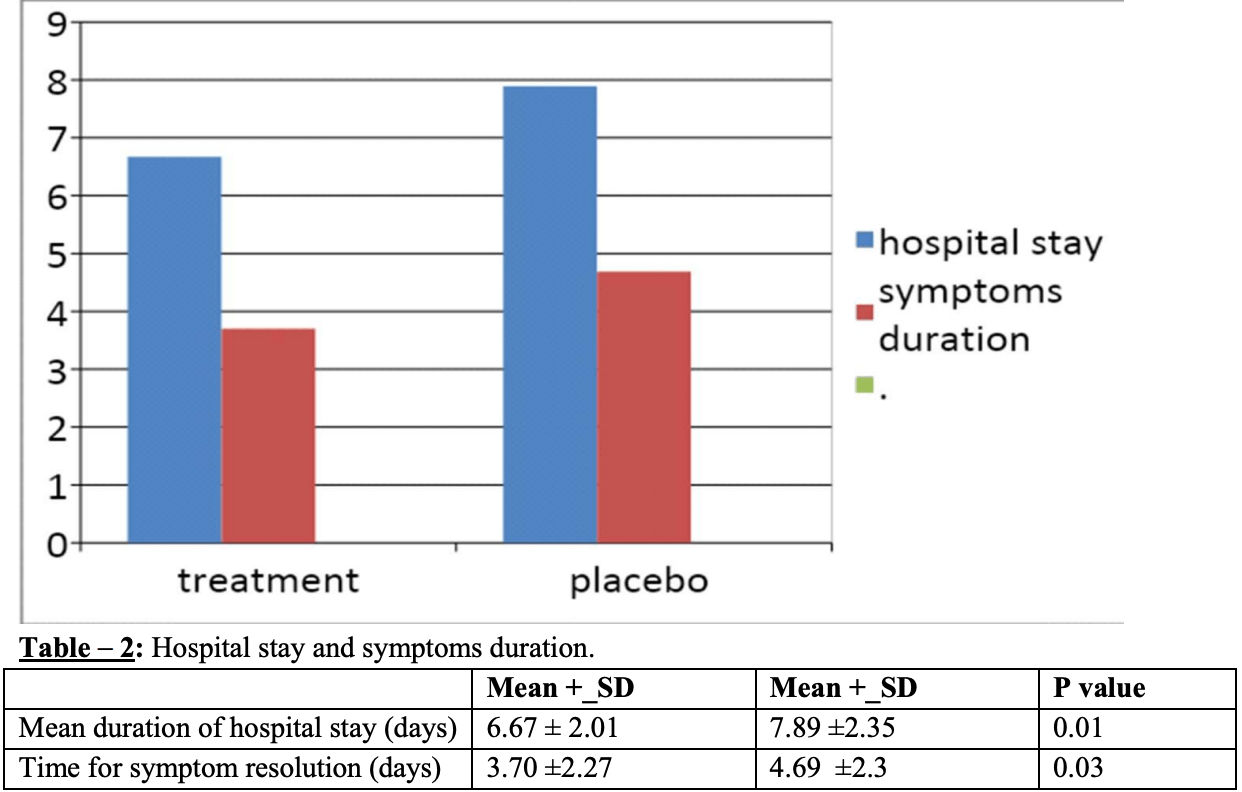
100 patient prospective trial of ivermectin + doxycycline showing reduced time to symptom resolution and shorter hospital stay with treatment.
52 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with
p=0.00000021.
|
recovery time, 21.1% lower, relative time 0.79, p = 0.03, treatment 50, control 50.
|
|
hospitalization time, 15.5% lower, relative time 0.84, p = 0.01, treatment 50, control 50.
|
|
Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates
|
Spoorthi et al., 14 Nov 2020, prospective, India, peer-reviewed, 2 authors, dosage not specified, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with doxycycline) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Utility of Ivermectin and Doxycycline combination for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2
Veerapaneni Spoorthi, Surapaneni Sasank
Background: On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) officially declared coronavirus disease 2019 a global pandemic. Ivermectin and Doxycycline against SARSCoV-2 under in-vitro conditions showed beneficial results. However, large population studies with this combination are not elaborately studied, which was the aim of our study. Materials and Methods: A total of 122 patients admitted in a tertiary care centre, who tested positive for Reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV2 were included in the study and a total sample size of 100 patients was obtained after exclusion. 50 patients of the treatment group were treated with Ivermectin-Doxycycline combination. Results: The results had shown a significant reduction not only in mean duration of hospital (3.70 ± 2.27 days vs 4.69 ± 2.3 days), but also in complete resolution of symptoms stay (6.67 ± 2.01 days vs 4.69 ± 2.3 days). In a small subset of 10 patients RT-PCR for COVID was tested on 10 th day after the symptom onset in both the groups and there was no difference to be found. There was no significant difference in the side effect profile of either groups. Conclusion: Our study supports the benefits of utilization of combination of Doxycycline and Ivermectin in mild to moderate COVID-19 infection in terms of early recovery based on the time for symptom resolution and the mean duration of hospital stay.
References
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Chowdhury, Shahbaz, Karim, Islam, Dan et al., A comparative observational study on Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin therapy on COVID19 patients, J. Clin Med Research
Conforti, Giuffrida, Zalaudek, Meo, Doxycycline, a widely used antibiotic in dermatology with a possible anti-inflammatory action against IL-6 in COVID-19 outbreak
Mccarthy, Laukas, Hotez, Chemotherapy of Helminth infections (Chapter 51
Patel, Desai, Grainger, Mehra, Usefulness of Ivermectin in COVID-19 Illness
Taiub, Chowdhury, Shahbaz, Karim, A Randomized Trial of Ivermectin-Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin therapy on COVID19 patients,
doi:.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-38896Ullah, Abdullah, Roomi, Safety and Efficacy of Hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Journal of clinical medical research
Vora, Arora, Behera, Tripathy, White paper on Ivermectin as a potential therapy for COVID-19, Indian J Tuberc
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirusinfected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA