Mehrotra A. Association of County-Level Prescriptions for Hydroxychloroquine and Ivermectin With County-Level Political Voting Patterns in the 2020 US Presidential Election. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182:452–4.",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 68,
"references-count": 68,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://virologyj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin under scrutiny: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and possible sources of controversies in COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "19"
}