Single Dose of Ivermectin is not Useful in Patients with Hematological Disorders and COVID-19 Illness: A Phase II B Open Labelled Randomized Controlled Trial
Biju George, Mahesh Moorthy, Uday Kulkarni, Sushil Selvarajan, Priscilla Rupali, D J Christopher, T Balamugesh, Winsley Rose, Kavitha M Lakshmi, Anup J Devasia, N A Fouzia, Anu Korula, Sharon Lionel, Aby Abraham, Vikram Mathews
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, doi:10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w
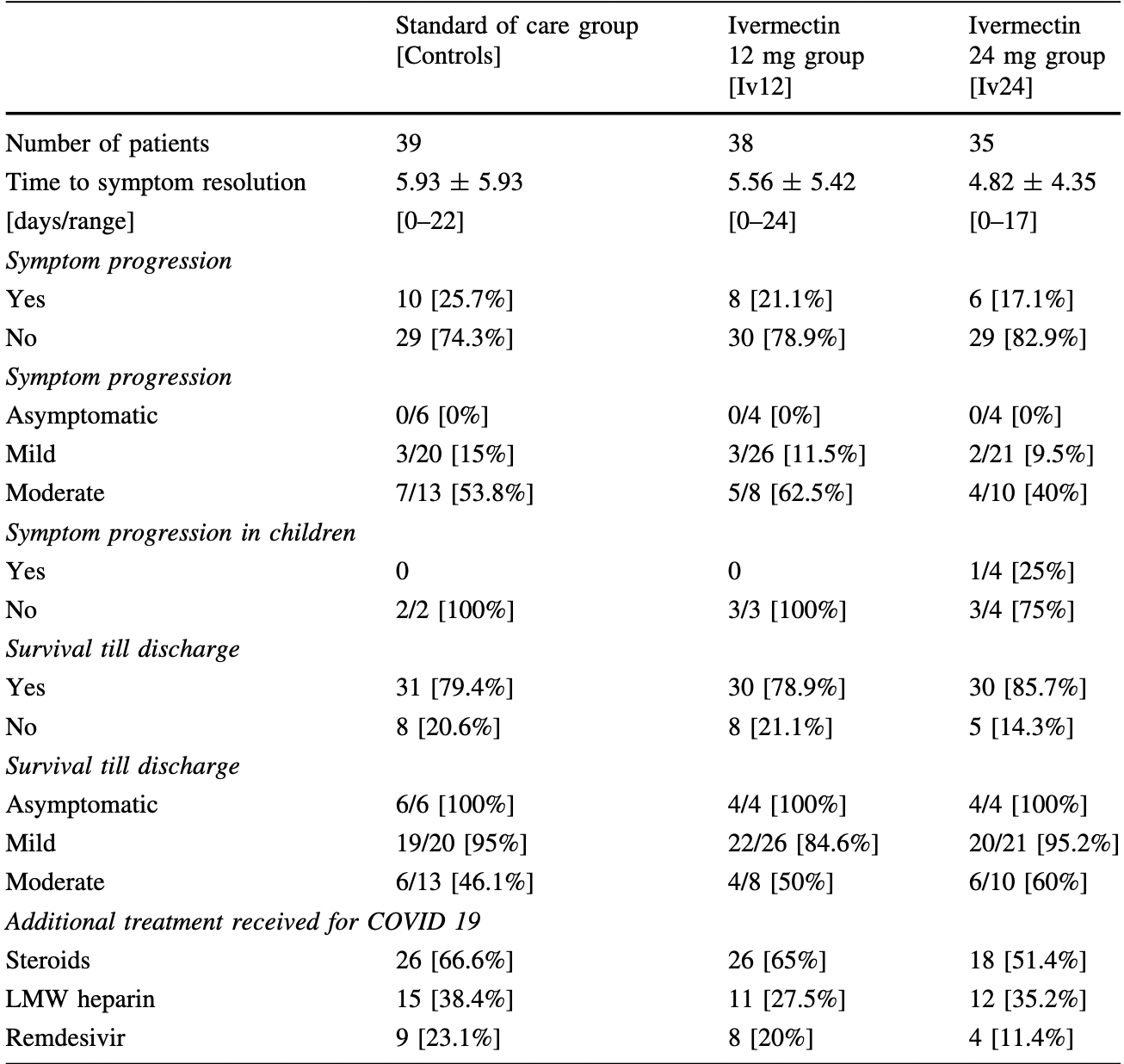
Repurposed drugs may reduce morbidity and mortality in patients with hematological disorders who develop COVID-19 illness. 112 patients with predominantly hematological illnesses were randomized to receive standard of care, ivermectin 12 mg [Iv 12] or 24 mg [Iv24] for asymptomatic, mild, or moderate COVID 19 illness. Serial respiratory samples for rRT-PCR samples were sent on Day 3, 5 and 7. rRT-PCR negativity and C 2 log 10 reduction in viral loads on day 3, 5 and 7 were similar between the 3 treatment groups across all disease categories. Symptom progression occurred in 26 patients [21.6%] with no difference across 3 treatment groups. Twenty-two patients [18.3%] have expired while 98 [81.7%] survived. Survival rates were similar across treatment groups [controls-80.5%, Iv12-77.5%, Iv24-87.2% respectively]. Overall, poorer survival was seen with moderate illness compared to others [51.6% vs 92.1%; p = 0.000] and was the only significant risk factor identified on multivariate analysis. In this Phase II randomised trial, single dose of 12 or 24 mg of ivermectin did not reduce viral loads, prevent symptom progression, or reduce mortality in patients with predominantly haematological illnesses who develop mild to moderate COVID 19 illness.
Author Contributions BG, UK designed the study, interpreted the data and drafted the paper. MM designed the study, acquired of laboratory data and drafted the paper. KML analysed the data, provided critical revision of the paper and approved the final version. SS, PR, DJC, BT, WR, AJD, FNA, AK, SL, AA and VM helped in acquiring the clinical data, interpretation of data and revising the manuscript critically. All authors have approved the final submitted version of the manuscript.
Declarations Conflict of interest No conflicts of interest to declare for any of the authors.
References
Abd-Elsalam, Noor, Badawi, Clinical study evaluating the efficacy of ivermectin in COVID-19 treatment: a randomized controlled study, J Med Virol,
doi:10.1002/jmv.27122Ahmed, Karim, Ross, A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID 19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis
Allo, Allogeneic transplant; Auto, Autologous transplant; ANC, Absolute neutrophil count # Consisted of severe hemophilia
Bartoszko, Siemieniuk, Kum, Prophylaxis against COVID-19: living systematic review and network metaanalysis, BMJ,
doi:10.1136/bmj.n949Biernat, Kolasinska, Kwiatkowski, Early administration of convalescent plasma improves survival in patients with hematological malignancies and COVID 19, Viruses
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Chaccour, Casellas, Matteo, The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, E Clin Med,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720Chang, Mo, Yuan, Tao, Peng et al., Time kinetics of viral clearance and resolution of symptoms in novel coronavirus infection, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Hueso, Pouderoux, Pere, Convalescent plasma therapy for B cell depleted patients with protracted COVID-19, Blood
Indian, Kuderer, Choueiri, Shah, Shyr et al., Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): a cohort study, Hematol Blood Transfus References
Jeyaraman, Agrawal, Bhargava, Convalescent plasma therapy for severe COVID 19 in patients with hematological malignancies, Transfus Apher Sci
Lee, Cazier, Angelis, Arnold, Bisht et al., COVID-19 mortality in patients with cancer on chemotherapy or other anticancer treatments: a prospective cohort study, Lancet
Liang, Guan, Chen, Li, Xu, Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China, Lancet Oncol
Liu, Yan, Xiang, Liu, Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19, Lancet Infect Dis
Lopez-Medina, Lopez, Hurtado, Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Mahmud, Rahman, Alam, Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial, J Int Med Res,
doi:10.1177/03000605211013550Mpn, Myeloproliferative disorders; ITP, Immune thrombocytopenia; AIHA, Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Okamus, Nemirturk, Cetinkaya, Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID 19 patients, BMC Infect Dis
Passamonti, Cattaneo, Arcaini, Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity in patients with hematological malignancies in Italy: a retrospective multicenter cohort study, Lancet Haematol
Pinana, Martino, Garcia, Risk factors and outcomes of COVID19 in patients with hematological malignancies, Exp Hematol Oncol,
doi:10.1186/s40164-020-00177-zPrca, Pure red cell aplasia; DM, Diabetes Mellitus; HT, Hypertension; IHD, Ischaemic heart disease
Samaha, Mouawia, Fawaz, Effects of a single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARS-Cov 2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon, Viruses
Shahbaznejad, Davoudi, Eslami, Effects of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, doubleblind, randomized, controlled clinical trial, Clin Ther,
doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.007Villegas, Poza, Talayero, IL-1R blockade is not effective in patients with hematological malignancies and severe SARS-Cov-2 infection, Ann Hematol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zou, Ruan, Huang, SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of infected patients, NEJM
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w",
"ISSN": [
"0971-4502",
"0974-0449"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w",
"alternative-id": [
"1546"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "8 February 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "26 April 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "27 May 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "No conflicts of interest to declare for any of the authors."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9847-9501",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "George",
"given": "Biju",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moorthy",
"given": "Mahesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kulkarni",
"given": "Uday",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selvarajan",
"given": "Sushil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rupali",
"given": "Priscilla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christopher",
"given": "D. J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balamugesh",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "Winsley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lakshmi",
"given": "Kavitha M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Devasia",
"given": "Anup J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fouzia",
"given": "N. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Korula",
"given": "Anu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lionel",
"given": "Sharon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abraham",
"given": "Aby",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathews",
"given": "Vikram",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion",
"container-title-short": "Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T06:02:46Z",
"timestamp": 1653631366000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T07:23:39Z",
"timestamp": 1653636219000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001843",
"award": [
"CVD/2020/000990"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Science and Engineering Research Board"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T07:41:20Z",
"timestamp": 1653637280094
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653609600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653609600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31187-9",
"author": "NM Kuderer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1907",
"issue": "395",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1546_CR1",
"unstructured": "Kuderer NM, Choueiri TK, Shah DP, Shyr Y, Rubinstein SM, Rivera DR et al (2020) Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): a cohort study. Lancet 20(395):1907–1918",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30096-6",
