Dexamethasone treatment interferes with the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin in young cattle
Marlene Areskog, Georg Von Samson-Himmelstjerna, Michel Alvinerie, Jean-François Sutra, Johan Höglund
Veterinary Parasitology, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011
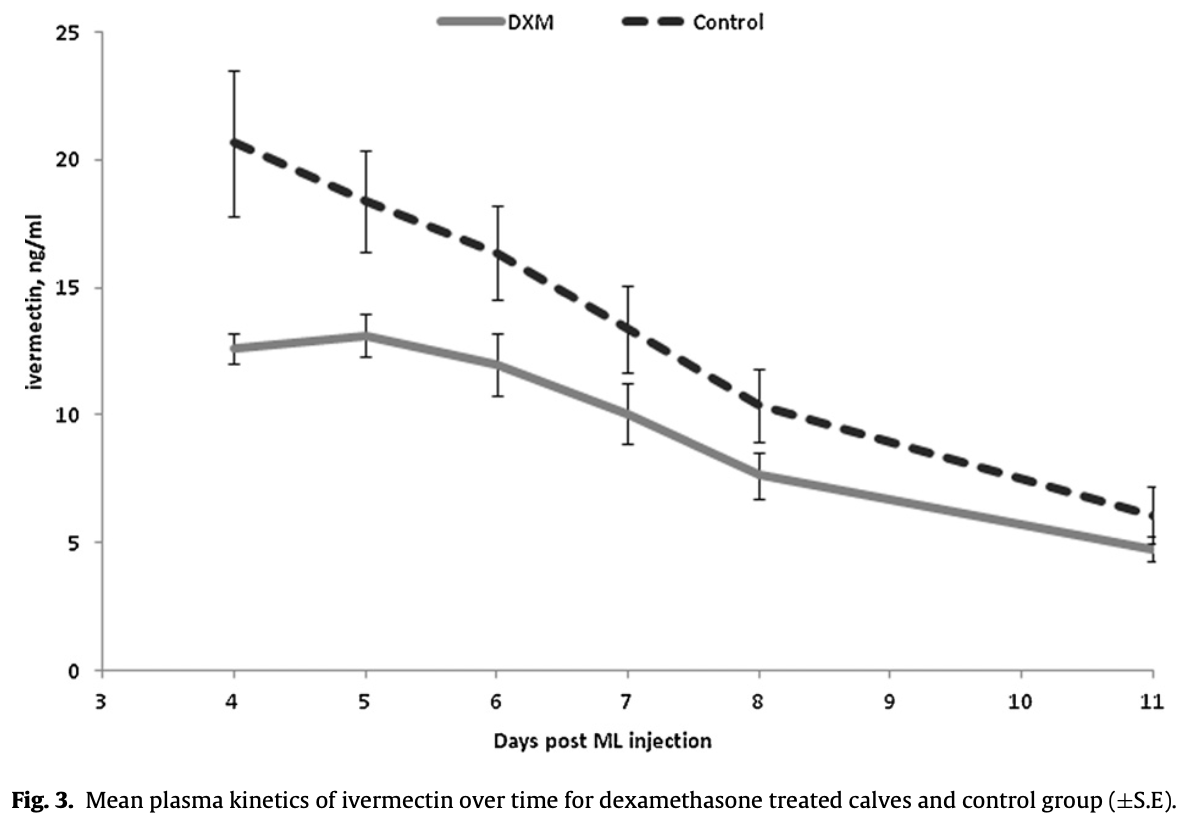
An experiment was carried out to study the possible interaction between dexamethasone (DXM) treatment and the efficacy of ivermectin (IVM) treatment in young cattle. Two groups, each of seven calves, were experimentally inoculated with an equal mixture containing 15,000 third stage larvae of Cooperia oncophora and Ostertagia ostertagi each, and with no history of being resistant to any anthelmintics. However, in this study C. oncophora was unexpectedly classified as IVM-resistant according to the outcome from the faecal egg count reduction test (FECRT). Blood parameters and faecal egg counts (FEC) were monitored from 0 to 35 days post infection (d.p.i.). The calves in one group received intramuscular injections of short and long-term acting DXM at 22 and 24 d.p.i., respectively. The other group remained as a control. Three days post patency (24 d.p.i.) both groups were injected subcutaneously with IVM (Merial) at the recommended dose (0.2 mg/kg). A significant difference (p < 0.001) in FEC patterns was observed between groups. Although both groups still excreted eggs (100-200 eggs per gram faeces) 11 days post anthelmintic treatment, the control group had a significantly higher reduction between 23 and 35 d.p.i. (p = 0.025). After 35 days, four animals per group were euthanized, and worms in the gastrointestinal tract were counted. No O. ostertagi were found in the abomasums, but low to high numbers (800-6200) of C. oncophora remained in the small intestines in both groups. Overall, these findings indicated that there was an interaction between the efficacy of IVM and DXM treatment. As significantly lower plasma levels of IVM were observed in the DXM group, we conclude that the impaired efficacy of ivermectin was most likely due to the altered pharmacokinetics.
References
Alvinerie, Sutra, Galtier, Ivermectin in goat plasma and milk after subcutaneous injection, Ann. Rech. Vet
Anderson, Watson, Coldiz, The effect of dexamethasone on some immunological parameters in cattle, Vet. Res. Commun
Anonymous, Manual of Veterinary Parasitological Laboratory Techniques
Borgsteede, Hendriks, Identification of infective larvae of gastrointestinal nematodes in cattle, Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd
Cabaret, Berrag, Faecal egg count reduction test for assessing anthelmintic efficacy: average versus individually based estimations, Vet. Parasitol
Coles, Bauer, Borgsteede, Geerts, Klei et al., World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology (WAAVP). Methods for the detection of anthelmintic resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance, Vet. Parasitol
Coles, Resistance in cattle worms, Vet. Rec
Coles, Watson, Anziani, Ivermectin-resistant Cooperia in cattle, Vet. Rec
Cringoli, FLOTAC, a novel apparatus for a multivalent faecal egg count technique, Parassitologia
Cringoli, Rinaldi, Veneziano, Capelli, Scala, The influence of flotation solution, sample dilution and the choice of McMaster slide area (volume) on the reliability of the McMaster technique in estimating the faecal egg counts of gastrointestinal strongyles and Dicrocoelium dendriticum in sheep, Vet. Parasitol
De Montigny, Shim, Pivnichny, Liquid chromatographic determination in animal plasma with trifluoroacetic anhydride and N-methylimidazole as the derivatization reagent, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal
Demeler, Küttler, Von Samson-Himmelstjerna, Adaptation and evaluation of three different in vitro tests for the detection of resistance to anthelmintics in gastro intestinal nematodes of cattle, Vet. Parasitol
Demeler, Van Zeveren, Kleinschmidt, Vercruysse, Höglund et al., Monitoring the efficacy of ivermectin and albendazole against gastro intestinal nematodes of cattle in Northern Europe, Vet. Parasitol
Dupuy, Alvinerie, Menez, Lespine, Interaction of anthelmintic drugs with P-glycoprotein in recombinant LLC-PK1mdr1a cells, Chem. Biol. Interact
El-Abdellati, Charlier, Geldhof, Levecke, Demeler et al., The use of a simplified faecal egg count reduction test for assessing anthelmintic efficacy on Belgian and German cattle farms, Vet. Parasitol
Gasbarre, Effects of gastrointestinal nematode infection on the ruminant immune system, Vet. Parasitol
Hamid, Mohi Aldeen, Effects of dexamethasone on leukocytes in sheep, Indian J. Vet. Med
Höglund, Parasite surveillance and novel use of anthelmintics in cattle, Acta Vet. Scand
Kanobana, Koets, Bakker, Ploeger, Vervelde, T-cell mediated immune responses in calves primary infected or re-infected with Cooperia oncophora: similar effector cells but different timing, Int. J. Parasitol
Kaplan, Drug resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance: a status report, Trends Parasitol
Kerboeuf, Guégnard, Anthelmintics are substrates and activators of nematode P-glycoprotein, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Kochapakdee, Pandey, Pralomkarm, Choldumrongkul, Ngampongsai et al., Anthelmintic resistance in goat in southern Thailand, Vet. Rec
Larsson, Dimander, Waller, Uggla, Höglund, A 3year field evaluation of pasture rotation and supplementary feeding to control parasite infection in first-season grazing cattle -dynamics of pasture infectivity, Vet. Parasitol
Lifschitz, Suarez, Sallovitz, Cristel, Imperiale et al., Cattle nematodes resistant to macrocyclic lactones: comparative effects of P-glycoprotein modulation on the efficacy and disposition kinetics of ivermectin and moxidectin, Exp. Parasitol
Lin, Chiba, Chen, Nishime, Deluna et al., Effect of dexamethasone on the intestinal first-pass metabolism of indinavir in rats: evidence of cytochrome P-450 3A [correction of P-450 A] and P-glycoprotein induction, Drug Metab. Dispos
Lomborg, Agerholm, Jensen, Nielsen, Effects of experimental immunosuppression in cattle with persistently high antibody levels to Salmonella dublin lipopolysaccharide O-antigens, BMC Vet. Res
Matthews, Brunsdon, Vlassoff, Effect of dexamethasone on the ability of sheep to resist reinfection with nematodes, Vet. Parasitol
Mckenna, Topically applied ivermectin and Cooperia infections in cattle, N. Z. Vet. J
Mejía, Fernandez Igartúa, Schmidt, Cabaret, Multispecies and multiple anthelmintic resistance on cattle nematodes in a farm in Argentina: the beginning of high resistance, Vet. Res
Molento, Lifschitz, Sallovitz, Lanusse, Prichard, Influence of verapamil on the pharmacokinetics of the antiparasitic drugs ivermectin and moxidectin in sheep, Parasitol. Res
Newton, Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action: what is important?, Thorax
Pe Ña, Miller, Horohov, Effect of dexamethasone treatment on the immune response of Gulf Coast Native lambs to Haemonchus contortus infection, Vet. Parasitol
Perloff, Von Moltke, Greenblatt, Ritonavir and dexamethasone induce expression of CYP3A and P-glycoprotein in rats, Xenobiotica
Prichard, Genetic variability following selection of Haemonchus contortus with anthelmintics, Trends Parasitol
Roth, Flaming, Model systems to study immunomodulation in domestic food animals
Soutello, Seno, Amarante, Anthelmintic resistance in cattle nematodes in northwestern Sao Paolo State, Brazil, Vet. Parasitol
Stafford, Morgan, Coles, Anthelmintic resistance in cattle, Vet. Rec
Suarez, Cristel, Anthelmintic resistance in cattle nematode in the western Pampeana region of Argentina, Vet. Parasitol
Sutherland, Leathwick, Anthelmintic resistance in nematode parasites of cattle: a global issue?, Trends Parasitol
Ueda, Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone, J. Biol. Chem
