Clinical features, demography, and predictors of outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection at a tertiary care hospital in India: A cohort study
Dr Sushma Bhatnagar, Arunmozhimaran Elavarasi, Harikrishna Raju Sagiraju, Rohitkumar Garg, Brajesh Ratre, Prashant Sirohiya, Nishkarsh Gupta, Rakesh Garg, Anuja Pandit, Saurabh Vig, Ram Singh, Balbir Kumar, Vedprakash Meena, Naveet Wig, Saurabh Mittal, Sourabh Pahuja, Karan Madan, Randeep Guleria, Anant Mohan, Tanima Dwivedi, Ritu Gupta, Ashimajain Vidyarthi, Rama Chaudhry, Arghya Das, Laxmitej Wundavalli, Angelrajan Singh, Sheetal Singh, Sunil Kumar, Manisha Pandey, Abhinav Mishra, Karanvirsingh Matharoo
Lung India, doi:10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_493_21
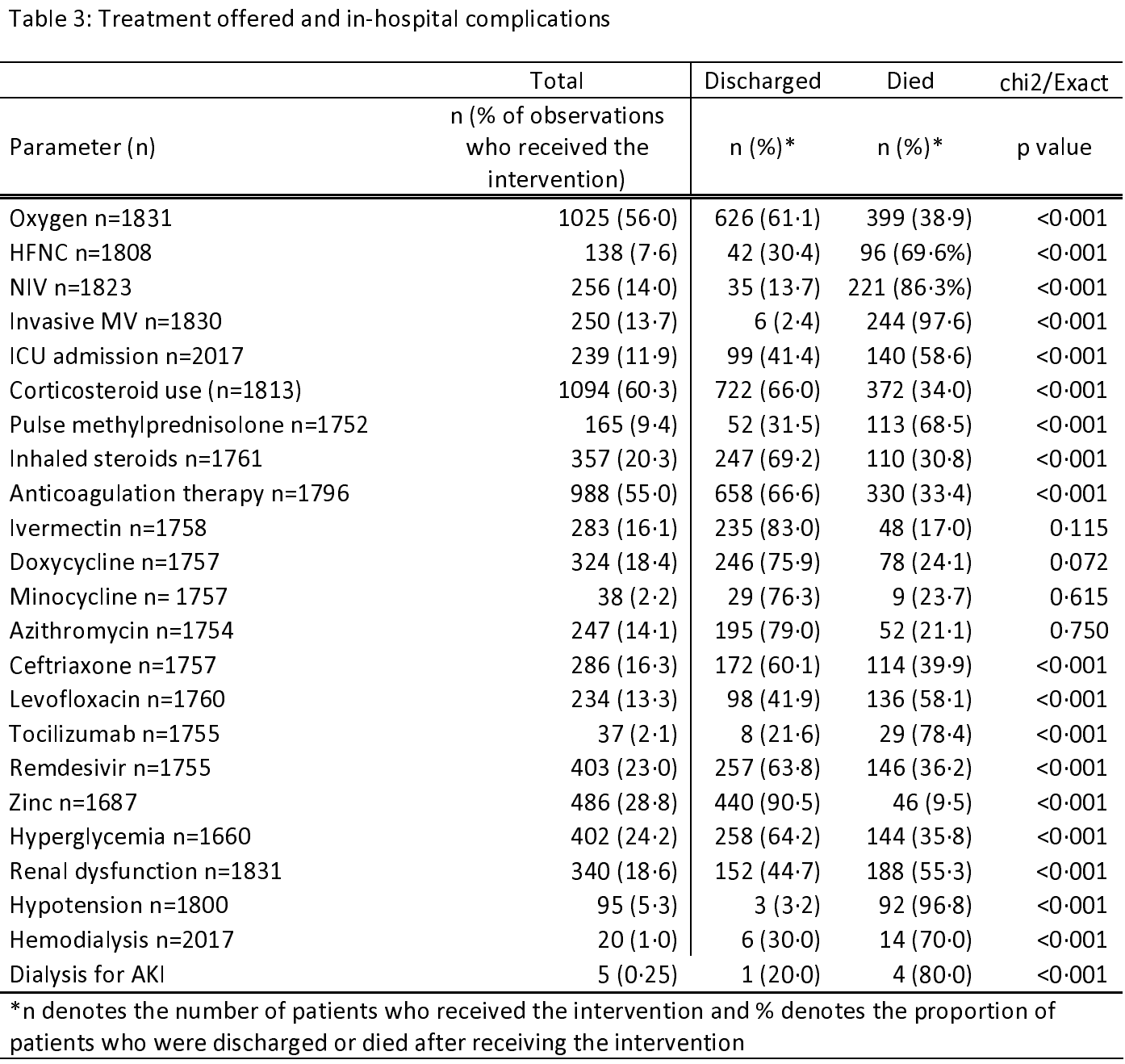
Background: The "second wave" of the COVID-19 pandemic hit India from early April 2021 to June 2021. We describe the clinical features, treatment trends, and baseline laboratory parameters of a cohort of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and their association with the outcome. Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study. Multivariate logistic regression models were fitted to identify clinical and biochemical predictors of developing hypoxia, deterioration during the hospital stay, and death. Results: A total of 2080 patients were included. The case fatality rate was 19.5%. Among the survivors, the median duration of hospital stay was 8 (5-11) days. Out of 853 (42.3%%) of patients who had COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome at presentation, 340 (39.9%) died. Patients aged >45 years had higher odds of death as compared to the 18-44 years age group. Vaccination reduced the odds of death by 40% (odds ratio [OR] [95% confidence interval [CI]]: 0.6 [0.4-0.9], P = 0.032). Patients with hyper inflammation at baseline as suggested by leukocytosis (OR [95% CI]: 2.1 [1.5-3.1], P < 0.001), raised d-dimer >500 mg/dL (OR [95% CI]: 3.2 [2.2-4.7], P < 0.001), and raised C-reactive peptide >0.5 mg/L (OR [95% CI]: 3.7 [2.2-13], P = 0.037) had higher odds of death. Patients who were admitted in the 2 nd week had lower odds and those admitted in the 3 rd week had higher odds of death.
