A phase 2 single center open label randomised control trial for convalescent plasma therapy in patients with severe COVID-19
Yogiraj Ray, Shekhar Ranjan Paul, Purbita Bandopadhyay, Ranit D’rozario, Jafar Sarif, Deblina Raychaudhuri, Debaleena Bhowmik, Abhishake Lahiri, Janani Srinivasa Vasudevan, Ranjeet Maurya, Akshay Kanakan, Sachin Sharma, Manish Kumar, Praveen Singh, Rammohan Roy, Kausik Chaudhury, Rajsekhar Maiti, Saugata Bagchi, Ayan Maiti, Md. Masoom Perwez, Abhinandan Mondal, Avinash Tewari, Samik Mandal, Arpan Roy, Moumita Saha, Durba Biswas, Chikam Maiti, Ritwik Bhaduri, Sayantan Chakraborty, Biswanath Sharma Sarkar, Anima Haldar, Bibhuti Saha, Shantanu Sengupta, Rajesh Pandey, Shilpak Chatterjee, Prasun Bhattacharya, Sandip Paul, Dipyaman Ganguly
Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28064-7
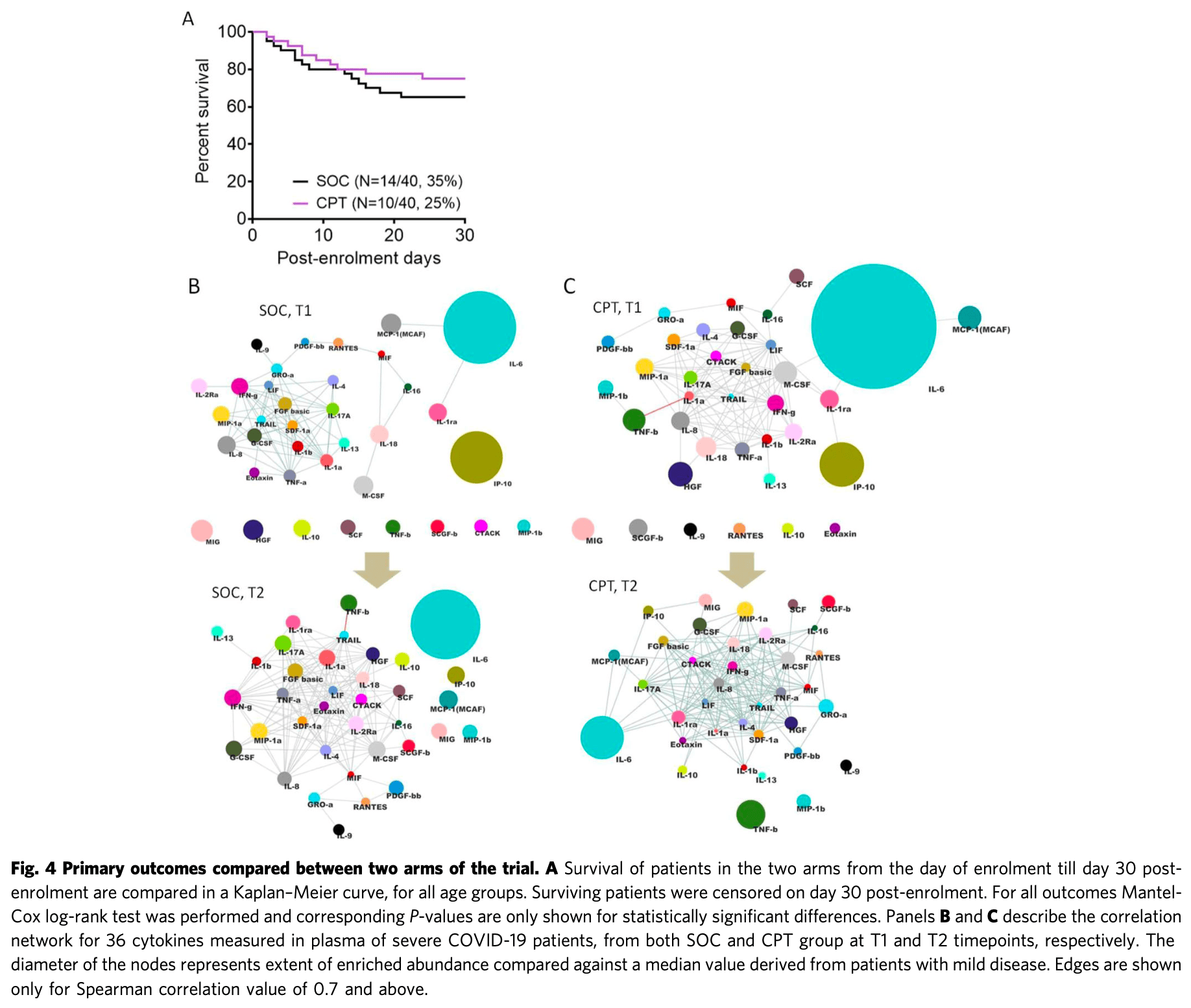
A single center open label phase 2 randomised control trial (Clinical Trial Registry of India No. CTRI/2020/05/025209) was done to assess clinical and immunological benefits of passive immunization using convalescent plasma therapy. At the Infectious Diseases and Beleghata General Hospital in Kolkata, India, 80 patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 disease and fulfilling the inclusion criteria (aged more than 18 years, with either mild ARDS having PaO2/FiO2 200-300 or moderate ARDS having PaO2/FiO2 100-200, not on mechanical ventilation) were recruited and randomized into either standard of care (SOC) arm (N = 40) or the convalescent plasma therapy (CPT) arm (N = 40). Primary outcomes were all-cause mortality by day 30 of enrolment and immunological correlates of response to therapy if any, for which plasma abundance of a large panel of cytokines was quantitated before and after intervention to assess the effect of CPT on the systemic hyper-inflammation encountered in these patients. The secondary outcomes were recovery from ARDS and time taken to negative viral RNA PCR as well as to report any adverse reaction to plasma therapy. Transfused convalescent plasma was characterized in terms of its neutralizing antibody content as well as proteome. The trial was completed and it was found that primary outcome of all-cause mortality was not significantly different among severe COVID-19 patients with ARDS randomized to two treatment arms (Mantel-Haenszel Hazard Ratio 0.6731, 95% confidence interval 0.3010-1.505, with a P value of 0.3424 on Mantel-Cox Log-rank test). No adverse effect was reported with CPT. In severe COVID-19 patients with mild or moderate ARDS no significant clinical benefit was registered in this clinical trial with convalescent plasma therapy in terms of prespecified outcomes.
Reporting summary. Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability All information regarding the availability of data and materials can be addressed to the corresponding authors. De-identified clinical data and experimental data are available on request sharing, which may need approval of the institutional ethical committees. The clinical outcome data for individual participants are provided in supplemental Table 4, which can be used for meta-analyses. The trial protocol is available as supplementary note 1 within the supplementary information file. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE partner repository 46 , with the dataset identifier PXD025453. The SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences have been uploaded on NCBI GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) with the GenBank accession number(s) OM169294-OM169315 and GISAID (https:// www.gisaid.org/) with IDs between EPI_ISL_1672634-EPI_ISL_1672658. Source data are provided with this paper.
Author contributions
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28064-7. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Yogiraj Ray or Dipyaman Ganguly. Peer review information Nature Communications..
