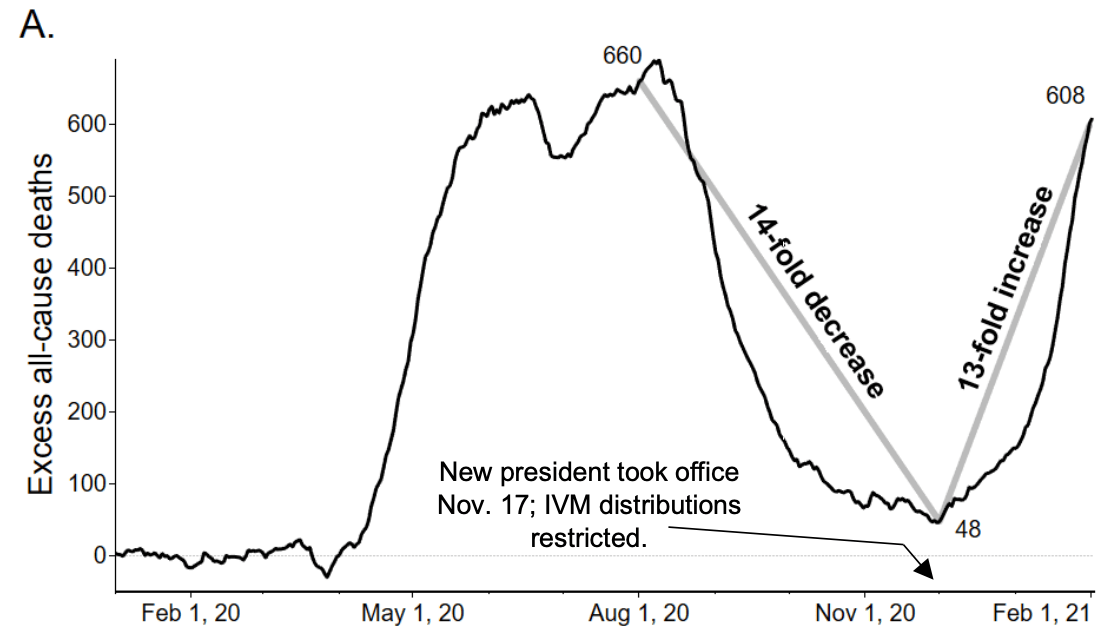
Ivermectin for COVID-19 in Peru: 14-fold reduction in nationwide excess deaths, p < 0.002 for effect by state, then 13-fold increase after ivermectin use restricted
Juan J Chamie-Quintero, DDS, MRCDC Jennifer A Hibberd, PhD David E Scheim
Objective. We aimed to identify mortality trends associated with COVID-19 deaths in Peru during April through November 2020, when mass treatments with ivermectin (IVM), a drug of Nobel Prize-honored distinction, were autonomously deployed at different times and to different extents in Peru's 25 states under a national policy that authorized these treatments. Design. Ecological study of publicly available data. Excess deaths were analyzed state by state. To identify potential confounding factors, Google mobility data, population densities, SARS-CoV-2 genetic variations, seropositivity rates and other auxiliary data were also examined. Primary outcome. Reductions in excess deaths, state by state, as compared with extent and time period of IVM treatments.
Participants. The study population was restricted to ages ≥ 60 to eliminate confounding effects of changing age distributions of COVID-19 incidence. Results. The 25 states of Peru were grouped by extent of IVM distributions: maximal (mass IVM distributions through operation MOT, a broadside effort led by the army); medium (locally managed IVM distributions); and minimal (restrictive policies in one state, Lima). The mean reduction in excess deaths 30 days after peak deaths was 74% for the maximal IVM distribution group, 53% for the medium group and 25% for Lima. Reduction of excess deaths correlated with extent of IVM distribution by state with p<0.002 using the Kendall τb test. Nationwide, excess deaths decreased 14-fold over four months through December 1, 2020, after which deaths then increased 13-fold when IVM use was restricted under a new president.
Conclusion. Mass treatments with IVM, a drug safely used in 3.7 billion doses worldwide since 1987, most likely caused these reductions in deaths during the time periods in which it was deployed. The indicated biological mechanism of IVM, competitive binding with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, is likely non-epitope specific, possibly yielding full efficacy against emerging viral mutant strains.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF THIS STUDY • The potential impact of mass IVM treatments in Peru, conducted autonomously in its 25 states, was analyzed using publicly accessible mortality data from national health sources. • The extent of IVM distributions in Peru's 25 states could be categorized in three tiers: intensive (through operation MOT, an army-led effort), moderate (locally managed), and restricted. • The correlation of extent of IVM treatments with reductions in excess deaths 30 days after peak deaths was found highly significant using the Kendall τb test. For nine MOT states that had a unique MOT start date, sharp reductions in deaths closely followed IVM treatments. • Confounding factors were ruled out by restricting analyses of deaths to ages ≥ 60, by comparing mortality trends with Google community mobility indices, and by examining other auxiliary data such as seropositivity rates. • This analysis is limited by its ecological study design,..
Contributors JJC located and extracted the data for this analysis from Peruvian national databases and other sources, developed the analytical approach and performed the main analyses. DES performed additional analyses, including that for the Kendall tau calculation. JAH coordinated the refinement of this manuscript from an earlier version and contributed to the interpretation of the results. All authors participated in drafting this manuscript and edited and approved the final version. Funding: Juan J. Chamie was funded by the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, a nonprofit organization. Competing Interests: None declared. Patient consent for publication: Not required; no patients were involved in this study. Ethics committee approval: Given the study design and the use of publicly available data, no ethical approval was considered necessary.
Abbreviations
IVM: ivermectin MOT: Mega-Operación Tayta
References
Arévalo, Pagotto, Pórfido, Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model, Scientific Reports
Badr, Du, Marshall, Association between mobility patterns and COVID-19 transmission in the USA: a mathematical modelling study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Bermúdez, Si un médico evalúa a una persona y le receta ivermectina, puede utilizarla, RPP
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines, American Journal of Therapeutics,
doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402Cabezas, Fiestas, García-Mendoza, Dengue en el Perú: a un cuarto de siglo de su reemergencia, Revista Peruana de Medicina Experimental y Salud Publica
Campbell, History of avermectin and ivermectin, with notes on the history of other macrocyclic lactone antiparasitic agents, Curr Pharm Biotechnol
Cenares, Ministerio de Salud de Peru
Cervantes, Peru confirms case of British variant of coronavirus, Reuters
Chamie, Hibberd, Scheim, Sharp reductions in COVID-19 case fatalities and excess deaths in Peru in close time conjunction, state-by
Chamie, Hibberd, Scheim, Sharp reductions in COVID-19 case fatalities and excess deaths in Peru in close time conjunction, state-by-state, with ivermectin treatments
Crump, Ivermectin: enigmatic multifaceted 'wonder' drug continues to surprise and exceed expectations, J Antibiot
El, Un viaje al mercado negro del COVID-19: Facebook
Epdsesa, Covid-19: a más de 22,000 personas atendió Operación Tayta-Yo Me Apunto en Cajamarca, Andina, Agencia Peruana de Noticias
Gorriti, Del pañuelazo a la ivermectina, IDL Reporteros
Gorriti, Rompeolas, None, IDL Reporteros
Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J Clin Pharmacol
Hariyanto, Halim, Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid-19 pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trial studies, Reviews in Medical Virology,
doi:10.1002/rmv.2265:e2265Hill, Garratt, Levi, Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infectious Diseases
Juscamayta-López, Tarazona, Valdivia, Phylogenomics reveals multiple introductions and early spread of SARS-CoV-2 into Peru, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.09.14.296814Karale, Bansal, Makadia, A Meta-analysis of Mortality, Need for ICU admission, Use of Mechanical Ventilation and Adverse Effects with Ivermectin Use in COVID-19 Patients, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.04.30.21256415Kory, Meduri, Varon, Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics
Kow, Merchant, Mustafa, The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Pharmacological Reports,
doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00245-zKrolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine
Llantoy, Mediante empadronamiento ejecutado por 60 brigadistas de la mph y "amachay
López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults With Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071Martín De Porres, incautan 20,000 frascos de ivermectina y detienen a 12 personas
Merchant, Work, in a nursing home. Here's why my colleagues are skipping the vaccine, Washington Post
Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Nicolelis, Raimundo, Peixoto, How super-spreader cities, highways, hospital bed availability, and dengue fever influenced the COVID-19 epidemic in Brazil,
doi:10.1101/2020.09.19.20197749Oh, Lee, Long, How well does societal mobility restriction help control the COVID-19 pandemic? Evidence from real-time evaluation, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.29.20222414Piura, Detienen a dos personas con más de 200 dosis de ivermectina de contrabando; coronavirus; COVID-19; nnpp
Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, Raygoza-Cortez, Garcia-Leal, A Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis SSRN
Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (version 1), medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.05.21.21257595v1Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.05.21.21257595Said, Readiness to Get COVID-19 Vaccine Steadies at 65%, Gallup
Scheim, From cold to killer: How SARS-CoV-2 evolved without hemagglutinin esterase to agglutinate, then clot blood cells in pulmonary and systemic microvasculature SSRN
Scheim, Hibberd, Chamie, Protocol violations in López-Medina et al.: 38 switched ivermectin (IVM) and placebo doses, failure of blinding,
doi:10.31219/osf.io/u7ewzStokes, Turner, Anselmi, The relative effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on early Covid-19 mortality: natural experiment in 130 countries, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.05.20206888Unwin, Mishra, Bradley, State-level tracking of COVID-19 in the United States, Nature Communications
Welsh, Inequality and corruption: Why Peru is losing its COVID-19 battle, Devex
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Global Trends in Clinical Studies of Ivermectin in COVID-19, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics
Yumbato, Coronavirus en Perú: conoce cómo funciona la Operación Tayta, RPP
Zaidi, Dehgani-Mobaraki, The mechanisms of action of Ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: An evidence-based clinical review article, The Journal of Antibiotics
Zein, Sulistiyana, Raffaelo, Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome,
doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186:102186