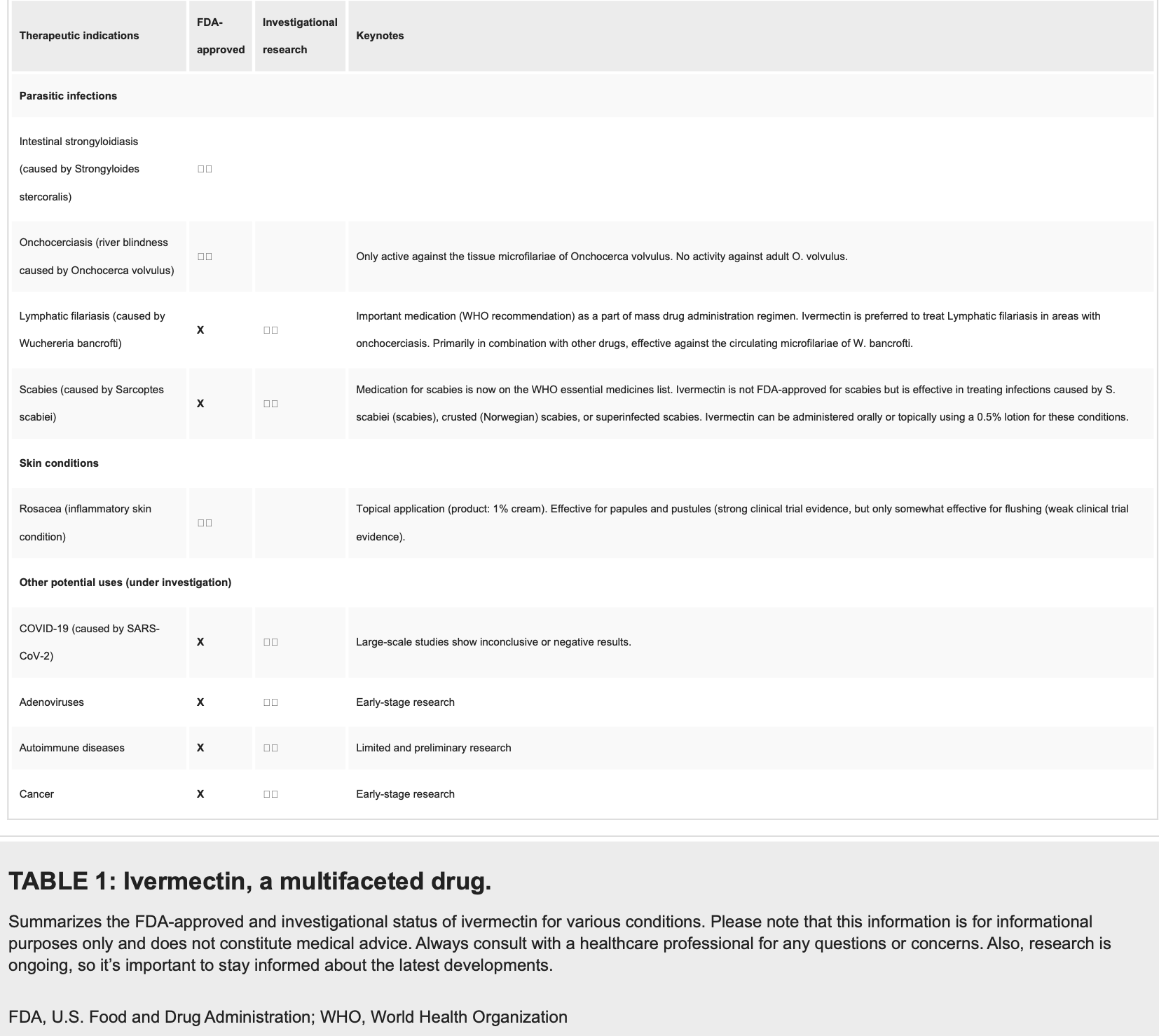
Ivermectin: A Multifaceted Drug With a Potential Beyond Anti-parasitic Therapy
Baneet Kaur, Cyril Blavo, Mayur S Parmar
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.56025
Ivermectin was first discovered in the 1970s by Japanese microbiologist Satoshi Omura and Irish parasitologist William C. Campbell. Ivermectin has become a versatile pharmaceutical over the past 50 years. Ivermectin is a derivative of avermectin originally used to treat parasitic infections. Emerging literature has suggested that its role goes beyond this and may help treat inflammatory conditions, viral infections, and cancers. Ivermectin's anti-parasitic, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anticancer effects were explored. Its traditional mechanism of action in parasitic diseases, such as scabies and malaria, rests on its ability to interfere with the glutamate-gated chloride channels in invertebrates and the lack of P-glycoprotein in many parasites. More recently, it has been discovered that the ability of ivermectin to block the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of the activated B (NF-κB) pathway that modulates the expression and production of proinflammatory cytokines is implicated in its role as an anti-inflammatory agent to treat rosacea. Ivermectin has also been evaluated for treating infections caused by viruses, such as SARS-CoV-2 and adenoviruses, through inhibition of viral protein transportation and acting on the importin α/β1 interface. It has also been suggested that ivermectin can inhibit the proliferation of tumorigenic cells through various pathways that lead to the management of certain cancers. The review aimed to evaluate its multifaceted effects and potential clinical applications beyond its traditional use as an anthelmintic agent.
