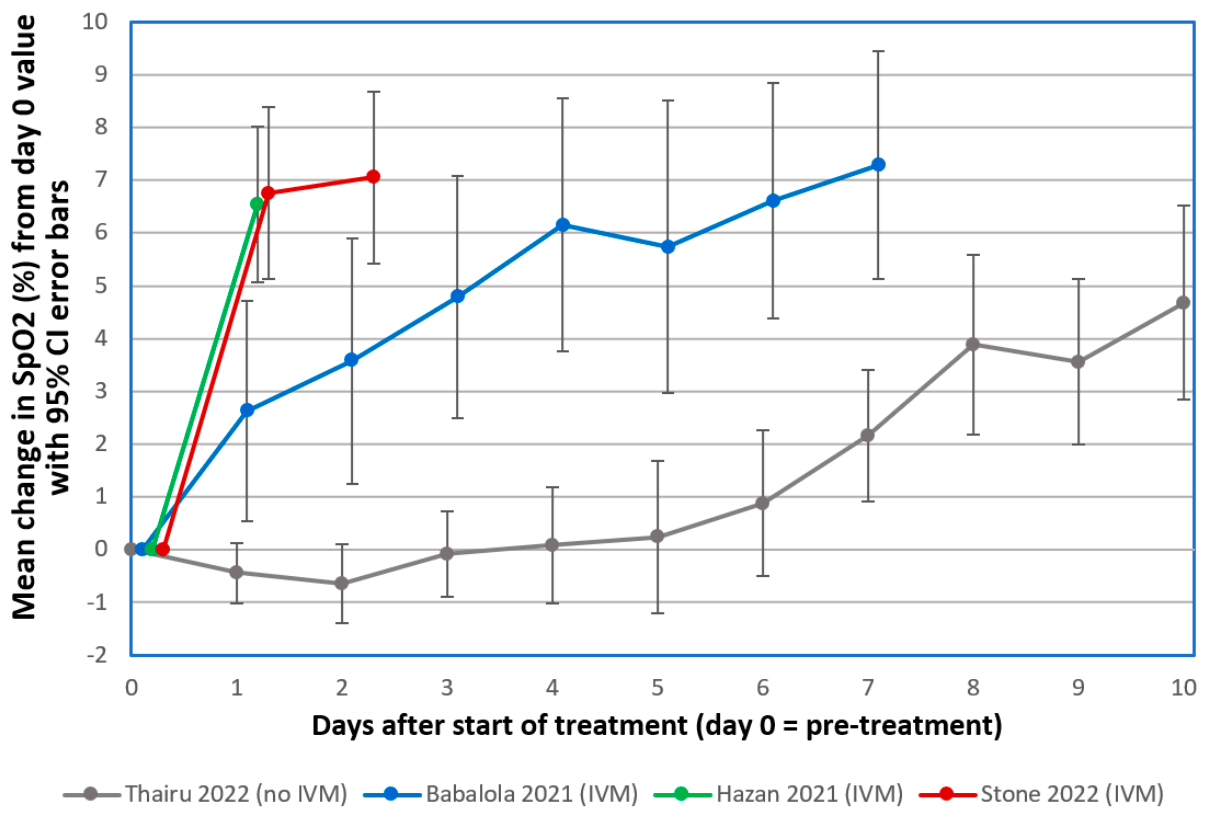
Changes in SpO2 on Room Air for 34 Severe COVID-19 Patients after Ivermectin-Based Combination Treatment: 62% Normalization within 24 Hours
Jaqueline C Stone, Pisirai Ndarukwa, David E Scheim, Barry M Dancis, Jerome Dancis, Martin G Gill, Colleen Aldous
Biologics, doi:10.3390/biologics2030015
The emergence of COVID-19 in March 2020 challenged Zimbabwe to respond with limited medical facilities and therapeutic options. Based on early clinical indications of efficacy for the macrocyclic lactone, Ivermectin (IVM), against COVID-19, IVM-based combination treatments were deployed to treat it. Oxygen saturation (SpO2) data were retrospectively analyzed for 34 severe, hypoxic COVID-19 patients all on room air (without supplemental oxygen). The patients, median age 56.5, were treated at clinics or at home between August 2020 and May 2021. All but three of these 34 patients had significantly increased SpO2 values within 24 h after the first IVM dose. The mean increase in SpO2 as a percentage of full normalization to SpO2 = 97 was 55.1% at +12 h and 62.3% at +24 h after the first IVM dose (paired t-test, p < 0.0000001). These results parallel similar sharp, rapid increases in SpO2, all on room air, for 24 mostly severe COVID-19 patients in the USA (California) who were given an IVM-based combination treatment. All patients in both of these critical series recovered. These rapid increases in SpO2 values after IVM treatment stand in sharp contrast to declines in SpO2 and associated pulmonary function through the second week following the onset of moderate or severe COVID-19 symptoms under standard care.
