The effect of ivermectin on non-severe and severe COVID-19 disease and gender-based difference of its effectiveness
Syed Muhammad Zubair, Muhammad Waleed Chaudhry, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi, Talha Shahzad, Aqusa Zahid, Ibrahim Ali Khan, Javaid Ahmed Khan, Muhammad Irfan
Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease, doi:10.4081/monaldi.2022.2062
Role of ivermectin in hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. To be presented as an 'e-poster' at virtual European Respiratory Society Congress 2021 on 07-09-2021.
References
Abbaspour, Hurrell, Kelishadi, Review on iron and its importance for human health, J Res Med Sci
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis
Buonfrate, Salas-Coronas, Muñoz, Multiple-dose versus single-dose ivermectin for Strongyloides stercoralis infection (Strong Treat 1 to 4): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled superiority trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Caly, Druce, Catton, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Camprubí, Almuedo-Riera, Martí-Soler, Lack of efficacy of standard doses of ivermectin in severe COVID-19 patients, PLoS One
Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, doubleblind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine
Chachar, Kahn, Asif, Effectiveness of ivermectin in SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 patients, Int J Sci
Drewe, Gutmann, Fricker, HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir: a more potent inhibitor of Pglycoprotein than the cyclosporine analog SDZ PSC 833, Biochem Pharmacol
Elgazzar, Abo Youssef, Hany, Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 pandemic
Galasso, Pons, Profeta, Gender differences in COVID-19 attitudes and behavior: Panel evidence from eight countries, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Gorial, Mashhadani, Sayaly, Effectiveness of ivermectin as add-on therapy in COVID-19 management (Pilot Trial), medRxiv
Haitao, Vermunt, Abeykoon, COVID-19 and sex differences: Mechanisms and biomarkers, Mayo Clin Proc
Hampton, Insight on sex-based immunity differences, with COVID-19 implications, JAMA
Hermine, Tharaux, Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Jin, Bai, He, Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: Focus on severity and mortality, Front Public Health
Kalil, Patterson, Mehta, Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Lepist, Phan, Roy, Cobicistat boosts the intestinal absorption of transport substrates, including HIV protease inhibitors and GS-7340, in vitro, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Mangia, Russo, Civitelli, say, and do not say
Okumuş, Demirtürk, Çetinkaya, Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of adding ivermectin to treatment in severe COVID-19 patients, BMC Infect Dis
Oudit, Pfeffer, Plasma angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: novel biomarker heart failure with implications for COVID-19, Eur Heart J
Padhy, Mohanty, Das, Meher, Therapeutic potential of ivermectin as add on treatment in COVID 19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Pharm Pharm Sci
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19 -Interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Priel, Silberberg, Mechanism of ivermectin facilitation of human P2X4 receptor channels, J Gen Physiol
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: the ivermectin in COVID nineteen study, Chest
Ravikirti, Pattadar, Ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19 -A double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial, medRxiv
Shakhsi, Nematollah, Peyman, Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multi-center clinical trial
Smit, Ochomo, Aljayyoussi, Human direct skin feeding versus membrane feeding to assess the mosquitocidal efficacy of high-dose ivermectin (IVERMAL Trial), Clin Infect Dis
Takahashi, Iwasaki, Sex differences in immune responses, Science
Tufan, Güler, Matucci-Cerinic, COVID-19, immune system response, hyperinflammation and repurposing antirheumatic drugs, Turk J Med Sci
Vahidy, Pan, Ahnstedt, Sex differences in susceptibility, severity, and outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019: Cross-sectional analysis from a diverse US metropolitan area, PLoS One
Wang, Lv, Ji, Ivermectin treatment inhibits the replication of Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) in vitro and mitigates the impact of viral infection in piglets, Virus Res