Additional Information Author Contributions All authors have reviewed the final version to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Concept and design
Disclosures
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
References
Almeida, Ianhez, Dal'forno, Long-term maintenance treatment of rosacea: experts' opinion, Int J Dermatol,
doi:10.1111/ijd.16920Awadzi, Dadzie, Schulz-Key, Gilles, Fulford et al., The chemotherapy of onchocerciasis. XI. A double-blind comparative study of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and placebo in human onchocerciasis in northern Ghana, Ann Trop Med Parasitol,
doi:10.1080/00034983.1986.11812044Aždajić, Bešlić, Gašić, Ferara, Pedić et al., Increased scabies incidence at the beginning of the 21st century: what do reports from Europe and the world show?, Life,
doi:10.3390/life12101598Bellinger, Jafari, Grant, Oral, ultra-long-lasting drug delivery: application toward malaria elimination goals, Sci Transl Med,
doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aag2374Chaccour, Casellas, Hammann, BOHEMIA: Broad One Health Endectocide-based Malaria Intervention in Africa-a phase III cluster-randomized, open-label, clinical trial to study the safety and efficacy of ivermectin mass drug administration to reduce malaria transmission in two African settings, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-023-07098-2Chen, Wang, Efficacy and safety of antibiotic agents in the treatment of rosacea: a systemic network meta-analysis, Front Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1169916Crump, Ōmura, wonder drug" from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,
doi:10.2183/pjab.87.13Cully, Vassilatis, Liu, Paress, Van Der Ploeg et al., Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans, Nature,
doi:10.1038/371707a0De Sole, Remme, Awadzi, Adverse reactions after large-scale treatment of onchocerciasis with ivermectin: combined results from eight community trials, Bull World Health Organ
Deng, Zhou, Ali, Heybati, Hou et al., Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, QJM,
doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab247Dhana, Yen, Okhovat, Cho, Keum et al., Ivermectin versus permethrin in the treatment of scabies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Am Acad Dermatol,
doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.09.006Diallo, Aziz, Lariviere, A double-blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in a placebo controlled study of Senegalese patients with onchocerciasis, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg,
doi:10.1016/0035-9203(86)90262-2Ebbelaar, Venema, Van Dijk Mr, Topical ivermectin in the treatment of papulopustular rosacea: a systematic review of evidence and clinical guideline recommendations, Dermatol Ther (Heidelb),
doi:10.1007/s13555-018-0249-yFeng, Wang, Cai, Bai, Zhu, Ivermectin accelerates autophagic death of glioma cells by inhibiting glycolysis through blocking GLUT4 mediated JAK/STAT signaling pathway activation, Environ Toxicol,
doi:10.1002/tox.23440Foy, Alout, Seaman, Efficacy and risk of harms of repeat ivermectin mass drug administrations for control of malaria (RIMDAMAL): a cluster-randomised trial, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32321-3Foy, Some, Magalhaes, Repeat ivermectin mass drug administrations for malaria control II: protocol for a double-blind, cluster-randomized, placebo-controlled trial for the integrated control of malaria, JMIR Res Protoc,
doi:10.2196/41197González, González, Ueno, Ivermectin in human medicine, an overview of the current status of its clinical applications, Curr Pharm Biotechnol,
doi:10.2174/138920112800399248Hadlett, Nagi, Sarkar, Paine, Weetman, High concentrations of membrane-fed ivermectin are required for substantial lethal and sublethal impacts on Aedes aegypti, Parasit Vectors,
doi:10.1186/s13071-020-04512-5Hashimoto, Messerli, Sudo, Maruta, Ivermectin inactivates the kinase PAK1 and blocks the PAK1dependent growth of human ovarian cancer and NF2 tumor cell lines, Drug Discov Ther
Hu, Liang, Lin, Lin, Ivermectin's role in the prevention of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Clin Pharmacol,
doi:10.1002/jcph.2178Hu, Tan, Yu, Liao, Guo, Repurposing Ivermectin to augment chemotherapy's efficacy in osteosarcoma, Hum Exp Toxicol,
doi:10.1177/09603271221143693Huang, He, Guo, Xu, Wu et al., Progress in redirecting antiparasitic drugs for cancer treatment, Drug Des Devel Ther,
doi:10.2147/DDDT.S308973Jans, Wagstaff, The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?, Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042Janssen, Derst, Buckinx, Van Den Eynden, Rigo et al., Dorsal unpaired median neurons of locusta migratoria express ivermectin-and fipronil-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channels, J Neurophysiol,
doi:10.1152/jn.01234.2006Janssen, Derst, Rigo, Van Kerkhove, Cys-loop ligand-gated chloride channels in dorsal unpaired median neurons of Locusta migratoria, J Neurophysiol,
doi:10.1152/jn.00466.2009Jawad, Richardson, Ivermectin augments the anti-cancer activity of pitavastatin in ovarian cancer cells, Diseases,
doi:10.3390/diseases11010049Kern, Müller, Chaccour, Liechti, Hammann et al., Pharmacokinetics of ivermectin metabolites and their activity against Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes, Malar J,
doi:10.1186/s12936-023-04624-0King, Tessier, Dodge, Weinberg, Mymryk, Inhibition of human adenovirus replication by the importin α/β1 nuclear import inhibitor ivermectin, J Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00710-20Kircik, Rosso, Layton, Schauber, Over 25 years of clinical experience with ivermectin: an overview of safety for an increasing number of indications, J Drugs Dermatol
Kositz, Bradley, Hutchins, Last, 'alessandro et al., Broadening the range of use cases for ivermectin -a review of the evidence, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg,
doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab114Kumar, Pasi, Yadav, Kaur, Sharma, Potential of ivermectin as an active ingredient of the attractive toxic sugar baits against the Indian malaria vectors Anopheles culicifacies and Anopheles stephensi, Pest Manag Sci,
doi:10.1002/ps.7217Kwon, Petrie, Leibovitch, Selective inhibition of SIN3 corepressor with avermectins as a novel therapeutic strategy in triple-negative breast cancer, Mol Cancer Ther,
doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0980-TLariviere, Vingtain, Aziz, Double-blind study of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in African onchocerciasis patients with ocular involvement, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91496-5Li, Zhang, Lu, Ivermectin induces nonprotective autophagy by downregulating PAK1 and apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,
doi:10.1007/s00280-023-04589-6Liu, Fang, Sun, Liu, Anthelmintic drug ivermectin inhibits angiogenesis, growth and survival of glioblastoma through inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.064Liu, Liang, Chen, Ivermectin induces autophagy-mediated cell death through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioma cells, Biosci Rep,
