Clinical protocol for early treatment of COVID-19 in a real-world scenario: Results of a series of patients
Silvestre Sobrinho, Fabiana Perrone, Guilherme Montal, Aroldo Bacellar
Medicina Clínica Práctica, doi:10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346
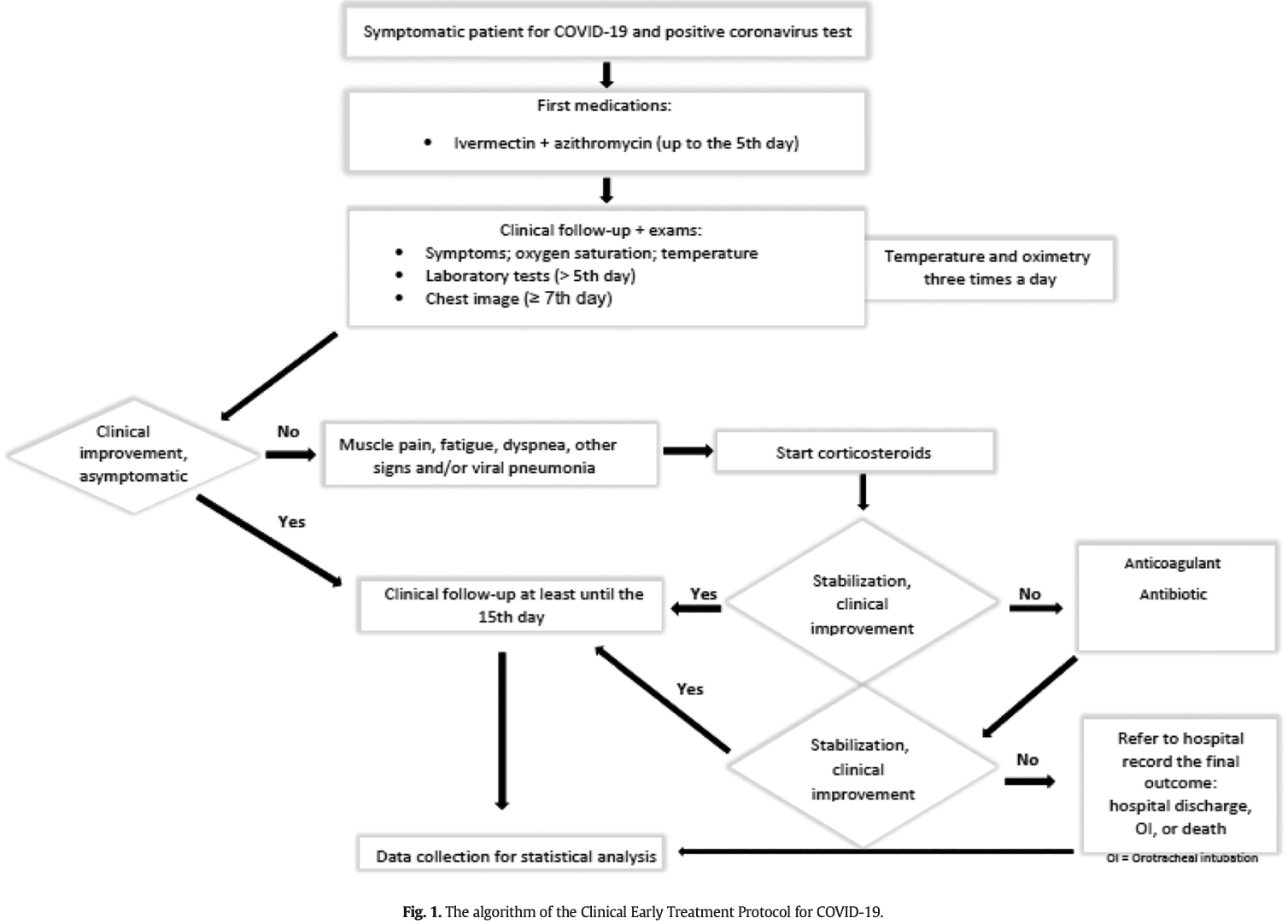
Introduction: Despite the advance in vaccination, the SARS-CoV-2 infection remains a challenge for the medical community. Outpatient and hospital therapy for COVID-19 are still improving. Our study aimed to report the results of a series of patients with COVID-19 who participated in an outpatient treatment protocol since the first clinical manifestation. Methods: A case series report of individuals aged ≥18 years with clinical symptoms and a confirmed test for COVID-19 submitted to a treatment protocol. Patients were enrolled between May and September 2020 and followed for at least 15 days. The assessed clinical outcomes were the need for hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, orotracheal intubation, and death. Results: We studied a 116 patients. The mean age was 48 ± 14 years. Females formed 53%. The main comorbidities wereobesity (15.5%), systemic arterial hypertension (10.3%) ,type II diabetes (6%), and lung diseases (6.0%). Temperature N 37.7 °C (51.7%), cough (55.2%), myalgia (37.1%), headache (37.9%), and fatigue (34.5%) were the most frequent signs and symptoms. According to different disease staging, the most administered drugs were: azithromycin, ivermectin, corticosteroid, antibiotics, and anticoagulants. There was no death, and hospitalization accounted for only 8.6% of the patients (1 in ICU); none required orotracheal intubation. The mean length of hospital stay was 5.8 days.
Author's contribution S.S. conceived the study idea, designed the methods, examined, and treated patients, collected data, and drafted the manuscript; F.P. collected data and cared for patients; G.M. performed the thorax imaging review end reviewed the manuscript. A.B. performed patient neurological reviews, drafted the manuscript, and executed English editing; All authors read, discussed, and approved the final manuscript.
Competitive interests There is no conflict of interest.
Financing
References
Al-Ani, Chehade, Lazo-Langner, Thrombosis risk associated with COVID-19 infection. A scoping review, Thromb Res
Alijotas-Reig, Immunomodulatory therapy for the management of severe COVID-19. Beyond the antiviral therapy: a comprehensive review, Autoimmun Rev
Antinori, Bacterial and fungal infections among patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, Infez Med
Ascencio-Montiel, A Multimodal Strategy to Reduce the Risk of Hospitalization/ death in Ambulatory Patients with COVID-19, Arch Med Res
Basolo, Adipose tissue in COVID-19: detection of SARS-CoV-2 in adipocytes and activation of the interferon-alpha response, J Endocrinol Invest
Becker, COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy, J Thromb Thrombolysis
Bimonte, Potential antiviral drugs for SARS-Cov-2 treatment: preclinical findings and ongoing clinical research, Vivo
Bloom, Risk of adverse outcomes in patients with underlying respiratory conditions admitted to hospital with COVID-19: a national, multicentre prospective cohort study using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol UK, Lancet Respir Med
Caly, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Chaccour, Ivermectin and COVID-19: keeping rigor in times of urgency, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Chaccour, The SARS-CoV-2 Ivermectin Navarra-ISGlobal Trial (SAINT) to evaluate the potential of ivermectin to reduce COVID-19 transmission in low risk, nonsevere COVID-19 patients in the first 48 hours after symptoms onset: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized control pilot trial, Trials
Chen, Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective study, BMJ
Conass, Painel Nacional: COVID-19
Demelo-Rodriguez, Incidence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and elevated D-dimer levels, Thromb Res
Demeulemeester, Obesity as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 and Complications: A Review, Cells
Esteban, Sobotka, Rockey, Coronavirus disease 2019 and the liver, Curr Opin Gastroenterol
Feeney, The COVIRL-001 Trial: a multicentre, prospective, randomized trial comparing standard of care (SOC) alone, SOC plus hydroxychloroquine monotherapy or SOC plus a combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in the treatment of non-critical, SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive population not requiring immediate resuscitation or ventilation but who have evidence of clinical decline: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Guo, The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -an update on the status, Mil Med Res
Gyselinck, Azithromycin for treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a randomized, multicentre, open-label clinical trial (DAWn-AZITHRO), ERJ Open Res
Han, Gatheral, Williams, Procalcitonin for patient stratification and identification of bacterial co-infection in COVID-19, Clin Med (Lond)
Hashem, Obstacles and Considerations Related to Clinical Trial Research During the COVID-19 Pandemic, Front Med
Hill, Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis
Hill, Retraction to: meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis
Karaahmet, Karaahmet, Potential effect of natural and anabolizan steroids in elderly patient with COVID-19, Med Hypotheses
Koffman, Uncertainty and COVID-19: how are we to respond?, J R Soc Med
Kutsuna, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): research progress and clinical practice, Glob Health Med
Levi, Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Haematol
Liu, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with Coronavirus Disease-2019 in Shiyan City, China, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Lv, Clinical characteristics and co-infections of 354 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Microbes Infect
Maier, COVID-19-associated hyperviscosity: a link between inflammation and thrombophilia?, Lancet
Martinho, Hospital exclusivo para Covid-19 será inaugurado nesta terça em Salvador
Mccreary, Pogue, Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: a review of early and emerging options, Open Forum Infect Dis
Mirjalili, Does Losartan reduce the severity of COVID-19 in hypertensive patients?, BMC Cardiovasc Disord
Popp, ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Rajpal, Rahimi, Ismail-Beigi, Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes, J Diabetes
Ramireddy, Experience with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in the Coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: implications for Q.T. interval monitoring, J Am Heart Assoc
Rizzo, Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol
Shaffer, 15 drugs being tested to treat COVID-19 and how they would work, Nat Med
Sharma, Surani, Searching an Effective Therapy for the Coronavirus Pandemic: Do We See Light at the End of the Tunnel?, Cureus
Sharun, Ivermectin, a new candidate therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob
Shirazi, Repurposing the drug, Ivermectin, in COVID-19: toxicological points of view, Eur J Med Res
Siddiqi, Mehra, COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transplant
Toro, Rhabdomyolysis as the presentation form of COVID-19 infection
Uol, Maio de 2020 torna-se o mês com maior número de mortes na história do Brasil
Vetter, Clinical features of covid-19, BMJ
Wang, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet
Wustner, Clinical Evidence Informing Treatment Guidelines on Repurposed Drugs for Hospitalized Patients During the Early COVID-19 Pandemic: Corticosteroids, Anticoagulants, (Hydroxy)chloroquine, Front Public Health
Yang, Coronavirus disease 2019: a clinical review, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Zhang, Efficacy of COVID-19 Treatments: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Front Public Health
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346",
"ISSN": [
"2603-9249"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346",
"alternative-id": [
"S2603924922000283"
],
"article-number": "100346",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Clinical protocol for early treatment of COVID-19 in a real-world scenario: Results of a series of patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Medicina Clínica Práctica"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobrinho",
"given": "Silvestre",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perrone",
"given": "Fabiana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montal",
