A study of impurities in the repurposed COVID‐19 drug hydroxychloroquine sulfate using ultra‐high‐performance liquid chromatography‐quadrupole/time‐of‐flight mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography‐solid‐phase extraction‐nuclear magnetic resonance
Donghai Xu, Fangfang Pan, Hao Ruan, Nan Sun
Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, doi:10.1002/rcm.9358
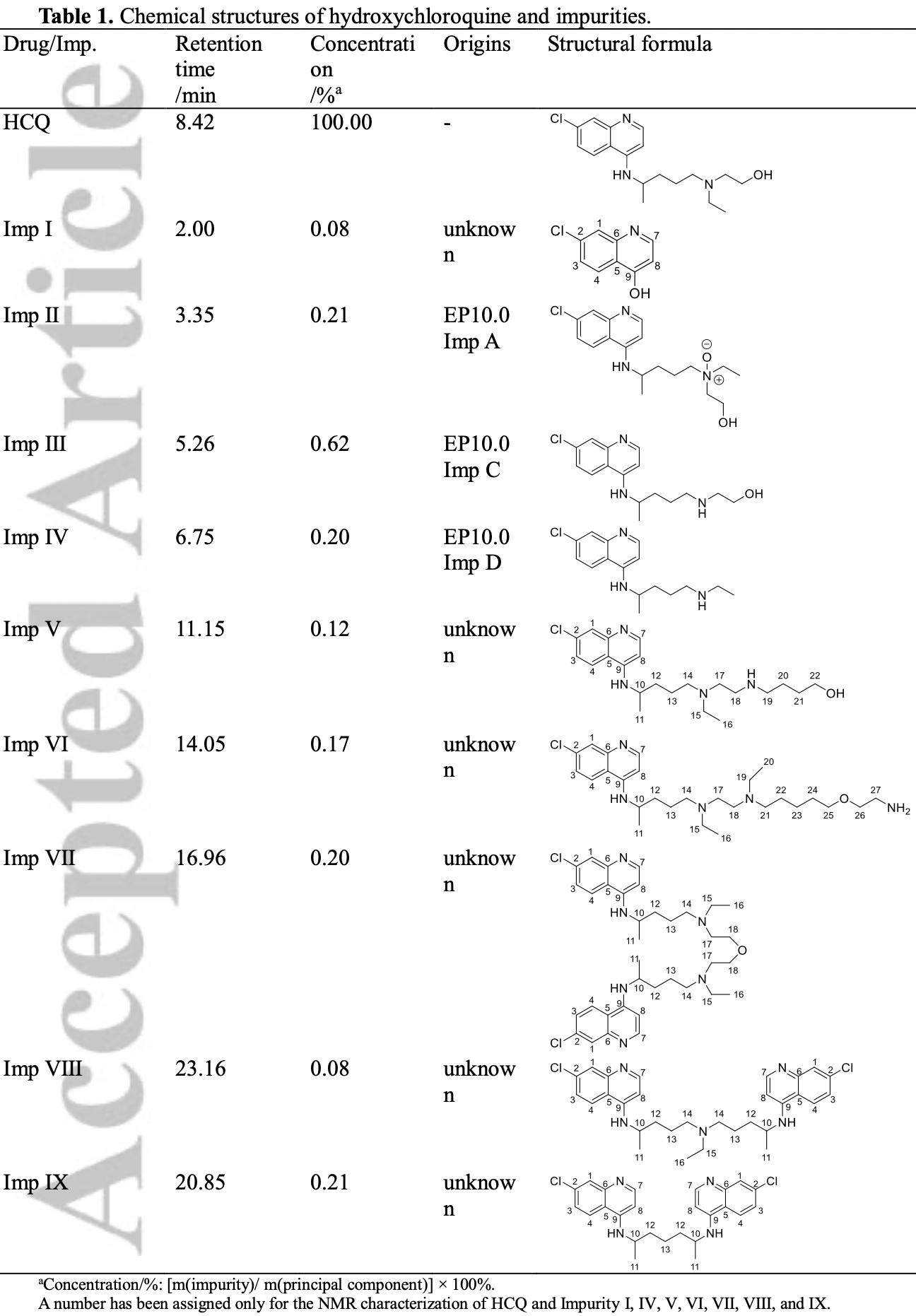
Rationale: Hydroxychloroquine sulfate is effective in the treatment of malaria, autoimmune diseases, and as an antiviral drug. However, unreported impurities are often detected in this drug, which pose a health risk. In this study, the structures of hydroxychloroquine and six unknown impurities were analyzed using ultra-high performance liquid chromatographyquadrupole/time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q/TOF MS), and the structures were characterized using liquid chromatography-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (LC-SPE-NMR).
Methods: The column was an Agilent InfinityLad Poroshell HPH-C18 (100 mm × 4.6 mm, 2.7 µm). For the analysis of hydroxychloroquine and six unknown impurities, the mobile phase was 20 mM ammonium formate aqueous solution and methanol/acetonitrile (80:20, v/v), using gradient elution. Full-scan MS and MS 2 were performed in order to obtain as much structural information as possible. Additionally, six unknown impurities were separated by semi-preparative liquid chromatography and characterized by LC-SPE-NMR.
Results: The MS 2 fragmentation patterns of the impurities were investigated, leading to more structural information and an understanding of the fragmentation pathways of the impurities. The unknown impurities' structures were confirmed by NMR. In addition, some possible This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. pathways of the formation of the impurities in the drugs were outlined, and these impurities were found to be process impurities.