References
Agarwal, Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ,
doi:10.1136/bmj.m3939Arunachalam, Systems biological assessment of immunity to mild versus severe COVID-19 infection in humans, Science
Avendaño-Solá, A multicenter randomized open-label clinical trial for convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia, J. Clin. Invest
Balcells, Early versus deferred anti-SARS-CoV-2 convalescent plasma in patients admitted for COVID-19: A randomized phase II clinical trial, PLoS Med
Bandopadhyay, Nature and dimensions of the systemic hyperinflammation and its attenuation by convalescent plasma in severe COVID-19, J. Infect. Dis
Billett, Anticoagulation in COVID-19: effect of enoxaparin, heparin, and apixaban on mortality, Thromb. Haemost
Briggs, Early but not late convalescent plasma is associated with better survival in moderate-to-severe COVID-19, PLoS ONE
Bégin, Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial, Nat. Med
Cao, The effectiveness of convalescent plasma for the treatment of novel corona virus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Med
Casadevall, Convalescent plasma use in the USA was inversely correlated with COVID-19 mortality, Elife
Duan, Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci
Edgar, MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput, Nucleic Acids Res
Gharbharan, Effects of potent neutralizing antibodies from convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat. Commun
Goldman, Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Hadfield, Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution, Bioinformatics
Hamilton, Is convalescent plasma futile in COVID-19? A Bayesian re-analysis of the RECOVERY randomized controlled trial, Int. J. Infect. Dis
Horby, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19preliminary report, N. Engl. J. Med
Huang, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Investigators, Effect of convalescent plasma on organ support-free days in critically Ill patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Janiaud, Association of convalescent plasma treatment with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA
Joyner, Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 20,000 hospitalized patients, Mayo Clin. Proc
Khan, Usefulness of convalescent plasma transfusion for the treatment of severely ill COVID-19 patients in Pakistan, BMC Infect. Dis
Kirenga, Efficacy of convalescent plasma for treatment of COVID-19 in Uganda, BMJ Open Respir. Res
Klassen, Convalescent plasma therapy for COVID-19: a graphical mosaic of the worldwide evidence, Front. Med
Klassen, The effect of convalescent plasma therapy on mortality among patients with COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Mayo Clin. Proc
Körper, Results of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19, J. Clin. Invest
Laing, A dynamic COVID-19 immune signature includes associations with poor prognosis, Nat. Med
Li, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Li, Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences, Bioinformatics
Libster, Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults, N. Engl. J. Med
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol
Liu, Convalescent plasma treatment of severe COVID-19: a propensity score-matched control study, Nat. Med
Loman, Quick, Simpson, A complete bacterial genome assembled de novo using only nanopore sequencing data, Nat. Methods
Lucas, Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19, Nature
Nickerson, Doucette, Rapid and quantitative protein precipitation for proteome analysis by mass spectrometry, J. Proteome Res
O'donnell, A randomized double-blind controlled trial of convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19, J. Clin. Invest
Okonechnikov, Golosova, Fursov, Ugene Team, Unipro UGENE: a unified bioinformatics toolkit, Bioinformatics
Perez-Riverol, The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data, Nucleic Acids Res
Rasheed, The therapeutic potential of convalescent plasma therapy on treating critically-ill COVID-19 patients residing in respiratory care units in hospitals in Baghdad, Iraq, Infez. Med
Rubin, Testing an old therapy against a new disease: convalescent plasma for COVID-19, JAMA
Sekine, Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: an open-label, randomised clinical trial, Eur. Respir. J,
doi:10.1183/13993003.01471-2021Simonovich, A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia, N. Engl. J. Med
Tan, A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction, Nat. Biotechnol
{ 'indexed': {'date-parts': [[2024, 8, 6]], 'date-time': '2024-08-06T20:13:24Z', 'timestamp': 1722975204267},
'reference-count': 46,
'publisher': 'Springer Science and Business Media LLC',
'issue': '1',
'license': [ { 'start': { 'date-parts': [[2022, 1, 19]],
'date-time': '2022-01-19T00:00:00Z',
'timestamp': 1642550400000},
'content-version': 'tdm',
'delay-in-days': 0,
'URL': 'https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0'},
{ 'start': { 'date-parts': [[2022, 1, 19]],
'date-time': '2022-01-19T00:00:00Z',
'timestamp': 1642550400000},
'content-version': 'vor',
'delay-in-days': 0,
'URL': 'https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0'}],
'funder': [ { 'DOI': '10.13039/501100001412',
'name': 'Council of Scientific and Industrial Research',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'award': ['MLP129'],
'id': [{'id': '10.13039/501100001412', 'id-type': 'DOI', 'asserted-by': 'publisher'}]}],
'content-domain': {'domain': ['link.springer.com'], 'crossmark-restriction': False},
'abstract': '<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>A single center open label phase 2 randomised '
'control trial (Clinical Trial Registry of India No. CTRI/2020/05/025209) was done to assess '
'clinical and immunological benefits of passive immunization using convalescent plasma '
'therapy. At the Infectious Diseases and Beleghata General Hospital in Kolkata, India, 80 '
'patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 disease and fulfilling the inclusion criteria '
'(aged more than 18 years, with either mild ARDS having PaO2/FiO2 200–300 or moderate ARDS '
'having PaO2/FiO2 100–200, not on mechanical ventilation) were recruited and randomized into '
'either standard of care (SOC) arm (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic>\u2009=\u200940) or the '
'convalescent plasma therapy (CPT) arm (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic>\u2009=\u200940). Primary '
'outcomes were all-cause mortality by day 30 of enrolment and immunological correlates of '
'response to therapy if any, for which plasma abundance of a large panel of cytokines was '
'quantitated before and after intervention to assess the effect of CPT on the systemic '
'hyper-inflammation encountered in these patients. The secondary outcomes were recovery from '
'ARDS and time taken to negative viral RNA PCR as well as to report any adverse reaction to '
'plasma therapy. Transfused convalescent plasma was characterized in terms of its neutralizing '
'antibody content as well as proteome. The trial was completed and it was found that primary '
'outcome of all-cause mortality was not significantly different among severe COVID-19 patients '
'with ARDS randomized to two treatment arms (Mantel-Haenszel Hazard Ratio 0.6731, 95% '
'confidence interval 0.3010-1.505, with a P value of 0.3424 on Mantel-Cox Log-rank test). No '
'adverse effect was reported with CPT. In severe COVID-19 patients with mild or moderate ARDS '
'no significant clinical benefit was registered in this clinical trial with convalescent '
'plasma therapy in terms of prespecified outcomes.</jats:p>',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41467-022-28064-7',
'type': 'journal-article',
'created': {'date-parts': [[2022, 1, 19]], 'date-time': '2022-01-19T11:02:56Z', 'timestamp': 1642590176000},
'update-policy': 'http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy',
'source': 'Crossref',
'is-referenced-by-count': 34,
'title': 'A phase 2 single center open label randomised control trial for convalescent plasma therapy in '
'patients with severe COVID-19',
'prefix': '10.1038',
'volume': '13',
'author': [ {'given': 'Yogiraj', 'family': 'Ray', 'sequence': 'first', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Shekhar Ranjan', 'family': 'Paul', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Purbita', 'family': 'Bandopadhyay', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Ranit', 'family': 'D’Rozario', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Jafar', 'family': 'Sarif', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Deblina', 'family': 'Raychaudhuri', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Debaleena', 'family': 'Bhowmik', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Abhishake', 'family': 'Lahiri', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{ 'given': 'Janani Srinivasa',
'family': 'Vasudevan',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []},
{ 'ORCID': 'http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0306-8970',
'authenticated-orcid': False,
'given': 'Ranjeet',
'family': 'Maurya',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Akshay', 'family': 'Kanakan', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Sachin', 'family': 'Sharma', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Manish', 'family': 'Kumar', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Praveen', 'family': 'Singh', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{ 'ORCID': 'http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7273-4132',
'authenticated-orcid': False,
'given': 'Rammohan',
'family': 'Roy',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Kausik', 'family': 'Chaudhury', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Rajsekhar', 'family': 'Maiti', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Saugata', 'family': 'Bagchi', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Ayan', 'family': 'Maiti', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Md. Masoom', 'family': 'Perwez', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Abhinandan', 'family': 'Mondal', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Avinash', 'family': 'Tewari', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Samik', 'family': 'Mandal', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Arpan', 'family': 'Roy', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Moumita', 'family': 'Saha', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Durba', 'family': 'Biswas', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Chikam', 'family': 'Maiti', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{ 'ORCID': 'http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1909-6167',
'authenticated-orcid': False,
'given': 'Ritwik',
'family': 'Bhaduri',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Sayantan', 'family': 'Chakraborty', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Biswanath Sharma', 'family': 'Sarkar', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Anima', 'family': 'Haldar', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Bibhuti', 'family': 'Saha', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{ 'ORCID': 'http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8461-0735',
'authenticated-orcid': False,
'given': 'Shantanu',
'family': 'Sengupta',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Rajesh', 'family': 'Pandey', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Shilpak', 'family': 'Chatterjee', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Prasun', 'family': 'Bhattacharya', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{ 'ORCID': 'http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7406-3598',
'authenticated-orcid': False,
'given': 'Sandip',
'family': 'Paul',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []},
{ 'ORCID': 'http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7786-1795',
'authenticated-orcid': False,
'given': 'Dipyaman',
'family': 'Ganguly',
'sequence': 'additional',
'affiliation': []}],
'member': '297',
'published-online': {'date-parts': [[2022, 1, 19]]},
'reference': [ { 'key': '28064_CR1',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '497',
'DOI': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5',
'volume': '395',
'author': 'C Huang',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Huang, C. et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel '
'coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395, 497–506 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Lancet'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR2',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e192',
'DOI': '10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7',
'volume': '20',
'author': 'WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 '
'infection.',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of '
'COVID-19 infection. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 '
'clinical research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 20, e192–e197 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Lancet Infect. Dis.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR3',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '11',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4',
'volume': '17',
'author': 'S Lim',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Lim, S., Bae, J. H., Kwon, H. S. & Nauck, M. A. COVID-19 and diabetes '
'mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat. Rev. '
'Endocrinol. 17, 11–30 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR4',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '623',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41591-020-01186-5',
'volume': '26',
'author': 'AG Laing',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Laing, A. G. et al. A dynamic COVID-19 immune signature includes '
'associations with poor prognosis. Nat. Med. 26, 623–1635 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Med'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR5',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1210',
'DOI': '10.1126/science.abc6261',
'volume': '369',
'author': 'PS Arunachalam',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Arunachalam, P. S. et al. Systems biological assessment of immunity to '
'mild versus severe COVID-19 infection in humans. Science 369, 1210–1220 '
'(2020).',
'journal-title': 'Science'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR6',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '463',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41586-020-2588-y',
'volume': '584',
'author': 'C Lucas',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Lucas, C. et al. Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in '
'severe COVID-19. Nature 584, 463–469 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Nature'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR7',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '827',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa2015301',
'volume': '383',
'author': 'JD Goldman',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Goldman, J. D. et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with '
'Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 827–1837 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'N. Engl. J. Med'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR8',
'first-page': '93',
'volume': '384',
'author': 'P Horby',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Horby, P. et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with '
'Covid-19—preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 93–704 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'N. Engl. J. Med'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR9',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1691',
'DOI': '10.1055/s-0040-1720978',
'volume': '120',
'author': 'HH Billett',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Billett, H. H. et al. Anticoagulation in COVID-19: effect of enoxaparin, '
'heparin, and apixaban on mortality. Thromb. Haemost. 120, 1691–1699 '
'(2020).',
'journal-title': 'Thromb. Haemost'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR10',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '2114',
'DOI': '10.1001/jama.2020.7456',
'volume': '323',
'author': 'R Rubin',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Rubin, R. Testing an old therapy against a new disease: convalescent '
'plasma for COVID-19. JAMA 323, 2114–2117 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'JAMA'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR11',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1888',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.028',
'volume': '95',
'author': 'MJ Joyner',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Joyner, M. J. et al. Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in '
'20,000 hospitalized patients. Mayo Clin. Proc. 95, 1888–1897 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Mayo Clin. Proc.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR12',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'm3939',
'DOI': '10.1136/bmj.m3939',
'volume': '371',
'author': 'A Agarwal',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Agarwal, A. et al. Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate '
'covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised '
'controlled trial (PLACID Trial). BMJ 371, m3939, '
