The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis
Chia Siang Kow, Hamid A Merchant, Zia Ul Mustafa, Syed Shahzad Hasan
Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z
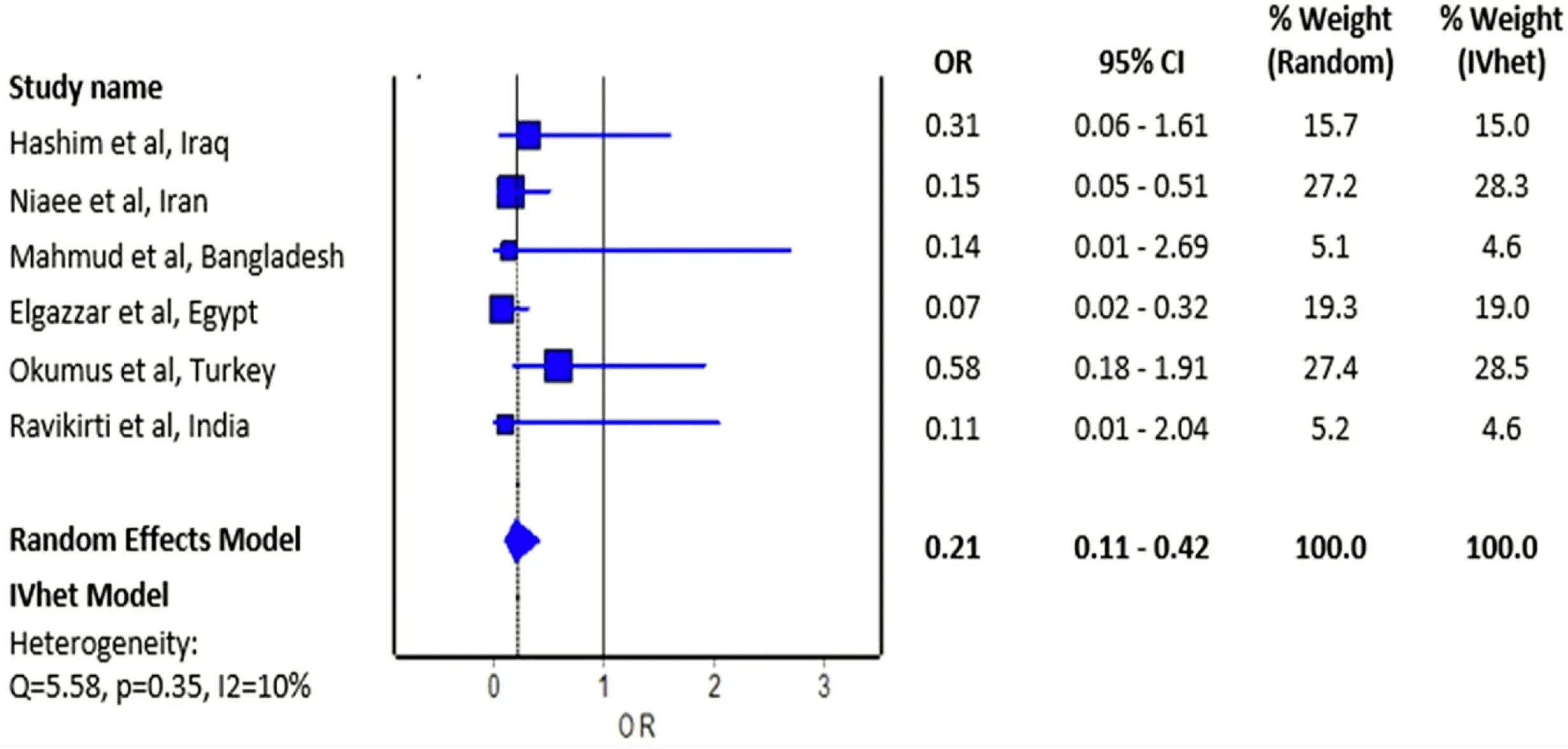
Objective The effect of ivermectin on mortality in patients with novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been investigated in many studies. We aimed to perform a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to investigate the overall effect of ivermectin on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19. Methods We systematically searched PubMed, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Google Scholar, and preprint repository databases (up to February 28, 2021). Random-effects and inverse variance heterogeneity meta-analysis were used to pool the odds ratio of individual trials. The risk of bias was appraised using Version 2 of the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials. Results Six randomized controlled trials were included in this analysis with a total of 658 patients who were randomized to receive ivermectin and 597 patients randomized in the control group who did not receive ivermectin. Of six trials, four had an overall high risk of bias. The estimated effect of ivermectin indicated mortality benefits (pooled odds ratio = 0.21; 95% confidence interval 0.11-0.42, n = 1255), with some evidence against the hypothesis of 'no significant difference' at the current sample size. Conclusion We observed a preliminary beneficial effect on mortality associated with ivermectin use in patients with COVID-19 that warrants further clinical evidence in appropriately designed large-scale randomized controlled trials.
Declarations Conflict of interest All named authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
References
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDAapproved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Clinicaltrials, Gov, Clinical Trial of Ivermectin Plus Doxycycline for the Treatment of Confirmed COVID-19 Infection
Elgazzar, Hany, Youssef, Hafez, Moussa, Efficacy and Safety of Ivermectin for Treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 Pandemic,
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs100956/v1Fig, 2 Forest plot showing the pooled odds ratio of mortality between ivermectin users and non-ivermectin users with COVID-19
Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Fatak, Kabah et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot
Horby, Mafham, Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Marik, EVMS COVID-19 Management Protocol: An overview of the MATH+ and I-MASK+ Protocols
Moher, Shamseer, Clarke, Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement, Syst Rev
Niaee, Gheibi, Namdar, Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multi-center clinical trial,
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-109670/v1Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of Ivermectin Is Associated with Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease
Ravikirti, Pattadar, Ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19-A double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial
Sterne, Savović, Page, RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Zografos, Georgiadou, Thomas, Kaltsas, Digalakis, Drug-induced esophagitis, Dis Esophagus
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z",
"ISSN": [
"1734-1140",
"2299-5684"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z",
"alternative-id": [
"245"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "6 January 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "27 February 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "6 March 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "29 March 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "All named authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8186-2926",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kow",
"given": "Chia Siang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merchant",
"given": "Hamid A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustafa",
"given": "Zia Ul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hasan",
"given": "Syed Shahzad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmacological Reports",
"container-title-short": "Pharmacol. Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-29T04:02:30Z",
"timestamp": 1616990550000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-22T18:39:57Z",
"timestamp": 1671734397000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-13T15:30:24Z",
"timestamp": 1713022224733
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 21,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1616976000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1616976000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1473-1479",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"author": "F Heidary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot (Tokyo).",
"key": "245_CR1",
"unstructured": "Heidary F, Gharebaghi R. Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020;73(9):593–602.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"author": "L Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res.",
"key": "245_CR2",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2020;178:104787.",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2046-4053-4-1",
"author": "D Moher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Syst Rev.",
"key": "245_CR3",
"unstructured": "Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4(1):1.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"author": "JAC Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "l4898",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "245_CR4",
"unstructured": "Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898.",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "245_CR5",
"unstructured": "Hashim HA, Maulood MF, Rasheed, AM, Fatak DF, Kabah KK, Abdulamir AS. Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq. Preprint. medRxiv. 2020;https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-109670/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "245_CR6",
"unstructured": "Niaee MS, Gheibi N, Namdar P, et al. Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multi-center clinical trial. Preprint. Research Square. 2020;https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-109670/v1."
},
{
"key": "245_CR7",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov. Clinical Trial of Ivermectin Plus Doxycycline for the Treatment of Confirmed COVID-19 Infection. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04523831"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs100956/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "245_CR8",
"unstructured": "Elgazzar A, Hany B, Youssef SA, Hafez M, Moussa H. Efficacy and Safety of Ivermectin for Treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 Pandemic. Preprint. Research Square. 2020;https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs100956/v1."
},
{
"key": "245_CR9",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov. Ivermectin for Severe COVID-19 Management. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04646109"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.05.21249310",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "245_CR10",
"unstructured": "Ravikirti, Roy R, Pattadar C, et al. Ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19—A double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Preprint. 2021;2021.01.05.21249310."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.06.20124461",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "245_CR11",
"unstructured": "Rajter JC, Sherman MS, Fatteh N, Vogel F, Sacks J, Rajter JJ. Use of Ivermectin Is Associated with Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: The ICON Study [published online ahead of print, 2020 Oct 13]. Chest. 2020;S0012–3692(20)34898–4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2022926",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "245_CR12",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Mafham M, et al. Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(21):2030–2040."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1442-2050.2009.00972.x",
"author": "GN Zografos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "633",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Dis Esophagus",
"key": "245_CR13",
"unstructured": "Zografos GN, Georgiadou D, Thomas D, Kaltsas G, Digalakis M. Drug-induced esophagitis. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22(8):633–7.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"key": "245_CR14",
"unstructured": "Marik P. EVMS COVID-19 Management Protocol: An overview of the MATH+ and I-MASK+ Protocols. https://www.evms.edu/media/evms_public/departments/internal_medicine/EVMS_Critical_Care_COVID-19_Protocol.pdf"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "73"
}