doi:10.1042/BSR20192489Marcolino, Meira, Guimarães, Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype, BMC Infect Dis,
doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8Marques, Beneti, Pinzon, Cardoso, Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols, Braz J Biol,
doi:10.1590/1519-6984.258325Mccavera, Rogers, Yates, Woods, Wolstenholme, An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus, Mol Pharmacol,
doi:10.1124/mol.108.053363Meltan, Panuganti, Tarbox, Evaluation and management of pruritus and scabies in the elderly population, Clin Geriatr Med,
doi:10.1016/j.cger.2023.09.010Meyers, Gray, Kuklinski, Characterization of the target of ivermectin, the glutamate-gated chloride channel, from Anopheles gambiae, J Exp Biol,
doi:10.1242/jeb.118570Meyersburg, Kaiser, Bauer, Loss of efficacy of topical 5% permethrin for treating scabies: an Austrian single-center study, J Dermatolog Treat,
doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1774489Meyersburg, Welponer, Kaiser, Selhofer, Tatarski et al., Comparison of topical benzyl benzoate vs. oral ivermectin in treating scabies: a randomized study, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol,
doi:10.1111/jdv.18573Mohebbipour, Saleh, Goldust, Amirnia, Zadeh et al., Treatment of scabies: comparison of ivermectin vs. lindane lotion 1%, Acta Dermatovenerol Croat
Moreno, Nabhan, Solomon, Mackenzie, Geary, Ivermectin disrupts the function of the excretory-secretory apparatus in microfilariae of Brugia malayi, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
doi:10.1073/pnas.1011983107Ménez, Mselli-Lakhal, Vignault, Balaguer, Alvinerie et al., Ivermectin induces Pglycoprotein expression and function through mRNA stabilization in murine hepatocyte cell line, Biochem Pharmacol,
doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.10.010Osman, Shokeir, Hassan, Khalifa, Pulsed dye laser alone versus its combination with topical ivermectin 1% in treatment of Rosacea: a randomized comparative study, J Dermatolog Treat,
doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1737636Patho, Grant, Russell, Ivermectin inhibits replication of the malignant catarrhal fever virus alcelaphine herpesvirus 1, Virology,
doi:10.1016/j.virol.2023.109958Pérez, Miró, Verna, Altamiranda, Barcos et al., Ivermectin antiviral activity against Varicellovirus bovinealpha 1: assessment of intracellular drug accumulation in virus-infected cells, Arch Microbiol,
doi:10.1007/s00203-023-03806-3Raza, Shahin, Zhai, Ivermectin inhibits bovine herpesvirus 1 DNA polymerase nuclear import and interferes with viral replication, Microorganisms,
doi:10.3390/microorganisms8030409Samy, Hussein, Munirathinam, Eprinomectin: a derivative of ivermectin suppresses growth and metastatic phenotypes of prostate cancer cells by targeting the β-catenin signaling pathway, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,
doi:10.1007/s00432-023-04829-5Schinkel, Smit, Van Tellingen, Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs, Cell,
doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90212-7White, Newland, Taylor, Controlled trial and dose-finding study of ivermectin for treatment of onchocerciasis, J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/infdis/156.3.463Yipsirimetee, Tipthara, Hanboonkunupakarn, Activity of ivermectin and its metabolites against asexual blood stage Plasmodium falciparum and its interactions with antimalarial drugs, Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
doi:10.1128/aac.01730-22Yotsu, Yoshizumi, Izri, Biology of Sarcoptes scabiei and Its Relevance to Human Scabies: Clinical Symptoms, Treatment, and Management,
doi:10.1007/978-3-031-26070-4_2Zhang, Song, Ci, Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflamm Res,
doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8Zhang, Zhang, Luo, Trends in prevalence and incidence of scabies from 1990 to 2017: findings from the global Burden of disease study 2017, Emerg Microbes Infect,
doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1754136DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.56025",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.56025",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "Baneet",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blavo",
"given": "Cyril",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parmar",
"given": "Mayur S",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-12T13:47:21Z",
"timestamp": 1710251241000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-12T13:47:27Z",
"timestamp": 1710251247000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-13T00:46:32Z",
"timestamp": 1710290792242
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/223832-ivermectin-a-multifaceted-drug-with-a-potential-beyond-anti-parasitic-therapy",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, \"wonder drug\" from Japan: the human use perspective",
"author": "Crump A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Crump A, Ōmura S. Ivermectin, \"wonder drug\" from Japan: the human use perspective. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2011, 87:13-28. 10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/trstmh/trab114",
"article-title": "Broadening the range of use cases for ivermectin - a review of the evidence",
"author": "Kositz C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Kositz C, Bradley J, Hutchins H, Last A, D'Alessandro U, Marks M. Broadening the range of use cases for ivermectin - a review of the evidence. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022, 116:201-12. 10.1093/trstmh/trab114",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Adverse reactions after large-scale treatment of onchocerciasis with ivermectin: combined results from eight community trials",
"author": "De Sole G",
"journal-title": "Bull World Health Organ",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "De Sole G, Remme J, Awadzi K, et al.. Adverse reactions after large-scale treatment of onchocerciasis with ivermectin: combined results from eight community trials. Bull World Health Organ. 1989, 67:707-19.",
"volume": "67",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/156.3.463",
"article-title": "Controlled trial and dose-finding study of ivermectin for treatment of onchocerciasis",
"author": "White AT",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "White AT, Newland HS, Taylor HR, et al.. Controlled trial and dose-finding study of ivermectin for treatment of onchocerciasis. J Infect Dis. 1987, 156:463-70. 10.1093/infdis/156.3.463",
"volume": "156",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91496-5",
"article-title": "Double-blind study of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in African onchocerciasis patients with ocular involvement",
"author": "Lariviere M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Lariviere M, Vingtain P, Aziz M, et al.. Double-blind study of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in African onchocerciasis patients with ocular involvement. Lancet. 1985, 2:174-7. 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91496-5",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0035-9203(86)90262-2",