Wimmersberger, Coulibaly, Schulz, Efficacy and safety of ivermectin against trichuris trichiura in preschool-aged and school-aged children: A randomized controlled dose-finding trial, Clin Infect Dis
Yang, Atkinson, Wang, The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Res
Zhang, Song, Ci, Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflamm Res
Zhou, She, Wang, Utility of ferritin, procalcitonin, and C-reactive protein in severe patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4081/monaldi.2022.2062",
"ISSN": [
"2532-5264",
"1122-0643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2022.2062",
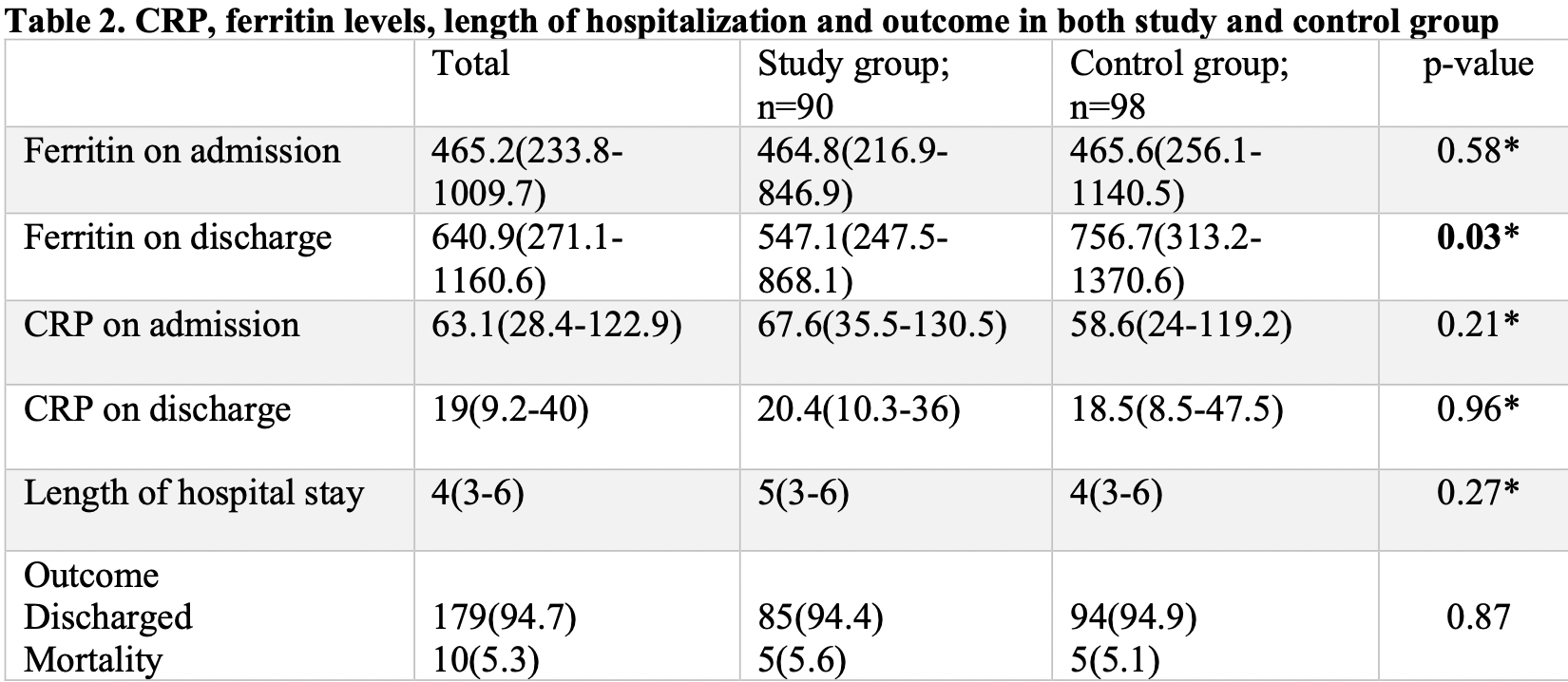
"abstract": "<jats:p>The COVID-19 pandemic has led to mortality and morbidity since December 2019. Many possible treatment options have been advised till date. The role of ivermectin in the treatment of COVID-19 disease remains controversial. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effect of ivermectin in hospitalized patients with non-severe and severe COVID-19 disease. We conducted a retrospective cohort study that compared outcomes in 2 groups of COVID-19 patients hospitalized at the largest tertiary care center of Pakistan. The study group was given ivermectin along with standard treatment of covid-19 disease; the comparison group was not. Data on mortality, inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and ferritin, length of hospital stay and baseline characteristics were collected from Aga Khan University’s database from October 2020 till February 2021. Statistical analysis was done to determine the effectiveness of ivermectin in non-severe and severe COVID-19. Comparison of effectiveness of Ivermectin in both the genders was also conducted. The cohort included 188 patients out of which 90 were treated with ivermectin. Mortality and length of hospitalization was not found to be significantly different in the study group compared with the control group (5.6% vs 5.1%; p=0.87 and 5 days vs 4 days; p=0.27). Analysis of secondary outcomes did not yield statistically significant results, apart from ferritin levels which were significantly less in patients treated with ivermectin (547.1 vs 756.7; p=0.03). The ferritin and CRP levels in affected males were higher than in females on admission and discharge. Our findings suggest ivermectin does not significantly affect all-cause mortality, length of hospitalization and CRP levels in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Large scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are required to further evaluate the role of ivermectin in covid-19 disease.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5917-246X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zubair",
"given": "Syed Muhammad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhry",
"given": "Muhammad Waleed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zubairi",
"given": "Ali Bin Sarwar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahzad",
"given": "Talha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zahid",
"given": "Aqusa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Ibrahim Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Javaid Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muhammad Irfan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-19T08:02:11Z",
"timestamp": 1642579331000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-19T08:02:11Z",
"timestamp": 1642579331000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-20T07:18:22Z",
"timestamp": 1642663102502
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2532-5264"
},
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1122-0643"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642464000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://monaldi-archives.org/index.php/macd/article/download/2062/1397",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://monaldi-archives.org/index.php/macd/article/download/2062/1397",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2549",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.4081",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "PAGEPress Publications",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Monaldi Arch Chest Dis"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine",
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The effect of ivermectin on non-severe and severe COVID-19 disease and gender-based difference of its effectiveness"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}