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Abbreviations The
References
Aminpour, Cannariato, Safaeeardebili, Preto, Moracchiato et al., In silico analysis of the multi-targeted mode of action of ivermectin and related compounds, Computation,
doi:10.3390/computation10040051Annunziata, Coppola, Carannante, Simioli, Lanza et al., Home management of patients with moderate or severe respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19, using remote monitoring and oxygen with or without HFNC, Pathogens,
doi:10.3390/pathogens10040413Aoki, Iwasawa, Hagiwara, Komatsu, Utsunomiya et al., Pulmonary vascular enlargement and lesion extent on computed tomography are correlated with COVID-19 disease severity, Jpn. J. Radiol,
doi:10.1007/s11604-020-01085-2Arévalo, Pagotto, Pórfido, Daghero, Segovia et al., Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model, Sci. Rep
Ayerbe, Risco, Ayis, The association between treatment with heparin and survival in patients with Covid-19, J. Thromb. Thrombolysis,
doi:10.1007/s11239-020-02162-zBabalola, Karu, Personal communication
Babalola, Ndanusa, Adesuyi, Ogedengbe, Thairu et al., A randomized controlled trial of ivermectin monotherapy versus HCQ, IVM, and AZ combination therapy in COVID-19 patients in Nigeria, J. Infect. Dis. Epidemiol,
doi:10.23937/2474-3658/1510233Campbell, History of avermectin and ivermectin, with notes on the history of other macrocyclic lactone antiparasitic agents, Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol,
doi:10.2174/138920112800399095Chirisa, Zimbabwe Confirms Its First Case of Coronavirus
Chung, Yang, Wu, Deng, Tsai, Agricultural avermectins: An uncommon but potentially fatal cause of pesticide poisoning, Ann. Emerg. Med,
doi:10.1016/S0196-0644(99)70271-4Crump, Ōmura, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: The human use perspective, Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci,
doi:10.2183/pjab.87.13De Castro, Jr, Gregianin, Burger, Continuous high-dose ivermectin appears to be safe in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia and could inform clinical repurposing for COVID-19 infection, Leuk Lymphoma
De Melo, Lazarini, Levallois, Hautefort, Michel et al., COVID-19-related anosmia is associated with viral persistence and inflammation in human olfactory epithelium and brain infection in hamsters, Sci. Transl. Med
Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Chen, Tipping et al., Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J. Clin. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1177/009127002401382731Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Fatak, Kabah et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq,
doi:10.22578/IJMS.19.1.14Hazan, Dave, Gunaratne, Dolai, Clancy et al., Effectiveness of ivermectin-based multidrug therapy in severely hypoxic, ambulatory COVID-19 patients, Future Microbiol,
doi:10.2217/fmb-2022-0014Hill, Garratt, Levi, Falconer, Ellis et al., Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab358Kory, Meduri, Varon, Iglesias, Marik, Review of the emerging evidence demonstrating the efficacy of ivermectin in the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, Am. J. Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377Krause, Buisson, Bertrand, Corringer, Galzi et al., Ivermectin: A positive allosteric effector of the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, Mol. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1124/mol.53.2.283Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Travacio, Valentini et al., Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959Lim, Hor, Tay, Mat, Jelani et al., Efficacy of ivermectin treatment on disease progression among adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 and comorbidities: The I-TECH randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern. Med,
doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Dávalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Mahmud, Rahman, Alam, Ahmed, Kabir et al., Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: A randomized trial, J. Int. Med. Res,
doi:10.1177/03000605211013550Metwally, Basha, Zaitoun, Abdalla, Nofal et al., Clinical and radiological imaging as prognostic predictors in COVID-19 patients, J. Radiol. Nucl. Med,
doi:10.1186/s43055-021-00470-9Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Antimicrob. Chemother
Negri, Piloto, Morinaga, Jardim, Lamy et al., Heparin therapy improving hypoxia in COVID-19 patients-A case series, Front. Physiol,
doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.573044Osman, Farouk, Osman, Abdrabou, Longitudinal assessment of chest computerized tomography and oxygen saturation for patients with COVID-19. Egypt, J. Radiol. Nucl. Med,
doi:10.1186/s43055-020-00376-yQuispe-Cholan, Anticona-De-La-Cruz, Cornejo-Cruz, Quispe-Chirinos, Moreno-Lazaro et al., Tomographic findings in patients with COVID-19 according to evolution of the disease, J. Radiol. Nucl. Med
Rajter, None
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 (ICON study), Chest,
doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009Reis, Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with ivermectin among patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2115869Ren, Tong, Li, Lu, Yao, The protective effect of alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation on critical illness and its mechanism, Int. J. Biol. Sci,
doi:10.7150/ijbs.16404Santin, Scheim, Mccullough, Yagisawa, Borody, Ivermectin: A multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honored distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, N. Microbes N. Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924Scheim, A deadly embrace: Hemagglutination mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein at its 22 N-glycosylation sites, red blood cell surface sialoglycoproteins, and antibody, Int. J. Mol. Sci,
doi:10.3390/ijms23052558Scheim, Hibberd, Chamie-Quintero, Protocol Violations in López-Medina et al.: 38 Switched Ivermectin (IVM) and Placebo Doses, Failure of Blinding,
doi:10.31219/osf.io/u7ewzStone, Ndarukwa, Scheim, Dancis, Dancis et al., Rapid increase of SpO 2 on room air for 34 severe COVID-19 patients after ivermectin-based combination treatment: 55-62% normalization within, Res. Sq
Thairu, Babalola, Ajayi, Ndanusa, Ogedengbe et al., A comparison of Ivermectin and non Ivermectin based regimen for COVID-19 in Abuja: Effects on virus clearance, days-to-discharge and mortality, Res. Sq,
doi:10.9734/jpri/2022/v34i44A36328Wang, Dong, Hu, Li, Ren et al., Temporal changes of CT findings in 90 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A longitudinal study, Radiology,
doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200843Wang, Yu, Ochani, Amella, Tanovic et al., Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation, Nature,
doi:10.1038/nature01339Who, COVID-19)
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Omura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, Jpn. J. Antibiot
Yin, Huang, Li, Tang, Difference of coagulation features between severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 and non-SARS-CoV2, J. Thromb. Thrombolysis,
doi:10.1007/s11239-020-02105-8DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biologics2030015",
"ISSN": [
"2673-8449"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/biologics2030015",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The emergence of COVID-19 in March 2020 challenged Zimbabwe to respond with limited medical facilities and therapeutic options. Based on early clinical indications of efficacy for the macrocyclic lactone, Ivermectin (IVM), against COVID-19, IVM-based combination treatments were deployed to treat it. Oxygen saturation (SpO2) data were retrospectively analyzed for 34 severe, hypoxic COVID-19 patients all on room air (without supplemental oxygen). The patients, median age 56.5, were treated at clinics or at home between August 2020 and May 2021. All but three of these 34 patients had significantly increased SpO2 values within 24 h after the first IVM dose. The mean increase in SpO2 as a percentage of full normalization to SpO2 = 97 was 55.1% at +12 h and 62.3% at +24 h after the first IVM dose (paired t-test, p < 0.0000001). These results parallel similar sharp, rapid increases in SpO2, all on room air, for 24 mostly severe COVID-19 patients in the USA (California) who were given an IVM-based combination treatment. All patients in both of these critical series recovered. These rapid increases in SpO2 values after IVM treatment stand in sharp contrast to declines in SpO2 and associated pulmonary function through the second week following the onset of moderate or severe COVID-19 symptoms under standard care.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"biologics2030015"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "Jaqueline C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6815-8088",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ndarukwa",
"given": "Pisirai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6841-7054",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Scheim",
"given": "David E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1498-4042",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dancis",
"given": "Barry M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dancis",
"given": "Jerome",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gill",
"given": "Martin G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldous",
"given": "Colleen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biologics",
"container-title-short": "Biologics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T03:53:21Z",
"timestamp": 1662004401000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T04:23:59Z",
"timestamp": 1662006239000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T04:51:53Z",
"timestamp": 1662007913312
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661904000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2673-8449/2/3/15/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "196-210",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Worldometer Coronovirus Statistics\nhttps://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/#countries"
},
{
"article-title": "Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19",
"author": "Yagisawa",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Jpn. J. Antibiot.",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2115869",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"author": "U.S. National Institutes of Health",
"key": "ref9",
"series-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines: Therapeutic Management of Patients with COVID-19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref10",
"series-title": "WHO Recommends against the Use of Remdesivir in COVID-19 Patients",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/computation10040051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23052558",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Zimbabwe Confirms Its First Case of Coronavirus, 20 March 2020\nhttps://iharare.com/zimbabwe-confirms-first-case-of-coronavirus-2/"
},
{
"key": "ref14",
"series-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Situation Report—72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138920112800399095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/009127002401382731",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkz524",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10428194.2020.1786559",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0196-0644(99)70271-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31219/osf.io/u7ewz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31219/osf.io/5cwmr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abf8396",
"article-title": "COVID-19-related anosmia is associated with viral persistence and inflammation in human olfactory epithelium and brain infection in hamsters",
"author": "de Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabf8396",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-86679-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211013550",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22578/IJMS.19.1.14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/j.1326-5377.1990.tb136833.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). The Basics of Oxygen Monitoring and Oxygen Therapy during the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43055-020-00376-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43055-021-00470-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11604-020-01085-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200843",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43055-020-00329-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10040413",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.9734/jpri/2022/v34i44A36328",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23937/2474-3658/1510233",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-020-02162-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2020.573044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-020-02105-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202005.0020.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"author": "Babalola",
"journal-title": "Personal communication",
"key": "ref44",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb-2022-0014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"author": "Rajter",
"journal-title": "Personal communication",
"key": "ref46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1048271/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature01339",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/mol.53.2.283",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.16404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical Spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH)",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"key": "ref53",
"series-title": "The 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine—Press Release",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2673-8449/2/3/15"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Environmental Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Changes in SpO2 on Room Air for 34 Severe COVID-19 Patients after Ivermectin-Based Combination Treatment: 62% Normalization within 24 Hours",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2"
}