Association between Ivermectin treatment and mortality in Covid-19: A hospital-based case-control study
Ravikirti, Alok Ranjan, Rajdeep Porel, Ketan Agarwal, S M Tahaseen, Shyama, Anjani Kumar
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1522422/v1
Introduction : This study was designed to test the hypothesis that exposure to ivermectin in early disease prevents mortality due to COVID-19. A secondary objective was to see if the drug has any impact on the length of hospital stay among the survivors.
Methods It was a hospital-based retrospective case control Study conducted at a tertiary teaching hospital in India. All patients with a diagnosis of COVID-19 who were admitted between 1st April and 15th May 2021 and received inpatient care were included. Important variables like demographic details, dates of admission and discharge or death, symptoms at the time of admission, comorbidities, severity of illness at the time of admission, whether ivermectin was administered or not during the course of the illness and other treatments received as part of the standard of care were retrieved from the medical records.
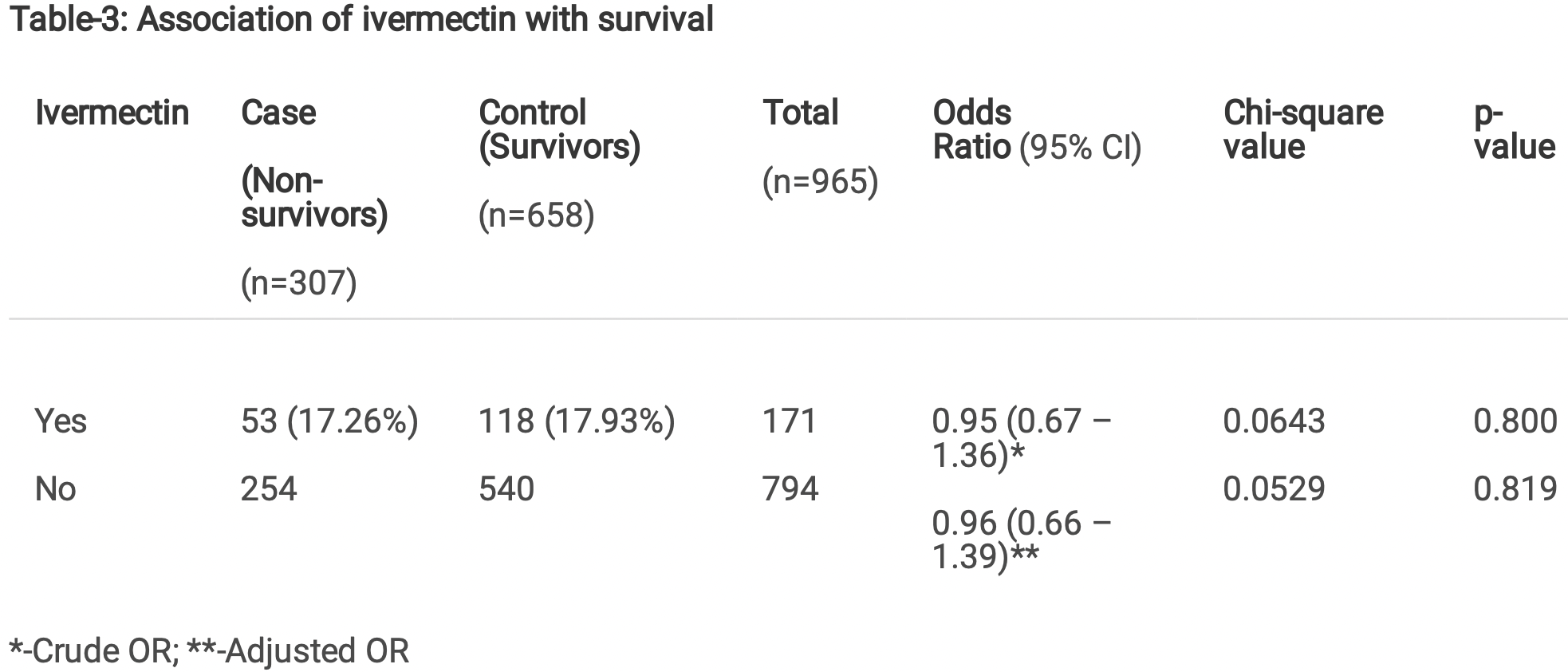
Results Of the 965 patients who received inpatient care, 307 died during their hospital stay while 658 were successfully discharged. The proportion of cases treated with ivermectin was 17.26% among the nonsurvivors (53/307) and 17.93% among the survivors (118/658). The effect was statistically insigni cant (crude OR = 0.954 ;95% CI: 0.668-1.364, p = 0.80). Among the survivors, the median length of stay was 11 days for patients who received ivermectin (IQR: 7-15) as well as for those who did not (IQR 7-16).