'https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3939 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'BMJ'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR13',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '460',
'DOI': '10.1001/jama.2020.10044',
'volume': '324',
'author': 'L Li',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Li, L. et al. Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical '
'improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a '
'randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324, 460–470 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'JAMA'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR14',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '619',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa2031304',
'volume': '384',
'author': 'VA Simonovich',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Simonovich, V. A. et al. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in '
'Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 619–629 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'N. Engl. J. Med'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR15',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41467-021-23469-2',
'volume': '12',
'author': 'A Gharbharan',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Gharbharan, A. et al. Effects of potent neutralizing antibodies from '
'convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized for severe SARS-CoV-2 '
'infection. Nat. Commun. 12, 3189 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Commun.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR16',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e1003415',
'DOI': '10.1371/journal.pmed.1003415',
'volume': '18',
'author': 'ME Balcells',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Balcells, M. E. et al. Early versus deferred anti-SARS-CoV-2 '
'convalescent plasma in patients admitted for COVID-19: A randomized '
'phase II clinical trial. PLoS Med. 18, e1003415 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'PLoS Med.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR17',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'unstructured': 'Sekine, L. et al. Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised '
'patients: an open-label, randomised clinical trial. Eur. Respir. J. '
'https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01471-2021 (2021).',
'DOI': '10.1183/13993003.01471-2021'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR18',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'unstructured': 'Devos, T. et al. Early high antibody-titre convalescent plasma for '
'hospitalised COVID-19 patients: DAWn-plasma. Eur. Respir. J. '
'https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01724-2021 (2021).',
'DOI': '10.1183/13993003.01724-2021'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR19',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e001017',
'DOI': '10.1136/bmjresp-2021-001017',
'volume': '8',
'author': 'B Kirenga',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Kirenga, B. et al. Efficacy of convalescent plasma for treatment of '
'COVID-19 in Uganda. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 8, e001017 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'BMJ Open Respir. Res.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR20',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '2012',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41591-021-01488-2',
'volume': '27',
'author': 'P Bégin',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Bégin, P. et al. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with '
'COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Nat. Med. 27, '
'2012–2024 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Med'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR21',
'unstructured': 'Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators et al. Effect of '
'convalescent plasma on organ support-free days in critically Ill '
'patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 326, 690–1702 '
'(2021).'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR22',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '9490',
'DOI': '10.1073/pnas.2004168117',
'volume': '117',
'author': 'K Duan',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Duan, K. et al. Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe '
'COVID-19 patients. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 9490–9496 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR23',
'first-page': '357',
'volume': '28',
'author': 'AM Rasheed',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Rasheed, A. M. et al. The therapeutic potential of convalescent plasma '
'therapy on treating critically-ill COVID-19 patients residing in '
'respiratory care units in hospitals in Baghdad, Iraq. Infez. Med. 28, '
'357–366 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Infez. Med.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR24',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'unstructured': 'Yoon, H. A. et al. Treatment of Severe COVID-19 with Convalescent Plasma '
'in the Bronx, NYC. Preprint at '
'https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.02.20242909v1.full, '
'https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.02.20242909',
'DOI': '10.1101/2020.12.02.20242909'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR25',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1708',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41591-020-1088-9',
'volume': '26',
'author': 'STH Liu',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Liu, S. T. H. et al. Convalescent plasma treatment of severe COVID-19: a '
'propensity score-matched control study. Nat. Med. 26, 1708–1713 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Med.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR26',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'DOI': '10.1186/s12879-021-06451-7',