"article-title": "A double-blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in a placebo controlled study of Senegalese patients with onchocerciasis",
"author": "Diallo S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Diallo S, Aziz MA, Lariviere M, et al.. A double-blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in a placebo controlled study of Senegalese patients with onchocerciasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986, 80:927-34. 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90262-2",
"volume": "80",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00034983.1986.11812044",
"article-title": "The chemotherapy of onchocerciasis. XI. A double-blind comparative study of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and placebo in human onchocerciasis in northern Ghana",
"author": "Awadzi K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann Trop Med Parasitol",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Awadzi K, Dadzie KY, Schulz-Key H, Gilles HM, Fulford AJ, Aziz MA. The chemotherapy of onchocerciasis. XI. A double-blind comparative study of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and placebo in human onchocerciasis in northern Ghana. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1986, 80:433-42. 10.1080/00034983.1986.11812044",
"volume": "80",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM198507183130301",
"article-title": "Comparison of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in the treatment of onchocerciasis",
"author": "Greene BM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Greene BM, Taylor HR, Cupp EW, et al.. Comparison of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in the treatment of onchocerciasis. N Engl J Med. 1985, 313:133-8. 10.1056/NEJM198507183130301",
"volume": "313",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/371707a0",
"article-title": "Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans",
"author": "Cully DF",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Cully DF, Vassilatis DK, Liu KK, Paress PS, Van der Ploeg LH, Schaeffer JM, Arena JP. Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1994, 371:707-11. 10.1038/371707a0",
"volume": "371",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/jn.01234.2006",
"article-title": "Dorsal unpaired median neurons of locusta migratoria express ivermectin- and fipronil-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channels",
"author": "Janssen D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Neurophysiol",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Janssen D, Derst C, Buckinx R, Van den Eynden J, Rigo JM, Van Kerkhove E. Dorsal unpaired median neurons of locusta migratoria express ivermectin- and fipronil-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channels. J Neurophysiol. 2007, 97:2642-50. 10.1152/jn.01234.2006",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/jn.00466.2009",
"article-title": "Cys-loop ligand-gated chloride channels in dorsal unpaired median neurons of Locusta migratoria",
"author": "Janssen D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Neurophysiol",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Janssen D, Derst C, Rigo JM, Van Kerkhove E. Cys-loop ligand-gated chloride channels in dorsal unpaired median neurons of Locusta migratoria. J Neurophysiol. 2010, 103:2587-98. 10.1152/jn.00466.2009",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/mol.108.053363",
"article-title": "An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus",
"author": "McCavera S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mol Pharmacol",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "McCavera S, Rogers AT, Yates DM, Woods DJ, Wolstenholme AJ. An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Mol Pharmacol. 2009, 75:1347-55. 10.1124/mol.108.053363",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1011983107",
"article-title": "Ivermectin disrupts the function of the excretory-secretory apparatus in microfilariae of Brugia malayi",
"author": "Moreno Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Moreno Y, Nabhan JF, Solomon J, Mackenzie CD, Geary TG. Ivermectin disrupts the function of the excretory-secretory apparatus in microfilariae of Brugia malayi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010, 107:20120-5. 10.1073/pnas.1011983107",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2011.10.010",
"article-title": "Ivermectin induces P-glycoprotein expression and function through mRNA stabilization in murine hepatocyte cell line",
"author": "Ménez C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Pharmacol",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Ménez C, Mselli-Lakhal L, Foucaud-Vignault M, Balaguer P, Alvinerie M, Lespine A. Ivermectin induces P-glycoprotein expression and function through mRNA stabilization in murine hepatocyte cell line. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012, 83:269-78. 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.10.010",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0092-8674(94)90212-7",
"article-title": "Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs",
"author": "Schinkel AH",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Schinkel AH, Smit JJ, van Tellingen O, et al.. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell. 1994, 77:491-502. 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90212-7",
"volume": "77",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.05.003",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: from theory to clinical application",
"author": "Ashour DS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Ashour DS. Ivermectin: from theory to clinical application. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019, 54:134-42. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.05.003",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD012994",
"article-title": "Ivermectin and permethrin for treating scabies",
"author": "Rosumeck S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Rosumeck S, Nast A, Dressler C. Ivermectin and permethrin for treating scabies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018, 4:CD012994. 10.1002/14651858.CD012994",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13555-018-0249-y",
"article-title": "Topical ivermectin in the treatment of papulopustular rosacea: a systematic review of evidence and clinical guideline recommendations",
"author": "Ebbelaar CC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Dermatol Ther (Heidelb)",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Ebbelaar CC, Venema AW, Van Dijk MR. Topical ivermectin in the treatment of papulopustular rosacea: a systematic review of evidence and clinical guideline recommendations. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018, 8:379-87. 10.1007/s13555-018-0249-y",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138920112800399248",
"article-title": "Ivermectin in human medicine, an overview of the current status of its clinical applications",
