Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial
Christopher C Butler, F D Richard Hobbs, Oghenekome A Gbinigie, Najib M Rahman, Gail Hayward, Duncan B Richards, Jienchi Dorward, David M Lowe, Joseph F Standing, Judith Breuer, Saye Khoo, PhD Stavros Petrou, Kerenza Hood, Jonathan S Nguyen-Van-Tam, Prof Mahendra G Patel, Benjamin R Saville, Joe Marion, Emma Ogburn, Julie Allen, Heather Rutter, Nick Francis, Nicholas P B Thomas, Philip Evans, Melissa Dobson, Tracie-Ann Madden, Jane Holmes, Victoria Harris, May Ee Png, Mark Lown, Oliver Van Hecke, Michelle A Detry, Christina T Saunders, Mark Fitzgerald, Nicholas S Berry, Lazaro Mwandigha, Ushma Galal, Sam Mort, Bhautesh D Jani, Nigel D Hart, Haroon Ahmed, Daniel Butler, Micheal Mckenna, Jem Chalk, Layla Lavallee, Elizabeth Hadley, Lucy Cureton, Magdalena Benysek, Monique Andersson, Maria Coates, Sarah Barrett, Clare Bateman, Jennifer C Davies, Ivy Raymundo-Wood, Andrew Ustianowski, Andrew Carson-Stevens, Ly-Mee Yu, Paul Little, Akosua A Agyeman, Tanveer Ahmed, Damien Allcock, Adrian Beltran-Martinez, Oluseye E Benedict, Nigel Bird, Laura Brennan, Julianne Brown, Gerard Burns, Mike Butler, Zelda Cheng, Ruth Danson, Nigel De Kare-Silver, Devesh Dhasmana, Jon Dickson, Serge Engamba, Stacey Fisher, Robin Fox, Eve Frost, Richard Gaunt, Sarit Ghosh, Ishtiaq Gilkar, Anna Goodman, Steve Granier, Aleksandra Howell, Iqbal Hussain, Simon Hutchinson, Marie Imlach, Greg Irving, Nicholas Jacobsen, James Kennard, Umar Khan, Kyle Knox, Christopher Krasucki, Tom Law, Rem Lee, Nicola Lester, David Lewis, James Lunn, Claire I Mackintosh, Mehul Mathukia, Patrick Moore, Seb Morton, Daniel Murphy, Rhiannon Nally, Chinonso Ndukauba, Olufunto Ogundapo, Henry Okeke, Amit Patel, Kavil Patel, Ruth Penfold, Satveer Poonian, Olajide Popoola, Alexander Pora, Vibhore Prasad, Rishabh Prasad, Omair Razzaq, Scot Richardson, Simon Royal, Afsana Safa, Satash Sehdev, Tamsin Sevenoaks, Divya Shah, Aadil Sheikh, Baljinder Vanessa Short, Baljinder S Sidhu, Ivor Singh, Yusuf Soni, Chris Thalasselis, Pete Wilson, David Wingfield, Michael Wong, Maximillian N J Woodall, Nick Wooding, Sharon Woods, Joanna Yong, Francis Yongblah, Azhar Zafar
The Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(22)02597-1
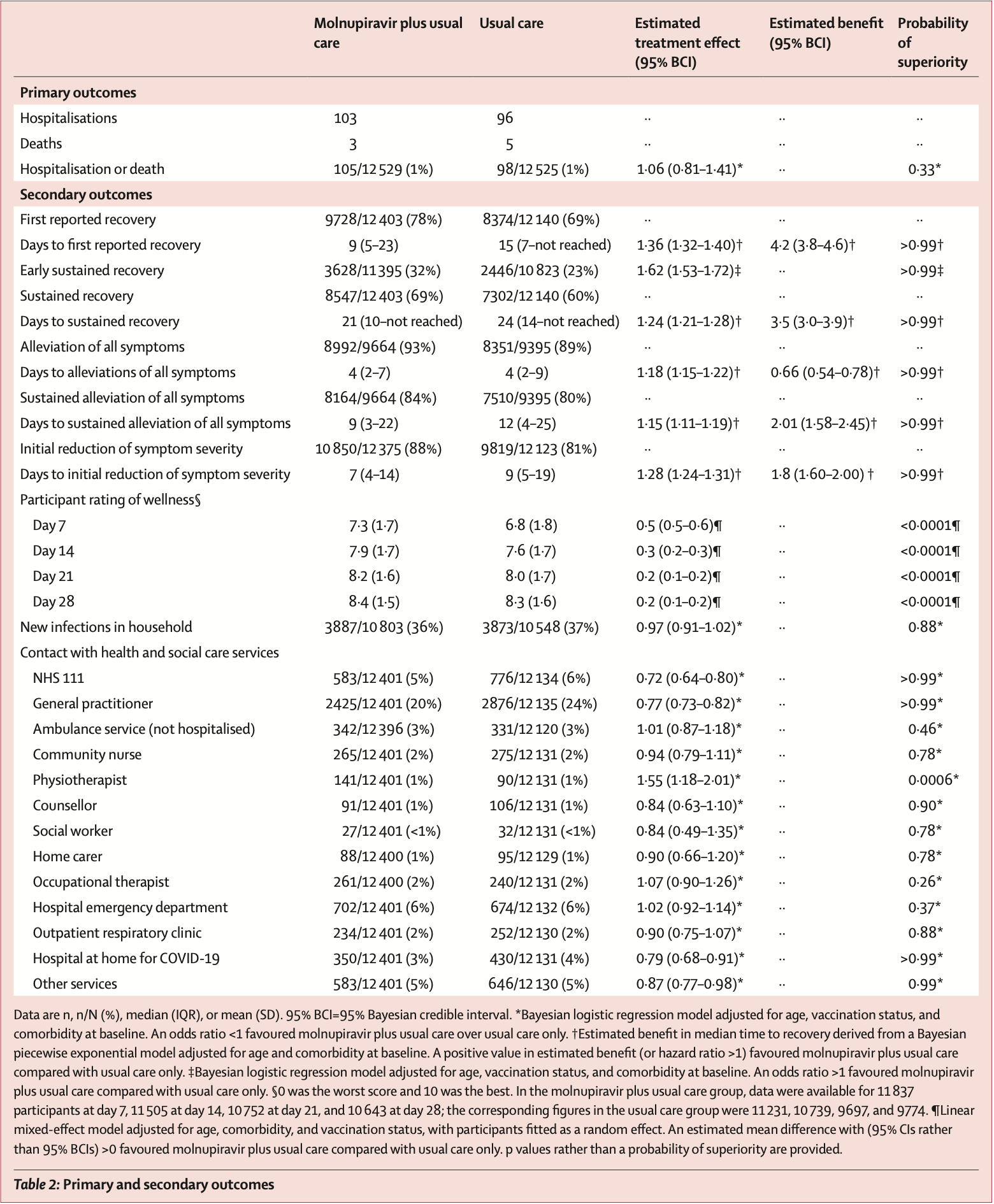
Background The safety, effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness of molnupiravir, an oral antiviral medication for SARS-CoV-2, has not been established in vaccinated patients in the community at increased risk of morbidity and mortality from COVID-19. We aimed to establish whether the addition of molnupiravir to usual care reduced hospital admissions and deaths associated with COVID-19 in this population. Methods PANORAMIC was a UK-based, national, multicentre, open-label, multigroup, prospective, platform adaptive randomised controlled trial. Eligible participants were aged 50 years or older-or aged 18 years or older with relevant comorbidities-and had been unwell with confirmed COVID-19 for 5 days or fewer in the community. Participants were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive 800 mg molnupiravir twice daily for 5 days plus usual care or usual care only. A secure, web-based system (Spinnaker) was used for randomisation, which was stratified by age (<50 years vs ≥50 years) and vaccination status (yes vs no). COVID-19 outcomes were tracked via a self-completed online daily diary for 28 days after randomisation. The primary outcome was all-cause hospitalisation or death within 28 days of randomisation, which was analysed using Bayesian models in all eligible participants who were randomly assigned. This trial is registered with ISRCTN, number 30448031.
