Ivermectin is associated with increase in SPO2 in hypoxemic SARS-Cov-2 patients: pharmacodynamic profile and correlates.
Olufemi Emmanuel Babalola, Adesuyi A Ajayi, Thairu Yunusa, Yahaya Ndanusa, John O Ogedengbe, Omede Ogu
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1576399/v1
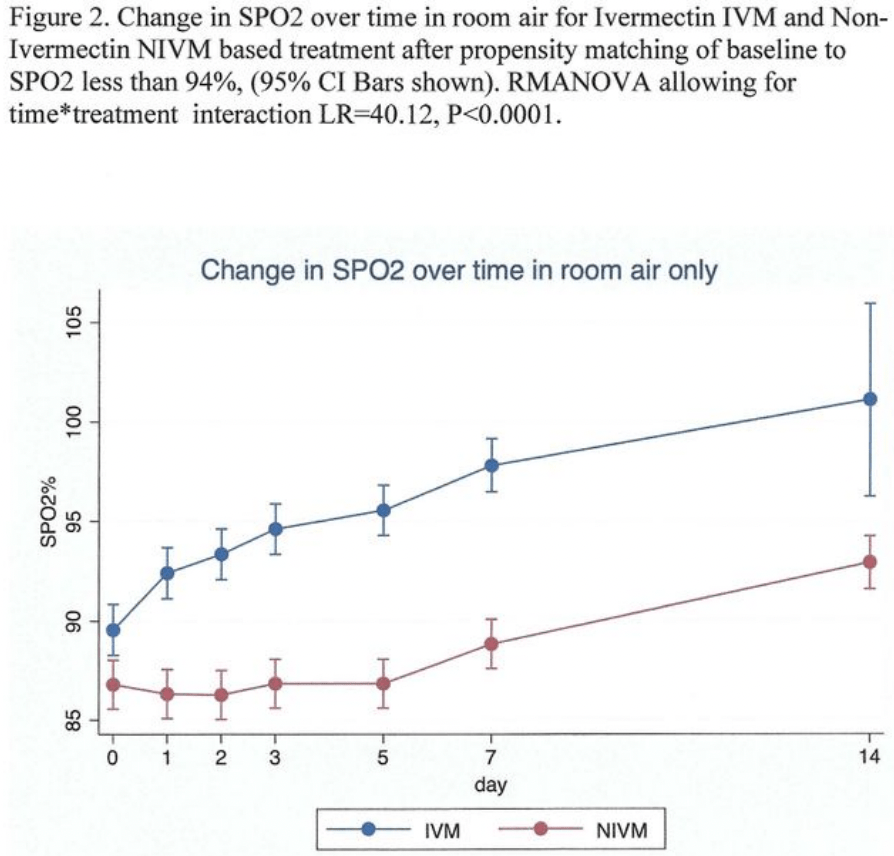
Background and Objectives: Hypoxemic respiratory failure is a common mode of demise in Covid 19 disease. We aimed to describe the time course of SPO2 changes in Covid 19 patients treated with and without ivermectin. Methods: This was a parallel group, prospective comparative study of propensity matched Covid 19 patients (Cycle threshold Ct < 25, SPO2 < 94%). 21 of the patients received Ivermectin (IVM) inclusive regime at 12 mg daily for 5 days, while 26 others received Non-ivermectin inclusive regime ( NIVM). Results: the IVM group demonstrated earlier and greater increase in SPO2 (p=0.000) which paralleled greater and faster virological clearance (p = 0.000) on Repeat measures Analysis of Variance RMANOVA. There was a signi cant correlation between absolute SPO2 and absolute Ct on day 5 (r = 0.77 ) and day 7 (r = 0.77) both p = 0.000. Incremental SPO2 also correlated with incremental Ct. by day 5
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Weite et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis and angiogenesis in Covid 19, N. Engl. J. Med
Ajayi, Mathur, Halushka, Testosterone increases human platelet Thromboxane A2 receptor density and aggregation responses, Circulation
Aminpour, Cannariatto, Preto, Safareeadebili, Morachiato, In silico analysis of multi targeted mode of action of ivermectin and related compounds, computation,
doi:10.3390/computation10040051Babalola, Bode, Ajayi, Alakaloko, Akase et al., Ivermectin shows clinical bene ts in mild to moderate Covid 19 : a randomized controlled double blind , dose response study in Lagos, QJM
Babalola, Ndanusa, Ajayi, Ogedengbe, Thairu et al., A randomized controlled trial of ivermectin monotherapy versus hydroxy chloroquine, ivermectin and azithromycin combination therapy in Covid 19 patients in Nigeria, J infect Dis Epidemiol,
doi:10.23937/2474-3658/1510233Bai, Zhou, Fang, Song, Chem, In ammatory cytokines and T lymphocyte subsets in serum and sputum in patients with bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Med Sci Monit
Batah, Todorovic, Pulmonary pathology of ARDS in Covid-19 : A pathological review for clinicians, Respir Med,
doi:10.1016/jmed.2020106239Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of Covid 19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther
Ci, Li, Yu, Zhang, Yu et al., Avermectin exerts anti-in ammatory effect by down regulating the nuclear transcription factor Kappa -B and Mitogen -activated protein kinase activation pathway, Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology
Dhage, Tilekar, Severity monitoring device for Covid 19 positive patients
Fda, Pulse oximeter accuracy and limitations
Hazan, Gunanatne, Dolai, Clancy, Mccullough, Effectiveness of ivermectin-based multi-drug therapy in severe hypoxic, ambulatory Covid 19 patients, Future Microbiol
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel Corona virus in Wuhan China, Lancet
Jang, Jeon, Kim, Sy, Drugs repurposed for Covid 19 by virtual screening of 6, 218 drugs and cell-based assays, Proceed Natl Acad Sci
Jiang, Huang, Xie, Lv, Quan, The association between severe Covid 19 and low platelet count: evidence from 31 observational studies involving 7613 participants, Br J Haematol
Jin, Bai, He, Wu, Liu et al., Gender differences in patients with Covid 19: Focus on severity and mortality, Front Public Health,
doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00152Kuo, Pavlidis, Loza, Baribaud, Rowe et al., T Helper cell type 2 ( Th2) and non -Th2 molecular phenotypes of asthma using sputum transcriptomics in U -BIOPRED, Eur Respir J
Lagomintzis, Chasapis, Alexandris, Kouretas, Tzartos et al., Nicotinic cholinergic system and COVID 19: In silico identi cation of interactions between alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and the cryptic epitopes of SARS -CoV and SARS-CoV -2 spike glycoproteins, Food and Chemical Toxicology
Lang, Som, Mendoza, Flores, Reid et al., Hypoxemia related to Covid 19 : Vascular and perfusion abnormalities on dual energy CT, Lancet infect Dis
Liu, Lin, Baine, Wainberg, Grumprecht et al., Convalescent plasma in severe Covid 19: a propensity matched control study, Nature Medicine
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., Consider cytokine storm and immunosuppression, Lancet
Munoz, Torres, Sampol, Rios, Marti et al., Accuracy and reliability of pulse oximetry at different carbon dioxide pressure level, Eur Respir J
Neufeldt, Cerikan, Franklin, Lee, Piociennikowska, SARS -CoV-2 infection induces a pro in ammatory response through CGAS -STING and NF -KB, Communications Biology
Nicolai, Leunig, Brambs, Kaiser, Weinberger et al., Immunothrombotic dysfunction in Covid 19 pneumonia is associated with respiratory failure and coagulopathy, Circulation
Stone, Ndarukwa, Scheim, Dancis, Dancis et al., Rapid increase in SPO2 on room air for 34 severe Covid 19 patients after ivermectin based combination treatment,
doi:10.21203/rs1048271/V1Thairu, Babalola, Ajayi, Ndanusa, Omede, A comparison of ivermectin and non-ivermectin based regimen for Covid 19 in Abuja: effect on virus clearance, days-to -discharge and mortality, Research square,
doi:10.21203/rs-1373673/v1Tipre, Cidon, Moats, Imaging pulmonary blood vessels and ventilation -perfusion mismatch in Covid 19, Mol. Imaging Biol
Who, Weekly epidemiology update on Covid-19
Zaidi, Dehgani-Mobaraki, Mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS -CoV-2 -an extensive review, The Journal of Antibiotics