Conflicts of interest There are no conflicts of interest. 1.2 (0.9-1.6), 0.199 1 (0.7-1.5), 0.980 1 (0.6-1.7), 0.943 1.1 (0.7-1.9), 0.708 Primary condition (Reference: COVID) Non-COVID 3.5 (1.7-7.2), 0.001 1.2 (0.4-3.5), 0.705 0.8 (0.3-2•6), 0.729 0.5 (0.1-1.8), 0.266 Mucor 0.5 (0.1-4.0), 0.472 0.9 (0.1-11), 0.940 Vaccinated 0.7 (0.5-1.0), 0.060 0.6 (0.4-0.9), 0.032 0.5 (0.3-0.9), 0.014 0.6 (0.3-0.9), 0.042 Symptom onset to hospitalization (Reference: 1 week) 2 weeks 0.6 (0.5-0.9), 0.003 0.6 (0.4-0.9), 0.027 0.5 (0.3-0.8), 0.002 0.5 (0.3-0.8), 0.003 3 or more weeks 1.9 (1.1-3.4), 0.032 0.9 (0.4-2.2), 0.828 0.6 (0.2-1.9), 0.372 0.5 (0.1-1.9), 0.336 Asymptomatic 1.1 (0.
References
Aggarwal, Shrivastava, Kumar, Ali, Clinical and epidemiological features of SARS-CoV-2 patients in SARI ward of a tertiary care centre in New Delhi, J Assoc Physicians India
Albalawi, Alharbi, Bakouri, Alqahtani, Alanazi et al., Clinical characteristics and predictors of mortality among COVID-19 patients in Saudi Arabia, J Infect Public Health
Ards Definition, Force, Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition, JAMA
Bairwa, Kumar, Ajmal, Bahurupi, Kant, Predictors of critical illness and mortality based on symptoms and initial physical examination for patients with SARS-CoV-2: A retrospective cohort study, J Infect Public Health
Bellani, Laffey, Pham, Brochard, Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 countries, JAMA
Chauhan, Shadrach, Garg, Bhatia, Bhardwaj et al., Predictors of clinical outcomes in adult COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary care hospital in India: An analytical cross-sectional study, Acta Biomed
Gregoriano, Koch, Haubitz, Conen, Fux et al., Characteristics, predictors and outcomes among 99 patients hospitalised with COVID-19 in a tertiary care centre in Switzerland: An observational analysis, Swiss Med Wkly
Gupta, Ish, Kumar, Dev, Yadav et al., Evaluation of the clinical profile, laboratory parameters and outcome of two hundred COVID-19 patients from a tertiary centre in India, Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease,
doi:10.4081/monaldi.2020.1507Mohan, Tiwari, Bhatnagar, Patel, Maurya et al., Clinico-demographic profile & hospital outcomes of COVID-19 patients admitted at a tertiary care centre in North India, Indian J Med Res
Sagiraju, Elavarasi, Gupta, Garg, Paul et al., The effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in preventing severe illness and death-real-world data from a cohort of patients hospitalized with COVID-19, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.08.26.21262705Sirohiya, Elavarasi, Sagiraju, Baruah, Gupta et al., Silent hypoxia in coronavirus disease-2019: Is it more dangerous? -A retrospective cohort study, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.08.26.21262668Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Zhang, Cao, Tan, Dong, Wang et al., Clinical, radiological, and laboratory characteristics and risk factors for severity and mortality of 289 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Allergy
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_493_21",
"ISSN": [
"0970-2113"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_493_21",
"alternative-id": [
"333732"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhatnagar",
"given": "Sushma",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elavarasi",
"given": "Arunmozhimaran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raju Sagiraju",
"given": "HariKrishna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garg",
"given": "RohitKumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ratre",
"given": "Brajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sirohiya",
"given": "Prashant",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Nishkarsh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garg",
"given": "Rakesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandit",
"given": "Anuja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vig",
"given": "Saurabh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Ram",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Balbir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meena",
"given": "VedPrakash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wig",
"given": "Naveet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mittal",
"given": "Saurabh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pahuja",
"given": "Sourabh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madan",
"given": "Karan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guleria",
"given": "Randeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohan",
"given": "Anant",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dwivedi",
"given": "Tanima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Ritu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vidyarthi",
"given": "AshimaJain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhry",
"given": "Rama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Das",
"given": "Arghya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wundavalli",
"given": "LaxmiTej",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "AngelRajan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Sheetal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Sunil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandey",
"given": "Manisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "Abhinav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matharoo",
"given": "KaranvirSingh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Lung India",
"container-title-short": "Lung India",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-28T16:38:46Z",
"timestamp": 1640709526000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-20T19:52:00Z",
"timestamp": 1674244320000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-19T13:44:50Z",
"timestamp": 1708350290717
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"member": "2581",
"original-title": [],
"page": "16",
"prefix": "10.4103",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"publisher": "Medknow",
"reference": [
{
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-1",
"unstructured": "COVID Live Update: 237,809,466 Cases and 4,853,001 Deaths from the Coronavirus – Worldometer. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. [Last accessed on 2021 Oct 09]."
},
{
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition",
"author": "ARDS",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-2",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-3",
"unstructured": "Clinical Spectrum. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/. [Last accessed on 2021 Jul 19]."
},
{
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-4",
"unstructured": "Available from: https://www.who.int/classifications/icd/Guidelines_Cause_of_Death_COVID-19.pdf. [Last accessed on 2021 Jul 19]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.08.26.21262705",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-5",
"unstructured": "Sagiraju HK, Elavarasi A, Gupta N, Garg RK, Paul SS, Vig S The effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in preventing severe illness and death-real-world data from a cohort of patients hospitalized with COVID-19. medRxiv 2021.08.26.21262705. [Doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.26.21262705]."
},
{
"article-title": "Predictors of clinical outcomes in adult COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary care hospital in India: An analytical cross-sectional study",
"author": "Chauhan",
"first-page": "e2021024",
"journal-title": "Acta Biomed",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.06.010",
"article-title": "Predictors of critical illness and mortality based on symptoms and initial physical examination for patients with SARS-CoV-2: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Bairwa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1028",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4414/smw.2020.20316",
"article-title": "Characteristics, predictors and outcomes among 99 patients hospitalised with COVID-19 in a tertiary care centre in Switzerland: An observational analysis",
"author": "Gregoriano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "w20316",
"journal-title": "Swiss Med Wkly",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.06.005",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and predictors of mortality among COVID-19 patients in Saudi Arabia",
"author": "Albalawi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "994",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14496",
"article-title": "Clinical, radiological, and laboratory characteristics and risk factors for severity and mortality of 289 hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1788_20",
"ISSN": "http://id.crossref.org/issn/0971-5916",
"article-title": "Clinico-demographic profile & hospital outcomes of COVID-19 patients admitted at a tertiary care centre in North India",
"author": "Mohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"issn-type": "print",
"journal-title": "Indian J Med Res",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical and epidemiological features of SARS-CoV-2 patients in SARI ward of a tertiary care centre in New Delhi",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "J Assoc Physicians India",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4081/monaldi.2020.1507",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-13",
"unstructured": "Gupta, N., Ish, P., Kumar, R. ., Dev, N., Yadav, S. R., Malhotra, N., Agrawal, S., Gaind, R., Sachdeva, H. and COVID 2019 working group, *Other members of the S. H. . (2020) “Evaluation of the clinical profile, laboratory parameters and outcome of two hundred COVID-19 patients from a tertiary centre in India”, Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease, 90(4). doi: 10.4081/monaldi.2020.1507."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.0291",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 countries",
"author": "Bellani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "788",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-15",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.08.26.21262668",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.333732-16",
"unstructured": "Sirohiya P, Elavarasi A, Raju Sagiraju HK, Baruah M, Gupta N, Garg RK, Silent hypoxia in coronavirus disease-2019: Is it more dangerous? – A retrospective cohort study. medRxiv 2021.08.26.21262668; [Doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.26.21262668]."
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/lungindia/Fulltext/2022/01000/Clinical_features,_demography,_and_predictors_of.5.aspx"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical features, demography, and predictors of outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection at a tertiary care hospital in India: A cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "39"
}