Patch-clamp studies and cell viability assays suggest a distinct site for viroporin inhibitors on the E protein of SARS-CoV-2
Ulrike Breitinger, Christine Adel Sedky, Heinrich Sticht, Hans-Georg Breitinger
Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y
Background SARS-CoV-2 has caused a worldwide pandemic since December 2019 and the search for pharmaceutical targets against COVID-19 remains an important challenge. Here, we studied the envelope protein E of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, a highly conserved 75-76 amino acid viroporin that is crucial for virus assembly and release. E protein channels were recombinantly expressed in HEK293 cells, a membrane-directing signal peptide ensured transfer to the plasma membrane. Methods Viroporin channel activity of both E proteins was investigated using patch-clamp electrophysiology in combination with a cell viability assay. We verified inhibition by classical viroporin inhibitors amantadine, rimantadine and 5-(N,N-hexamethylene)-amiloride, and tested four ivermectin derivatives.
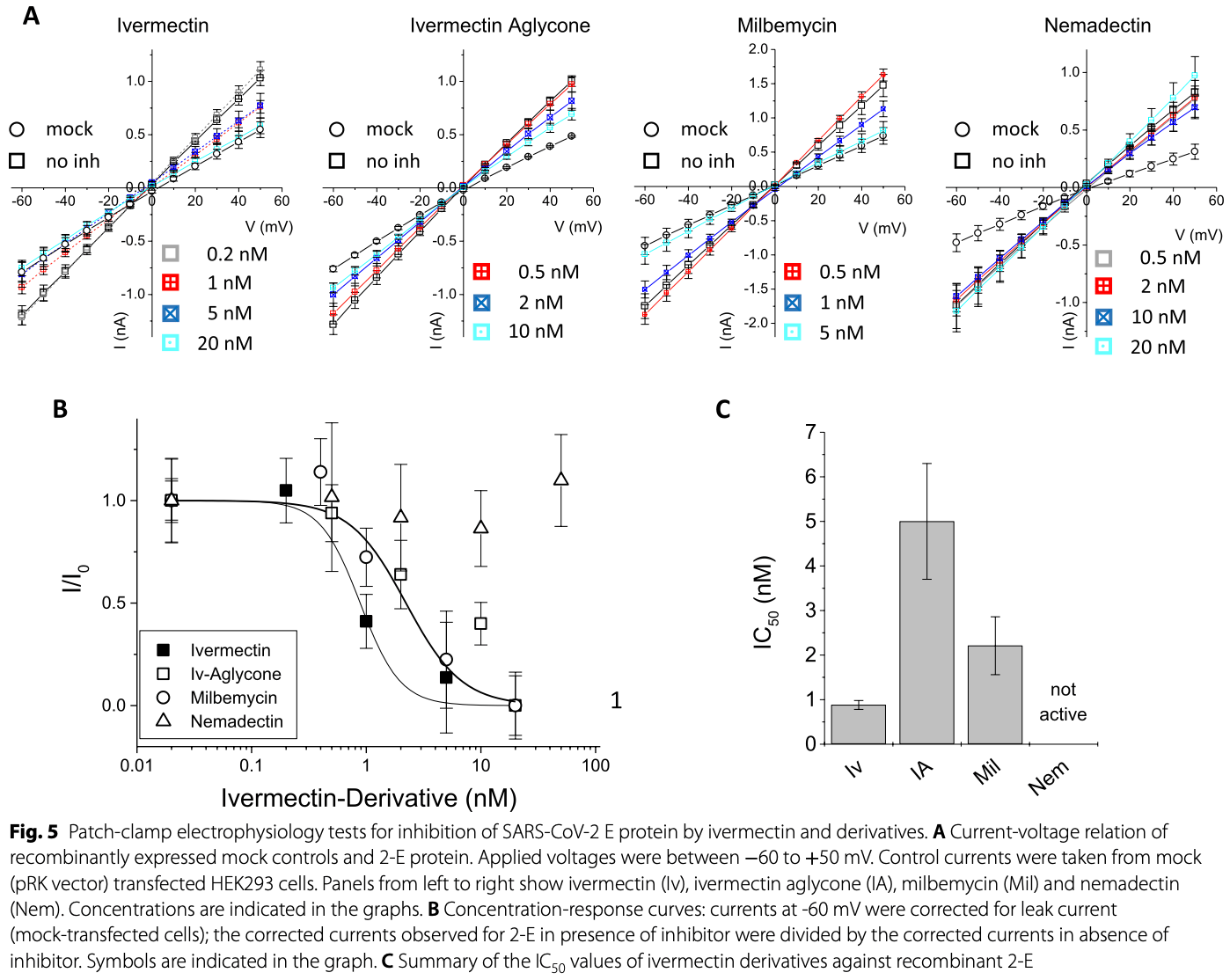
Results Classical inhibitors showed potent activity in patch-clamp recordings and viability assays. In contrast, ivermectin and milbemycin inhibited the E channel in patch-clamp recordings but displayed only moderate activity on the E protein in the cell viability assay, which is also sensitive to general cytotoxic activity of the tested compounds. Nemadectin and ivermectin aglycon were inactive. All ivermectin derivatives were cytotoxic at concentrations > 5 µM, i.e. below the level required for E protein inhibition.