'volume': '21',
'author': 'TNS Khan',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Khan, T. N. S. et al. Usefulness of convalescent plasma transfusion for '
'the treatment of severely ill COVID-19 patients in Pakistan. BMC Infect. '
'Dis. 21, 1014 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'BMC Infect. Dis.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR27',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e0254453',
'DOI': '10.1371/journal.pone.0254453',
'volume': '16',
'author': 'N Briggs',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Briggs, N. et al. Early but not late convalescent plasma is associated '
'with better survival in moderate-to-severe COVID-19. PLoS ONE 16, '
'e0254453 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'PLoS ONE'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR28',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '610',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa2033700',
'volume': '384',
'author': 'R Libster',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Libster, R. et al. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe '
'Covid-19 in older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 610–618 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'N. Engl. J. Med'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR29',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e150646',
'DOI': '10.1172/JCI150646',
'volume': '131',
'author': 'MR O’Donnell',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'O’Donnell, M. R. et al. A randomized double-blind controlled trial of '
'convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19. J. Clin. Invest. '
'131, e150646 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'J. Clin. Invest.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR30',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e152264',
'DOI': '10.1172/JCI152264',
'volume': '131',
'author': 'S Körper',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Körper, S. et al. Results of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose '
'convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19. J. Clin. Invest. '
'131, e152264 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'J. Clin. Invest.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR31',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e152740',
'DOI': '10.1172/JCI152740',
'volume': '131',
'author': 'C Avendaño-Solá',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Avendaño-Solá, C. et al. A multicenter randomized open-label clinical '
'trial for convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 '
'pneumonia. J. Clin. Invest. 131, e152740 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'J. Clin. Invest.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR32',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1185',
'DOI': '10.1001/jama.2021.2747',
'volume': '325',
'author': 'P Janiaud',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Janiaud, P. et al. Association of convalescent plasma treatment with '
'clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and '
'meta-analysis. JAMA 325, 1185–1195 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'JAMA'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR33',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1262',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.02.008',
'volume': '96',
'author': 'SA Klassen',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Klassen, S. A. et al. The effect of convalescent plasma therapy on '
'mortality among patients with COVID-19: systematic review and '
'meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 96, 1262–1275 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Mayo Clin. Proc.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR34',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '641429',
'DOI': '10.3389/fmed.2021.641429',
'volume': '8',
'author': 'H Cao',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Cao, H. et al. The effectiveness of convalescent plasma for the '
'treatment of novel corona virus disease 2019: a systematic review and '
'meta-analysis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, 641429 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Front. Med. (Lausanne)'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR35',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'e69866',
'DOI': '10.7554/eLife.69866',
'volume': '10',
'author': 'A Casadevall',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Casadevall, A. et al. Convalescent plasma use in the USA was inversely '
'correlated with COVID-19 mortality. Elife 10, e69866 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Elife'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR36',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '114',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.ijid.2021.06.034',
'volume': '109',
'author': 'FW Hamilton',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Hamilton, F. W. et al. Is convalescent plasma futile in COVID-19? A '
'Bayesian re-analysis of the RECOVERY randomized controlled trial. Int. '
'J. Infect. Dis. 109, 114–117 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Int. J. Infect. Dis.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR37',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '684151',
'DOI': '10.3389/fmed.2021.684151',
'volume': '8',
'author': 'SA Klassen',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Klassen, S. A. et al. Convalescent plasma therapy for COVID-19: a '
'graphical mosaic of the worldwide evidence. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, '