"author": "W Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "335",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Lancet Oncol",
"key": "1546_CR2",
"unstructured": "Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, Wang W, Li J, Xu K et al (2020) Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol 21(3):335–337",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "LYW Lee",
"first-page": "1907",
"issue": "395",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1546_CR3",
"unstructured": "Lee LYW, Cazier J-B, Angelis V, Arnold R, Bisht V, Campton NA et al (2020) COVID-19 mortality in patients with cancer on chemotherapy or other anticancer treatments: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 20(395):1907–1926",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30251-9",
"author": "F Passamonti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e737",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Lancet Haematol",
"key": "1546_CR4",
"unstructured": "Passamonti F, Cattaneo C, Arcaini L et al (2020) Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity in patients with hematological malignancies in Italy: a retrospective multicenter cohort study. Lancet Haematol 7(10):e737–e745",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40164-020-00177-z",
"author": "JL Pinana",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Exp Hematol Oncol",
"key": "1546_CR5",
"unstructured": "Pinana JL, Martino R, Garcia IG et al (2020) Risk factors and outcomes of COVID19 in patients with hematological malignancies. Exp Hematol Oncol 9:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-020-00177-z",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001737",
"author": "L Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1177",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "NEJM",
"key": "1546_CR6",
"unstructured": "Zou L, Ruan F, Huang M et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of infected patients. NEJM 382(12):1177–1179",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30232-2",
"author": "Y Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "656",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "1546_CR7",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Yan L-M, Wan L, Xiang T-X, Le A, Liu J-M et al (2020) Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Lancet Infect Dis 20(6):656–657",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202003-0524LE",
"author": "D Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1150",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "1546_CR8",
"unstructured": "Chang D, Mo G, Yuan X, Tao Y, Peng X, Wang F et al (2020) Time kinetics of viral clearance and resolution of symptoms in novel coronavirus infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 201(9):1150–1152",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1546_CR9",
"unstructured": "Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z et al (2020) Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 395(10229):1054–1062",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13060989",
"author": "AA Samaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "989",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "1546_CR10",
"unstructured": "Samaha AA, Mouawia H, Fawaz M et al (2021) Effects of a single dose of ivermectin on viral and clinical outcomes in asymptomatic SARS—Cov 2 infected subjects: a pilot clinical trial in Lebanon. Viruses 13(6):989",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n949",
"author": "JJ Bartoszko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "n949",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1546_CR11",
"unstructured": "Bartoszko JJ, Siemieniuk RAC, Kum E et al (2021) Prophylaxis against COVID-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 373:n949. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n949",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"author": "C Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100720",
"journal-title": "E Clin Med",
"key": "1546_CR12",
"unstructured": "Chaccour C, Casellas A, Di Matteo AB et al (2021) The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. E Clin Med 32:100720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"author": "E Lopez-Medina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1546_CR13",