Conclusions This study demonstrates direct inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 E protein by classical viroporin inhibitors. Ivermectin and milbemycin inhibit the E protein channel but their cytotoxicity argues against clinical application.
Author contributions UB: conception, design of work, data acquisition and analysis, interpretation of data, drafting, writing and revising the manuscript. CS: data acquisition and analysis, interpretation of data, revising the manuscript. HS: conception, data analysis, interpretation of data, revising the manuscript. HGB: conception, design of work, data acquisition and analysis, interpretation of data, drafting, writing and revising the manuscript. All authors have approved the submitted version (and any substantially modified version that involves the author's contribution to the study); all authors have agreed both to be personally accountable for their own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Acharya, Carnevale, Fiorin, Levine, Polishchuk et al., Structure and mechanism of proton transport through the transmembrane tetrameric M2 protein bundle of the influenza A virus, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Alhetheel, Albarrag, Shakoor, Alswat, Abdo et al., Assessment of pro-inflammatory cytokines in sera of patients with hepatitis C virus infection before and after anti-viral therapy, J Infect Dev Ctries
Arbely, Khattari, Brotons, Akkawi, Salditt et al., A highly unusual palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin formed by SARS coronavirus E protein, J Mol Biol
Azeem, Ashraf, Rasheed, Anjum, Hameed, Evaluation of cytotoxicity and antiviral activity of ivermectin against Newcastle disease virus, Pak J Pharm Sci
Babalola, Bode, Ajayi, Alakaloko, Akase et al., Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos, QJM
Behera, Patro, Padhy, Mohapatra, Bal et al., Prophylactic role of ivermectin in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection among healthcare workers, Cureus
Breitinger, Ali, Sticht, Breitinger, Inhibition of SARS CoV envelope protein by flavonoids and classical viroporin inhibitors, Front Microbiol
Breitinger, Breitinger, Modulators of the inhibitory glycine receptor, ACS Chem Neurosci
Breitinger, Farag, Ali, Ahmed, El-Azizi et al., Cell viability assay as a tool to study activity and inhibition of hepatitis C p7 channels, J Gen Virol
Breitinger, Farag, Ali, Breitinger, Patch-clamp study of hepatitis C p7 channels reveals genotype-specific sensitivity to inhibitors, Biophys J
Breitinger, Farag, Sticht, Breitinger, Viroporins: structure, function, and their role in the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2, Int J Biochem Cell Biol
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Castano-Rodriguez, Honrubia, Gutierrez-Alvarez, Dediego, Nieto-Torres et al., Role of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus viroporins E, 3a, and 8a in replication and pathogenesis, MBio,
doi:10.1128/mBio.02325-17Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, Pineda, Fernandez-Montero et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled
Clarke, Griffin, Beales, Gelais, Burgess et al., Evidence for the formation of a heptameric ion channel complex by the hepatitis C virus p7 protein in vitro, J Biol Chem
Cobos-Campos, Apinaniz, Parraza, Cordero, Garcia et al., Potential use of ivermectin for the treatment and prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Curr Res Transl Med
Crump, Omura, Ivermectin, wonder drug" from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci
Du, Lu, Wu, Cheng, Gouaux, Glycine receptor mechanism elucidated by electron cryo-microscopy, Nature
Ewart, Sutherland, Gage, Cox, The Vpu protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 forms cation-selective ion channels, J Virol
Fam, Sedky, Turky, Breitinger, Breitinger, Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Sci Rep
Farag, Breitinger, Breitinger, Azizi, Viroporins and inflammasomes: a key to understand virus-induced inflammation, Int J Biochem Cell Biol
Farag, Breitinger, El-Azizi, Breitinger, The p7 viroporin of the hepatitis C virus contributes to liver inflammation by stimulating production of Interleukin-1β, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis
Fett, Dediego, Regla-Nava, Enjuanes, Perlman, Complete protection against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirusmediated lethal respiratory disease in aged mice by immunization with a mouse-adapted virus lacking E protein, J Virol
Freeman, Swartz, Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in severe COVID-19, Front Immunol
Galan, Santos, Asato, Araujo, De Lima et al., Phase 2 randomized study on chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine or ivermectin in hospitalized patients with severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Griffin, Stgelais, Owsianka, Patel, Rowlands et al., Genotype-dependent sensitivity of hepatitis C virus to inhibitors of the p7 ion channel, Hepatology
Guan, Yang, Sun, Wang, Ma et al., Association of influenza virus infection and inflammatory cytokines with acute myocardial infarction, Inflamm Res
Hover, Foster, Barr, Mankouri, Viral dependence on cellular ion channels-an emerging anti-viral target?, J Gen Virol
Ichinohe, Pang, Iwasaki, Influenza virus activates inflammasomes via its intracellular M2 ion channel, Nat Immunol
Khan, Hashmi, Goel, Ahmad, Gupta et al., COVID-19 pandemic and vaccines update on challenges and resolutions, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Kien, Ma, Gaisenband, Nal, Viroporins: Differential Functions at Late stages of Viral Life Cycles
Kinobe, Owens, A systematic review of experimental evidence for antiviral effects of ivermectin and an in silico analysis of ivermectin's possible mode of action against SARS-CoV-2, Fundam Clin Pharmacol
Krause, Buisson, Bertrand, Corringer, Galzi et al., Ivermectin: a positive allosteric effector of the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, Mol Pharmacol
Krusek, Zemkova, Effect of ivermectin on gamma-aminobutyric acidinduced chloride currents in mouse hippocampal embryonic neurones, Eur J Pharmacol
Laing, Devaney, Ivermectin-old drug, new tricks?, Trends Parasitol
Liu, Xie, Wang, Xiong, Chen et al., A comparative overview of COVID-19, MERS and SARS: review article, Int J Surg
Lynagh, Lynch, Ivermectin binding sites in human and invertebrate Cys-loop receptors, Trends Pharmacol Sci
Lynagh, Lynch, Molecular mechanisms of Cys-loop ion channel receptor modulation by ivermectin, Front Mol Neurosci
Mccavera, Rogers, Yates, Woods, Wolstenholme, An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus, Mol Pharmacol
Morgenstern, Redondo, Olavarria, Rondon, Roca et al., Ivermectin as a SARS-CoV-2 pre-exposure prophylaxis method in healthcare workers: a propensity score-matched retrospective cohort study, Cureus
Naqvi, Mohammad, Fatima, Singh, Singh et al., Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: structural genomics approach, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis
Nieto-Torres, Dediego, Alvarez, Jimenez-Guardeno, Nava et al., Subcellular location and topology of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein, Virology
Nieva, Madan, Carrasco, Viroporins: structure and biological functions, Nat Rev Microbiol
Okumus, Demirturk, Cetinkaya, Guner, Avci et al., Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID-19 patients, BMC Infect Dis
Parvez, Karim, Hasan, Jaman, Karim et al., Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach, Int J Biol Macromol
Pavlovic, Fischer, Hussey, Durantel, Durantel et al., Long alkylchain iminosugars block the HCV p7 ion channel, Adv Exp Med Biol
Pervushin, Tan, Parthasarathy, Lin, Jiang et al., Structure and inhibition of the SARS coronavirus envelope protein ion channel, PLoS Pathog
Pinto, Holsinger, Lamb, Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity, Cell
Ruch, Machamer, The coronavirus E protein: assembly and beyond, Viruses
Schulze, Hartl, Höler, Hemming, Lehn et al., SARS-CoV-2 envelope-protein corruption of homeostatic signaling mechanisms in mammalian cells
Scott, Griffin, Viroporins: structure, function and potential as antiviral targets, J Gen Virol
Surya, Li, Torres, Structural model of the SARS coronavirus E channel in LMPG micelles, Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr
Torres, Maheswari, Parthasarathy, Ng, Liu et al., Conductance and amantadine binding of a pore formed by a lysine-flanked transmembrane domain of SARS coronavirus envelope protein, Protein Sci
Torres, Parthasarathy, Lin, Saravanan, Kukol et al., Model of a putative pore: the pentameric alpha-helical bundle of SARS coronavirus E protein in lipid bilayers, Biophys J
Turkia, The history of methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin protocol and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocol for COVID-19, Cureus
Wilson, Gage, Ewart, Hexamethylene amiloride blocks E protein ion channels and inhibits coronavirus replication, Virology
Wilson, Mckinlay, Gage, Ewart, SARS coronavirus E protein forms cation-selective ion channels, Virology
Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin alpha/beta1 heterodimer, Antiviral Res
Zein, Sulistiyana, Raffaelo, Pranata, Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials, Diabetes Metab Syndr
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y",
"ISSN": [
"1743-422X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>SARS-CoV-2 has caused a worldwide pandemic since December 2019 and the search for pharmaceutical targets against COVID-19 remains an important challenge. Here, we studied the envelope protein E of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, a highly conserved 75–76 amino acid viroporin that is crucial for virus assembly and release. E protein channels were recombinantly expressed in HEK293 cells, a membrane-directing signal peptide ensured transfer to the plasma membrane.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Viroporin channel activity of both E proteins was investigated using patch-clamp electrophysiology in combination with a cell viability assay. We verified inhibition by classical viroporin inhibitors amantadine, rimantadine and 5-(N,N-hexamethylene)-amiloride, and tested four ivermectin derivatives.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Classical inhibitors showed potent activity in patch-clamp recordings and viability assays. In contrast, ivermectin and milbemycin inhibited the E channel in patch-clamp recordings but displayed only moderate activity on the E protein in the cell viability assay, which is also sensitive to general cytotoxic activity of the tested compounds. Nemadectin and ivermectin aglycon were inactive. All ivermectin derivatives were cytotoxic at concentrations > 5 µM, i.e. below the level required for E protein inhibition.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This study demonstrates direct inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 E protein by classical viroporin inhibitors. Ivermectin and milbemycin inhibit the E protein channel but their cytotoxicity argues against clinical application.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"2095"
],
"article-number": "142",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "30 July 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "8 June 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "8 July 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Breitinger",
"given": "Ulrike",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sedky",
"given": "Christine Adel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sticht",
"given": "Heinrich",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Breitinger",
"given": "Hans-Georg",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Virology Journal",
"container-title-short": "Virol J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-08T12:01:46Z",
"timestamp": 1688817706000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-08T13:04:03Z",
"timestamp": 1688821443000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-09T04:12:41Z",
"timestamp": 1688875961572
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688774400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688774400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.07.032",
"author": "J Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Surg",
"key": "2095_CR1",
"unstructured": "Liu J, Xie W, Wang Y, Xiong Y, Chen S, Han J, Wu Q. A comparative overview of COVID-19, MERS and SARS: review article. Int J Surg. 2020;81:1–8.",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105738",
"author": "NS Farag",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105738",
"journal-title": "Int J Biochem Cell Biol",
"key": "2095_CR2",
"unstructured": "Farag NS, Breitinger U, Breitinger HG, El Azizi MA. Viroporins and inflammasomes: a key to understand virus-induced inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;122:105738.",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165878",
"author": "AAT Naqvi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165878",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis",
"key": "2095_CR3",
"unstructured": "Naqvi AAT, Fatima K, Mohammad T, Fatima U, Singh IK, Singh A, Atif SM, Hariprasad G, Hasan GM, Hassan MI. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: structural genomics approach. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866:165878.",
"volume": "1866",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01518",
"author": "TL Freeman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1518",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2095_CR4",
"unstructured": "Freeman TL, Swartz TH. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in severe COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1518.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.7595",
"author": "A Alhetheel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1093",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dev Ctries",
"key": "2095_CR5",
"unstructured": "Alhetheel A, Albarrag A, Shakoor Z, Alswat K, Abdo A, Al-Hamoudi W. Assessment of pro-inflammatory cytokines in sera of patients with hepatitis C virus infection before and after anti-viral therapy. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2016;10:1093–8.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.12.006",
"author": "NS Farag",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "712",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis",
"key": "2095_CR6",
"unstructured": "Farag NS, Breitinger U, El-Azizi M, Breitinger HG. The p7 viroporin of the hepatitis C virus contributes to liver inflammation by stimulating production of Interleukin-1β. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863:712–20.",
"volume": "1863",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-012-0449-3",
"author": "X Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "591",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "2095_CR7",
"unstructured": "Guan X, Yang W, Sun X, Wang L, Ma B, Li H, Zhou J. Association of influenza virus infection and inflammatory cytokines with acute myocardial infarction. Inflamm Res. 2012;61:591–8.",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.690621",
"author": "WH Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "690621",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "2095_CR8",
"unstructured": "Khan WH, Hashmi Z, Goel A, Ahmad R, Gupta K, Khan N, Alam I, Ahmed F, Ansari MA. COVID-19 pandemic and vaccines update on challenges and resolutions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:690621.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biocel.2022.106185",
"author": "U Breitinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106185",
"journal-title": "Int J Biochem Cell Biol",
"key": "2095_CR9",
"unstructured": "Breitinger U, Farag NS, Sticht H, Breitinger HG. Viroporins: structure, function, and their role in the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022;145:106185.",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2095_CR10",
"unstructured": "Kien F, Ma H, Gaisenband S, Nal B. Viroporins: Differential Functions at Late stages of Viral Life Cycles. In Microbial Pathogenesis: Infection and Immunity. Edited by Kishore U, Nayak A: Landes Bioscience and Springer Science + Business Media; 2013: pp 38–62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro2820",
"author": "JL Nieva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "563",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "2095_CR11",
"unstructured": "Nieva JL, Madan V, Carrasco L. Viroporins: structure and biological functions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10:563–74.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.02325-17",
"author": "C Castano-Rodriguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "MBio",
"key": "2095_CR12",
"unstructured": "Castano-Rodriguez C, Honrubia JM, Gutierrez-Alvarez J, DeDiego ML, Nieto-Torres JL, Jimenez-Guardeno JM, Regla-Nava JA, Fernandez-Delgado R, Verdia-Baguena C, Queralt-Martin M, et al. Role of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus viroporins E, 3a, and 8a in replication and pathogenesis. MBio. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02325-17.",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jgv.0.000712",
"author": "S Hover",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "345",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "2095_CR13",
"unstructured": "Hover S, Foster B, Barr JN, Mankouri J. Viral dependence on cellular ion channels—an emerging anti-viral target? J Gen Virol. 2017;98:345–51.",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1007071107",
"author": "R Acharya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15075",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "2095_CR14",
"unstructured": "Acharya R, Carnevale V, Fiorin G, Levine BG, Polishchuk AL, Balannik V, Samish I, Lamb RA, Pinto LH, DeGrado WF, Klein ML. Structure and mechanism of proton transport through the transmembrane tetrameric M2 protein bundle of the influenza A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:15075–80.",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.1861",
"author": "T Ichinohe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "404",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "2095_CR15",
"unstructured": "Ichinohe T, Pang IK, Iwasaki A. Influenza virus activates inflammasomes via its intracellular M2 ion channel. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:404–10.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0092-8674(92)90452-I",
"author": "LH Pinto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "517",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2095_CR16",
"unstructured": "Pinto LH, Holsinger LJ, Lamb RA. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell. 1992;69:517–28.",
"volume": "69",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M602434200",
"author": "D Clarke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37057",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "2095_CR17",
"unstructured": "Clarke D, Griffin S, Beales L, Gelais CS, Burgess S, Harris M, Rowlands D. Evidence for the formation of a heptameric ion channel complex by the hepatitis C virus p7 protein in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:37057–68.",
"volume": "281",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2016.04.018",
"author": "U Breitinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2419",
"journal-title": "Biophys J",
"key": "2095_CR18",
"unstructured": "Breitinger U, Farag NS, Ali NK, Breitinger HG. Patch-clamp study of hepatitis C p7 channels reveals genotype-specific sensitivity to inhibitors. Biophys J. 2016;110:2419–29.",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.70.10.7108-7115.1996",
"author": "GD Ewart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7108",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "2095_CR19",
"unstructured": "Ewart GD, Sutherland T, Gage PW, Cox GB. The Vpu protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 forms cation-selective ion channels. J Virol. 1996;70:7108–15.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.000201",
"author": "C Scott",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2000",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "2095_CR20",
"unstructured": "Scott C, Griffin S. Viroporins: structure, function and potential as antiviral targets. J Gen Virol. 2015;96:2000–27.",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2004.06.044",
"author": "E Arbely",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "769",
"journal-title": "J Mol Biol",
"key": "2095_CR21",
"unstructured": "Arbely E, Khattari Z, Brotons G, Akkawi M, Salditt T, Arkin IT. A highly unusual palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin formed by SARS coronavirus E protein. J Mol Biol. 2004;341:769–79.",
"volume": "341",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000511",
"author": "K Pervushin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1000511",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "2095_CR22",
"unstructured": "Pervushin K, Tan E, Parthasarathy K, Lin X, Jiang FL, Yu D, Vararattanavech A, Soong TW, Liu DX, Torres J. Structure and inhibition of the SARS coronavirus envelope protein ion channel. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000511.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2011.03.029",
"author": "JL Nieto-Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "2095_CR23",
"unstructured": "Nieto-Torres JL, Dediego ML, Alvarez E, Jimenez-Guardeno JM, Regla-Nava JA, Llorente M, Kremer L, Shuo S, Enjuanes L. Subcellular location and topology of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein. Virology. 2011;415:69–82.",
"volume": "415",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1529/biophysj.105.080119",
"author": "J Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "938",
"journal-title": "Biophys J",
"key": "2095_CR24",
"unstructured": "Torres J, Parthasarathy K, Lin X, Saravanan R, Kukol A, Liu DX. Model of a putative pore: the pentameric alpha-helical bundle of SARS coronavirus E protein in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 2006;91:938–47.",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2004.09.033",
"author": "L Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "322",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "2095_CR25",
"unstructured": "Wilson L, McKinlay C, Gage P, Ewart G. SARS coronavirus E protein forms cation-selective ion channels. Virology. 2004;330:322–31.",
"volume": "330",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00087-13",
"author": "C Fett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6551",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "2095_CR26",
"unstructured": "Fett C, DeDiego ML, Regla-Nava JA, Enjuanes L, Perlman S. Complete protection against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-mediated lethal respiratory disease in aged mice by immunization with a mouse-adapted virus lacking E protein. J Virol. 2013;87:6551–9.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v4030363",
"author": "TR Ruch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "2095_CR27",
"unstructured": "Ruch TR, Machamer CE. The coronavirus E protein: assembly and beyond. Viruses. 2012;4:363–82.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1110/ps.062730007",
"author": "J Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2065",
"journal-title": "Protein Sci",
"key": "2095_CR28",
"unstructured": "Torres J, Maheswari U, Parthasarathy K, Ng L, Liu DX, Gong X. Conductance and amantadine binding of a pore formed by a lysine-flanked transmembrane domain of SARS coronavirus envelope protein. Protein Sci. 2007;16:2065–71.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jgv.0.001571",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2095_CR29",
"unstructured": "Breitinger U, Farag NS, Ali NKM, Ahmed M, El-Azizi M, Breitinger HG: Cell viability assay as a tool to study activity and inhibition of hepatitis C p7 channels. J Gen Virol 2021, in revision."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2006.05.028",
"author": "L Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "294",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "2095_CR30",
"unstructured": "Wilson L, Gage P, Ewart G. Hexamethylene amiloride blocks E protein ion channels and inhibits coronavirus replication. Virology. 2006;353:294–306.",
"volume": "353",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/0-387-25515-X_2",
"author": "D Pavlovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol",
"key": "2095_CR31",
"unstructured": "Pavlovic D, Fischer W, Hussey M, Durantel D, Durantel S, Branza-Nichita N, Woodhouse S, Dwek RA, Zitzmann N. Long alkylchain iminosugars block the HCV p7 ion channel. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2005;564:3–4.",
"volume": "564",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2021.692423",
"author": "U Breitinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "692423",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "2095_CR32",
"unstructured": "Breitinger U, Ali NK, Sticht H, Breitinger HG. Inhibition of SARS CoV envelope protein by flavonoids and classical viroporin inhibitors. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:692423.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"author": "A Crump",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci",
"key": "2095_CR33",
"unstructured": "Crump A, Omura S. Ivermectin, “wonder drug” from Japan: the human use perspective. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2011;87:13–28.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnmol.2012.00060",
