Clinical Effect of the Combination Therapy of Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin and Ivermectin in Patients with COVID-19
Satyanandsathi, Anil Kumar Garg, Amit Mittal, Dr Savita Verma, Virendra Singh Saini, Manoj Kumar Singh, Devinder Vohra, Sushil Kumar
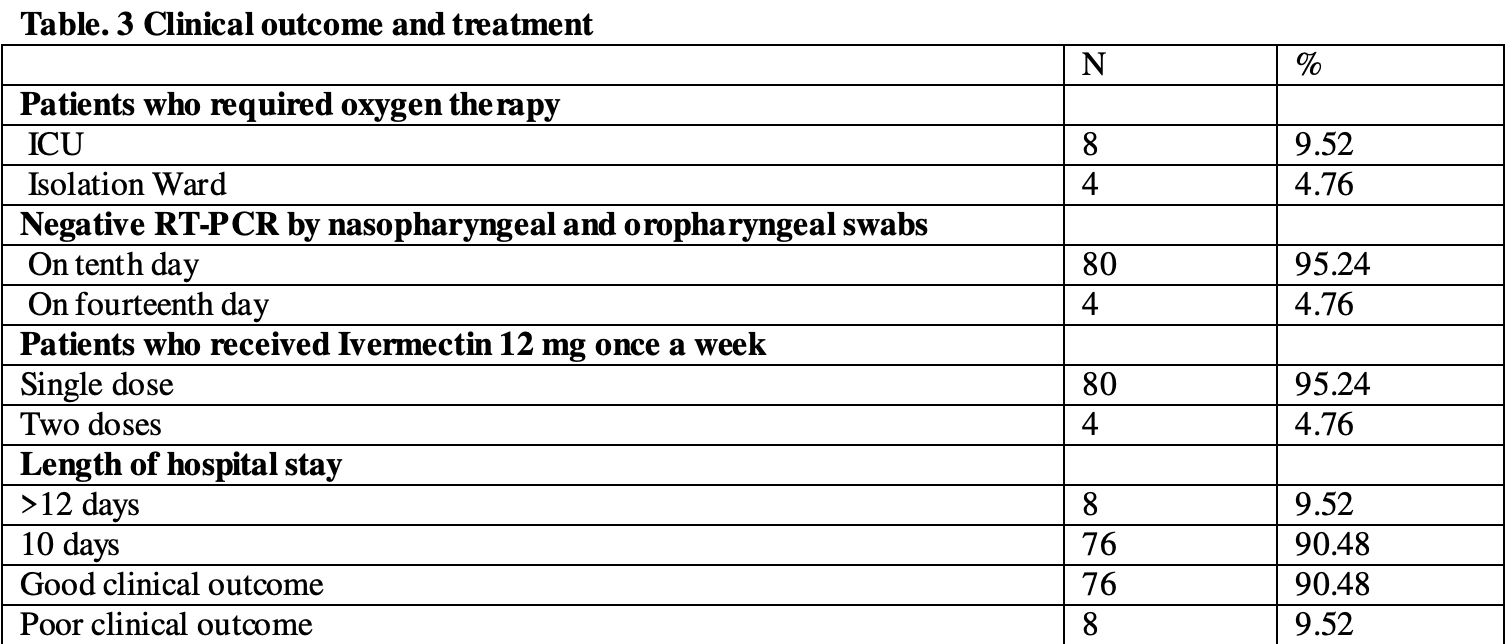
Background: The ongoing pandemic has highlighted the need for an effective treatment of COVID-19 patients and prevention of SARS-CoV-2 community transmission.Methods: We conducted a prospective observational study on a cohort of 85 COVID-19 patients (80% males, median age 46 years, range 18-80 years). Patients were treated with a triple drug therapy: ivermectin 12 mg once a week, hydroxychloroquine 400 mg twice a day on the first day and 200 mg twice a day for the next 4 days, and azithromycin 500 mg once a day for 5 days. Endpoints were assessed by clinical outcomes, death, negative SARS-CoV-2 RNA-PCR test on the tenth day, and length of the hospital stay.Results: All patients improved except one 70-year-old female, who died on the third day of admission. The clinical outcome was considered good as 95.24% (80/84) of patients presented a negative SARS-CoV-2 RNA-PCR test on the tenth day of admission and 90.48% (76/84) were discharged in stable condition.Conclusions: The response must focus on immediate isolation of COVID-19 patients and their early treatment to prevent irreversible severe respiratory injury. Our study shows the beneficial effect of triple drug therapy in terms of clinical recovery, shorter duration of viral carriage, community spread prevention, and minimal cost of therapy.
Conflict of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Funding Statement The authors declare that they have no financial interests related to the material in the manuscript.
Ethics Statement The authors followed the guidelines for human studies and the research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (1964). Information revealing the subject's identity was avoided. Patients gave written informed consent for the study and publication of study data.
References
Andreani, Bideau, Duflot, Jardot, Rolland et al., In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARSCoV-2 shows synergistic effect, Microbial Pathogenesis
Bacharier, Guilbert, Mauger, Boehmer, Beigelman et al., Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Biot, Daher, Chavain, Fandeur, Khalife et al., Design and synthesis of hydroxyferroquine derivatives with antimalarial and antiviral activities, J Med Chem
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDAapproved Drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir Res
Chatre, Roubille, Vernhet, Jorgensen, Pers, Cardiac complications attributed to chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine: a systematic review of the literature, Drug Saf
Chen, Liu, Liu, Liu, Xu et al., A pilot study of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of patients with common coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hoang, Meddeb et al., Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Van Thuan, Hoang et al., clinical and microbiological effect of a combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in 80 COVID-19 patients with at least a six-day follow up: a pilot observational study, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Harapanharapan, Yufika, Wirawinardi, Synatkeam, Haypheng, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review, Journal of Infection and Public Health
Lu, Stratton, Tang, Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology inWuhan China: the mystery and the miracle, J Med Virol
Madrid, Panchal, Warren, Shurtleff, Endsley et al., Evaluation of Ebola Virus Inhibitors for Drug Repurposing, ACS Infect Dis
Marmor, Kellner, Lai, Melles, Mieler, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Recommendations on Screening for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy (2016Revision), Ophthalmology
Million, Lagier, Gautret, Colson, Fournier et al., Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective analysis of 1061 cases in Marseille; France, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Mo, Yuan, Tao, Peng, Wang, Time kinetics of viral clearance and resolution of symptoms in novel coronavirus infection, Am J RespirCrit Care Med
Molinaa, Delaugerreb, Le Goffb, Mela-Limaad, Ponscarmeal et al., Letter to the editor ; No evidence of rapid antiviral clearance or clinical ben-efit with the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection, Médecineet maladies infectieuses
Perica`s, Hernandez-Meneses, Sheahan, Quintana, Ambrosioni et al., COVID-19: from epidemiology to treatment, European Heart Journal
Retallack, Lullo, Arias, Knopp, Laurie et al., Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin, ProcNatlAcadSci U S A
Smith, Sausville, Vishruthgirish, Lou Yuan, Anandvasudevan et al., Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Inflammatory Signaling Increase the Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 in the Respiratory Tract, Developmental Cell June
To, Tsang, Leung, Tam, Wu et al., Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an observational cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Wang, Pan, Zhang, Han, Zhao, Epidemiological and clinical features of 125 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Fuyang, Anhui, China, Int J Infect Dis
Who Director, General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 -11
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, J Am Med Assoc
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet