SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein induces neurodegeneration via affecting Golgi-mitochondria interaction
Fang Wang, Hailong Han, Caifang Wang, Jingfei Wang, Yanni Peng, Ye Chen, Yaohui He, Zhouyang Deng, Fang Li, Yikang Rong, Danling Wang, Wen Liu, Hualan Chen, Zhuohua Zhang
Translational Neurodegeneration, doi:10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1
Background Neurological complications are a significant concern of Coronavirus Disease 2019 . However, the pathogenic mechanism of neurological symptoms associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is poorly understood.
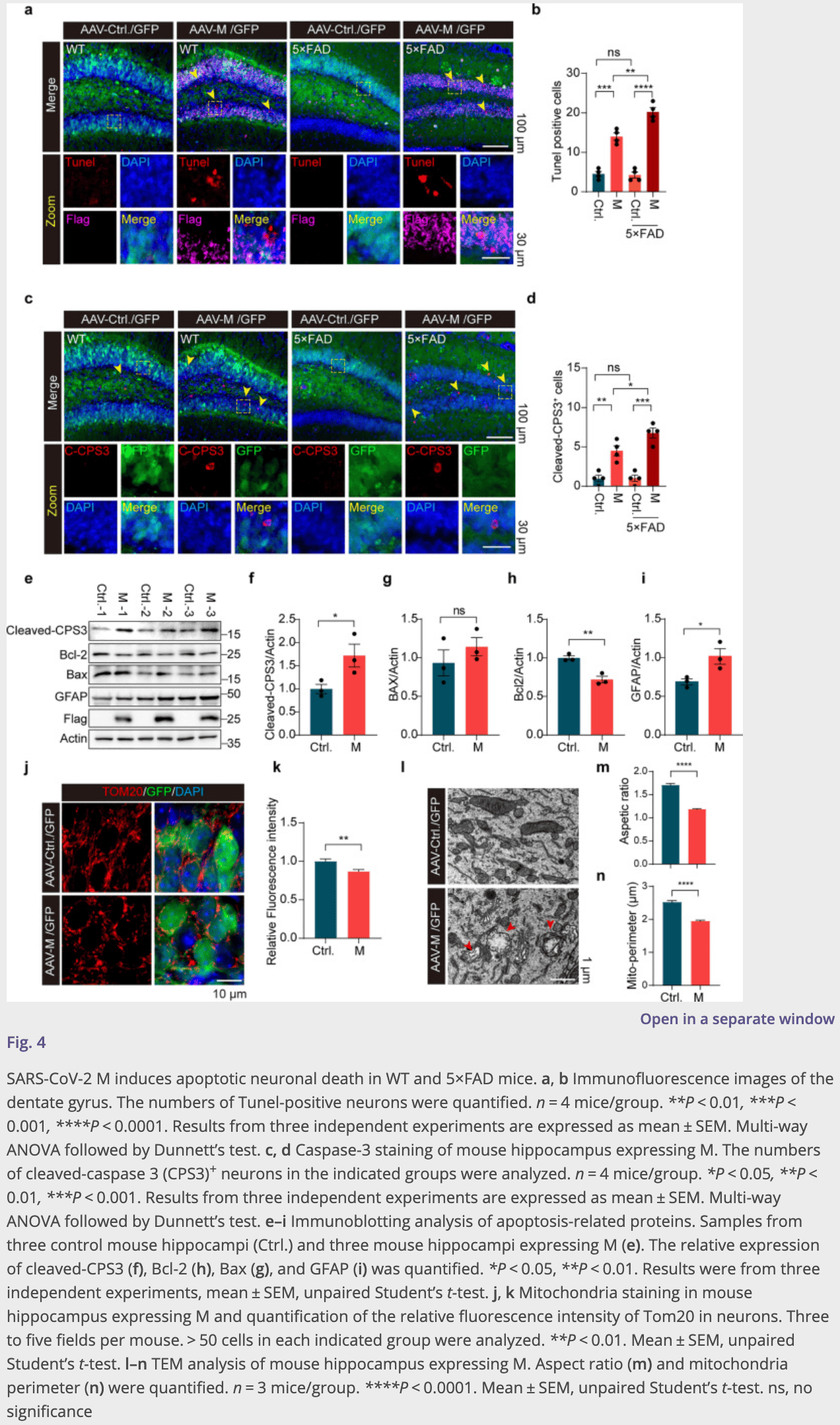
Methods We used Drosophila as a model to systematically analyze SARS-CoV-2 genes encoding structural and accessory proteins and identified the membrane protein (M) that disrupted mitochondrial functions in vivo. The M protein was stereotaxically injected to further assess its effects in the brains of wild-type (WT) and 5 × FAD mice. Omics technologies, including RNA sequencing and interactome analysis, were performed to explore the mechanisms of the effects of M protein both in vitro and in vivo. Results Systematic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 structural and accessory proteins in Drosophila identified that the M protein induces mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction, leading to reduced ATP production, ROS overproduction, and eventually cell death in the indirect flight muscles. In WT mice, M caused hippocampal atrophy, neural apoptosis, glial activation, and mitochondrial damage. These changes were further aggravated in 5 × FAD mice. M was localized to the Golgi apparatus and genetically interacted with four wheel drive (FWD, a Drosophila homolog of mammalian PI4KIIIβ) to regulate Golgi functions in flies. Fwd RNAi, but not PI4KIIIα RNAi, reversed the M-induced Golgi abnormality, mitochondrial fragmentation, and ATP reduction. Inhibition of PI4KIIIβ activity suppressed the M-induced neuronal cell death. Therefore, M induced mitochondrial fragmentation and apoptosis likely through disruption of Golgiderived PI(4)P-containing vesicles. Conclusions M disturbs the distribution and function of Golgi, leading to mitochondrial abnormality and eventually neurodegeneration via a PI4KIIIβ-mediated mechanism. This study reveals a potential mechanism for COVID-19 neurological symptoms and opens a new avenue for development of therapeutic strategies targeting SARS-CoV-2 M or mitochondria.
Abbreviations
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi . org/ 10. 1186/ s40035-024-00458-1. Additional file 1. Figure S1 .
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate All animal studies had complied with all relevant ethical regulations for the animal testing and research, and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University.
Consent for publication All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
Al-Sarraj, Troakes, Hanley, Osborn, Richardson et al., Invited review: the spectrum of neuropathology in COVID-19, Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol
Baden, Sahly, Essink, Kotloff, Frey et al., Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, N Engl J Med
Barranco, Pla, Alcolea, Sanchez-Dominguez, Fischer-Colbrie et al., Dense core vesicle markers in CSF and cortical tissues of patients with Alzheimer's disease, Transl Neurodegener
Beckman, Bonillas, Diniz, Ott, Roh et al., SARS-CoV-2 infects neurons and induces neuroinflammation in a non-human primate model of COVID-19, Cell Rep
Braak, Braak, Staging of Alzheimer's disease-related neurofibrillary changes, Neurobiol Aging
Braga, Lepra, Kish, Rusjan, Nasser et al., Neuroinflammation after COVID-19 with persistent depressive and cognitive symptoms, JAMA Psychiat
Burte, Carelli, Chinnery, Yu-Wai-Man, Disturbed mitochondrial dynamics and neurodegenerative disorders, Nat Rev Neurol
Chan, Ma, Chan, Chan, The SARS-coronavirus membrane protein induces apoptosis through modulating the Akt survival pathway, Arch Biochem Biophys
Chang, Ha, Lee, Sy, Cognitive impairments in patients with subacute coronavirus disease: initial experiences in a post-coronavirus disease clinic, Front Aging Neurosci
Chun, Im, Kang, Kim, Shin et al., Severe reactive astrocytes precipitate pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease via H 2 O 2 production, Nat Neurosci
Coyne, STING'ing Zika virus in neurons, Nat Microbiol
Douaud, Lee, Alfaro-Almagro, Arthofer, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK Biobank, Nature
Ellul, Benjamin, Singh, Lant, Michael et al., Neurological associations of COVID-19, Lancet Neurol
Enserink, Coronavirus rips through Dutch mink farms, triggering culls, Science
Gagliardi, Poloni, Pandini, Garofalo, Dragoni et al., Detection of SARS-CoV-2 genome and whole transcriptome sequencing in frontal cortex of COVID-19 patients, Brain Behav Immun
Gao, Tian, Han, Slone, Wang et al., PINK1-mediated Drp 1(S616) phosphorylation modulates synaptic development and plasticity via promoting mitochondrial fission, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Granholm, Long-Term effects of SARS-CoV-2 in the brain: clinical consequences and molecular mechanisms, J Clin Med
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Nair, Mahajan et al., Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat Med
Halliday, Pathology and hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer's disease, Lancet Neurol
Han, Tan, Wang, Wan, He et al., PINK1 phosphorylates Drp 1(S616) to regulate mitophagy-independent mitochondrial dynamics, EMBO Rep
Hao, Sakurai, Watanabe, Sorensen, Nidom et al., Drosophila RNAi screen identifies host genes important for influenza virus replication, Nature
Herrera, Cauchi, Functional characterisation of the ACE2 orthologues in Drosophila provides insights into the neuromuscular complications of COVID-19, Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Molec Basis Disease
Ho, Salimian, Hegert, 'brien, Choi et al., Postmortem assessment of olfactory tissue degeneration and microvasculopathy in patients with COVID-19, JAMA Neurol
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol
Hu, Yang, Hou, Chen, Zhang et al., COVID-19 related outcomes among individuals with neurodegenerative diseases: a cohort analysis in the UK biobank, BMC Neurol
Joyce, Moore, Goswami, Harrell, Taylor et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infects peripheral and central neurons before viremia, facilitated by neuropilin-1, bioRxiv
Kaabi, Zhang, Xia, Yang, Qahtani et al., Effect of 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Kim, Lee, Yang, Kim, Kim et al., The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome, Cell
Kujawska, Mostafavi, Kaushik, SARS-CoV-2 getting into the brain; neurological phenotype of COVID-19, and management by nano-biotechnology, Neural Regen Res
Lau, Ingelsson, Watts, The existence of Abeta strains and their potential for driving phenotypic heterogeneity in Alzheimer's disease, Acta Neuropathol
Leal, Yassa, Neurocognitive aging and the hippocampus across species, Trends Neurosci
Lee, Wang, Zeger, Gallagher, Knierim, Heterogeneity of agerelated neural hyperactivity along the CA3 transverse axis, J Neurosci
Lewis, Frontera, Placantonakis, Lighter, Galetta et al., Cerebrospinal fluid in COVID-19: a systematic review of the literature, J Neurol Sci
Li, Liu, Lin, Shang, COVID-19 and risk of neurodegenerative disorders: a Mendelian randomization study, Transl Psychiatry
Lin, Beal, Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases, Nature
Liu, Chen, Wang, Wang, Jiang et al., One-year trajectory of cognitive changes in older survivors of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a longitudinal cohort study, JAMA Neurol
Liu, Cherry, Zika virus infection activates sting-dependent antiviral autophagy in the Drosophila brain, Autophagy
Liu, Gordesky-Gold, Leney-Greene, Weinbren, Tudor et al., Inflammation-induced, STING-dependent autophagy restricts zika virus infection in the Drosophila brain, Cell Host Microbe
Logunov, Dolzhikova, Zubkova, Tukhvatullin, Shcheblyakov et al., Safety and immunogenicity of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine in two formulations: two open, non-randomised phase 1/2 studies from Russia, Lancet
Mahtarin, Islam, Islam, Ullah, Ali et al., Structure and dynamics of membrane protein in SARS-CoV-2, J Biomol Struct Dyn
Mao, Wang, Hu, Chen, He, Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, JAMA Neurol
Marques-Pereira, Pires, Gouveia, Pereira, Caniceiro et al., SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein: from genomic data to structural new insights, Int J Mol Sci
Martina, Vicenti, Bauer, Crespan, Rango et al., Bithiazole inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase (PI4KIIIβ) as broadspectrum antivirals blocking the replication of SARS-CoV-2, Zika virus, and human rhinoviruses, ChemMedChem
Martinez-Marmol, Giordano-Santini, Kaulich, Cho, Przybyla et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection and viral fusogens cause neuronal and glial fusion that compromises neuronal activity, Sci Adv
Masters, The molecular biology of coronaviruses, Adv Virus Res
Matschke, Lutgehetmann, Hagel, Sperhake, Schroder et al., Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: a postmortem case series, Lancet Neurol
Michel, Mayer, Poch, Thompson, Characterization of accessory genes in coronavirus genomes, J Virol
Nagashima, Tabara, Tilokani, Paupe, Anand et al., Golgi-derived PI(4)P-containing vesicles drive late steps of mitochondrial division, Science
Oakley, Cole, Logan, Maus, Shao et al., Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer's disease mutations: potential factors in amyloid plaque formation, J Neurosci
Pacheco-Herrero, Soto-Rojas, Harrington, Flores-Martinez, Villegas-Rojas, Elucidating the neuropathologic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Front Neurol
Perlman, Netland, Coronaviruses post-SARS: update on replication and pathogenesis, Nat Rev Microbiol
Perrier, Bonnin, Desmarets, Danneels, Goffard et al., The C-terminal domain of the MERS coronavirus M protein contains a trans-Golgi network localization signal, J Biol Chem
Poggio, Vallese, Hartel, Morgenstern, Kanner et al., Perturbation of the host cell Ca 2+ homeostasis and ER-mitochondria contact sites by the SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins E and M, Cell Death Dis
Polack, Thomas, Kitchin, Absalon, Gurtman et al., Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, N Engl J Med
Rahmati, Yon, Lee, Soysal, Koyanagi et al., Newonset neurodegenerative diseases as long-term sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol
Romero-Sanchez, Diaz-Maroto, Fernandez-Diaz, Sanchez-Larsen, Layos-Romero et al., Neurologic manifestations in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: the ALBACOVID registry, Neurology
Rudnicka-Drozak, Drozak, Mizerski, Zaborowski, Slusarska et al., Links between COVID-19 and Alzheimer's disease-what do we already know?, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Sadoff, Gray, Vandebosch, Cardenas, Shukarev et al., Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Shen, Zheng, Zhou, Chi, Pan et al., A dRASSF-STRIPAK-Imd-JAK/STAT axis controls antiviral immune response in Drosophila, Cell Rep
Slavik, Morehouse, Ragucci, Zhou, Chen, cGAS-like receptors sense RNA and control 3′2′-cGAMP signalling in Drosophila, Nature
Terriente-Felix, Whitworth, Drosophila phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase fwd promotes mitochondrial fission and can suppress Pink1/ parkin phenotypes, PLoS Genet
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Microbiol
Voysey, Clemens, Madhi, Weckx, Folegatti et al., Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK, Lancet
Wan, Tang, Liao, Zeng, Zhang et al., Analysis of neuronal phosphoproteome reveals PINK1 regulation of BAD function and cell death, Cell Death Differ
Wang, Tan, Chen, Han, Tian et al., ATP13A2 facilitates HDAC6 recruitment to lysosome to promote autophagosome-lysosome fusion, J Cell Biol
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Song, A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature
Wu, Zou, Chen, Wang, Feng et al., Severe COVID-19-associated sepsis is different from classical sepsis induced by pulmonary infection with carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumonia (CrKP), Chin J Traumatol
Xiong, Wang, Chen, Choo, Ma et al., PINK1, and DJ-1 form a ubiquitin E3 ligase complex promoting unfolded protein degradation, J Clin Invest
Xu, Fromholt, Chakrabarty, Zhu, Liu et al., Diversity in Abeta deposit morphology and secondary proteome insolubility across models of Alzheimer-type amyloidosis, Acta Neuropathol Commun
Yang, Wu, Meng, Wang, Younis et al., SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein causes the mitochondrial apoptosis and pulmonary edema via targeting BOK, Cell Death Differ
Yun, Puri, Yang, Lizzio, Wu et al., MUL1 acts in parallel to the PINK1/parkin pathway in regulating mitofusin and compensates for loss of PINK1/parkin, Elife
Zawilska, Kuczynska, Psychiatric and neurological complications of long COVID, J Psychiatr Res
Zhang, Nomura, Muramoto, Ekimoto, Uemura et al., Structure of SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein essential for virus assembly, Nat Commun
Zhang, Xue, Li, Tang, Wang, BNIP3 protein suppresses PINK1 kinase proteolytic cleavage to promote mitophagy, J Biol Chem
Zhu, Lee, Van De Leemput, Lee, Han, Functional analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in Drosophila identifies Orf6-induced pathogenic effects with Selinexor as an effective treatment, Cell Biosci
Zhu, Wang, Huang, Lee, Lee et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6 damages Drosophila heart and mouse cardiomyocytes through MGA/MAX complex-mediated increased glycolysis, Commun Biol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1",
"ISSN": [
"2047-9158"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Neurological complications are a significant concern of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the pathogenic mechanism of neurological symptoms associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is poorly understood.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We used <jats:italic>Drosophila</jats:italic> as a model to systematically analyze SARS-CoV-2 genes encoding structural and accessory proteins and identified the membrane protein (M) that disrupted mitochondrial functions in vivo. The M protein was stereotaxically injected to further assess its effects in the brains of wild-type (WT) and 5 × FAD mice. Omics technologies, including RNA sequencing and interactome analysis, were performed to explore the mechanisms of the effects of M protein both in vitro and in vivo.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Systematic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 structural and accessory proteins in <jats:italic>Drosophila</jats:italic> identified that the M protein induces mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction, leading to reduced ATP production, ROS overproduction, and eventually cell death in the indirect flight muscles. In WT mice, M caused hippocampal atrophy, neural apoptosis, glial activation, and mitochondrial damage. These changes were further aggravated in 5 × FAD mice. M was localized to the Golgi apparatus and genetically interacted with four wheel drive (FWD, a <jats:italic>Drosophila</jats:italic> homolog of mammalian PI4KIIIβ) to regulate Golgi functions in flies. <jats:italic>Fwd</jats:italic> RNAi, but not PI4KIIIα RNAi, reversed the M-induced Golgi abnormality, mitochondrial fragmentation, and ATP reduction. Inhibition of PI4KIIIβ activity suppressed the M-induced neuronal cell death. Therefore, M induced mitochondrial fragmentation and apoptosis likely through disruption of Golgi-derived PI(4)P-containing vesicles.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>M disturbs the distribution and function of Golgi, leading to mitochondrial abnormality and eventually neurodegeneration via a PI4KIIIβ-mediated mechanism. This study reveals a potential mechanism for COVID-19 neurological symptoms and opens a new avenue for development of therapeutic strategies targeting SARS-CoV-2 M or mitochondria.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"458"
],
"article-number": "68",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "25 May 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "12 November 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "27 December 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "All animal studies had complied with all relevant ethical regulations for the animal testing and research, and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "All authors read and approved the final manuscript."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Fang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Hailong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Caifang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jingfei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Yanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Ye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Yaohui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Zhouyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Fang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rong",
"given": "Yikang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Danling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Hualan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1394-0697",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Zhuohua",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Translational Neurodegeneration",
"container-title-short": "Transl Neurodegener",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-27T01:50:03Z",
"timestamp": 1735264203000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-27T03:03:59Z",
"timestamp": 1735268639000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81429002",
"31330031",
"31872778",
"82201412"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "the National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"B13036"
],
"name": "the Discipline Innovative Engineering Plan (111 Program) of China"
},
{
"award": [
"2016TP1006"
],
"name": "a Key Laboratory Grant from Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department"
},
{
"award": [
"2018SK1030"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Major Project of Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department"
},
{
"award": [
"2021SK1014"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002858",
"award": [
"271004"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100002858",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "The China Postdoctoral Science Foundation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-27T16:44:49Z",
"timestamp": 1735317889506,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735257600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735257600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"author": "F Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "7798",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "458_CR1",
"unstructured": "Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen YM, Wang W, Song ZG, et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579(7798):265–9.",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.11.001",
"author": "M Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Chin J Traumatol",
"key": "458_CR2",
"unstructured": "Wu M, Zou ZY, Chen YH, Wang CL, Feng YW, Liu ZF. Severe COVID-19-associated sepsis is different from classical sepsis induced by pulmonary infection with carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumonia (CrKP). Chin J Traumatol. 2022;25(1):17–24.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"author": "A Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1017",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "458_CR3",
"unstructured": "Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, Nair N, Mahajan S, Sehrawat TS, et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2020;26(7):1017–32.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035389",
"author": "LR Baden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "403",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "458_CR4",
"unstructured": "Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(5):403–16.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2034577",
"author": "FP Polack",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2603",
"issue": "27",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "458_CR5",
"unstructured": "Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(27):2603–15.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1",
"author": "M Voysey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "99",
"issue": "10269",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "458_CR6",
"unstructured": "Voysey M, Clemens SAC, Madhi SA, Weckx LY, Folegatti PM, Aley PK, et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 2021;397(10269):99–111.",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2101544",
"author": "J Sadoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2187",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "458_CR7",
"unstructured": "Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, Cardenas V, Shukarev G, Grinsztejn B, et al. Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(23):2187–201.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31866-3",
"author": "DY Logunov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "887",
"issue": "10255",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "458_CR8",
"unstructured": "Logunov DY, Dolzhikova IV, Zubkova OV, Tukhvatullin AI, Shcheblyakov DV, Dzharullaeva AS, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine in two formulations: two open, non-randomised phase 1/2 studies from Russia. Lancet. 2020;396(10255):887–97.",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.8565",
"author": "N Al Kaabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "458_CR9",
"unstructured": "Al Kaabi N, Zhang Y, Xia S, Yang Y, Al Qahtani MM, Abdulrazzaq N, et al. Effect of 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021;326(1):35–45.",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127",
"author": "L Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "683",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "458_CR10",
"unstructured": "Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(6):683–90.",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30221-0",
"author": "MA Ellul",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "767",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Lancet Neurol",
"key": "458_CR11",
"unstructured": "Ellul MA, Benjamin L, Singh B, Lant S, Michael BD, Easton A, et al. Neurological associations of COVID-19. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(9):767–83.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.0154",
"author": "CY Ho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "544",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "458_CR12",
"unstructured": "Ho CY, Salimian M, Hegert J, O’Brien J, Choi SG, Ames H, et al. Postmortem assessment of olfactory tissue degeneration and microvasculopathy in patients with COVID-19. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(6):544–53.",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0000000000009937",
"author": "CM Romero-Sanchez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1060",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Neurology",
"key": "458_CR13",
"unstructured": "Romero-Sanchez CM, Diaz-Maroto I, Fernandez-Diaz E, Sanchez-Larsen A, Layos-Romero A, Garcia-Garcia J, et al. Neurologic manifestations in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: the ALBACOVID registry. Neurology. 2020;95(8):e1060–70.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41398-022-02052-3",
"author": "C Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "283",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Psychiatry",
"key": "458_CR14",
"unstructured": "Li C, Liu J, Lin J, Shang H. COVID-19 and risk of neurodegenerative disorders: a Mendelian randomization study. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12(1):283.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph20032146",
"author": "E Rudnicka-Drozak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2146",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health.",
"key": "458_CR15",
"unstructured": "Rudnicka-Drozak E, Drozak P, Mizerski G, Zaborowski T, Slusarska B, Nowicki G, et al. Links between COVID-19 and Alzheimer’s disease-what do we already know? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(3):2146.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2021.117316",
"author": "A Lewis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Neurol Sci",
"key": "458_CR16",
"unstructured": "Lewis A, Frontera J, Placantonakis DG, Lighter J, Galetta S, Balcer L, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid in COVID-19: a systematic review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 2021;421: 117316.",
"volume": "421",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30308-2",
"author": "J Matschke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "919",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Lancet Neurol",
"key": "458_CR17",
"unstructured": "Matschke J, Lutgehetmann M, Hagel C, Sperhake JP, Schroder AS, Edler C, et al. Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: a post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(11):919–29.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nan.12667",
"author": "S Al-Sarraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol",
"key": "458_CR18",
"unstructured": "Al-Sarraj S, Troakes C, Hanley B, Osborn M, Richardson MP, Hotopf M, et al. Invited review: the spectrum of neuropathology in COVID-19. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2021;47(1):3–16.",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2021.05.012",
"author": "S Gagliardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "458_CR19",
"unstructured": "Gagliardi S, Poloni ET, Pandini C, Garofalo M, Dragoni F, Medici V, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 genome and whole transcriptome sequencing in frontal cortex of COVID-19 patients. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;97:13–21.",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"author": "P V’kovski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol.",
"key": "458_CR20",
"unstructured": "V’kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder H, Thiel V. Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020;19(3):155–70.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.011",
"author": "D Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "914",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "458_CR21",
"unstructured": "Kim D, Lee J-Y, Yang J-S, Kim JW, Kim VN, Chang H. The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome. Cell. 2020;181(4):914-21.e10.",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-020-01402-1",
"author": "CJ Michel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Virol.",
"key": "458_CR22",
"unstructured": "Michel CJ, Mayer C, Poch O, Thompson JD. Characterization of accessory genes in coronavirus genomes. J Virol. 2020;17(1):1–13.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "458_CR23",
"unstructured": "Masters PS. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 2006:66:193–292."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro2147",
"author": "S Perlman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "439",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "458_CR24",
"unstructured": "Perlman S, Netland J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7(6):439–50.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03743-5",
"author": "KM Slavik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109",
"issue": "7874",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "458_CR25",
"unstructured": "Slavik KM, Morehouse BR, Ragucci AE, Zhou W, Ai X, Chen Y, et al. cGAS-like receptors sense RNA and control 3′2′-cGAMP signalling in Drosophila. Nature. 2021;597(7874):109–13.",
"volume": "597",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111143",
"author": "R Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111143",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "458_CR26",
"unstructured": "Shen R, Zheng K, Zhou Y, Chi X, Pan H, Wu C, et al. A dRASSF-STRIPAK-Imd-JAK/STAT axis controls antiviral immune response in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2022;40(4):111143.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature07151",
"author": "L Hao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "890",
"issue": "7206",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "458_CR27",
"unstructured": "Hao L, Sakurai A, Watanabe T, Sorensen E, Nidom CA, Newton MA, et al. Drosophila RNAi screen identifies host genes important for influenza virus replication. Nature. 2008;454(7206):890–3.",
"volume": "454",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-018-0232-5",
"author": "CB Coyne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "975",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "458_CR28",
"unstructured": "Coyne CB. STING’ing Zika virus in neurons. Nat Microbiol. 2018;3(9):975–6.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.022",
"author": "Y Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "458_CR29",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Gordesky-Gold B, Leney-Greene M, Weinbren NL, Tudor M, Cherry S. Inflammation-induced, STING-dependent autophagy restricts zika virus infection in the Drosophila brain. Cell Host Microbe. 2018;24(1):57-68.e3.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2018.1528813",
"author": "Y Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "174",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "458_CR30",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Cherry S. Zika virus infection activates sting-dependent antiviral autophagy in the Drosophila brain. Autophagy. 2018;15(1):174–5.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166818",
"author": "P Herrera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "166818",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Molec Basis Disease.",
"key": "458_CR31",
"unstructured": "Herrera P, Cauchi RJ. Functional characterisation of the ACE2 orthologues in Drosophila provides insights into the neuromuscular complications of COVID-19. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Molec Basis Disease. 2023;1869:166818.",
"volume": "1869",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13578-021-00567-8",
"author": "J-Y Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Biosci.",
"key": "458_CR32",
"unstructured": "Zhu J-Y, Lee J-G, van de Leemput J, Lee H, Han Z. Functional analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in Drosophila identifies Orf6-induced pathogenic effects with Selinexor as an effective treatment. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):1–13.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-022-03986-6",
"author": "J-Y Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1039",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Commun Biol.",
"key": "458_CR33",
"unstructured": "Zhu J-Y, Wang G, Huang X, Lee H, Lee J-G, Yang P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6 damages Drosophila heart and mouse cardiomyocytes through MGA/MAX complex-mediated increased glycolysis. Commun Biol. 2022;5(1):1039.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00933-z",
"author": "Q Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "458_CR34",
"unstructured": "Gao Q, Tian R, Han H, Slone J, Wang C, Ke X, et al. PINK1-mediated Drp 1(S616) phosphorylation modulates synaptic development and plasticity via promoting mitochondrial fission. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):103.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI37617",
"author": "H Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "650",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "458_CR35",
"unstructured": "Xiong H, Wang D, Chen L, Choo YS, Ma H, Tang C, et al. Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 form a ubiquitin E3 ligase complex promoting unfolded protein degradation. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(3):650–60.",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M116.733410",
"author": "T Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21616",
"issue": "41",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "458_CR36",
"unstructured": "Zhang T, Xue L, Li L, Tang C, Wan Z, Wang R, et al. BNIP3 protein suppresses PINK1 kinase proteolytic cleavage to promote mitophagy. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(41):21616–29.",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.201948686",
"author": "H Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep",
"key": "458_CR37",
"unstructured": "Han H, Tan J, Wang R, Wan H, He Y, Yan X, et al. PINK1 phosphorylates Drp 1(S616) to regulate mitophagy-independent mitochondrial dynamics. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(8): e48686.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201804165",
"author": "R Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "267",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Cell Biol",
"key": "458_CR38",
"unstructured": "Wang R, Tan J, Chen T, Han H, Tian R, Tan Y, et al. ATP13A2 facilitates HDAC6 recruitment to lysosome to promote autophagosome-lysosome fusion. J Cell Biol. 2019;218(1):267–84.",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-017-0027-x",
"author": "H Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "904",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "458_CR39",
"unstructured": "Wan H, Tang B, Liao X, Zeng Q, Zhang Z, Liao L. Analysis of neuronal phosphoproteome reveals PINK1 regulation of BAD function and cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2017;25(5):904–17.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1673-5374.346486",
"author": "M Kujawska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "519",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Neural Regen Res",
"key": "458_CR40",
"unstructured": "Kujawska M, Mostafavi E, Kaushik A. SARS-CoV-2 getting into the brain; neurological phenotype of COVID-19, and management by nano-biotechnology. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):519–20.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2021.660087",
"author": "M Pacheco-Herrero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Neurol",
"key": "458_CR41",
"unstructured": "Pacheco-Herrero M, Soto-Rojas LO, Harrington CR, Flores-Martinez YM, Villegas-Rojas MM, Leon-Aguilar AM, et al. Elucidating the neuropathologic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front Neurol. 2021;12: 660087.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.368.6496.1169",
"author": "M Enserink",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1169",
"issue": "6496",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "458_CR42",
"unstructured": "Enserink M. Coronavirus rips through Dutch mink farms, triggering culls. Science. 2020;368(6496):1169.",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnagi.2022.994331",
"author": "JG Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Aging Neurosci",
"key": "458_CR43",
"unstructured": "Chang JG, Ha EH, Lee W, Lee SY. Cognitive impairments in patients with subacute coronavirus disease: initial experiences in a post-coronavirus disease clinic. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14: 994331.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.0461",
"author": "YH Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "458_CR44",
"unstructured": "Liu YH, Chen Y, Wang QH, Wang LR, Jiang L, Yang Y, et al. One-year trajectory of cognitive changes in older survivors of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a longitudinal cohort study. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(5):509–17.",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1202-06.2006",
"author": "H Oakley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10129",
"issue": "40",
"journal-title": "J Neurosci",
"key": "458_CR45",
"unstructured": "Oakley H, Cole SL, Logan S, Maus E, Shao P, Craft J, et al. Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J Neurosci. 2006;26(40):10129–40.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593-020-00735-y",
"author": "H Chun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1555",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nat Neurosci",
"key": "458_CR46",
"unstructured": "Chun H, Im H, Kang YJ, Kim Y, Shin JH, Won W, et al. Severe reactive astrocytes precipitate pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease via H2O2-production. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23(12):1555–66.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32019-3",
"author": "Z Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4399",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "458_CR47",
"unstructured": "Zhang Z, Nomura N, Muramoto Y, Ekimoto T, Uemura T, Liu K, et al. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein essential for virus assembly. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):4399.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1861983",
"author": "R Mahtarin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4725",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "458_CR48",
"unstructured": "Mahtarin R, Islam S, Islam MJ, Ullah MO, Ali MA, Halim MA. Structure and dynamics of membrane protein in SARS-CoV-2. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(10):4725–38.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23062986",
"author": "C Marques-Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2986",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci.",
"key": "458_CR49",
"unstructured": "Marques-Pereira C, Pires MN, Gouveia RP, Pereira NN, Caniceiro AB, Rosario-Ferreira N, et al. SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein: from genomic data to structural new insights. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):2986.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA119.008964",
"author": "A Perrier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14406",
"issue": "39",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "458_CR50",
"unstructured": "Perrier A, Bonnin A, Desmarets L, Danneels A, Goffard A, Rouille Y, et al. The C-terminal domain of the MERS coronavirus M protein contains a trans-Golgi network localization signal. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(39):14406–21.",
"volume": "294",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-022-00928-x",
"author": "Y Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1395",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "458_CR51",
"unstructured": "Yang Y, Wu Y, Meng X, Wang Z, Younis M, Liu Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein causes the mitochondrial apoptosis and pulmonary edema via targeting BOK. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(7):1395–408.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2007.01.012",
"author": "C-M Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "197",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Arch Biochem Biophys",
"key": "458_CR52",
"unstructured": "Chan C-M, Ma C-W, Chan W-Y, Chan HYE. The SARS-coronavirus membrane protein induces apoptosis through modulating the Akt survival pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;459(2):197–207.",
"volume": "459",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aax6089",
"author": "S Nagashima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1366",
"issue": "6484",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "458_CR53",
"unstructured": "Nagashima S, Tabara LC, Tilokani L, Paupe V, Anand H, Pogson JH, et al. Golgi-derived PI(4)P-containing vesicles drive late steps of mitochondrial division. Science. 2020;367(6484):1366–71.",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.01958",
"author": "J Yun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "458_CR54",
"unstructured": "Yun J, Puri R, Yang H, Lizzio MA, Wu C, Sheng ZH, et al. MUL1 acts in parallel to the PINK1/parkin pathway in regulating mitofusin and compensates for loss of PINK1/parkin. Elife. 2014;3: e01958.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgen.1008844",
"author": "A Terriente-Felix",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLoS Genet",
"key": "458_CR55",
"unstructured": "Terriente-Felix A, Wilson EL, Whitworth AJ. Drosophila phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase fwd promotes mitochondrial fission and can suppress Pink1/parkin phenotypes. PLoS Genet. 2020;16(10): e1008844.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm12093190",
"author": "AC Granholm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3190",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med.",
"key": "458_CR56",
"unstructured": "Granholm AC. Long-Term effects of SARS-CoV-2 in the brain: clinical consequences and molecular mechanisms. J Clin Med. 2023;12(9):3190.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.10.045",
"author": "JB Zawilska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "349",
"journal-title": "J Psychiatr Res",
"key": "458_CR57",
"unstructured": "Zawilska JB, Kuczynska K. Psychiatric and neurological complications of long COVID. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;156:349–60.",
"volume": "156",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28909",
"author": "M Rahmati",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "458_CR58",
"unstructured": "Rahmati M, Yon DK, Lee SW, Soysal P, Koyanagi A, Jacob L, et al. New-onset neurodegenerative diseases as long-term sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2023;95(7): e28909.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12883-021-02536-7",
"author": "Y Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Neurol",
"key": "458_CR59",
"unstructured": "Hu Y, Yang H, Hou C, Chen W, Zhang H, Ying Z, et al. COVID-19 related outcomes among individuals with neurodegenerative diseases: a cohort analysis in the UK biobank. BMC Neurol. 2022;22(1):15.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04569-5",
"author": "G Douaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"issue": "7907",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "458_CR60",
"unstructured": "Douaud G, Lee S, Alfaro-Almagro F, Arthofer C, Wang C, McCarthy P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK Biobank. Nature. 2022;604(7907):697–707.",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.adg2248",
"author": "R Martinez-Marmol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eadg2248",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv.",
"key": "458_CR61",
"unstructured": "Martinez-Marmol R, Giordano-Santini R, Kaulich E, Cho AN, Przybyla M, Riyadh MA, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and viral fusogens cause neuronal and glial fusion that compromises neuronal activity. Sci Adv. 2023;9(23):eadg2248.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.05.20.492834",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "458_CR62",
"unstructured": "Joyce JD, Moore GA, Goswami P, Harrell TL, Taylor TM, Hawks SA, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infects peripheral and central neurons before viremia, facilitated by neuropilin-1. bioRxiv. 2023:2022.05.20.492834"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111573",
"author": "D Beckman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "458_CR63",
"unstructured": "Beckman D, Bonillas A, Diniz GB, Ott S, Roh JW, Elizaldi SR, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects neurons and induces neuroinflammation in a non-human primate model of COVID-19. Cell Rep. 2022;41(5): 111573.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature05292",
"author": "MT Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "787",
"issue": "7113",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "458_CR64",
"unstructured": "Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443(7113):787–95.",
"volume": "443",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrneurol.2014.228",
"author": "F Burte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Neurol",
"key": "458_CR65",
"unstructured": "Burte F, Carelli V, Chinnery PF, Yu-Wai-Man P. Disturbed mitochondrial dynamics and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(1):11–24.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-023-05817-w",
"author": "E Poggio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "297",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis.",
"key": "458_CR66",
"unstructured": "Poggio E, Vallese F, Hartel AJW, Morgenstern TJ, Kanner SA, Rauh O, et al. Perturbation of the host cell Ca2+ homeostasis and ER-mitochondria contact sites by the SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins E and M. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(4):297.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0197-4580(95)00021-6",
"author": "H Braak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "271",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Neurobiol Aging.",
"key": "458_CR67",
"unstructured": "Braak H, Braak E. Staging of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1995;16(3):271–8.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2405-20.2020",
"author": "H Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "663",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Neurosci",
"key": "458_CR68",
"unstructured": "Lee H, Wang Z, Zeger SL, Gallagher M, Knierim JJ. Heterogeneity of age-related neural hyperactivity along the CA3 transverse axis. J Neurosci. 2021;41(4):663–73.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30343-5",
"author": "G Halliday",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "862",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Lancet Neurol",
"key": "458_CR69",
"unstructured": "Halliday G. Pathology and hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(11):862–4.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tins.2015.10.003",
"author": "SL Leal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "800",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Trends Neurosci",
"key": "458_CR70",
"unstructured": "Leal SL, Yassa MA. Neurocognitive aging and the hippocampus across species. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38(12):800–12.",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.1321",
"author": "J Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "787",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA Psychiat",
"key": "458_CR71",
"unstructured": "Braga J, Lepra M, Kish SJ, Rusjan PM, Nasser Z, Verhoeff N, et al. Neuroinflammation after COVID-19 with persistent depressive and cognitive symptoms. JAMA Psychiat. 2023;80(8):787–95.",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40035-021-00263-0",
"author": "N Barranco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Neurodegener",
"key": "458_CR72",
"unstructured": "Barranco N, Pla V, Alcolea D, Sanchez-Dominguez I, Fischer-Colbrie R, Ferrer I, et al. Dense core vesicle markers in CSF and cortical tissues of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Neurodegener. 2021;10(1):37.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40478-020-00911-y",
"author": "G Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "43",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Neuropathol Commun",
"key": "458_CR73",
"unstructured": "Xu G, Fromholt SE, Chakrabarty P, Zhu F, Liu X, Pace MC, et al. Diversity in Abeta deposit morphology and secondary proteome insolubility across models of Alzheimer-type amyloidosis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020;8(1):43.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00401-020-02201-2",
"author": "HHC Lau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Neuropathol",
"key": "458_CR74",
"unstructured": "Lau HHC, Ingelsson M, Watts JC. The existence of Abeta strains and their potential for driving phenotypic heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2021;142(1):17–39.",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"author": "B Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "458_CR75",
"unstructured": "Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(3):141–54.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cmdc.202100483",
"author": "M Grazia Martina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3548",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "ChemMedChem",
"key": "458_CR76",
"unstructured": "Grazia Martina M, Vicenti I, Bauer L, Crespan E, Rango E, Boccuto A, et al. Bithiazole inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase (PI4KIIIβ) as broad-spectrum antivirals blocking the replication of SARS-CoV-2, Zika virus, and human rhinoviruses. ChemMedChem. 2021;16(23):3548–52.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 76,
"references-count": 76,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://translationalneurodegeneration.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40035-024-00458-1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein induces neurodegeneration via affecting Golgi-mitochondria interaction",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "13"
}