"given": "Guilherme",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bacellar",
"given": "Aroldo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicina Clínica Práctica",
"container-title-short": "Medicina Clínica Práctica",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-22T08:38:03Z",
"timestamp": 1663835883000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-19T19:50:26Z",
"timestamp": 1668887426000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-20T05:48:16Z",
"timestamp": 1668923296564
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1664582400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1663286400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2603924922000283?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2603924922000283?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100346",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019: a clinical review",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "4585",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0005",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical features of covid-19",
"author": "Vetter",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0010",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "470",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0015",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00284",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with Coronavirus Disease-2019 in Shiyan City, China",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "284",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0020",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective study",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0025",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "CONASS",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0030"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0141076820930665",
"article-title": "Uncertainty and COVID-19: how are we to respond?",
"author": "Koffman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J R Soc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0035",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.039",
"article-title": "Thrombosis risk associated with COVID-19 infection. A scoping review",
"author": "Al-Ani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0040",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-020-02134-3",
"article-title": "COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy",
"author": "Becker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Thrombolysis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0045",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30145-9",
"article-title": "Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Levi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e438",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Haematol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0050",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31209-5",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated hyperviscosity: a link between inflammation and thrombophilia?",
"author": "Maier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1758",
"issue": "10239",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0055",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.018",
"article-title": "Incidence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and elevated D-dimer levels",
"author": "Demelo-Rodriguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0060",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.35772/ghm.2020.01031",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): research progress and clinical practice",
"author": "Kutsuna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "78",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Glob Health Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0065",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"article-title": "COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal",
"author": "Siddiqi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0070",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Bacterial and fungal infections among patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia",
"author": "Antinori",
"first-page": "29",
"issue": "suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Infez Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0075",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.007",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and co-infections of 354 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Lv",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"issue": "45",
"journal-title": "Microbes Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0080",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04407-x",
"author": "Feeney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0085",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Procalcitonin for patient stratification and identification of bacterial co-infection in COVID-19",
"author": "Han",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Med (Lond)",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0090",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.120.017144",
"article-title": "Experience with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in the Coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: implications for Q.T. interval monitoring",
"author": "Ramireddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Am Heart Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0095",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0271",
"article-title": "Ivermectin and COVID-19: keeping rigor in times of urgency",
"author": "Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1156",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0100",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01902-5",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action",
"author": "Rizzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1153",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0105",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12941-020-00368-w",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, a new candidate therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19",
"author": "Sharun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0110",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0115",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04421-z",
"author": "Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0120",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa105",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: a review of early and emerging options",
"author": "McCreary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofaa105",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0125",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102569",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory therapy for the management of severe COVID-19. Beyond the antiviral therapy: a comprehensive review",