Vercruysse, Holdswroth, Letonja, Barth, Conder et al., International harmonization of anthelmintic efficacy guidelines, Vet. Parasitol
Vermunt, West, Pomroy, Multiple resistance to ivermectin and oxfendazole in Cooperia species of cattle in New Zealand, Vet. Rec
Waghorn, Leathwick, Rhodes, Jackson, Pomroy et al., Prevalence of anthelmintic resistance on 62 beef cattle farms in the North Island of New Zealand, N. Z. Vet. J
West, Vermunt, Pomroy, Bentall, Inefficacy of ivermectin against Cooperia spp. infection in cattle, N. Z. Vet. J
Wolstenholme, Fairweather, Prichard, Von Samson-Himmelstjerna, Sangster, Drug resistance in veterinary helminthes, Trends Parasitol
Zeng, Andrew, Arison, Luffer-Atlas, Wang, Identification of cytochrome P4503A4 as the major enzyme responsible for the metabolism of ivermectin by human liver microsomes, Xenobiotica
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011",
"ISSN": [
"0304-4017"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011",
"alternative-id": [
"S0304401712003652"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Areskog",
"given": "Marlene",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "von Samson-Himmelstjerna",
"given": "Georg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvinerie",
"given": "Michel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutra",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Höglund",
"given": "Johan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Veterinary Parasitology",
"container-title-short": "Veterinary Parasitology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2012,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2012-07-20T07:41:11Z",
"timestamp": 1342770071000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-22T10:29:40Z",
"timestamp": 1642847380000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "PARASOL"
},
{
"name": "GLOWWORM (EU-projects)"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-15T17:35:57Z",
"timestamp": 1700069757139
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issue": "3-4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2012,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3-4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2012,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2012,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2012-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1354320000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0304401712003652?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0304401712003652?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "482-488",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2012,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2012,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin in goat plasma and milk after subcutaneous injection",
"author": "Alvinerie",
"first-page": "417",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rech. Vet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0005",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1006365324335",
"article-title": "The effect of dexamethasone on some immunological parameters in cattle",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Vet. Res. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0010",
"volume": "23",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"author": "Anonymous",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0015",
"series-title": "Manual of Veterinary Parasitological Laboratory Techniques. Reference Book 418",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"article-title": "Identification of infective larvae of gastrointestinal nematodes in cattle",
"author": "Borgsteede",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0020",
"volume": "99",
"year": "1974"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.01.020",
"article-title": "Faecal egg count reduction test for assessing anthelmintic efficacy: average versus individually based estimations",
"author": "Cabaret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0025",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0304-4017(92)90141-U",
"article-title": "World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology (WAAVP). Methods for the detection of anthelmintic resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance",
"author": "Coles",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0030",
"volume": "44",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"article-title": "Resistance in cattle worms",
"author": "Coles",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "Vet. Rec.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0035",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin-resistant Cooperia in cattle",
"author": "Coles",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Vet. Rec.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0040",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "FLOTAC, a novel apparatus for a multivalent faecal egg count technique",
"author": "Cringoli",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Parassitologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0045",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.05.021",
"article-title": "The influence of flotation solution, sample dilution and the choice of McMaster slide area (volume) on the reliability of the McMaster technique in estimating the faecal egg counts of gastrointestinal strongyles and Dicrocoelium dendriticum in sheep",
"author": "Cringoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0050",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.01.032",
"article-title": "Adaptation and evaluation of three different in vitro tests for the detection of resistance to anthelmintics in gastro intestinal nematodes of cattle",