References
Abdelnabi, Foo, Kaptein, The combined treatment of molnupiravir and favipiravir results in a potentiation of antiviral efficacy in a SARS-CoV-2 hamster infection model, EBioMedicine
Agarwal, Rochwerg, Lamontagne, A living WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19, BMJ
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Burki, Omicron variant and booster COVID-19 vaccines, Lancet Respir Med
Butler, Yu, Dorward, Doxycycline for community treatment of suspected COVID-19 in people at high risk of adverse outcomes in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, openlabel, adaptive platform trial, Lancet Respir Med
Caraco, Crofoot, Moncada, Phase 2/3 trial of molnupiravir for treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized adults, NEJM Evidence
Cox, Wolf, Plemper, Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets, Nat Microbiol
Dorward, Yu, Hayward, Colchicine for COVID-19 in the community (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial, Br J Gen Pract
Gastine, Pang, Boshier, Systematic review and patientlevel meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics to model response to antiviral therapies, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Hayward, Butler, Yu, Platform randomised trial of interventions against COVID-19 in older people (PRINCIPLE): protocol for a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform, trial of community treatment of COVID-19 syndromic illness in people at higher risk, BMJ Open
Khoo, Fitzgerald, Fletcher, Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a phase I, openlabel, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study, J Antimicrob Chemother
Khoo, Fitzgerald, Saunders, Molnupiravir versus placebo in unvaccinated and vaccinated patients with early SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK (AGILE CST-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial, Lancet Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00644-2Laouénan, Guedj, Mentré, Clinical trial simulation to evaluate power to compare the antiviral effectiveness of two hepatitis C protease inhibitors using nonlinear mixed effect models: a viral kinetic approach, BMC Med Res Methodol
Little, Rumsby, Kelly, Information leaflet and antibiotic prescribing strategies for acute lower respiratory tract infection: a randomized controlled trial, JAMA
Little, Stuart, Moore, Amoxicillin for acute lowerrespiratory-tract infection in primary care when pneumonia is not suspected: a 12-country, randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Lowe, Brown, Chowdhury, Favipiravir, lopinavirritonavir or combination therapy (FLARE): a randomised, double blind, 2 × 2 factorial placebo-controlled trial of early antiviral therapy in COVID-19, PLoS Med
Macpherson, Pragmatic clinical trials, Complement Ther Med
Malone, Campbell, Molnupiravir: coding for catastrophe, Nat Struc Mol Biol
Merck, Merck and Ridgeback's investigational oral antiviral molnupiravir reduced the risk of hospitalization or death by approximately 50 percent compared to placebo for patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 in positive interim analysis of phase 3 study
Painter, Holman, Bush, Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Rosenke, Hansen, Schwarz, Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model, Nat Commun
Siemieniuk, Bartoszko, Ge, Drug treatments for COVID-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis, BMJ
Singh, Mitra, Arora, Two Indian drugmakers to end trials of generic Merck pill for moderate COVID-19
Thorlund, Sheldrick, Meyerowitz-Katz, Singh, Hill, Making statistical sense of the molnupiravir MOVe-OUT clinical trial, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Urakova, Kuznetsova, Crossman, β-d-N 4-hydroxycytidine is a potent anti-alphavirus compound that induces a high level of mutations in the viral genome, J Virol
Wahl, Gralinski, Johnson, SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801, Nature
Wendler, Kington, Madans, Are racial and ethnic minorities less willing to participate in health research?, PLoS Med
Woodcock, Lavange, Master protocols to study multiple therapies, multiple diseases, or both, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"ISSN": [
"0140-6736"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"alternative-id": [
"S0140673622025971"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02593-4"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Christopher C",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobbs",
"given": "F D Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gbinigie",
"given": "Oghenekome A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahman",
"given": "Najib M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayward",
"given": "Gail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richards",
"given": "Duncan B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dorward",
"given": "Jienchi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "David M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Standing",
"given": "Joseph F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Breuer",
"given": "Judith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khoo",
"given": "Saye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petrou",
"given": "Stavros",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hood",
"given": "Kerenza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen-Van-Tam",
"given": "Jonathan S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Mahendra G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saville",
"given": "Benjamin R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marion",
"given": "Joe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogburn",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rutter",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Francis",
"given": "Nick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Nicholas P B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dobson",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madden",
"given": "Tracie-Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holmes",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Png",
"given": "May Ee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lown",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van Hecke",
"given": "Oliver",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Detry",
"given": "Michelle A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "Christina T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fitzgerald",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Nicholas S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mwandigha",
"given": "Lazaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galal",
"given": "Ushma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mort",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jani",
"given": "Bhautesh D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hart",
"given": "Nigel D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Haroon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKenna",
"given": "Micheal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chalk",
"given": "Jem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lavallee",
"given": "Layla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadley",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cureton",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benysek",
"given": "Magdalena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andersson",
"given": "Monique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coates",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrett",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bateman",
"given": "Clare",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Jennifer C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raymundo-Wood",
"given": "Ivy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ustianowski",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carson-Stevens",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Ly-Mee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Little",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agyeman",
"given": "Akosua A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Tanveer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allcock",
"given": "Damien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beltran-Martinez",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benedict",
"given": "Oluseye E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bird",
"given": "Nigel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brennan",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Julianne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "Gerard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Mike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Zelda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Danson",
"given": "Ruth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Kare-Silver",
"given": "Nigel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhasmana",
"given": "Devesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dickson",
"given": "Jon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Engamba",
"given": "Serge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "Stacey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "Robin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frost",
"given": "Eve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaunt",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "Sarit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilkar",
"given": "Ishtiaq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodman",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Granier",
"given": "Steve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howell",
"given": "Aleksandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "Iqbal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imlach",
"given": "Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irving",
"given": "Greg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacobsen",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennard",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Umar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knox",
"given": "Kyle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krasucki",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Law",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Rem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lester",
"given": "Nicola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lunn",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackintosh",
"given": "Claire I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathukia",
"given": "Mehul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morton",
"given": "Seb",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nally",
"given": "Rhiannon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ndukauba",
"given": "Chinonso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogundapo",
"given": "Olufunto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okeke",
"given": "Henry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Amit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Kavil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penfold",
"given": "Ruth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poonian",
"given": "Satveer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Popoola",
"given": "Olajide",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pora",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasad",
"given": "Vibhore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasad",
"given": "Rishabh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razzaq",
"given": "Omair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "Scot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Royal",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Safa",
"given": "Afsana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sehdev",
"given": "Satash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sevenoaks",
"given": "Tamsin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Divya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheikh",
"given": "Aadil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Short",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sidhu",
"given": "Baljinder S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Ivor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soni",
"given": "Yusuf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thalasselis",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Pete",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wingfield",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodall",
"given": "Maximillian N J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wooding",
"given": "Nick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Sharon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yong",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yongblah",
"given": "Francis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zafar",
"given": "Azhar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"em-consulte.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-22T23:41:15Z",
"timestamp": 1671752475000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-22T23:41:29Z",
"timestamp": 1671752489000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-23T15:57:04Z",
"timestamp": 1671811024762
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669852800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 19,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1671494400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0140673622025971?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0140673622025971?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aax5866",
"article-title": "Characterization of orally efficacious influenza drug with high resistance barrier in ferrets and human airway epithelia",
"author": "Toots",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"article-title": "A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus",
"author": "Fischer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib2",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00657-8",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir: coding for catastrophe",
"author": "Malone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nat Struc Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib3",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"article-title": "Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets",