"author": "González P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharm Biotechnol",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "González P, González FA, Ueno K. Ivermectin in human medicine, an overview of the current status of its clinical applications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012, 13:1103-9. 10.2174/138920112800399248",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13071-020-04512-5",
"article-title": "High concentrations of membrane-fed ivermectin are required for substantial lethal and sublethal impacts on Aedes aegypti",
"author": "Hadlett M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Parasit Vectors",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Hadlett M, Nagi SC, Sarkar M, Paine MJ, Weetman D. High concentrations of membrane-fed ivermectin are required for substantial lethal and sublethal impacts on Aedes aegypti. Parasit Vectors. 2021, 14:9. 10.1186/s13071-020-04512-5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-023-07098-2",
"article-title": "BOHEMIA: Broad One Health Endectocide-based Malaria Intervention in Africa-a phase III cluster-randomized, open-label, clinical trial to study the safety and efficacy of ivermectin mass drug administration to reduce malaria transmission in two African settings",
"author": "Chaccour C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Chaccour C, Casellas A, Hammann F, et al.. BOHEMIA: Broad One Health Endectocide-based Malaria Intervention in Africa-a phase III cluster-randomized, open-label, clinical trial to study the safety and efficacy of ivermectin mass drug administration to reduce malaria transmission in two African settings. Trials. 2023, 24:128. 10.1186/s13063-023-07098-2",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ps.7217",
"article-title": "Potential of ivermectin as an active ingredient of the attractive toxic sugar baits against the Indian malaria vectors Anopheles culicifacies and Anopheles stephensi",
"author": "Kumar G",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pest Manag Sci",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Kumar G, Pasi S, Yadav CP, Kaur J, Sharma A. Potential of ivermectin as an active ingredient of the attractive toxic sugar baits against the Indian malaria vectors Anopheles culicifacies and Anopheles stephensi. Pest Manag Sci. 2023, 79:474-80. 10.1002/ps.7217",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.01730-22",
"article-title": "Activity of ivermectin and its metabolites against asexual blood stage Plasmodium falciparum and its interactions with antimalarial drugs",
"author": "Yipsirimetee A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Yipsirimetee A, Tipthara P, Hanboonkunupakarn B, et al.. Activity of ivermectin and its metabolites against asexual blood stage Plasmodium falciparum and its interactions with antimalarial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023, 67:e0173022. 10.1128/aac.01730-22",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12936-023-04624-0",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of ivermectin metabolites and their activity against Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes",
"author": "Kern C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Malar J",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Kern C, Müller P, Chaccour C, Liechti ME, Hammann F, Duthaler U. Pharmacokinetics of ivermectin metabolites and their activity against Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes. Malar J. 2023, 22:194. 10.1186/s12936-023-04624-0",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1169916",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of antibiotic agents in the treatment of rosacea: a systemic network meta-analysis",
"author": "Xiao W",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Xiao W, Chen M, Wang B, et al.. Efficacy and safety of antibiotic agents in the treatment of rosacea: a systemic network meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2023, 14:1169916. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1169916",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105207",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, a potential anticancer drug derived from an antiparasitic drug",
"author": "Tang M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Tang M, Hu X, Wang Y, et al.. Ivermectin, a potential anticancer drug derived from an antiparasitic drug. Pharmacol Res. 2021, 163:105207. 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105207",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/09603271221143693",
"article-title": "Repurposing Ivermectin to augment chemotherapy's efficacy in osteosarcoma",
"author": "Hu B",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Hum Exp Toxicol",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Hu B, Tan H, Yu L, Liao Q, Guo W. Repurposing Ivermectin to augment chemotherapy's efficacy in osteosarcoma. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022, 41:9603271221143693. 10.1177/09603271221143693",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diseases11010049",
"article-title": "Ivermectin augments the anti-cancer activity of pitavastatin in ovarian cancer cells",
"author": "Jawad MJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diseases",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Jawad MJ, Richardson A. Ivermectin augments the anti-cancer activity of pitavastatin in ovarian cancer cells. Diseases. 2023, 11:10.3390/diseases11010049",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00432-023-04829-5",
"article-title": "Eprinomectin: a derivative of ivermectin suppresses growth and metastatic phenotypes of prostate cancer cells by targeting the β-catenin signaling pathway",
"author": "Samy A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cancer Res Clin Oncol",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Samy A, Hussein MA, Munirathinam G. Eprinomectin: a derivative of ivermectin suppresses growth and metastatic phenotypes of prostate cancer cells by targeting the β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023, 149:9085-104. 10.1007/s00432-023-04829-5",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1519-6984.258325",
"article-title": "Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols",
"author": "Marques LL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Braz J Biol",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Marques LL, Beneti SC, Pinzon C, Cardoso FA. Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols. Braz J Biol. 2022, 84:e258325. 10.1590/1519-6984.258325",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0296",
"article-title": "Scabies: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment",
"author": "Sunderkötter C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Dtsch Arztebl Int",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Sunderkötter C, Wohlrab J, Hamm H. Scabies: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021, 118:695-704. 10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0296",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life12101598",