"author": "Demeler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0055",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.10.030",
"article-title": "Monitoring the efficacy of ivermectin and albendazole against gastro intestinal nematodes of cattle in Northern Europe",
"author": "Demeler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0060",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0731-7085(90)80060-3",
"article-title": "Liquid chromatographic determination in animal plasma with trifluoroacetic anhydride and N-methylimidazole as the derivatization reagent",
"author": "De Montigny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0065",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2010.05.013",
"article-title": "Interaction of anthelmintic drugs with P-glycoprotein in recombinant LLC-PK1-mdr1a cells",
"author": "Dupuy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "280",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol. Interact.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0070",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.01.015",
"article-title": "The use of a simplified faecal egg count reduction test for assessing anthelmintic efficacy on Belgian and German cattle farms",
"author": "El-Abdellati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "352",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0075",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0304-4017(97)00104-0",
"article-title": "Effects of gastrointestinal nematode infection on the ruminant immune system",
"author": "Gasbarre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0080",
"volume": "72",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of dexamethasone on leukocytes in sheep",
"author": "Hamid",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Vet. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0085",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1751-0147-52-S1-S25",
"article-title": "Parasite surveillance and novel use of anthelmintics in cattle",
"author": "Höglund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Acta Vet. Scand.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0090",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0020-7519(03)00211-X",
"article-title": "T-cell mediated immune responses in calves primary infected or re-infected with Cooperia oncophora: similar effector cells but different timing",
"author": "Kanobana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1503",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0095",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2004.08.001",
"article-title": "Drug resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance: a status report",
"author": "Kaplan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "477",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0100",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01477-10",
"article-title": "Anthelmintics are substrates and activators of nematode P-glycoprotein",
"author": "Kerboeuf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2224",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0105",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/vr.137.5.124",
"article-title": "Anthelmintic resistance in goat in southern Thailand",
"author": "Kochapakdee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "Vet. Rec.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0110",
"volume": "137",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.12.005",
"article-title": "A 3-year field evaluation of pasture rotation and supplementary feeding to control parasite infection in first-season grazing cattle – dynamics of pasture infectivity",
"author": "Larsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0115",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exppara.2010.01.009",
"article-title": "Cattle nematodes resistant to macrocyclic lactones: comparative effects of P-glycoprotein modulation on the efficacy and disposition kinetics of ivermectin and moxidectin",
"author": "Lifschitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "Exp. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0120",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of dexamethasone on the intestinal first-pass metabolism of indinavir in rats: evidence of cytochrome P-450 3A [correction of P-450 A] and P-glycoprotein induction",
"author": "Lin",
"first-page": "1187",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0125",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1746-6148-3-17",
"article-title": "Effects of experimental immunosuppression in cattle with persistently high antibody levels to Salmonella dublin lipopolysaccharide O-antigens",
"author": "Lomborg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "BMC Vet. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0130",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0304-4017(79)90041-4",
"article-title": "Effect of dexamethasone on the ability of sheep to resist reinfection with nematodes",
"author": "Matthews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0135",
"volume": "5",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00480169.1995.35844",
"article-title": "Topically applied ivermectin and Cooperia infections in cattle",
"author": "McKenna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "N. Z. Vet. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0140",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1051/vetres:2003018",
"article-title": "Multispecies and multiple anthelmintic resistance on cattle nematodes in a farm in Argentina: the beginning of high resistance",