"author": "Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib4",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03312-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801",
"author": "Wahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib5",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22580-8",
"article-title": "Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model",
"author": "Rosenke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib6",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkab318",
"article-title": "Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a phase I, open-label, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study",
"author": "Khoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3286",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib7",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02428-20",
"article-title": "Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Painter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02428",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib8",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Phase 2/3 trial of molnupiravir for treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized adults",
"author": "Caraco",
"journal-title": "NEJM Evidence",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib9",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib10",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Singh",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00644-2",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir versus placebo in unvaccinated and vaccinated patients with early SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK (AGILE CST-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial",
"author": "Khoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra1510062",
"article-title": "Master protocols to study multiple therapies, multiple diseases, or both",
"author": "Woodcock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib13",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib14",
"series-title": "COVID-19 rapid guideline: managing COVID-19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2223",
"article-title": "Systematic review and patient-level meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics to model response to antiviral therapies",
"author": "Gastine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib17",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-13-60",
"article-title": "Clinical trial simulation to evaluate power to compare the antiviral effectiveness of two hepatitis C protease inhibitors using nonlinear mixed effect models: a viral kinetic approach",
"author": "Laouénan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med Res Methodol",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib18",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19",
"author": "Agarwal",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib19",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Drug treatments for COVID-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis",
"author": "Siemieniuk",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib20",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of publication bias for 12 clinical trials of molnupiravir to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in 13 694 patients",
"author": "Lawrence",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00559-2",
"article-title": "Omicron variant and booster COVID-19 vaccines",
"author": "Burki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e17",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib23",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.21-1339",
"article-title": "Making statistical sense of the molnupiravir MOVe-OUT clinical trial",
"author": "Thorlund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1301",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib24",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70300-6",
"article-title": "Amoxicillin for acute lower-respiratory-tract infection in primary care when pneumonia is not suspected: a 12-country, randomised, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Little",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib25",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.293.24.3029",
"article-title": "Information leaflet and antibiotic prescribing strategies for acute lower respiratory tract infection: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Little",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3029",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib26",
"volume": "293",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1004120",
"article-title": "Favipiravir, lopinavir-ritonavir or combination therapy (FLARE): a randomised, double blind, 2 × 2 factorial placebo-controlled trial of early antiviral therapy in COVID-19",
"author": "Lowe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib27",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.0030019",
"article-title": "Are racial and ethnic minorities less willing to participate in health research?",
"author": "Wendler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e19",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib28",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103595",
"article-title": "The combined treatment of molnupiravir and favipiravir results in a potentiation of antiviral efficacy in a SARS-CoV-2 hamster infection model",
"author": "Abdelnabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib31",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01965-17",
"article-title": "β-d-N 4-hydroxycytidine is a potent anti-alphavirus compound that induces a high level of mutations in the viral genome",
"author": "Urakova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01965",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib32",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046799",
"article-title": "Platform randomised trial of interventions against COVID-19 in older people (PRINCIPLE): protocol for a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform, trial of community treatment of COVID-19 syndromic illness in people at higher risk",
"author": "Hayward",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib33",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00310-6",
"article-title": "Doxycycline for community treatment of suspected COVID-19 in people at high risk of adverse outcomes in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial",
"author": "Butler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib34",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3399/BJGP.2022.0083",
"article-title": "Colchicine for COVID-19 in the community (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial",
"author": "Dorward",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e446",
"journal-title": "Br J Gen Pract",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib35",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2004.07.043",
"article-title": "Pragmatic clinical trials",
"author": "MacPherson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "136",
"journal-title": "Complement Ther Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1_bib36",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2004"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673622025971"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}