"article-title": "Increased scabies incidence at the beginning of the 21st century: what do reports from Europe and the world show?",
"author": "Aždajić MD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Life (Basel)",
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "Aždajić MD, Bešlić I, Gašić A, Ferara N, Pedić L, Lugović-Mihić L. Increased scabies incidence at the beginning of the 21st century: what do reports from Europe and the world show?. Life (Basel). 2022, 12:10.3390/life12101598",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1754136",
"article-title": "Trends in prevalence and incidence of scabies from 1990 to 2017: findings from the global Burden of disease study 2017",
"author": "Zhang W",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Zhang W, Zhang Y, Luo L, et al.. Trends in prevalence and incidence of scabies from 1990 to 2017: findings from the global Burden of disease study 2017. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020, 9:813-6. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1754136",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-031-26070-4_2",
"article-title": "Biology of Sarcoptes scabiei and Its Relevance to Human Scabies: Clinical Symptoms, Treatment, and Management.",
"author": "Yotsu RR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Yotsu RR, Yoshizumi J, Izri A. Biology of Sarcoptes scabiei and Its Relevance to Human Scabies: Clinical Symptoms, Treatment, and Management.. Scabies. Fischer K, Chosidow O (ed): Springer, Cham; 2023. 19-34. 10.1007/978-3-031-26070-4_2",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cger.2023.09.010",
"article-title": "Evaluation and management of pruritus and scabies in the elderly population",
"author": "Meltan S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Geriatr Med",
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "Meltan S, Panuganti B, Tarbox M. Evaluation and management of pruritus and scabies in the elderly population. Clin Geriatr Med. 2024, 40:91-116. 10.1016/j.cger.2023.09.010",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09546634.2020.1774489",
"article-title": "Loss of efficacy of topical 5% permethrin for treating scabies: an Austrian single-center study",
"author": "Meyersburg D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Dermatolog Treat",
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Meyersburg D, Kaiser A, Bauer JW. Loss of efficacy of topical 5% permethrin for treating scabies: an Austrian single-center study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022, 33:774-7. 10.1080/09546634.2020.1774489",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.18573",
"article-title": "Comparison of topical benzyl benzoate vs. oral ivermectin in treating scabies: a randomized study",
"author": "Meyersburg D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Meyersburg D, Welponer T, Kaiser A, Selhofer S, Tatarski R, Handisurya A, Bauer JW. Comparison of topical benzyl benzoate vs. oral ivermectin in treating scabies: a randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023, 37:160-5. 10.1111/jdv.18573",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1525-1470.2001.018001063.x",
"article-title": "Topical ivermectin: a new successful treatment for scabies",
"author": "Victoria J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Dermatol",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Victoria J, Trujillo R. Topical ivermectin: a new successful treatment for scabies. Pediatr Dermatol. 2001, 18:63-5. 10.1046/j.1525-1470.2001.018001063.x",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaad.2017.09.006",
"article-title": "Ivermectin versus permethrin in the treatment of scabies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Dhana A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Am Acad Dermatol",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Dhana A, Yen H, Okhovat JP, Cho E, Keum N, Khumalo NP. Ivermectin versus permethrin in the treatment of scabies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018, 78:194-8. 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.09.006",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Treatment of scabies: comparison of ivermectin vs. lindane lotion 1%",
"author": "Mohebbipour A",
"journal-title": "Acta Dermatovenerol Croat",
"key": "ref40",
"unstructured": "Mohebbipour A, Saleh P, Goldust M, Amirnia M, Zadeh YJ, Mohamadi RM, Rezaee E. Treatment of scabies: comparison of ivermectin vs. lindane lotion 1%. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2012, 20:251-5.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carres.2023.108887",
"article-title": "Carbohydrate derivatives fight against malaria parasite as anti-plasmodial agents",
"author": "Singh K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Carbohydr Res",
"key": "ref41",
"unstructured": "Singh K, Tripathi RP. Carbohydrate derivatives fight against malaria parasite as anti-plasmodial agents. Carbohydr Res. 2023, 531:108887. 10.1016/j.carres.2023.108887",
"volume": "531",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1242/jeb.118570",
"article-title": "Characterization of the target of ivermectin, the glutamate-gated chloride channel, from Anopheles gambiae",
"author": "Meyers JI",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Exp Biol",
"key": "ref42",
"unstructured": "Meyers JI, Gray M, Kuklinski W, et al.. Characterization of the target of ivermectin, the glutamate-gated chloride channel, from Anopheles gambiae. J Exp Biol. 2015, 218:1478-86. 10.1242/jeb.118570",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aag2374",
"article-title": "Oral, ultra-long-lasting drug delivery: application toward malaria elimination goals",
"author": "Bellinger AM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "ref43",
"unstructured": "Bellinger AM, Jafari M, Grant TM, et al.. Oral, ultra-long-lasting drug delivery: application toward malaria elimination goals. Sci Transl Med. 2016, 8:365ra157. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aag2374",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32321-3",
"article-title": "Efficacy and risk of harms of repeat ivermectin mass drug administrations for control of malaria (RIMDAMAL): a cluster-randomised trial",
"author": "Foy BD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref44",
"unstructured": "Foy BD, Alout H, Seaman JA, et al.. Efficacy and risk of harms of repeat ivermectin mass drug administrations for control of malaria (RIMDAMAL): a cluster-randomised trial. Lancet. 2019, 393:1517-26. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32321-3",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31663-0",
"article-title": "Analysis of the RIMDAMAL trial",
"author": "Bradley J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref45",
"unstructured": "Bradley J, Moulton LH, Hayes R. Analysis of the RIMDAMAL trial. Lancet. 2019, 394:1005-6. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31663-0",
"volume": "394",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32139-7",