Conclusions: Based on the identification and characterization of these impurities, this study also describes the cause of the production of the impurities and provides insights for companies to improve their production processes and a scientific basis for the improvement of the related pharmacopoeias.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Accinelli, Ynga-Meléndez, León-Abarca, Hydroxychloroquine/ azithromycin in COVID-19: The association between time to treatment and case fatality rate, Trav. Med. and Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102163Bodur, Erarpat, Günkara, Bakırdere, Accurate and sensitive determination of hydroxychloroquine sulfate used on COVID-19 patients in human urine, serum and saliva samples by GC-MS, J. Pharm. Anal,
doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2021.01.006Bodur, Erarpat, Günkara, Bakırdere, One step derivatization and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of hydroxychloroquine sulfate for its sensitive and accurate determination using GC-MS, J. Pharmacol. Tox. Met,
doi:10.1016/j.vascn.2021.107130Chang, Piette, Foering, Tenhave, Okawa et al., Response to antimalarial agents in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a prospective analysis, Arch. Dermatol,
doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.19.Chhonker, Sleightholm, Li, Simultaneous quantitation of hydroxychloroquine and its metabolites in mouse blood and tissues using LC-ESI-MS/MS: An application for pharmacokinetic studies, J. Chromatogr. B,
doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.11.026Christian, Jean-Marc, New insights on the antiviral effects of chloroquine against coronavirus: what to expect for COVID-19?, Int. J. Antimicrob. Ag,
doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105938Dongre, Ghugare, Karmuse, Identification and characterization of process related impurities in chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine by LC/IT/MS, LC/TOF/MS and NMR, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal,
doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2009.01.013Jacobs, Stammers, Louis, Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the treatment of severe pulmonary and cardiac compromise in COVID-19: Experience with Patients, ASAIO J,
doi:10.1097/MAT.0000000000001185Kenny, Smyth, Hewage, 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid derivatives of inositol from dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) root characterised using LC-SPE-NMR and LC-MS techniques, Phytochemistry,
doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.11.022Mckinnon, Wang, Zervos, Safety and Tolerability of Hydroxychloroquine in healthcare workers and first responders for the prevention of COVID-19: WHIP COVID-19 Study, Int. J. of Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.343Narayanam, Sahu, Singh, Use of LC-MS/TOF, LC-MS n , NMR and LC-NMR in characterization of stress degradation products: Application to cilazapril, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal,
doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2015.03.038Noureddine, Issaoui, Medimagh, Quantum chemical studies on molecular structure, AIM, ELF, RDG and antiviral activities of hybrid hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19: Molecular docking and DFT calculations, J. King Saud Univer. -Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2020.101334Pendela, Béni, Haghedooren, Combined use of liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance for the identification of degradation compounds in an erythromycin formulation, Anal. Bioanal. Chem,
doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5450-0Recovery, Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, New England J. of Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022926Saini, Bansal, Characterization of four new photodegradation products of hydroxychloroquine through LC-PDA, ESI-MS n and LC-MS-TOF studies, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal,
doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.06.014Seet, Quek, Ooi, Positive impact of oral hydroxychloroquine and povidone-iodine throat spray for COVID-19 prophylaxis: An open-label randomized trial, Int. J. of Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.035Sogut, Can, Guven, Safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in 152 outpatients with confirmed COVID-19: A pilot observational study, Am. J. Emerg. Med,
doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.014Soichot, Mégarbane, Houzé, Development, validation and clinical application of a LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of hydroxychloroquine and its active metabolites in human whole blood, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal,
doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.009Wahie, Daly, Cordell, Clinical and pharmacogenetic influences on response to hydroxychloroquine in discoid lupus erythematosus: a retrospective cohort study, J. Invest. Dermatol,
doi:10.1038/jid.2011.167Wang, Ong, Chin, Method development and validation for rapid quantification of hydroxychloroquine in human blood using liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry, J. Pharm. and Biomed. Anal,
doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.11.034Wright, Ross, Goldrick, Are hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine effective in the treatment of SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) ?, Evid. Based. Dent,
doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa130Yao, Ye, Zhang, Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237Zeidi, Kim, Werth, Increased Myeloid Dendritic Cells and TNF-a Expression Predicts Poor Response to Hydroxychloroquine in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus, J. Invest. Dermatol,
doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.07.041DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rcm.9358",
"ISSN": [
"0951-4198",
"1097-0231"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/rcm.9358",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/rcm.9358"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-04-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-07-12"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-07-26"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Zhejiang University of Technology Hangzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Donghai",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Zhejiang Institute for Food and Drug Control, National Medical Product Administration Key Laboratory for Core Technology of Generic Drug Evaluation Hangzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Fangfang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7096-0635",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Zhejiang University of Technology Hangzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Zhejiang Institute for Food and Drug Control, National Medical Product Administration Key Laboratory for Core Technology of Generic Drug Evaluation Hangzhou China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ruan",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Zhejiang University of Technology Hangzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Nan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry",
"container-title-short": "Rapid Comm Mass Spectrometry",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T20:29:33Z",
"timestamp": 1658867373000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T20:29:33Z",
"timestamp": 1658867373000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-27T04:49:24Z",
"timestamp": 1658897364796
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1658793600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1658793600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rcm.9358",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rcm.9358",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/rcm.9358"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Organic Chemistry",
"Spectroscopy",
"Analytical Chemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A study of impurities in the repurposed COVID‐19 drug hydroxychloroquine sulfate by UHPLC‐Q/TOF‐MS and LC‐SPE‐NMR",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}