Early terminated REMAP-CAP results delayed >600 days, showing
no significant differences with very low dose, poor administration, very late
treatment of ICU patients.
Results trend towards benefit for non-critical patients, with
32% lower mortality in unadjusted results, despite higher baseline severity in
the treatment group. Results are currently only available in a CCR24
presentation.
There are many critical issues as below. Authors appear to have
post-hoc removed adjustment for severity to favor the control group.
Preliminary analysis, please report errors or other
issues.
Severity adjustment deleted in second post-hoc SAP.
There are two post-hoc statistical analysis plans, details below. The first one, 5 months after completion, includes baseline disease state in adjustments, as does the protocol
1,2. This SAP has "FINAL" in the name, however a second post-hoc SAP
3, dated over a year after completion, deletes the baseline disease state adjustment, thereby favoring the control group which had lower baseline severity.
Baseline severity favors control.
Randomization resulted in 58% more critical patients at baseline in the treatment group (38 vs. 24). Baseline APACHE II scores were higher in both critical and non-critical groups (11 vs. 9 and 7 vs. 6). 25% of critical treatment patients had APACHE II ≥17 while the corresponding value for the control group is 12. The difference in expected mortality for APACHE II 17 vs. 12 is about 2x. The PaO2/FiO2 medians show severe ARDS for treatment versus moderate ARDS for control.
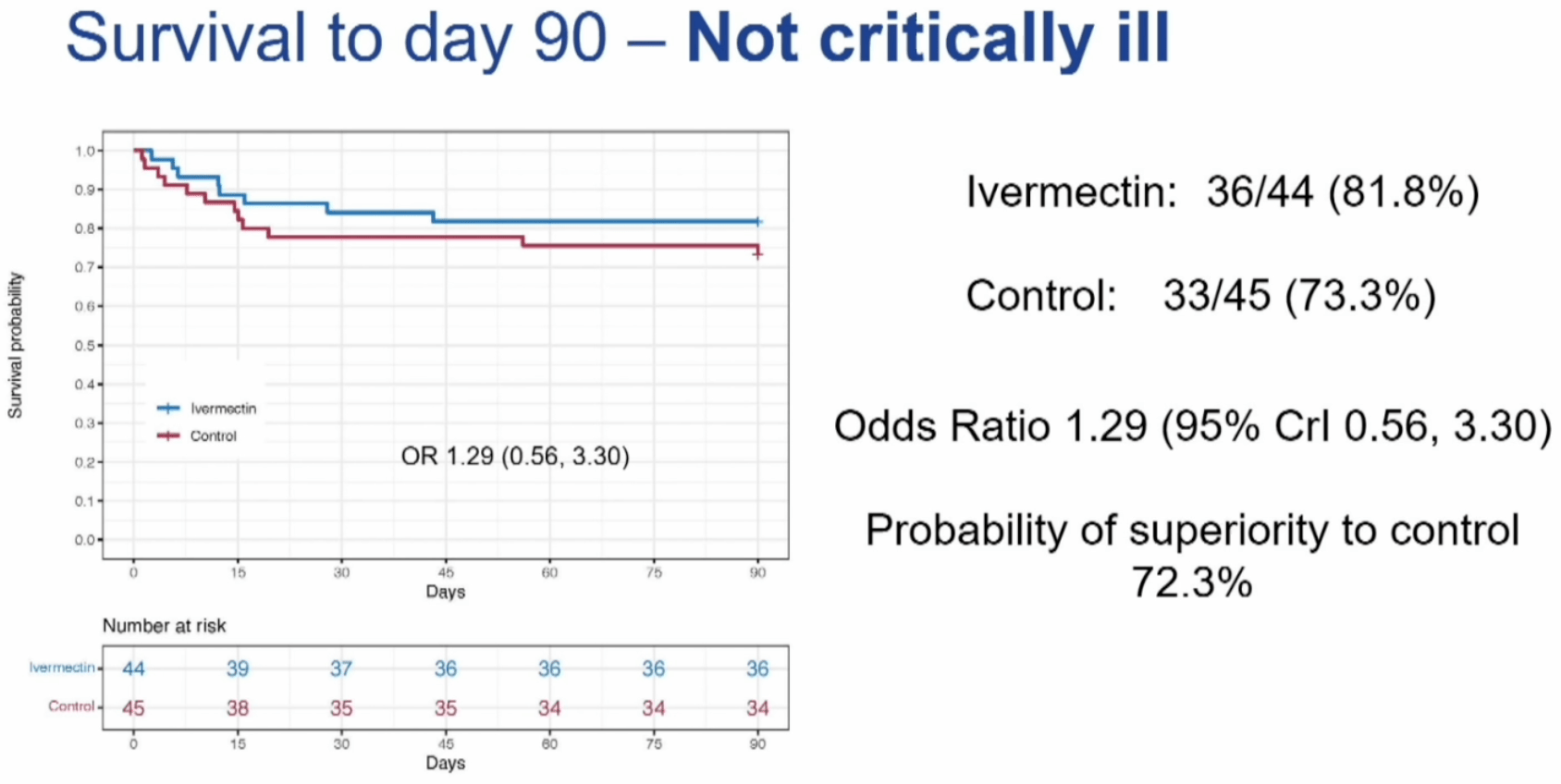
32% lower mortality for non-critical patients.
While authors describe the result as negative, there was 32% lower mortality for non-critical patients, despite greater baseline severity in the treatment group, very low dose, poor administration, and very late treatment. 18% died in the treatment group versus 27% for the control group.
Expected failure based on design.
In the protocol authors note that previous trials used 0.2mg/kg - 0.6mg/kg and they note that a dose-response effect has been seen, however they chose the lowest dose 0.2mg/kg, and further do not specify administration with food
4, suggesting that the expected outcome is failure. The presentation acknowledges that the dose is too low and not expected to be effective. They also note poor absorption in severe disease and presence of ileus, exarcerbated in critical illness, and they note studies show improved absorption with ivermectin oral solution. However, administration was done with tablets dissolved in water, which is noted to be a poor choice.