'684151 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'Front. Med. (Lausanne)'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR38',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1073',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41587-020-0631-z',
'volume': '38',
'author': 'CW Tan',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Tan, C. W. et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based '
'on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. '
'Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 1073–1078 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Biotechnol.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR39',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '65',
'DOI': '10.1093/infdis/jiab010',
'volume': '224',
'author': 'P Bandopadhyay',
'year': '2021',
'unstructured': 'Bandopadhyay, P. et al. Nature and dimensions of the systemic '
'hyperinflammation and its attenuation by convalescent plasma in severe '
'COVID-19. J. Infect. Dis. 224, 65–574 (2021).',
'journal-title': 'J. Infect. Dis'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR40',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '3094',
'DOI': '10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191',
'volume': '34',
'author': 'H Li',
'year': '2018',
'unstructured': 'Li, H. Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 34, '
'3094–3100 (2018).',
'journal-title': 'Bioinformatics'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR41',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '733',
'DOI': '10.1038/nmeth.3444',
'volume': '12',
'author': 'NJ Loman',
'year': '2015',
'unstructured': 'Loman, N. J., Quick, J. & Simpson, J. T. A complete bacterial genome '
'assembled de novo using only nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 12, '
'733–735 (2015).',
'journal-title': 'Nat. Methods'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR42',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1792',
'DOI': '10.1093/nar/gkh340',
'volume': '32',
'author': 'RC Edgar',
'year': '2004',
'unstructured': 'Edgar, R. C. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and '
'high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797 (2004).',
'journal-title': 'Nucleic Acids Res.'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR43',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '1166',
'DOI': '10.1093/bioinformatics/bts091',
'volume': '28',
'author': 'K Okonechnikov',
'year': '2012',
'unstructured': 'Okonechnikov, K., Golosova, O. & Fursov, M., UGENE team. Unipro UGENE: a '
'unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 28, 1166–1167 (2012).',
'journal-title': 'Bioinformatics'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR44',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '4121',
'DOI': '10.1093/bioinformatics/bty407',
'volume': '34',
'author': 'J Hadfield',
'year': '2018',
'unstructured': 'Hadfield, J. et al. Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen '
'evolution. Bioinformatics 34, 4121–4123 (2018).',
'journal-title': 'Bioinformatics'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR45',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': '2035',
'DOI': '10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00867',
'volume': '19',
'author': 'JL Nickerson',
'year': '2020',
'unstructured': 'Nickerson, J. L. & Doucette, A. A. Rapid and quantitative protein '
'precipitation for proteome analysis by mass spectrometry. J. Proteome '
'Res. 19, 2035–2042 (2020).',
'journal-title': 'J. Proteome Res'},
{ 'key': '28064_CR46',
'doi-asserted-by': 'publisher',
'first-page': 'D442',
'DOI': '10.1093/nar/gky1106',
'volume': '47',
'author': 'Y Perez-Riverol',
'year': '2019',
'unstructured': 'Perez-Riverol, Y. et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and '
'resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic '
'Acids Res. 47, D442–D450 (2019).',
'journal-title': 'Nucleic Acids Res.'}],
'container-title': 'Nature Communications',
'original-title': [],
'language': 'en',
'link': [ { 'URL': 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-28064-7.pdf',
'content-type': 'application/pdf',
'content-version': 'vor',
'intended-application': 'text-mining'},
{ 'URL': 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-28064-7',
'content-type': 'text/html',
'content-version': 'vor',
'intended-application': 'text-mining'},
{ 'URL': 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-28064-7.pdf',
'content-type': 'application/pdf',
'content-version': 'vor',
'intended-application': 'similarity-checking'}],
'deposited': { 'date-parts': [[2022, 11, 24]],
'date-time': '2022-11-24T16:07:22Z',
'timestamp': 1669306042000},
'score': 1,
'resource': {'primary': {'URL': 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-28064-7'}},
'subtitle': [],
'short-title': [],
'issued': {'date-parts': [[2022, 1, 19]]},
'references-count': 46,
'journal-issue': {'issue': '1', 'published-online': {'date-parts': [[2022, 12]]}},
'alternative-id': ['28064'],
'URL': 'http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28064-7',
'relation': { 'has-preprint': [ { 'id-type': 'doi',
'id': '10.1101/2020.11.25.20237883',
'asserted-by': 'object'}]},
'ISSN': ['2041-1723'],
'subject': [],
'container-title-short': 'Nat Commun',
'published': {'date-parts': [[2022, 1, 19]]},
'assertion': [ { 'value': '19 February 2021',
'order': 1,
'name': 'received',
'label': 'Received',
'group': {'name': 'ArticleHistory', 'label': 'Article History'}},
{ 'value': '7 January 2022',
'order': 2,
'name': 'accepted',
'label': 'Accepted',
'group': {'name': 'ArticleHistory', 'label': 'Article History'}},
{ 'value': '19 January 2022',
'order': 3,
'name': 'first_online',
'label': 'First Online',
'group': {'name': 'ArticleHistory', 'label': 'Article History'}},
{ 'value': 'The authors declare no competing interests.',
'order': 1,
'name': 'Ethics',
'group': {'name': 'EthicsHeading', 'label': 'Competing interests'}}],
'article-number': '383'}