Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon
Ali A Samaha, Hussein Mouawia, Mirna Fawaz, Hamad Hassan, Ali Salami, Ali Al Bazzal, Hamid Bou Saab, Mohamed Al-Wakeel, Ahmad Alsaabi, Mohamad Chouman, Mahmoud Al Moussawi, Hassan Ayoub, Ali Raad, Ola Hajjeh, Ali H Eid, Houssam Raad
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13060989
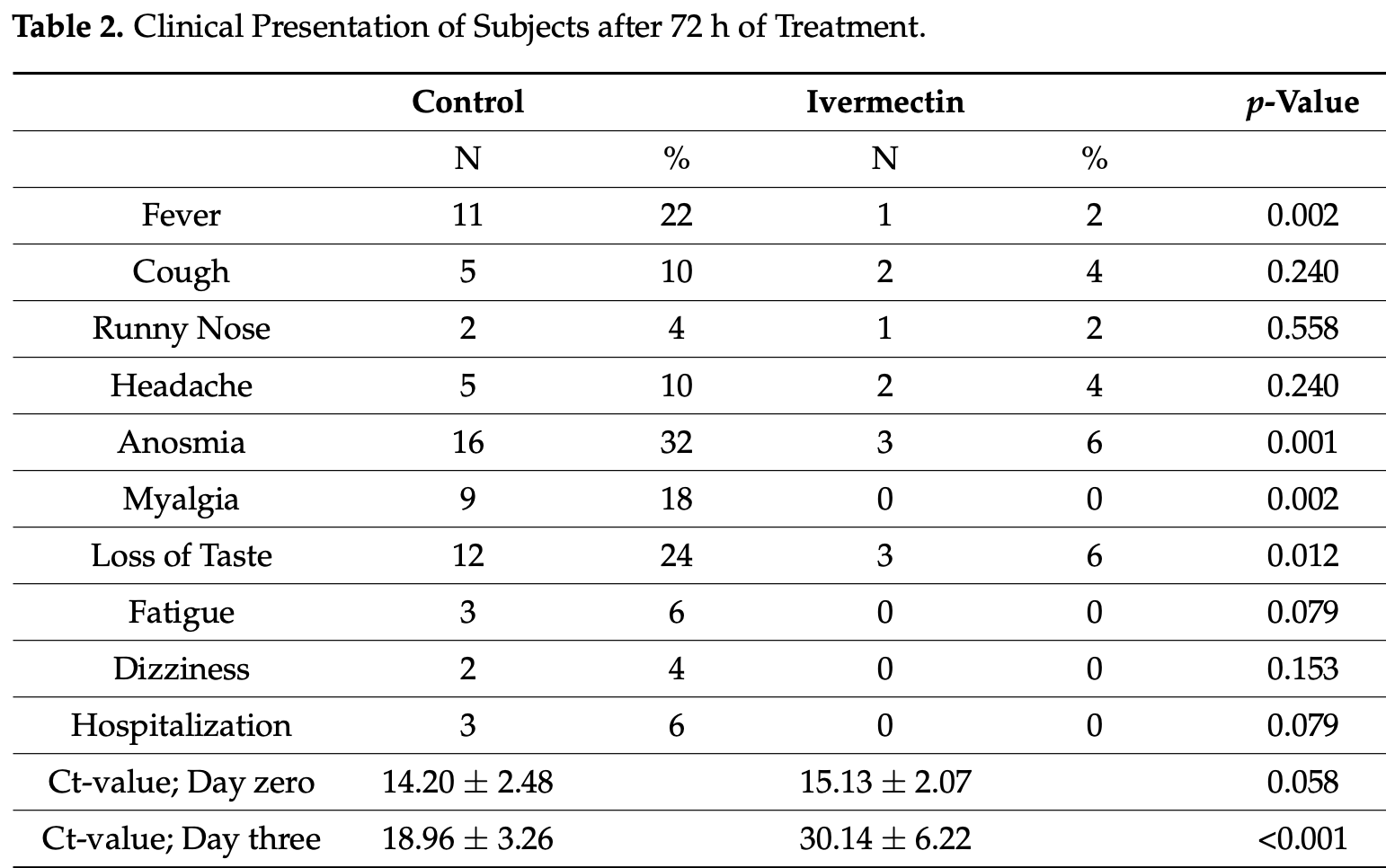
Objective: This study was designed to determine the efficacy of ivermectin, an FDAapproved drug, in producing clinical benefits and decreasing the viral load of SARS-CoV-2 among asymptomatic subjects that tested positive for this virus in Lebanon. Methods: A randomized controlled trial was conducted in 100 asymptomatic Lebanese subjects that have tested positive for SARS-CoV2. Fifty patients received standard preventive treatment, mainly supplements, and the experimental group received a single dose (according to body weight) of ivermectin, in addition to the same supplements the control group received. Results: There was no significant difference (p = 0.06) between Ct-values of the two groups before the regimen was started (day zero), indicating that subjects in both groups had similar viral loads. At 72 h after the regimen started, the increase in Ct-values was dramatically higher in the ivermectin than in the control group. In the ivermectin group, Ct increased from 15.13 ± 2.07 (day zero) to 30.14 ± 6.22 (day three; mean ± SD), compared to the control group, where the Ct values increased only from 14.20 ± 2.48 (day zero) to 18.96 ± 3.26 (day three; mean ± SD). Moreover, more subjects in the control group developed clinical symptoms. Three individuals (6%) required hospitalization, compared to the ivermectin group (0%). Conclusion: Ivermectin appears to be efficacious in providing clinical benefits in a randomized treatment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects, effectively resulting in fewer symptoms, lower viral load and reduced hospital admissions. However, larger-scale trials are warranted for this conclusion to be further cemented.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, Hossain, Clemens et al., A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int. J. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients,
doi:10.3390/nu12082358Arévalo, Pagotto, Pórfido, Daghero, Segovia et al., Ivermectin reduces coronavirus infection in vivo: A mouse experimental model, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.11.02.363242Booz, Altara, Eid, Wehbe, Fares et al., Macrophage responses associated with COVID-19: A pharmacological perspective, Eur. J. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173547Buonfrate, Salas-Coronas, Munoz, Maruri, Rodari et al., Multiple-dose versus single-dose ivermectin for Strongyloides stercoralis infection (Strong Treat 1 to 4): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled superiority trial, Lancet Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30289-0Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, Pineda, Fernandez-Montero et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720Dingens, Crawford, Adler, Steele, Lacombe et al., Serological identification of SARS-CoV-2 infections among children visiting a hospital during the initial Seattle outbreak, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18178-1Dinicolantonio, Barroso, Mccarty, Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart,
doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350Finzi, Harrington, Zinc treatment of outpatient COVID-19: A retrospective review of 28 consecutive patients, J. Med. Virol,
doi:10.1002/jmv.26812Giordo, Zinellu, Eid, Pintus, Therapeutic Potential of Resveratrol in COVID-19-Associated Hemostatic Disorders, Molecules,
doi:10.3390/molecules26040856Gotz, Magar, Dornfeld, Giese, Pohlmann et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci. Rep,
doi:10.1038/srep23138Hall, Jr, Ji, A search for medications to treat COVID-19 via in silico molecular docking models of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and 3CL protease, Travel. Med. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101646Hammoud, Wehbe, Abdelhady, Kobeissy, Eid et al., Dysregulation of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Expression and Function in Comorbid Disease Conditions Possibly Contributes to Coronavirus Infectious Disease 2019 Complication Severity, Mol. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1124/molpharm.120.000119Hashim, Maulood, Rasheed, Fatak, Kabah et al., Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Hussein, Elkhair, Molecular docking identification for the efficacy of some zinc complexes with chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine against main protease of COVID-19, J. Mol. Struct,
doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129979Kaddoura, Alibrahim, Hijazi, Soudani, Audi et al., COVID-19 Therapeutic Options Under Investigation, Front. Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01196Kaur, Shekhar, Sharma, Sarma, Prakash et al., Ivermectin as a potential drug for treatment of COVID-19: An in-sync review with clinical and computational attributes, Pharmacol. Rep,
doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00195-yKinobe, Owens, A systematic review of experimental evidence for antiviral effects of ivermectin and an in-silico analysis of ivermectin's possible mode of action against SARS-CoV-2, Fundam Clin. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1111/fcp.12644Lorenz, Dias Bocewicz, Correa De Azevedo Marques, Reis Santana, Chiaravalloti-Neto et al., Have measures against COVID-19 helped to reduce dengue cases in Brazil? Travel, Med. Infect. Dis
Martin, Jans, Antivirals that target the host IMPalpha/beta1-virus interface, Biochem. Soc. Trans,
doi:10.1042/BST20200568Navarro, Camprubi, Requena-Mendez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Antimicrob. Chemother,
doi:10.1093/jac/dkz524Noreen, Maqbool, Madni, Dexamethasone: Therapeutic potential, risks, and future projection during COVID-19 pandemic, Eur. J. Pharmacol,
doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173854Rabi, Al Zoubi, Kasasbeh, Salameh, Al-Nasser, SARS-CoV-2 and Coronavirus Disease 2019: What We Know So Far, Pathogens,
doi:10.3390/pathogens9030231Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study, Chest
Shakkour, Habashy, Berro, Takkoush, Abdelhady et al., Drug Repurposing in Neurological Disorders: Implications for Neurotherapy in Traumatic Brain Injury, Neuroscientist,
doi:10.1177/1073858420961078Shakoor, Feehan, Al Dhaheri, Ali, Platat et al., Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: Could they help against COVID-19?, Maturitas
Tay, Fraser, Chan, Moreland, Rathore et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw. Open,
doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369Vargas-Estrada, Gutierrez, Juarez-Rodriguez, Sumano, Pharmacokinetics of doxycycline and tissue concentrations of an experimental long-acting parenteral formulation of doxycycline in Wistar rats, Arzneimittelforschung
Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin alpha/betamediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem. J,
doi:10.1042/BJ20120150Wehbe, Hammoud, Soudani, Zaraket, El-Yazbi et al., Molecular Insights Into SARS COV-2 Interaction With Cardiovascular Disease: Role of RAAS and MAPK Signaling, Front. Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00836Westblade, Brar, Pinheiro, Paidoussis, Rajan et al., SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Predicts Mortality in Patients with and without Cancer Who Are Hospitalized with COVID-19, Cancer Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.007Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin alpha/beta1 heterodimer, Antivir. Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760Younis, Zareef, Al Hassan, Bitar, Eid et al., Hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 Patients: Pros and Cons, Front. Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.597985Zareef, Younis, Bitar, Eid, Arabi, COVID-19 in Pediatric Patients: A Focus on CHD Patients, Front. Cardiovasc. Med,
doi:10.3389/fcvm.2020.612460DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13060989",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v13060989",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Objective: This study was designed to determine the efficacy of ivermectin, an FDA-approved drug, in producing clinical benefits and decreasing the viral load of SARS-CoV-2 among asymptomatic subjects that tested positive for this virus in Lebanon. Methods: A randomized controlled trial was conducted in 100 asymptomatic Lebanese subjects that have tested positive for SARS-CoV2. Fifty patients received standard preventive treatment, mainly supplements, and the experimental group received a single dose (according to body weight) of ivermectin, in addition to the same supplements the control group received. Results: There was no significant difference (p = 0.06) between Ct-values of the two groups before the regimen was started (day zero), indicating that subjects in both groups had similar viral loads. At 72 h after the regimen started, the increase in Ct-values was dramatically higher in the ivermectin than in the control group. In the ivermectin group, Ct increased from 15.13 ± 2.07 (day zero) to 30.14 ± 6.22 (day three; mean ± SD), compared to the control group, where the Ct values increased only from 14.20 ± 2.48 (day zero) to 18.96 ± 3.26 (day three; mean ± SD). Moreover, more subjects in the control group developed clinical symptoms. Three individuals (6%) required hospitalization, compared to the ivermectin group (0%). Conclusion: Ivermectin appears to be efficacious in providing clinical benefits in a randomized treatment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects, effectively resulting in fewer symptoms, lower viral load and reduced hospital admissions. However, larger-scale trials are warranted for this conclusion to be further cemented.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v13060989"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samaha",
"given": "Ali A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6035-6071",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mouawia",
"given": "Hussein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fawaz",
"given": "Mirna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassan",
"given": "Hamad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3343-4035",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Salami",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bazzal",
"given": "Ali Al",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saab",
"given": "Hamid Bou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Wakeel",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alsaabi",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chouman",
"given": "Mohamad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moussawi",
"given": "Mahmoud Al",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ayoub",
"given": "Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raad",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajjeh",
"given": "Ola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3004-5675",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Eid",
"given": "Ali H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9562-2934",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Raad",
"given": "Houssam",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-27T01:56:44Z",
"timestamp": 1622080604000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-24T01:30:07Z",
"timestamp": 1624498207000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T16:01:31Z",
"timestamp": 1715616091750
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 32,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1621987200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/6/989/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "989",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens9030231",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1073858420961078",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/molpharm.120.000119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.00836",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2020.612460",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101646",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26040856",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.597985",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173547",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/fcp.12644",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.11.02.363242",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127448",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20120150",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep23138",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ceb.2019.01.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BST20200568",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18178-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00195-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26812",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkz524",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30883-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082358",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173854",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129979",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30354-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30289-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0031-1296512",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.26.20219345",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/6/989"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of a Single Dose of Ivermectin on Viral and Clinical Outcomes in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects: A Pilot Clinical Trial in Lebanon",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}