"author": "T Lynagh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "60",
"journal-title": "Front Mol Neurosci",
"key": "2095_CR34",
"unstructured": "Lynagh T, Lynch JW. Molecular mechanisms of Cys-loop ion channel receptor modulation by ivermectin. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012;5:60.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.retram.2021.103309",
"author": "R Cobos-Campos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103309",
"journal-title": "Curr Res Transl Med",
"key": "2095_CR35",
"unstructured": "Cobos-Campos R, Apinaniz A, Parraza N, Cordero J, Garcia S, Orruno E. Potential use of ivermectin for the treatment and prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Curr Res Transl Med. 2021;69:103309.",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "S Azeem",
"first-page": "597",
"journal-title": "Pak J Pharm Sci",
"key": "2095_CR36",
"unstructured": "Azeem S, Ashraf M, Rasheed MA, Anjum AA, Hameed R. Evaluation of cytotoxicity and antiviral activity of ivermectin against Newcastle disease virus. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015;28:597–602.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "OE Babalola",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "QJM",
"key": "2095_CR37",
"unstructured": "Babalola OE, Bode CO, Ajayi AA, Alakaloko FM, Akase IE, Otrofanowei E, Salu OB, Adeyemo WL, Ademuyiwa AO, Omilabu S. Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomised controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos. QJM. 2021;91:157.",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/fcp.12644",
"author": "RT Kinobe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "260",
"journal-title": "Fundam Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2095_CR38",
"unstructured": "Kinobe RT, Owens L. A systematic review of experimental evidence for antiviral effects of ivermectin and an in silico analysis of ivermectin’s possible mode of action against SARS-CoV-2. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2021;35:260–76.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186",
"author": "A Zein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102186",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "2095_CR39",
"unstructured": "Zein A, Sulistiyana CS, Raffaelo WM, Pranata R. Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021;15:102186.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9",
"author": "MS Fam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5328",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2095_CR40",
"unstructured": "Fam MS, Sedky CA, Turky NO, Breitinger HG, Breitinger U. Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites. Sci Rep. 2023;13:5328.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.22555",
"author": "SD Griffin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1779",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "2095_CR41",
"unstructured": "Griffin SD, Stgelais C, Owsianka AM, Patel AH, Rowlands DJ, Harris M. Genotype-dependent sensitivity of hepatitis C virus to inhibitors of the p7 ion channel. Hepatology. 2008;48:1779–90.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2017.02.004",
"author": "R Laing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol",
"key": "2095_CR42",
"unstructured": "Laing R, Gillan V, Devaney E. Ivermectin—old drug, new tricks? Trends Parasitol. 2017;33:463–72.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00054",
"author": "U Breitinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1706",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem Neurosci",
"key": "2095_CR43",
"unstructured": "Breitinger U, Breitinger HG. Modulators of the inhibitory glycine receptor. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020;11:1706–25.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2012.05.002",
"author": "T Lynagh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "432",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "2095_CR44",
"unstructured": "Lynagh T, Lynch JW. Ivermectin binding sites in human and invertebrate Cys-loop receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012;33:432–41.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0014-2999(94)90500-2",
"author": "J Krusek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "2095_CR45",
"unstructured": "Krusek J, Zemkova H. Effect of ivermectin on gamma-aminobutyric acid-induced chloride currents in mouse hippocampal embryonic neurones. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;259:121–8.",
"volume": "259",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/mol.53.2.283",
"author": "RM Krause",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Mol Pharmacol",
"key": "2095_CR46",
"unstructured": "Krause RM, Buisson B, Bertrand S, Corringer PJ, Galzi JL, Changeux JP, Bertrand D. Ivermectin: a positive allosteric effector of the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;53:283–94.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/mol.108.053363",
"author": "S McCavera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1347",
"journal-title": "Mol Pharmacol",
"key": "2095_CR47",