Inclusion change to ICU only.
The protocol indicates inclusion of hospitalized (non-ICU and ICU) patients
4, it's unclear why this appears to have been changed to ICU only.
>600 days delay in reporting.
Results were delayed over 600 days with two very late post-hoc statistical analysis plans that make changes in outcomes and analysis, 5 months and over a year after completion. This suggests the delay was primarily to make changes in the outcomes and analysis.
Adjustment direction different from expected.
Given the baseline differences adjusted results are expected to move towards increased benefit, however results do not match expectations, consistent with baseline severity being removed from adjustments.
Remdesivir use.
Remdesivir use was higher in the treatment group which adds risk given the ICU population and 90 day outcomes. Meta regression with followup duration for remdesivir shows declining efficacy with harm past ~60 days followup, which may reflect antiviral efficacy being offset by side effects
5. Authors do not adjust for remdesivir use.
Bias in closing and presentation.
The trial was closed with an incorrect statement on the evidence base at the time, suggesting significant bias
6.
Post hoc SAP one year post completion.
As above, authors created a post-hoc statistical analysis plan. The first one is dated 19 February 2023
1, long after the trial completed, and the second one is dated 16 October 2023, over a year after completion on September 9, 2022
3.
Primary outcome changed.
The primary outcome in the protocol is 90 day mortality
2. It's unclear why this was changed in the antiviral domain
7 to organ support-free days. Authors do not report 90 day mortality at all, only 90 day survival which shows a lower relative change for the observed trend of lower mortality in non-critical patients.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta
analysis:
baseline severity favors control, post-hoc outcome and SAP changes, see discussion.
Hashmi et al., 13 Jun 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Pakistan, preprint, 2 authors, study period 11 June, 2021 - 9 September, 2022, dosage 200μg/kg days 1-5, trial
NCT02735707 (history) (REMAP-CAP).