"author": "Alijotas-Reig",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0130",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/invivo.11949",
"article-title": "Potential antiviral drugs for SARS-Cov-2 treatment: preclinical findings and ongoing clinical research",
"author": "Bimonte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1597",
"issue": "3 Suppl",
"journal-title": "In Vivo",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0135",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofab358",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0140",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac056",
"article-title": "Retraction to: meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofac056",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0145",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19",
"author": "Popp",
"first-page": "CD015017",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_bb0150",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak - an update on the status",
"author": "Guo, Y.R.",
"first-page": "p.11",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur1",
"volume": "7 (1)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109772",
"article-title": "Potential effect of natural and anabolizan steroids in elderly patient with COVID-19.",
"author": "Karaahmet, F. and O.Z. Karaahmet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 109772",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur2",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "15 drugs being tested to treat COVID-19 and how they would work.",
"author": "Shaffer, L.",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Searching an Effective Therapy for the Coronavirus Pandemic: Do We See Light at the End of the Tunnel?",
"author": "Sharma, M. and S. Surani",
"first-page": "p. 7415",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur4",
"volume": "12 (3)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.804404",
"article-title": "Clinical Evidence Informing Treatment Guidelines on Repurposed Drugs for Hospitalized Patients During the Early COVID-19 Pandemic: Corticosteroids, Anticoagulants, (Hydroxy)chloroquine.",
"author": "Wustner, S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 804404",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur5",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.598038",
"article-title": "Obstacles and Considerations Related to Clinical Trial Research During the COVID-19 Pandemic.",
"author": "Hashem, H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 598038",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur6",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Martinho, K.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur7"
},
{
"author": "Uol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur8"
},
{
"article-title": "ESCMID COVID-19 living guidelines: drug treatment and clinical management.",
"first-page": "p. 222",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur9",
"volume": "28(2)",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-022-00645-8",
"article-title": "Repurposing the drug, Ivermectin, in COVID-19: toxicological points of view.",
"author": "Shirazi, F.M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 21",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur10",
"volume": "27 (1)",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.729559",
"article-title": "Efficacy of COVID-19 Treatments: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.",
"author": "Zhang, C.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 729559",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur11",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19: A systematic review and update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.",
"first-page": "p. 115",
"journal-title": "MedComm",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur12",
"volume": "3 (1)",
"year": "20202022"
},
{
"article-title": "Azithromycin for treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a randomized, multicentre, open-label clinical trial (DAWn-AZITHRO)",
"author": "Gyselinck, I.",
"journal-title": "ERJ Open Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur13",
"volume": "8 (1)",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.01.002",
"article-title": "A Multimodal Strategy to Reduce the Risk of Hospitalization/death in Ambulatory Patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Ascencio-Montiel, I.J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Obesity as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 and Complications: A Review.",
"author": "Demeulemeester, F.",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur15",
"volume": "10 (4)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Adipose tissue in COVID-19: detection of SARS-CoV-2 in adipocytes and activation of the interferon-alpha response.",
"author": "Basolo, A.",
"first-page": "p. 1",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes.",
"author": "Rajpal, A., L. Rahimi, and F. Ismail-Beigi",
"first-page": "p. 895",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur17",
"volume": "12 (12)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12872-022-02548-2",
"article-title": "Does Losartan reduce the severity of COVID-19 in hypertensive patients?",
"author": "Mirjalili, M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 116",
"journal-title": "BMC Cardiovasc Disord",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur18",
"volume": "22 (1)",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00013-8",
"article-title": "Risk of adverse outcomes in patients with underlying respiratory conditions admitted to hospital with COVID-19: a national, multicentre prospective cohort study using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol UK",
"author": "Bloom, C.I.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "p. 699",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur20",
"volume": "9 (7)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "[Rhabdomyolysis as the presentation form of COVID-19 infection. Report of one case]",
"author": "Toro, L.",
"first-page": "p. 796",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Chil",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur21",
"volume": "149 (5)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 and the liver",
"author": "Esteban, J.P., L. Sobotka, and D.C. Rockey",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mcpsp.2022.100346_fur22",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 51,
"references-count": 51,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2603924922000283"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical protocol for early treatment of COVID-19 in a real-world scenario: Results of a series of patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "5"
}