"unstructured": "McCavera S, Rogers AT, Yates DM, Woods DJ, Wolstenholme AJ. An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;75:1347–55.",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.06.16.448640",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2095_CR48",
"unstructured": "Schulze T, Hartl A, Höler S, Hemming C, Lehn R, Tandl D, Greiner T, Bertl A, Shepard K, Moroni A, Rauh O. SARS-CoV-2 envelope-protein corruption of homeostatic signaling mechanisms in mammalian cells. bioRxiv 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"author": "L Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "2095_CR49",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2020;178:104787.",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.098",
"author": "MSA Parvez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "2095_CR50",
"unstructured": "Parvez MSA, Karim MA, Hasan M, Jaman J, Karim Z, Tahsin T, Hasan MN, Hosen MJ. Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;163:1787–97.",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"author": "SNY Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104760",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "2095_CR51",
"unstructured": "Yang SNY, Atkinson SC, Wang C, Lee A, Bogoyevitch MA, Borg NA, Jans DA. The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin alpha/beta1 heterodimer. Antiviral Res. 2020;177:104760.",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "M Turkia",
"first-page": "e12403",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2095_CR52",
"unstructured": "Turkia M. The history of methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin protocol and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocol for COVID-19. Cureus. 2020;12:e12403.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "P Behera",
"first-page": "e16897",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2095_CR53",
"unstructured": "Behera P, Patro BK, Padhy BM, Mohapatra PR, Bal SK, Chandanshive PD, Mohanty RR, Ravikumar SR, Singh A, Singh SR, et al. Prophylactic role of ivermectin in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection among healthcare workers. Cureus. 2021;13:e16897.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "J Morgenstern",
"first-page": "e17455",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2095_CR54",
"unstructured": "Morgenstern J, Redondo JN, Olavarria A, Rondon I, Roca S, De Leon A, Canela J, Tavares J, Minaya M, Lopez O, et al. Ivermectin as a SARS-CoV-2 pre-exposure prophylaxis method in healthcare workers: a propensity score-matched retrospective cohort study. Cureus. 2021;13:e17455.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"author": "C Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100720",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "2095_CR55",
"unstructured": "Chaccour C, Casellas A, Blanco-Di Matteo A, Pineda I, Fernandez-Montero A, Ruiz-Castillo P, Richardson MA, Rodriguez-Mateos M, Jordan-Iborra C, Brew J, et al. The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;32:100720.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/20477724.2021.1890887",
"author": "LEB Galan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "235",
"journal-title": "Pathog Glob Health",
"key": "2095_CR56",
"unstructured": "Galan LEB, Santos NMD, Asato MS, Araujo JV, de Lima MA, Araujo AMM, Paiva ADP, Portella DGS, Marques FSS, Silva GMA, et al. Phase 2 randomized study on chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine or ivermectin in hospitalized patients with severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Pathog Glob Health. 2021;115:235–42.",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06104-9",
"author": "N Okumus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "411",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "2095_CR57",
"unstructured": "Okumus N, Demirturk N, Cetinkaya RA, Guner R, Avci IY, Orhan S, Konya P, Saylan B, Karalezli A, Yamanel L, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID-19 patients. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21:411.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature14853",
"author": "J Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "224",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2095_CR58",
"unstructured": "Du J, Lu W, Wu S, Cheng Y, Gouaux E. Glycine receptor mechanism elucidated by electron cryo-microscopy. Nature. 2015;526:224–9.",
"volume": "526",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.02.017",
"author": "W Surya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1309",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr",
"key": "2095_CR59",
"unstructured": "Surya W, Li Y, Torres J. Structural model of the SARS coronavirus E channel in LMPG micelles. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018;1860:1309–17.",
"volume": "1860",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://virologyj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12985-023-02095-y"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Patch-clamp studies and cell viability assays suggest a distinct site for viroporin inhibitors on the E protein of SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "20"
}