Abstract: 828
Cartas Científicas / Arch Bronconeumol. 2020;56(12):816–830
María Teresa Gómez-Hernández a,∗ , Nuria M. Novoa a ,
Patricia Antúnez b , Marcelo F. Jiménez a
∗ Corresponding author.
E-mail address: mteresa.gomez.hernandez@gmail.com
(M.T. Gómez-Hernández).
a
Service of Thoracic Surgery, Salamanca University Hospital,
Salamanca, Spain
b Service of Anatomical Pathology, Salamanca University Hospital,
Salamanca, Spain
Ivermectin Treatment May Improve the
Prognosis of Patients With COVID-19
El tratamiento con ivermectina puede mejorar el pronóstico de
los pacientes con COVID-19
Dear Editor:
The pandemic coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), caused by
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2),
has been spread rapidly worldwide with considerable morbidity
and mortality. COVID-19 patients have various clinical presentations: asymptomatic, exhibit mild flu-like symptoms, be severely
ill or death.1,2 In addition to elder age and comorbidities, higher
levels of D-dimer and C-reactive protein (CRP) and lower levels of
lymphocyte and eosinophil as well as a cytokine storm are associated with disease severity in COVID-19 patients.3–6 The virus load
may be a main determinant underlying the pathological diversity
in COVID-19 patients.1,2,6 Thus, an effective antiviral treatment is
essential to improve the prognosis of patients with COVID-19.7 In
the absence of specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, various drugs with
antiviral potential are now used to contain the virus in COVID-19
patients. Ivermectin, a US FDA-approved anthelminthic, has garnered enormous interest for treating COVID-19 as it is safe and cheap
and has strong antiviral activities against board ranges of viruses
including SARS-CoV-2 in vitro.8–10 Despite the widespread use of
ivermectin, to our knowledge, there is currently no published clinical reports of ivermectin in COVID-19 patients. Here, we assessed
the clinical efficacy of ivermectin in COVID-19 patients.
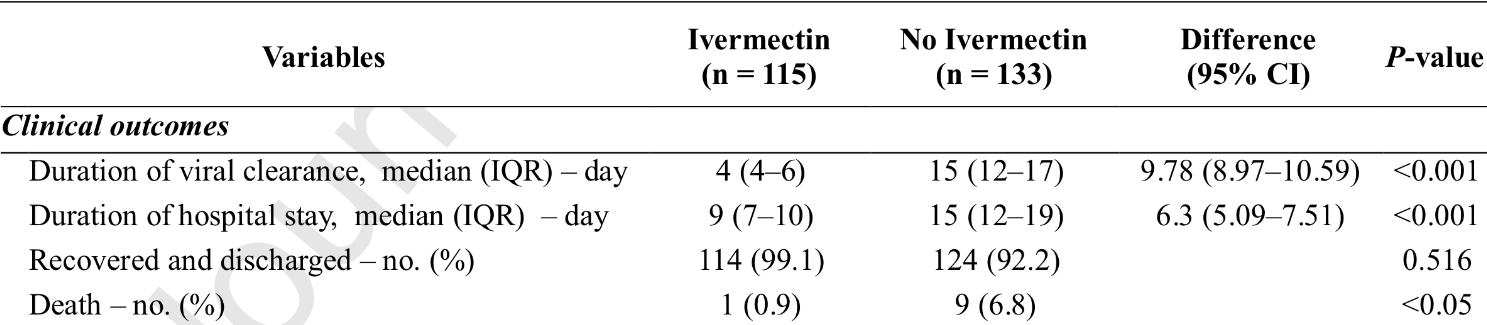
This retrospective study enrolled a total of 325 consecutive
patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed by polymerase chain
reaction (PCR) of nasal swabs in SK hospital, a unit dedicated
to COVID-19 at Mymensingh Medical College Hospital (MMCH),
Mymensingh, Bangladesh, from April to June 2020. Of these, the
present study included 248 adult COVID-19 patients free from
any other serious pathological conditions: 115 received ivermectin
plus standard care (SC), while 133 received only SC. Remaining 77
patients who were under 18 years of age or transferred from other
facilities and received different management approaches including
partial hospital stays or treated with different therapeutic agents
prior to hospital admission were excluded from the analysis. The
two groups were compared in terms of time to SARS-CoV-2 negativity, disease progression (develop pneumonia to severe respiratory
distress), duration of hospital stays, and mortality rate. Ivermectin
was given once at dose of 12 mg within 24-h after hospital admission. SC was provided as required and included antipyretics for
fever, anti-histamines for cough, and antibiotics to control secondary infection. The study was approved by MMCH and informed
consent was obtained from all patients or their relatives before
starting treatment. Categorical variables are shown as frequencies
and percentages and continuous variables as the median and interquartile range (IQR). Differences with 95% confidence intervals (CI)
were computed to show the level of certainty...
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007",
"ISSN": [
"0300-2896"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007",
"alternative-id": [
"S030028962030288X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Ivermectin Treatment May Improve the Prognosis of Patients With COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Archivos de Bronconeumología"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2020.09.004"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.012"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 SEPAR. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Md. Saiful Islam",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Md. Sakirul Islam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Debnath",
"given": "Chitto Ranjan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nath",
"given": "Progga Nanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahtab",
"given": "Mamun Al",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nabeka",
"given": "Hiroaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matsuda",
"given": "Seiji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akbar",
"given": "Sheikh Mohammad Fazle",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Archivos de Bronconeumología",
"container-title-short": "Archivos de Bronconeumología",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.es",
"elsevier.es",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-25T00:10:25Z",
"timestamp": 1600992625000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-04T13:04:30Z",
"timestamp": 1607087070000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-28T16:46:38Z",
"timestamp": 1711644398256
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 28,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1606780800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S030028962030288X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S030028962030288X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "828-830",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Pathophysiology, transmission diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review",
"author": "Wiersinga",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0080",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x",
"article-title": "Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019",
"author": "Wölfel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0085",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Comorbidities and mortality in patients with COVID-19 aged 60 years and older in a university hospital in Spain",
"author": "Posso",
"journal-title": "Arch Bronconeumol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0090",
"volume": "S0300–2896",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of peripheral blood eosinophil counts in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Xie",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0095",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14364",
"article-title": "Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID-19",
"author": "Azkur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1564",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0100",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa388",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and factors associated with long-term viral excretion in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a single center 28-day study",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13063",
"article-title": "Early antiviral treatment contributes to alleviate the severity and improve the prognosis of patients with novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19)",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0110",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen",
"author": "Heidary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot (Tokyo)",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0115",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0120",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties of ivermectin and its potential use in COVID-19",
"author": "Portmann-Baracco",
"journal-title": "Arch Bronconeumol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0125",
"volume": "S0300–2896",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02893-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load in sputum correlates with risk of COVID-19 progression",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "170",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0130",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1443",
"article-title": "Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1443",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0135",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4",
"article-title": "Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial",
"author": "Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1695",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0140",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0145",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.08.007_bib0150",
"series-title": "Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation Report – 197 on August 04",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S030028962030288X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin Treatment May Improve the Prognosis of Patients With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "56"
}