"article-title": "Analysis of the RIMDAMAL trial - Authors' reply",
"author": "Foy BD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref46",
"unstructured": "Foy BD, Rao S, Parikh S, Slater HC, Dabiré RK. Analysis of the RIMDAMAL trial - Authors' reply. Lancet. 2019, 394:1006-7. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32139-7",
"volume": "394",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/41197",
"article-title": "Repeat ivermectin mass drug administrations for malaria control II: protocol for a double-blind, cluster-randomized, placebo-controlled trial for the integrated control of malaria",
"author": "Foy BD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JMIR Res Protoc",
"key": "ref47",
"unstructured": "Foy BD, Some A, Magalhaes T, et al.. Repeat ivermectin mass drug administrations for malaria control II: protocol for a double-blind, cluster-randomized, placebo-controlled trial for the integrated control of malaria. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023, 12:e41197. 10.2196/41197",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Over 25 years of clinical experience with ivermectin: an overview of safety for an increasing number of indications",
"author": "Kircik LH",
"journal-title": "J Drugs Dermatol",
"key": "ref48",
"unstructured": "Kircik LH, Del Rosso JQ, Layton AM, Schauber J. Over 25 years of clinical experience with ivermectin: an overview of safety for an increasing number of indications. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15:325-32.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice",
"author": "Zhang X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "ref49",
"unstructured": "Zhang X, Song Y, Ci X, et al.. Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice. Inflamm Res. 2008, 57:524-9. 10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6",
"article-title": "The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2-an extensive review",
"author": "Zaidi AK",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot (Tokyo)",
"key": "ref50",
"unstructured": "Zaidi AK, Dehgani-Mobaraki P. The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2-an extensive review. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2022, 75:60-71. 10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1203475419867611",
"article-title": "The role of IL-17 in papulopustular rosacea and future directions",
"author": "Amir Ali A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cutan Med Surg",
"key": "ref51",
"unstructured": "Amir Ali A, Vender R, Vender R. The role of IL-17 in papulopustular rosacea and future directions. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019, 23:635-41. 10.1177/1203475419867611",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-00633-7",
"article-title": "An aberrant STAT pathway is central to COVID-19",
"author": "Matsuyama T",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "ref52",
"unstructured": "Matsuyama T, Kubli SP, Yoshinaga SK, Pfeffer K, Mak TW. An aberrant STAT pathway is central to COVID-19. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27:3209-25. 10.1038/s41418-020-00633-7",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijd.16920",
"article-title": "Long-term maintenance treatment of rosacea: experts' opinion",
"author": "Almeida LM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Dermatol",
"key": "ref53",
"unstructured": "Almeida LM, Ianhez M, Dal'Forno T, et al.. Long-term maintenance treatment of rosacea: experts' opinion. Int J Dermatol. 2024, 63:94-101. 10.1111/ijd.16920",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ddg.14849",
"article-title": "S2k guideline: Rosacea",
"author": "Clanner-Engelshofen BM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Dtsch Dermatol Ges",
"key": "ref54",
"unstructured": "Clanner-Engelshofen BM, Bernhard D, Dargatz S, et al.. S2k guideline: Rosacea. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2022, 20:1147-65. 10.1111/ddg.14849",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09546634.2020.1737636",
"article-title": "Pulsed dye laser alone versus its combination with topical ivermectin 1% in treatment of Rosacea: a randomized comparative study",
"author": "Osman M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Dermatolog Treat",
"key": "ref55",
"unstructured": "Osman M, Shokeir HA, Hassan AM, Khalifa MA. Pulsed dye laser alone versus its combination with topical ivermectin 1% in treatment of Rosacea: a randomized comparative study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022, 33:184-90. 10.1080/09546634.2020.1737636",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14656566.2018.1447562",
"article-title": "Ivermectin 1% (CD5024) for the treatment of rosacea",
"author": "Sahni DR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Pharmacother",
"key": "ref56",
"unstructured": "Sahni DR, Feldman SR, Taylor SL. Ivermectin 1% (CD5024) for the treatment of rosacea. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018, 19:511-6. 10.1080/14656566.2018.1447562",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BST20200568",
"article-title": "Antivirals that target the host IMPα/β1-virus interface",
"author": "Martin AJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Soc Trans",
"key": "ref57",
"unstructured": "Martin AJ, Jans DA. Antivirals that target the host IMPα/β1-virus interface. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021, 49:281-95. 10.1042/BST20200568",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042",
"article-title": "The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?",
"author": "Jans DA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "ref58",
"unstructured": "Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021, 538:163-72. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042",
"volume": "538",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00710-20",
"article-title": "Inhibition of human adenovirus replication by the importin α/β1 nuclear import inhibitor ivermectin",
"author": "King CR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "ref59",
"unstructured": "King CR, Tessier TM, Dodge MJ, Weinberg JB, Mymryk JS. Inhibition of human adenovirus replication by the importin α/β1 nuclear import inhibitor ivermectin. J Virol. 2020, 94:10.1128/JVI.00710-20",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00203-023-03806-3",
"article-title": "Ivermectin antiviral activity against Varicellovirus bovinealpha 1: assessment of intracellular drug accumulation in virus-infected cells",
"author": "Pérez S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Microbiol",
"key": "ref60",
"unstructured": "Pérez S, Miró MV, Verna A, Altamiranda EG, Barcos O, Lanusse C, Lifschitz A. Ivermectin antiviral activity against Varicellovirus bovinealpha 1: assessment of intracellular drug accumulation in virus-infected cells. Arch Microbiol. 2024, 206:78. 10.1007/s00203-023-03806-3",
"volume": "206",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2023.109958",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits replication of the malignant catarrhal fever virus alcelaphine herpesvirus 1",
