Abstracts • OFID 2021:8 (Suppl 1) • S365
Session: P-24. Background. Monoclonal antibodies for the outpatient treatment of the novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 first received emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration in November 2020. These antibodies have been associated with a reduction in emergency department visits and hospitalization through randomized controlled trials. However, modest data is available to describe the outcomes of patients who were hospitalized despite treatment. This study describes real-world outcomes concerning the treatment of COVID-19 with the first approved monoclonal antibody for COVID-19, bamlanivimab, as well as hospital courses associated with patients admitting after receiving the therapy. Methods. This single-center, retrospective study evaluated real-world data of patients treated with bamlanivimab. The primary endpoint was a composite of emergency department (ED) visits or hospitalization due to worsening COVID-19. Data was analyzed from November 23, 2020 to March 5, 2021. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the primary endpoint. Secondary endpoints include reported symptoms 24-hours post-infusion and time to symptom resolution in days. Additionally, clinical course of patients hospitalized were analyzed and include average oxygen requirements, median length of stay, and mortality. A subgroup analysis was conducted between patients less than sixty-five years of age and those sixty-five and older. Results. 619 patients received bamlanivimab during the specified timeframe. The primary endpoint occurred in 34 patients; 11 ED visits and 23 hospitalizations. Baseline characteristics of the patients hospitalized include median age 69 years (IQR 55, 74), 56.5% male, and 82.6% Caucasian. The most common risk factors for severe disease among those hospitalized were age ≥ 65 years and history of diabetes. The clinical course of hospitalized patients varied but 52.9% required nasal cannula for respiratory support and the average length of stay was 4.5 + 4.5 days. Other COVID-19 therapies included dexamethasone in 76.5% of patients and remdesivir in 47.1% of patients. There were no major differences in the subgroup analysis. Conclusion. Bamlanivimab appears to attenuate the clinical course of COVID-19 in patients who are hospitalized despite treatment. Disclosures.
Background. In response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, an emergency use authorization (EUA) was issued for neutralizing antibody therapies including BAM. Licensing trials suggest that use of BAM reduces hospitalizations when compared with placebo (1.6% vs 6.3%). However, the real world impact of BAM is not well-described. In this study, risk factors, outcomes, and hospitalization rates among high-risk outpatients presenting with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who received BAM were examined. Methods. This is a single center retrospective analysis of all patients who received BAM monotherapy between 11/11/2020 and 3/16/2021. Electronic health records were reviewed for baseline demographics, EUA indications, comorbidities, and outcomes to include infusion reactions, hospitalizations, and deaths occurring within 29 days of BAM administration. Moderate COVID-19 was defined as having any infiltrate on chest imaging prior to BAM administration. Chi-squared or Fisher's exact tests were used to compare categorical values as appropriate, and Mann-Whitney U for continuous variables. Results. Of the 101 patients who received BAM (median age 64 years; 21% black; 4% Hispanic; 55% male), 13 were subsequently admitted. 22 patients (22%) had moderately severe disease as evidenced by abnormal imaging. Severity on presentation, number of indications for therapy, hypertension, stroke, diabetes, and number of co-morbidities were significantly associated with subsequent admission (table 1 ). No..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab466.728",
"ISSN": [
"2328-8957"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab466.728",
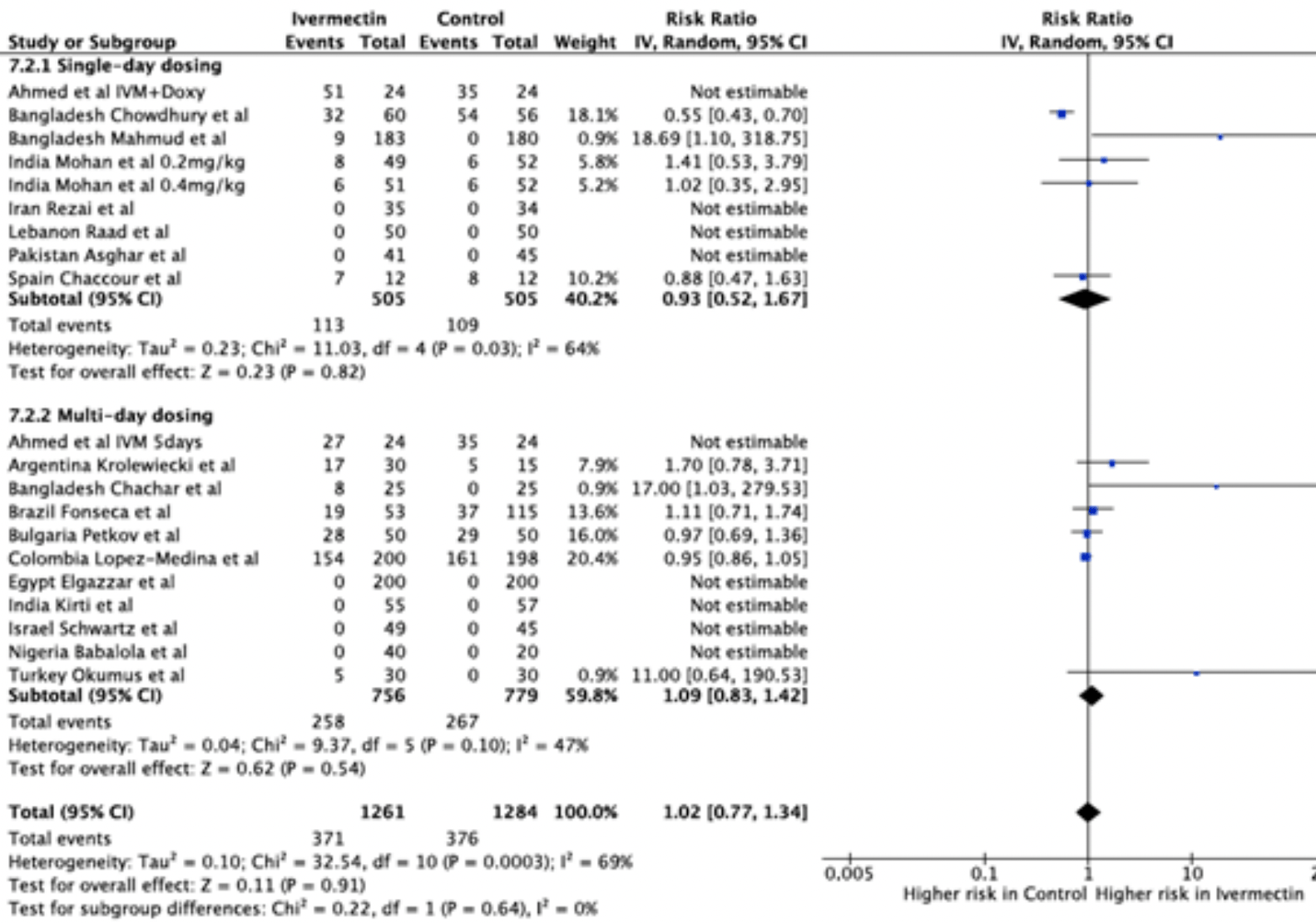
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>There is a continued and pressing need for safe and effective treatment of COVID-19. Significant survival benefits have been shown by dexamethasone, tocilizumab and sarilumab, however they are only recommended in hospitalised COVID-19 patients. Ivermectin is a well-established and readily available antiparasitic drug which may be suitable for treatment in mild and moderate disease stages. It recently demonstrated anti-viral properties in vitro and now over 80 clinical trials have been registered worldwide to test its effectiveness in COVID-19 patients. This meta-analysis aims to collect data on adverse events reported in new COVID-19 treatment trials for the use of ivermectin as a repurposed medication.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Data was extracted from randomised trials of COVID-19 treatment trials identified through systematic searches of PUBMED, EMBASE, MedRxiv and trial registries. The primary outcome of this meta-analysis is the frequency of adverse events. Key safety events included serious, gastrointestinal, neurological, cardiovascular and dermatological adverse events.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Overall, 18 trials investigating ivermectin for COVID-19 in a total of 2496 participants reported safety data and were included. There was no significant difference in the proportion of all adverse events between ivermectin and the comparator. There were 371/1261 (29%) adverse events recorded in the ivermectin containing arms and 376/1284 (29%) in the control arms (RR 1.02 [95% CI 0.77 - 1.34]; p = 0.91). There was no significant difference in the rate of serious adverse events across treatment arms (RR 1.95 [95% CI 0.75 - 5.11]; p = 0.18). No significant differences between ivermectin and the control were seen across different subcategories of adverse events. Figure 1 shows a summary of the results for all adverse events.</jats:p>\n <jats:p />\n <jats:p>Forest plot comparing ivermectin and the control for all adverse events in COVID-19 trials, subdivided into single-day dosing trials and multi-day dosing trials.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The results of recent COVID-19 trials show that overall, ivermectin is safe and well-tolerated. No significant difference in adverse event reporting was found across all subgroups in single and multi-day treatment regimens for the studies analysed. Safety reporting methodologies often varied across trials. Future and ongoing trials should be encouraged to collect and monitor safety data systematically.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Disclosures</jats:title>\n <jats:p>All Authors: No reported disclosures</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Wentzel",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Junzheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Dayanamby",
"given": "Abbienaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Oxford, Oxford, UK"
}
],
"family": "Pilkington",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University College London Hospitals, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Levi",
"given": "Jacob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College London, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Leah",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Open Forum Infectious Diseases"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-05T10:22:01Z",
"timestamp": 1638699721000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-05T10:49:46Z",
"timestamp": 1638701386000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-02T00:14:45Z",
"timestamp": 1648858485258
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2328-8957"
}
],
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 33,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638576000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/8/Supplement_1/S365/41525671/ofab466.728.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/8/Supplement_1/S365/41525671/ofab466.728.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "S365-S365",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
4
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/8/Supplement_1/S365/6450290"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Oncology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"529. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Ivermectin Safety Profile in COVID-19 Trials"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "8"
}