"unstructured": "Lopez-Medina E, Lopez P, Hurtado IC et al (2021) Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 325(14):1426–1435",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27122",
"author": "S Abd-Elsalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1546_CR14",
"unstructured": "Abd-Elsalam S, Noor RA, Badawi R et al (2021) Clinical study evaluating the efficacy of ivermectin in COVID-19 treatment: a randomized controlled study. J Med Virol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.27122",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.007",
"author": "L Shahbaznejad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Ther",
"key": "1546_CR15",
"unstructured": "Shahbaznejad L, Davoudi A, Eslami G et al (2021) Effects of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Ther. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.007",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211013550",
"author": "R Mahmud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "300060521101355",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Int Med Res",
"key": "1546_CR16",
"unstructured": "Mahmud R, Rahman MM, Alam I et al (2021) Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial. J Int Med Res 49(5):3000605211013550. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211013550",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13030436",
"author": "MM Biernat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "436",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "1546_CR17",
"unstructured": "Biernat MM, Kolasinska A, Kwiatkowski J et al (2021) Early administration of convalescent plasma improves survival in patients with hematological malignancies and COVID 19. Viruses 13(3):436",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020008423",
"author": "T Hueso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2290",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "1546_CR18",
"unstructured": "Hueso T, Pouderoux C, Pere H et al (2020) Convalescent plasma therapy for B cell depleted patients with protracted COVID-19. Blood 136(20):2290–2295",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2021.103075",
"author": "P Jeyaraman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103075",
"journal-title": "Transfus Apher Sci",
"key": "1546_CR19",
"unstructured": "Jeyaraman P, Agrawal N, Bhargava R et al (2021) Convalescent plasma therapy for severe COVID 19 in patients with hematological malignancies. Transfus Apher Sci 60:103075",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00277-020-04160-w",
"author": "C Villegas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2953",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Ann Hematol",
"key": "1546_CR20",
"unstructured": "Villegas C, Poza M, Talayero P et al (2020) IL-1R blockade is not effective in patients with hematological malignancies and severe SARS-Cov-2 infection. Ann Hematol 99(12):2953–2956",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"author": "L Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "1546_CR21",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM (2020) The FDA-approved drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res 178:104787",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"author": "S Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "1546_CR22",
"unstructured": "Ahmed S, Karim MM, Ross AG et al (2021) A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID 19 may reduce the duration of illness. Int J Infect Dis 103:214–216",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06104-9",
"author": "N Okamus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "411",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "1546_CR23",
"unstructured": "Okamus N, Nemirturk N, Cetinkaya RA et al (2021) Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID 19 patients. BMC Infect Dis 21(1):411",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12288-022-01546-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Hematology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Single Dose of Ivermectin is not Useful in Patients with Hematological Disorders and COVID-19 Illness: A Phase II B Open Labelled Randomized Controlled Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}