"author": "Mejía",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "461",
"journal-title": "Vet. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0145",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00436-003-1022-3",
"article-title": "Influence of verapamil on the pharmacokinetics of the antiparasitic drugs ivermectin and moxidectin in sheep",
"author": "Molento",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Parasitol. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0150",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.55.7.603",
"article-title": "Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action: what is important?",
"author": "Newton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0155",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2003.11.002",
"article-title": "Effect of dexamethasone treatment on the immune response of Gulf Coast Native lambs to Haemonchus contortus infection",
"author": "Peña",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0160",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00498250310001630215",
"article-title": "Ritonavir and dexamethasone induce expression of CYP3A and P-glycoprotein in rats",
"author": "Perloff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Xenobiotica",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0165",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1471-4922(01)01983-3",
"article-title": "Genetic variability following selection of Haemonchus contortus with anthelmintics",
"author": "Prichard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0170",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "Model systems to study immunomodulation in domestic food animals",
"author": "Roth",
"first-page": "21",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0175",
"series-title": "Immunomodulation in Domestic Food Animals",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.06.023",
"article-title": "Anthelmintic resistance in cattle nematodes in northwestern Sao Paolo State, Brazil",
"author": "Soutello",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "360",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0180",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/vr.160.19.671-a",
"article-title": "Anthelmintic resistance in cattle",
"author": "Stafford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "671",
"journal-title": "Vet. Rec.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0185",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.09.016",
"article-title": "Anthelmintic resistance in cattle nematode in the western Pampeana region of Argentina",
"author": "Suarez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0190",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2010.11.008",
"article-title": "Anthelmintic resistance in nematode parasites of cattle: a global issue?",
"author": "Sutherland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "176",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0195",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(18)35757-0",
"article-title": "Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone",
"author": "Ueda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24248",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0200",
"volume": "267",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0304-4017(00)00443-X",
"article-title": "International harmonization of anthelmintic efficacy guidelines",
"author": "Vercruysse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Vet. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0205",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/vr.137.2.43",
"article-title": "Multiple resistance to ivermectin and oxfendazole in Cooperia species of cattle in New Zealand",
"author": "Vermunt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Vet. Rec.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0210",
"volume": "137",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00480169.2006.36711",
"article-title": "Prevalence of anthelmintic resistance on 62 beef cattle farms in the North Island of New Zealand",
"author": "Waghorn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "N. Z. Vet. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0215",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00480169.1994.35820",
"article-title": "Inefficacy of ivermectin against Cooperia spp. infection in cattle",
"author": "West",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "192",
"journal-title": "N. Z. Vet. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0220",
"volume": "42",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2004.07.010",
"article-title": "Drug resistance in veterinary helminthes",
"author": "Wolstenholme",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "469",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0225",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/004982598239597",
"article-title": "Identification of cytochrome P4503A4 as the major enzyme responsible for the metabolism of ivermectin by human liver microsomes",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "313",
"journal-title": "Xenobiotica",
"key": "10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011_bib0230",
"volume": "28",
"year": "1998"
}
],
"reference-count": 46,
"references-count": 46,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304401712003652"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Veterinary",
"General Medicine",
"Parasitology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Dexamethasone treatment interferes with the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin in young cattle",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "190"
}