"author": "Patho B",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref61",
"unstructured": "Patho B, Grant DM, Percival A, Russell GC. Ivermectin inhibits replication of the malignant catarrhal fever virus alcelaphine herpesvirus 1. Virology. 2024, 590:109958. 10.1016/j.virol.2023.109958",
"volume": "590",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8030409",
"article-title": "Ivermectin inhibits bovine herpesvirus 1 DNA polymerase nuclear import and interferes with viral replication",
"author": "Raza S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "ref62",
"unstructured": "Raza S, Shahin F, Zhai W, et al.. Ivermectin inhibits bovine herpesvirus 1 DNA polymerase nuclear import and interferes with viral replication. Microorganisms. 2020, 8:10.3390/microorganisms8030409",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab247",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Deng J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "QJM",
"key": "ref63",
"unstructured": "Deng J, Zhou F, Ali S, Heybati K, Hou W, Huang E, Wong CY. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM. 2021, 114:721-32. 10.1093/qjmed/hcab247",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8",
"article-title": "Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype",
"author": "Marcolino MS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "ref64",
"unstructured": "Marcolino MS, Meira KC, Guimarães NS, et al.. Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype. BMC Infect Dis. 2022, 22:639. 10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcph.2178",
"article-title": "Ivermectin’s role in the prevention of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Hu GY",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref65",
"unstructured": "Hu GY, Liang CA, Lin PC, Lin CY. Ivermectin’s role in the prevention of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2023, 63:288-97. 10.1002/jcph.2178",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S308973",
"article-title": "Progress in redirecting antiparasitic drugs for cancer treatment",
"author": "Huang H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Drug Des Devel Ther",
"key": "ref66",
"unstructured": "Huang H, He Q, Guo B, Xu X, Wu Y, Li X. Progress in redirecting antiparasitic drugs for cancer treatment. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021, 15:2747-67. 10.2147/DDDT.S308973",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2887",
"article-title": "Ivermectin induces cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK1/AKT axis in breast cancer",
"author": "Dou Q",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "ref67",
"unstructured": "Dou Q, Chen HN, Wang K, et al.. Ivermectin induces cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK1/AKT axis in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76:4457-69. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2887",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00280-023-04589-6",
"article-title": "Ivermectin induces nonprotective autophagy by downregulating PAK1 and apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells",
"author": "Li MY",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cancer Chemother Pharmacol",
"key": "ref68",
"unstructured": "Li MY, Zhang J, Lu X, et al.. Ivermectin induces nonprotective autophagy by downregulating PAK1 and apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2024, 93:41-54. 10.1007/s00280-023-04589-6",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.064",
"article-title": "Anthelmintic drug ivermectin inhibits angiogenesis, growth and survival of glioblastoma through inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress",
"author": "Liu Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "ref69",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Fang S, Sun Q, Liu B. Anthelmintic drug ivermectin inhibits angiogenesis, growth and survival of glioblastoma through inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016, 480:415-21. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.064",
"volume": "480",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/tox.23440",
"article-title": "Ivermectin accelerates autophagic death of glioma cells by inhibiting glycolysis through blocking GLUT4 mediated JAK/STAT signaling pathway activation",
"author": "Feng Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Environ Toxicol",
"key": "ref70",
"unstructured": "Feng Y, Wang J, Cai B, Bai X, Zhu Y. Ivermectin accelerates autophagic death of glioma cells by inhibiting glycolysis through blocking GLUT4 mediated JAK/STAT signaling pathway activation. Environ Toxicol. 2022, 37:754-64. 10.1002/tox.23440",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin inactivates the kinase PAK1 and blocks the PAK1-dependent growth of human ovarian cancer and NF2 tumor cell lines",
"author": "Hashimoto H",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov Ther",
"key": "ref71",
"unstructured": "Hashimoto H, Messerli SM, Sudo T, Maruta H. Ivermectin inactivates the kinase PAK1 and blocks the PAK1-dependent growth of human ovarian cancer and NF2 tumor cell lines. Drug Discov Ther. 2009, 3:243-6.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0980-T",
"article-title": "Selective inhibition of SIN3 corepressor with avermectins as a novel therapeutic strategy in triple-negative breast cancer",
"author": "Kwon YJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mol Cancer Ther",
"key": "ref72",
"unstructured": "Kwon YJ, Petrie K, Leibovitch BA, et al.. Selective inhibition of SIN3 corepressor with avermectins as a novel therapeutic strategy in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015, 14:1824-36. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0980-T",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41582-019-0220-2",
"article-title": "Genetic and molecular epidemiology of adult diffuse glioma",
"author": "Molinaro AM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Neurol",
"key": "ref73",
"unstructured": "Molinaro AM, Taylor JW, Wiencke JK, Wrensch MR. Genetic and molecular epidemiology of adult diffuse glioma. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019, 15:405-17. 10.1038/s41582-019-0220-2",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20192489",
"article-title": "Ivermectin induces autophagy-mediated cell death through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioma cells",
"author": "Liu J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biosci Rep",
"key": "ref74",
"unstructured": "Liu J, Liang H, Chen C, et al.. Ivermectin induces autophagy-mediated cell death through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioma cells. Biosci Rep. 2019, 39:10.1042/BSR20192489",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 74,
"references-count": 74,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/223832-ivermectin-a-multifaceted-drug-with-a-potential-beyond-anti-parasitic-therapy"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin: A Multifaceted Drug With a Potential Beyond Anti-parasitic Therapy",
"type": "journal-article"
}