Conclusion This study did not show any effect of ivermectin on in-patient mortality in patients with COVID-19 and there was no effect of the drug on the length of hospital stay among the survivors.
Declarations Authorship Statement: All authors meet the ICMJE authorship criteria.
Con icts of interest: None Funding: None
References
Abdulamir, Ahmed, Asghar, Hill, Preliminary meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection
Ahmed, Karim, A ve day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, International Journal of Infectious Diseases,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11Alam, Murshed, A Case Series of 100 COVID-19 Positive Patients Treated with Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline, J Bangladesh Coll Phys Surg,
doi:10.3329/jbcps.v38i0.47512Babalola, Bode, Ajayi, Ivermectin shows clinical bene ts in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos, QJM-Int J Med,
doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab035Bryant, Lawrie, Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines, Am J Ther,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402Chowdhury, Shahbaz, Karim, A Comparative Study on Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin Therapy on COVID-19 Patients, EJMO
Espitia-Hernandez, Munguia, Effects of Ivermectin-azithromycin-cholecalciferol combined therapy on COVID-19 infected patients: A proof of concept study, Biomedical Research
Gonzalez, Gámez, Enciso, E cacy and safety of Ivermectin and Hydroxychloroquine in patients with severe COVID-19. A randomized controlled trial, medRxiv
Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Chen, Tipping et al., Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1177/009127002401382731Hashim, Maulood, Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345Hector, Roberto, Safety and E cacy of the combined use of ivermectin, dexamethasone, enoxaparin and aspirin against COVID-19 -The I.D.E.A. Protocol, Journal of Clinical Trials
Hill, Mirchandani, Pilkington, Ivermectin for COVID-19: Addressing potential bias and medical fraud, Open Forum Infectious Diseases
Karale, Bansal, Makadia, A Meta-analysis of Mortality, Need for ICU admission, Use of Mechanical Ventilation and Adverse Effects with Ivermectin Use in COVID-19 Patients, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.04.30.21256415Khan, Khan, Ivermectin treatment may improve the prognosis of patients with COVID-19, Archivos de Bronconeumologia
Lamontagne, Agoritsas, Macdonald, A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ2020,
doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379Lim, Hor, Tay, Effect of Ivermectin on Disease Progression among Adults with Mild to Moderate COVID-19 and Comorbidities, JAMA Intern Med. Published online,
doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0189López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults With Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Mahmud, Rahman, Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial, J Int Med Res,
doi:10.1177/03000605211013550Mohan, Tiwari, Suri, Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): A single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial, J Infect Chemother,
doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021Niaee, Namdar, Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multi-center clinical trial, Asian Pac J Trop Med
Peña-Silva, Duffull, Steer, Jaramillo-Rincon, Gwee et al., Pharmacokinetic considerations on the repurposing of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Rajter, Sherman, Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 -The ICON Study
Ravikirti, Evaluation of Ivermectin as a Potential Treatment for Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial in Eastern India, J Pharm Pharm Sci,
doi:10.18433/jpps32105DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1522422/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1522422/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Introduction\n : This study was designed to test the hypothesis that exposure to ivermectin in early disease prevents mortality due to COVID-19. A secondary objective was to see if the drug has any impact on the length of hospital stay among the survivors.\nMethods\n It was a hospital-based retrospective case control Study conducted at a tertiary teaching hospital in India. All patients with a diagnosis of COVID-19 who were admitted between 1st April and 15th May 2021 and received inpatient care were included. Important variables like demographic details, dates of admission and discharge or death, symptoms at the time of admission, comorbidities, severity of illness at the time of admission, whether ivermectin was administered or not during the course of the illness and other treatments received as part of the standard of care were retrieved from the medical records.\nResults\n Of the 965 patients who received inpatient care, 307 died during their hospital stay while 658 were successfully discharged. The proportion of cases treated with ivermectin was 17.26% among the non-survivors (53/307) and 17.93% among the survivors (118/658). The effect was statistically insignificant (crude OR = 0.954 ;95% CI: 0.668–1.364, p = 0.80). Among the survivors, the median length of stay was 11 days for patients who received ivermectin (IQR: 7–15) as well as for those who did not (IQR 7–16).\nConclusion\n This study did not show any effect of ivermectin on in-patient mortality in patients with COVID-19 and there was no effect of the drug on the length of hospital stay among the survivors.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
4
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Ravikirti",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Ranjan",
"given": "Alok",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Porel",
"given": "Rajdeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Agarwal",
"given": "Ketan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Tahaseen",
"given": "SM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Shyama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna"
}
],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Anjani",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-06T15:29:04Z",
"timestamp": 1649258944000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-06T15:29:06Z",
"timestamp": 1649258946000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-06T16:12:44Z",
"timestamp": 1649261564193
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1649203200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1522422/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1522422/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1522422/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": [
"Association between Ivermectin treatment and mortality in Covid-19: A hospital-based case-control study"
],
"type": "posted-content"
}